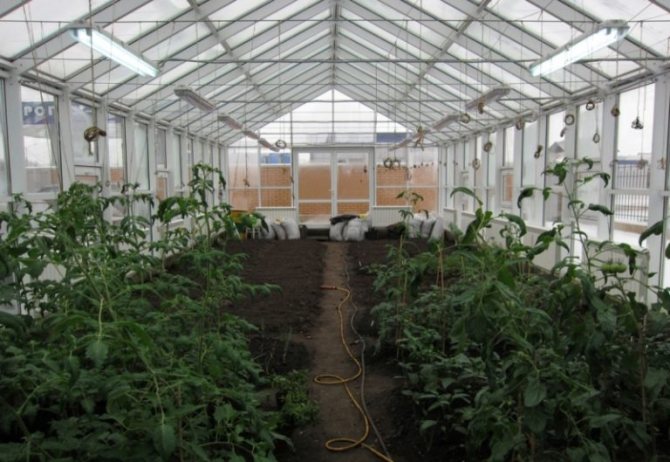
Making warm beds in the greenhouse: types of heating
The sun's heat warms up the beds only by the beginning of May, in some regions and towards its end. The artificially heated soil is suitable for planting plants already in March, while the root shoots are in comfortable conditions, which contributes to their strengthening and plant growth. In addition, the heat generated by the ground helps warm up the air in the greenhouse.

Advantages of warm beds:
- Early planting and reaching maximum yield in the first summer months;
- Getting a good result even on relatively fertile soil;
- Reducing the need for plant nutrition;
- Increased fruiting period;
- Reducing water consumption during irrigation;
- Weed control.
The preparation of a warm bed in a greenhouse is carried out in autumn or early spring. There are several options for heating the garden: electric cable, water pipes, biological compost. When using a cable, it is laid under the soil in advance and heated with the help of electricity. These designs are highly efficient but costly to maintain.
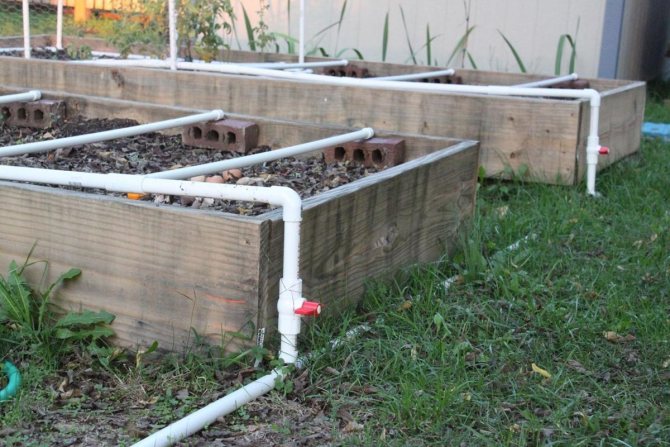
Water heating is used with the use of special pipes made of polymer material, which are laid under the ground.
Hot water flows through the pipes, which can heat the earth. For biological beds, plant residues and manure from livestock activities are used. The decay process becomes a heating element, as a result of which the temperature of the soil rises. This is the most economical way to heat your beds. Each method has its own pros and cons. The gardener selects the most appropriate option based on his own views on growing plants.
Chemical and biological heating method
The best soil heating in a greenhouse is the use of biologically or chemically active substances in the soil. This is one of the oldest ways to heat the earth. In practice, it is realized by ordinary decay. In the process of rotting manure for a short period (about 7 days), the latter heats up to almost 60ºC and maintains this temperature parameter for almost 4 months.


You can also use straw along with organic fertilizers. To do this, lay out the chopped straw in a layer (the layer should be at least 7 cm deep, and the length of the straw fractions should be no more than 4 cm). Next, the straw is sprinkled with ammonium nitrate and superphosphate (the proportions are given by the manufacturer of mineral fertilizers), after which the bookmark should be watered with hot water, sprinkled with soil.
Instead of animal feces, you can use humus of plant origin. It is prepared as follows:
- grass is placed in a container, which is poured with nitrogen fertilizers (or urine);
- then cover with a lid, which should tightly press down the contents of the container;
- then the mixture is allowed to infuse for about 2 weeks.
The modern chemical industry has also developed special substances that can heat the earth. They are often based on lime and nitrogen, but there are other options.
This method has a controversial drawback - there will be a smell of humus or manure in the greenhouse, which is unpleasant for human perception, however, the concentration of substances from the reaction of humus in the air has a positive effect on plants, saturating them with minerals and useful substances.


Heating the greenhouse in this way is quite simple and relatively cheap.
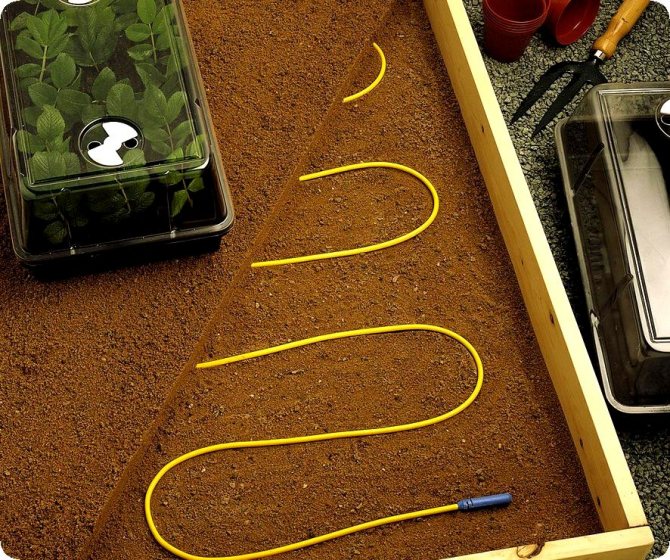
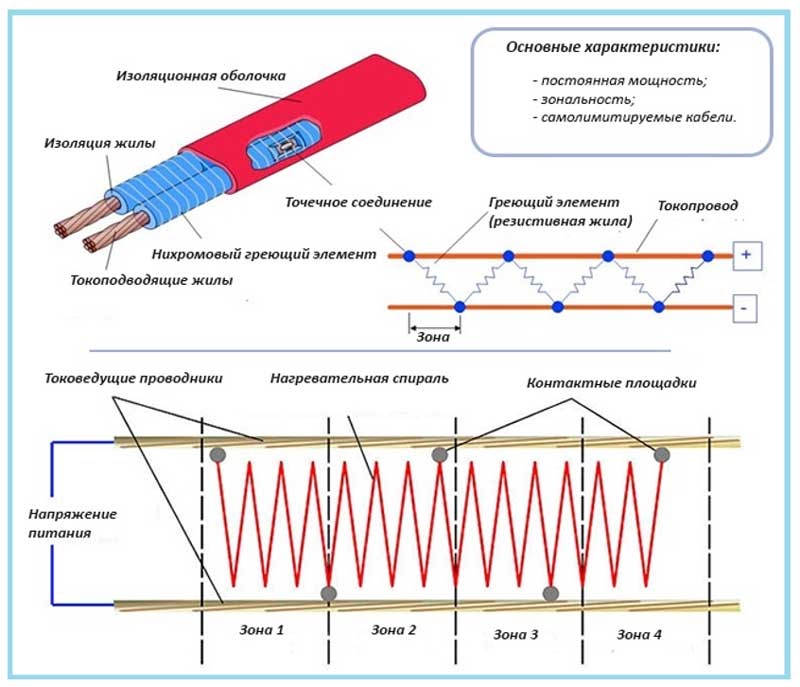
Heating the ground in a greenhouse using an electric cable
Cable heating of greenhouse beds allows you to maintain the soil temperature as accurately as possible, which makes it possible to effectively grow plants.
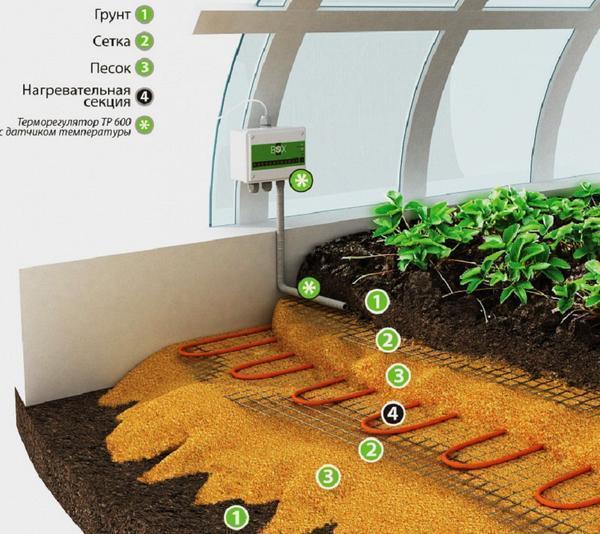


The main advantages of the electric heating system are:
- The ability to grow any, even exotic crops;
- Increased productivity;
- Possibility to regulate soil temperature;
- Ease of installation of the cable system;
- Long service life.
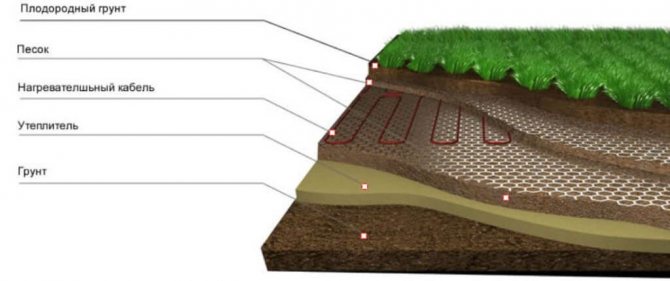
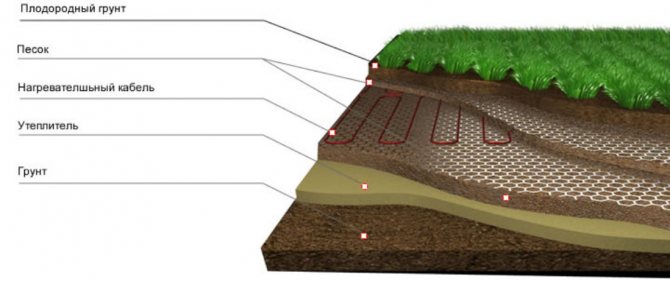
To arrange the beds, it is necessary to remove up to 40 cm of the upper soil. Next, lay the material for thermal insulation so that the energy does not go into the lower layers of the earth. Prepare a 5 cm pillow with sifted sand, spill with water and tamp.
To protect the cable from various rodents, you need to install a special mesh over the sand.
Next, lay the electric cable on the mesh with a snake. The laying distance between the tape should be no more than 20 cm. Using special clamps, fasten the wire to the mesh, fill it with sand and tamp it, creating another pillow. Further, in order to avoid mechanical damage to the cable during excavation work, put another mesh and cover the entire structure with earth. Thanks to such a device, plants can be grown in greenhouses regardless of weather conditions, using additional lighting in autumn and winter. In return, the family will receive fresh vegetables at any time of the year.
Simple do-it-yourself greenhouse with heated soil
Water heated beds also have a number of advantages. Firstly, the condensate that forms on the pipes additionally moistens the soil. This design provides uniform heating of the air in the room. To heat the greenhouse, you will need a gas or electric boiler, you can also use a small brick or metal stove with wood.
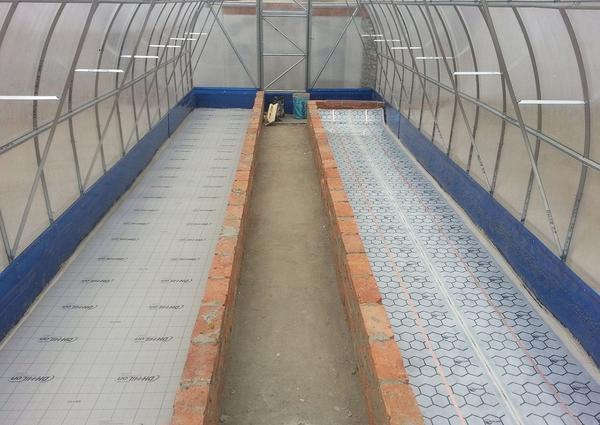


You need to purchase a smoke outlet pipe for it. The selection is made in accordance with the configuration of the heater.
To install a furnace or boiler, it is necessary to prepare a foundation, for a brick structure - a concrete one. The metal boiler can be placed on a sheet made from a mixture of asbestos and cement. Further, the structures provide stability and attach the chimney, hermetically sealing the connection points.
Thermal insulation of beds with pipes, necessary work:
- Remove soil 35-40 mm thick;
- At the bottom of the resulting trench, material is laid out for thermal insulation, usually foam is used;
- Water pipes are placed on top and connected to the heating system;
- Fertile soil is laid on top of the pipes.
This heating method is considered optimal, however, it is necessary to ensure that the water temperature in the pipes does not exceed 45 ° C, otherwise the roots of the plants can be burned.
A warm bed in a polycarbonate greenhouse: a biological method
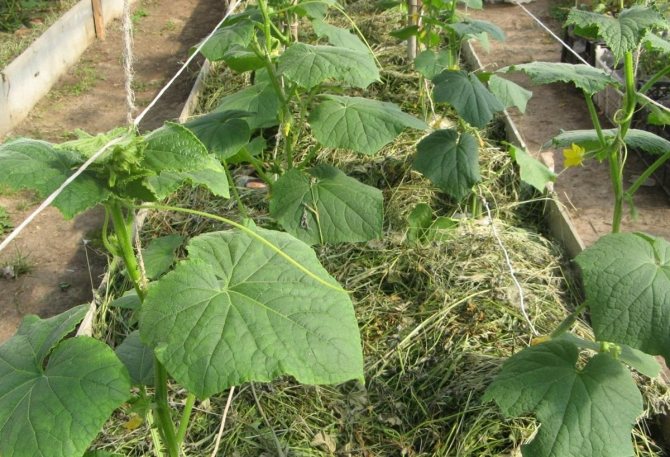
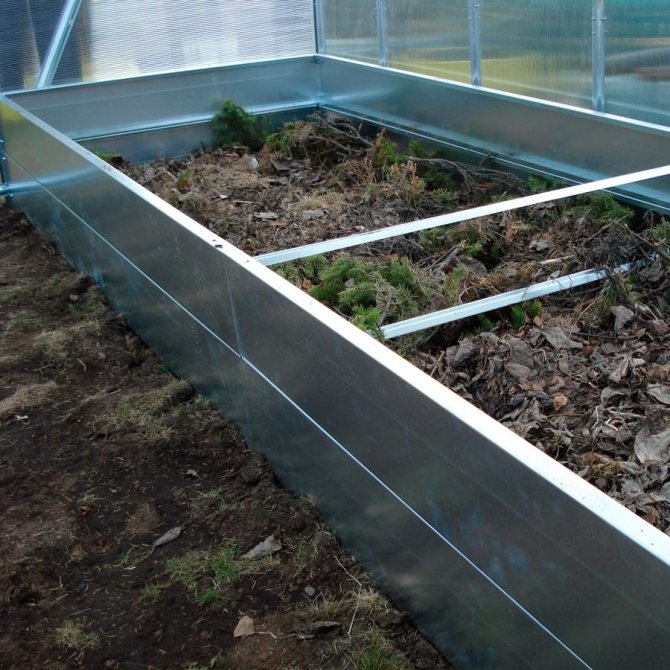
The biological method of heating the beds is made using natural biofuel, laid in the subsoil. As a filler, plant residues, sawdust and manure are used, which are shed with water for the decay process. Such beds are the most economical design.


Warm beds powered by natural fuel are usually divided according to the type of construction:
- Buried, when fertile soil is removed, a trench is pulled out, compost is laid and filled from above with soil so that it is at the level of the total mass of the earth;
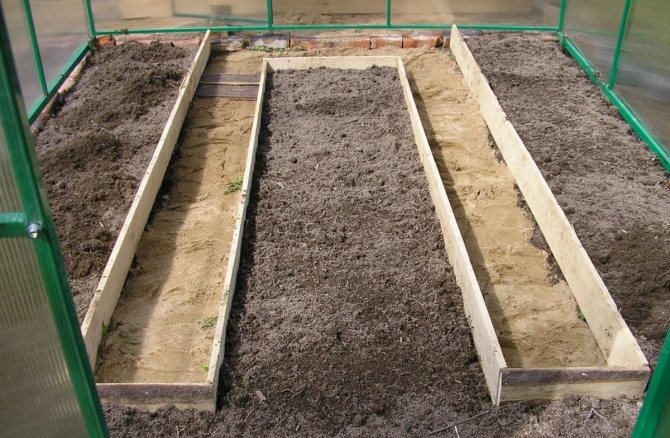
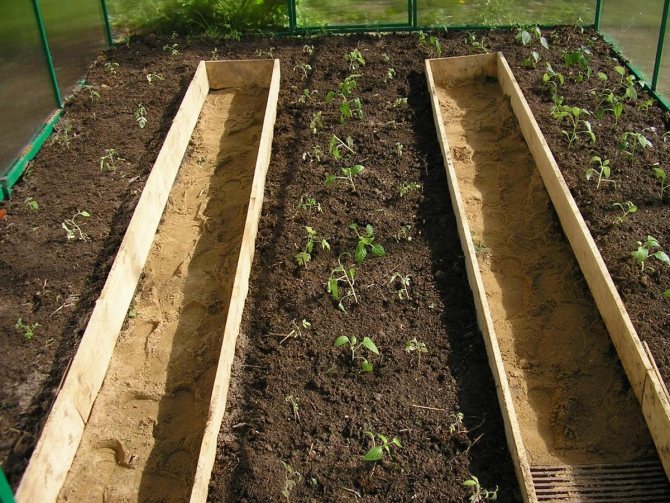
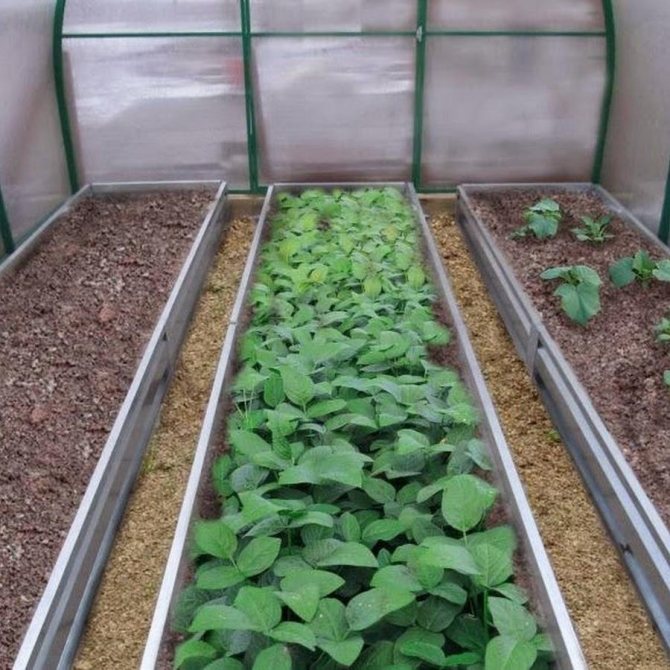
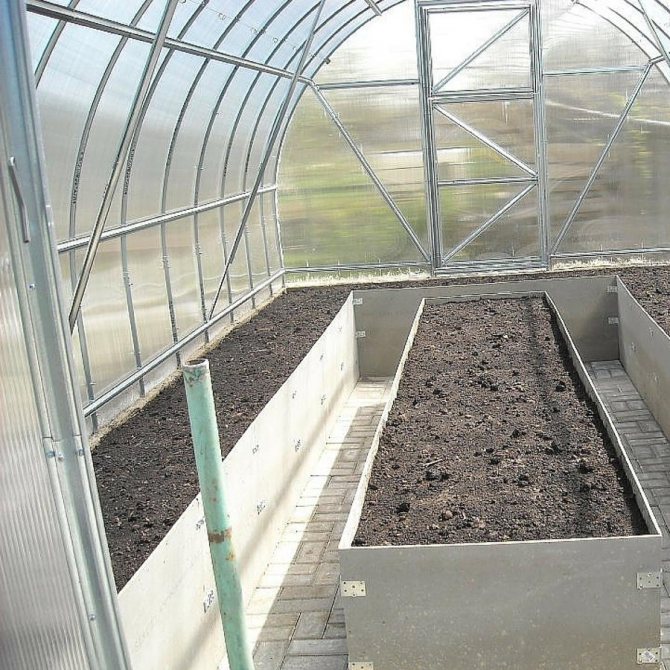
- Raised beds, the top layer of earth is removed from the surface and placed in special wooden boxes, which serve as protection against crumbling and leaching of the earth during operation;
- Hilly bed, laid without a box on top of the main platform;
- A combined option, when the lower layers with organic matter are laid at ground level, and the fertile soil layer is fixed with a box.
To make the construction of a combined warm ridge, it is necessary to mark places for future plantings. Then carefully remove the sod layer, setting the fertile soil aside.Next, you need to dig a trench up to 60 cm deep. To protect it from freezing, foam plastic or a closed plastic container is placed on the bottom of the trench. Next, the first layer of organic matter begins, consisting of large branches, wooden chocks, large objects of plants.
This layer will play a drainage role. Then a paper backing consisting of waste paper is laid.
After that comes a layer of finer organic matter, food waste, tree leaves, small stems of grass. Next, we fill in ready-made compost, or semi-rotted manure, to start the decay process. We install a pre-prepared box, into which we will pour fertile soil. Each applied layer must be well shed with water. We cover the last layer with fertile soil. Organic soil is perfect for planting tomatoes, pumpkins and cucumbers. The decay process is able to warm the ground for 2 months.
How to heat the soil in the greenhouse
Judging by the reviews of practitioners, everyone who wants to make a warm floor in a greenhouse has only one way out: a water floor. It is the most economical. The way of organizing it can be different. Someone puts a separate boiler, which serves only pipes buried in the ground, someone supplies them with water from the "return" of the radiator heating.
Water heating pipes are laid both in the ground and in pallets. Both options are used and work well. The only difference is that it takes more time to warm up the soil than to warm up the soil in pallets. This is understandable: the mass is different. In any case, solid pipes are buried into the ground without connections and fittings. So there will be no leaks. The number of underfloor heating loops per bed depends on the heat-loving culture. Cucumbers, for example, like warm soil, tomatoes can be cooler. Most often, one circuit (supply and return) of the warm floor goes to one bed.
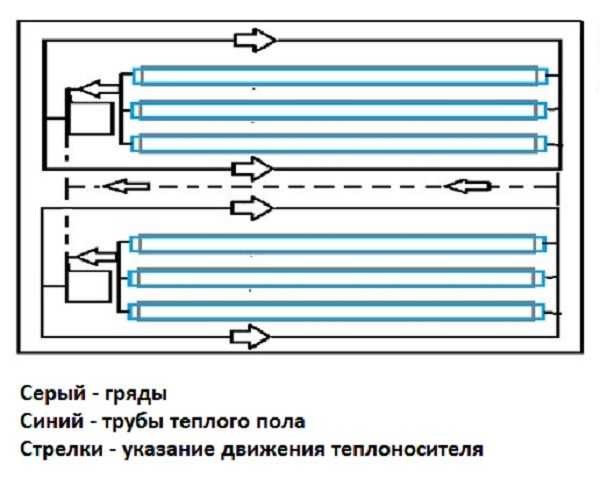

One of the options for connecting a warm water floor: first, the coolant goes to the registers or radiators located around the perimeter of the greenhouse, and then to the contours of the warm floor. In this scheme, two boilers are used, and there are two complementary circuits
To preserve heat, it is advisable to spread Izolon or foil material at the very bottom. Then, after reaching the operating temperature, the fuel consumption for maintaining it will be small. And in general, the less heat goes away, the better. Therefore, if you plan to grow something on the ground, it is advisable to make a heat-saving layer. It is necessary to remove the soil to a certain depth, and fill (or lay) a layer of some kind of heat-insulating material. Optimally - polystyrene foam of sufficient thickness. Already lay "Izolon" or similar material on the heat insulator, and then the warm floor.
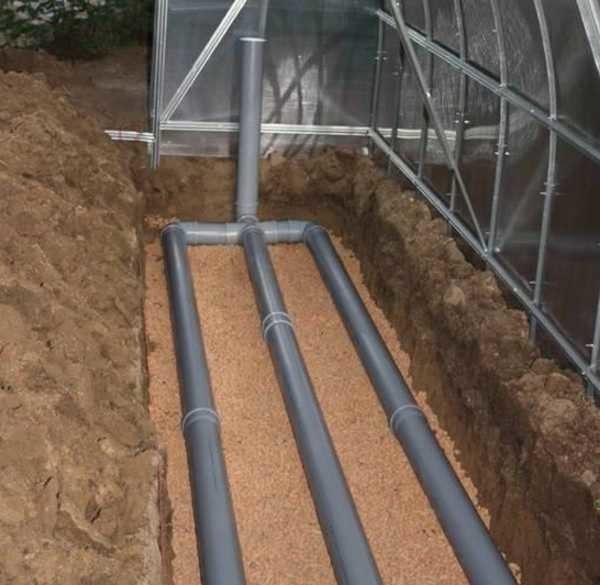


Here, a layer of expanded clay is used as a heat insulator. But for greater efficiency, it was necessary to lay more metalized film or foil
The depth of laying pipes depends, firstly, on the crops grown, and secondly, on the wishes of the owner. Someone thinks that it is optimal to lay it 40-50 cm deep, while someone bury it only 20 cm. Both options work. The inertia of the system is changing. With deep laying, it is required to warm the soil for a long time and stubbornly to reach normal temperature (two weeks or even more). But then you can turn off the floor heating in the greenhouse for the night (or vice versa - for the day): the large thermal inertia will not allow the plants to freeze. With a shallow setting, you cannot afford this, but the return to normal temperature is faster in 6-10 days. In this case, you need to carefully control the temperatures: you can burn the root system, and you also need to be careful when working in the ground.
The second option in terms of economy and efficiency: air heating of the soil. Asbestos pipes are buried in the ground, heated air is supplied to them with the help of fans of the air duct system.The system is not very efficient due to the low heat capacity of the air. But it is possible to increase the flow rate by using more power fans.


The depth of pipe laying can be different - from 50-70 cm to 20-30 cm
How to heat the air in this case? One of the convectors. The most efficient of the solid fuel is Buleryan. Around it, you can make a special box that will collect the heated air, and from this box, dilute the air ducts to pipes buried in the ground. This system is gentle and comfortable for plant roots.
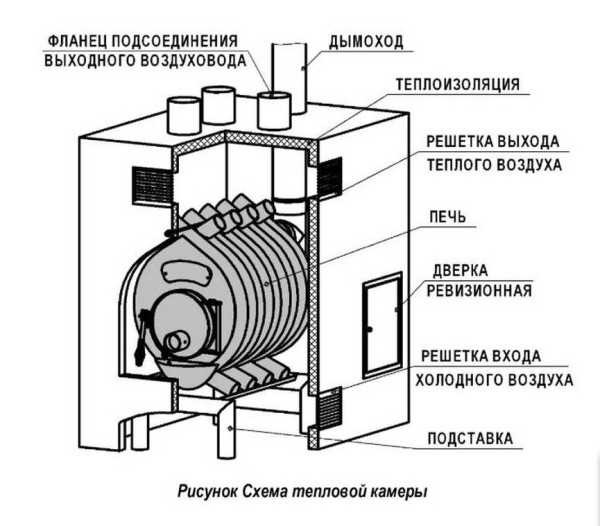

Having made such a chamber to collect warm air, you can then "drive" it into pipes, under the beds
Electric underfloor heating in a greenhouse can be installed only in one case: if there is a lot of money and a three-phase transformer. With a legal connection, the production cost (any) will be higher than the market price. Therefore, there is not a single review on the use of this method of heating the soil in a greenhouse. They just don't use it.
How to warm up the ground in a greenhouse in spring
Having a polycarbonate greenhouse, I want to start sowing plants in early spring. To do this, it is necessary to warm up the soil and air in the greenhouse.
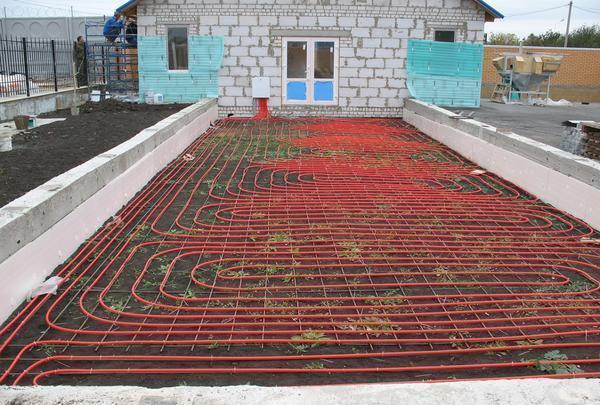


There are various ways to increase soil temperature:
- Electric heating by air, a simple and affordable method, it is necessary to purchase a heater-fan and connect it to electricity;
- Electric heating of beds with a cable, an easy-to-install system that allows you to heat the soil to the required temperature and maintain it in this state;
- The infrared method, using special lamps, a feature of this option is the ability to heat only plants without increasing the air temperature in the greenhouse;
- Water pipes serve as an excellent heating element for the ground, beds and shelves while moisturizing the soil with condensate.
Technical options for the implementation of heating
In fact, the technical options for heating the soil are reduced to the arrangement of "warm floors" (both water and electric) or the installation of heating elements in the greenhouse. The latter option is less effective, since in this case only the soil surface heats up.


The most effective use of embedded heat-generating elements. This will require the construction of a capital greenhouse with a foundation. Next, heating elements are laid out on the foundation, similar to the arrangement of "warm floors". Then they are poured with concrete (so that the concrete layer is about 2-3 mm above the level of the cable or pipe), then soil is poured. However, the layer of heated soil should not be more than half a meter - in this case, heating efficiency decreases and energy consumption increases.
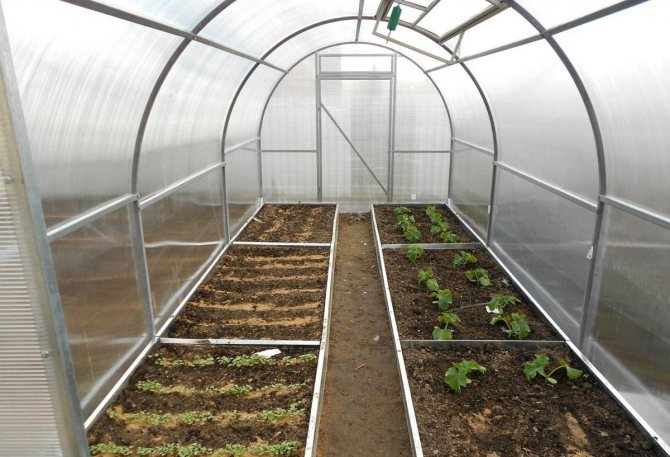
Examples of warm beds in a greenhouse (photo)
- Author: admin
Rate the article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(2 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
Share with your friends!