Many people, having installed a new stainless steel water heated towel rail in the bathroom, after a while notice that small specks of rust have appeared on the metal surface, the diameter of which usually does not exceed 5-6 mm. This "scattering" is nothing more than a banal metal corrosion. And the point here is not at all a defective plumbing product or improper operation, but in wandering currents. What is it? Where do they come from? And how to neutralize their detrimental effect on the heated towel rail? We understand the issue.
What you need to know about stray currents?
Any metal objects in water or in the ground, regardless of their purpose, are susceptible to corrosion, which can be:
Electroplating
It is related to the reaction between different metals. So, for example, a galvanic pair leading to destruction can be created by steel and brass or steel and aluminum. The reaction begins as soon as a "duet" of different metals is formed and the resulting unit comes into contact with the electrolyte. In a situation with a heated towel rail, the role of the electrolyte is played by ordinary tap water, which reacts with metals due to the content of a significant amount of minerals (the same reaction will occur with sea water rich in salt). And the higher the water temperature, the more active is the process of metal destruction. That is why the hulls of ships sailing in the warm southern seas wear out faster than ships in the northern fleet.
Corrosion of stray currents
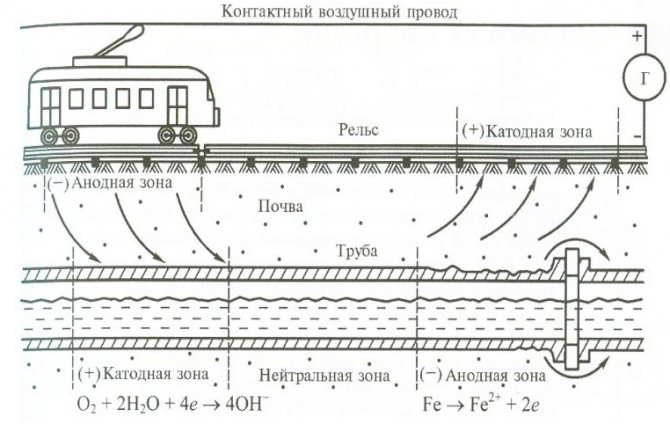
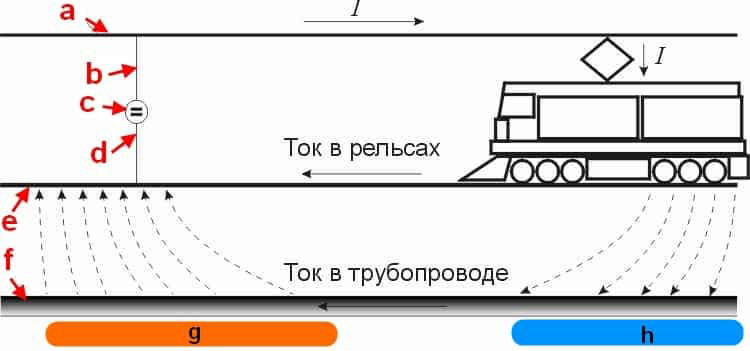
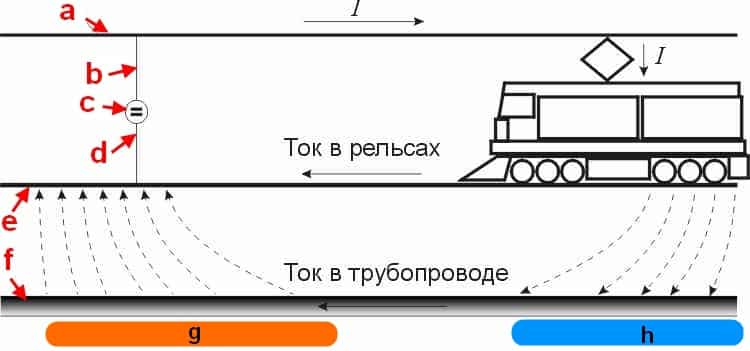
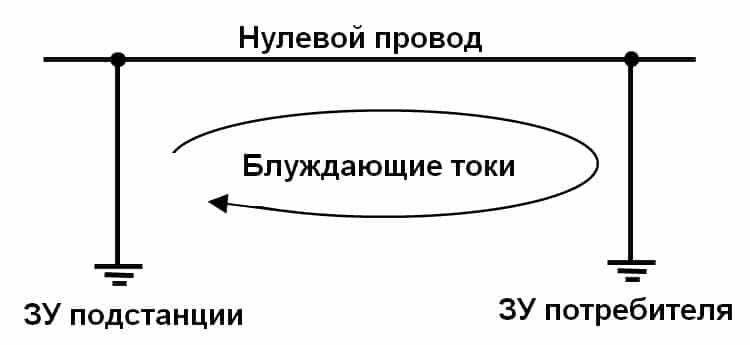
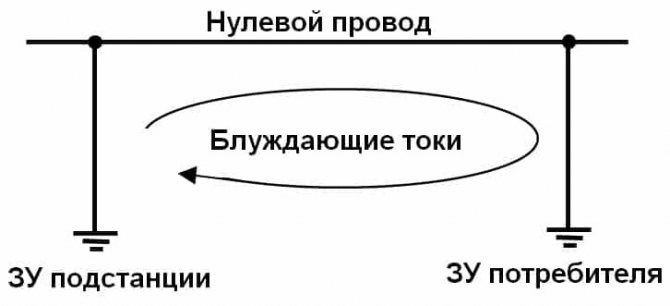
This process is caused by the so-called stray currents that occur in the earth if it acts as a conductive medium. In this case, not only metal objects that are completely in the ground are subjected to a destructive effect, but also those that only come into contact with it. But where do these currents come from? It's simple: in most cases, their appearance is the result of leaks from power lines. This group also includes the so-called zero currents present in ungrounded structures.
Possible protection options
To protect metal products from harmful effects, various methods are used, which are divided by the nature of their application into passive and active.
Passive option
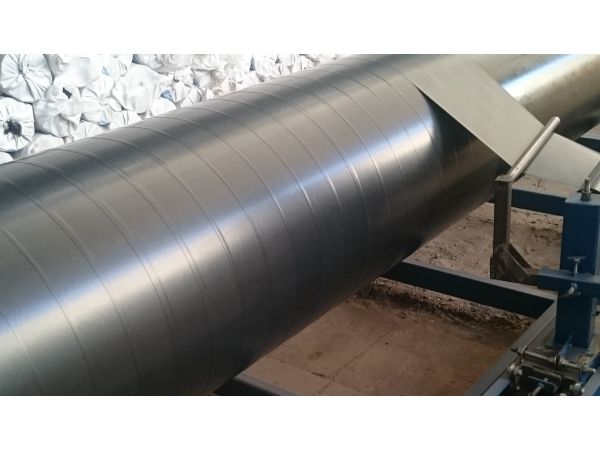

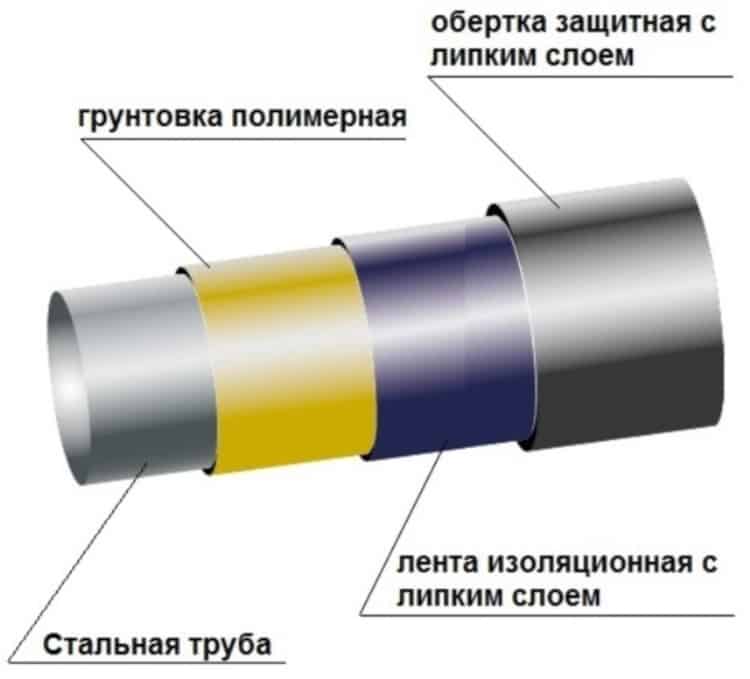
Passive isolation
This option is the use of a different insulating material that forms a protection between the conductor and the metal. It is used as insulation:
- epoxy resin mixtures;
- inclusion in the composition of polymers;
- bitumen coating.
But if we restrict ourselves to only this option, then full-fledged protection will not work, since the insulating material is not one hundred percent barrier due to the presence of diffusion permeability. Therefore, the isolation takes place in a partial way. In addition, in the process of moving pipes, such a layer can be damaged, resulting in significant scratches, notches, through holes and other flaws.
Important! Therefore, a passive method of protection can be used only as a supplement.
Active defense
Indicates the use of an active method of localizing the source of exposure through the use of cathodic polarization, where a negative charge displaces the natural one.
To implement such protection, you need to use one of two tools:
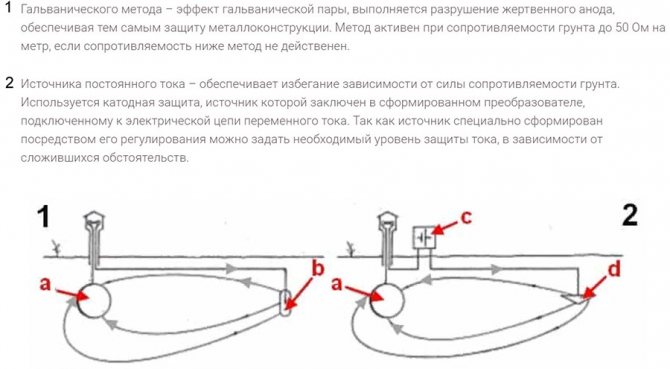
- Galvanic method - the effect of a galvanic pair, the destruction of the sacrificial anode is performed, thereby ensuring the protection of the metal structure. The method is active with soil resistance up to 50 Ohm per meter, if the resistance is lower than the method is not effective.
- DC power source - avoids dependence on the strength of the soil resistance. Cathodic protection is used, the source of which is enclosed in a formed converter connected to an alternating current electric circuit. Since the source is specially formed by regulating it, you can set the required level of current protection, depending on the circumstances.
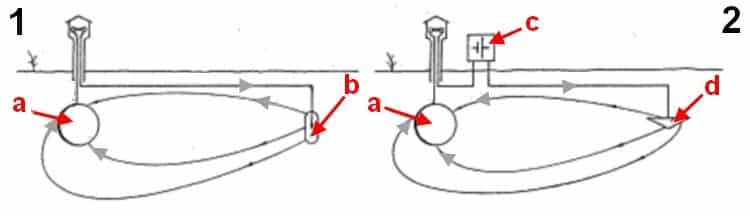

Active isolation
A similar method can provide a negative impact:
- re-protection - exceeding the required potential, as a result, the destruction of a metal product occurs;
- incorrect calculation of protection - leading to accelerated corrosive destruction of nearby metal objects.
The examples given can be considered on the protection of such a product as a heated towel rail.
Corrosion processes on such products or other terminal plumbing products have never occurred, but this was real before the use of metal-plastic pipes, where there is contact with aluminum inside the wall. As a result, the formation of wandering elements occurs not only due to the use of plastic pipes in the immediate room, but also in others, since in an apartment building they can be used by a neighbor from another floor.
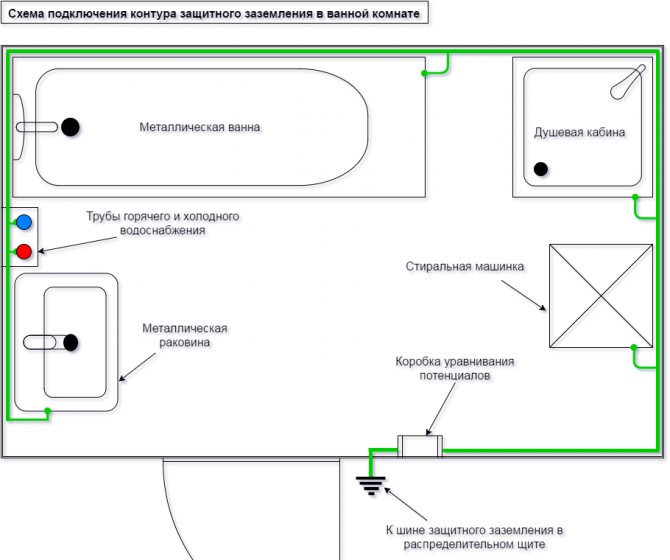
Important! To avoid the negative effect of the generated currents on your own structure, it is necessary to equalize the potentials by providing a heated towel rail, battery and water pipes with a grounding element.
In this case, the use of the so necessary grounding occurs in relation to any communication that is made of metal pipes, for example, a gas pipeline in the ground.
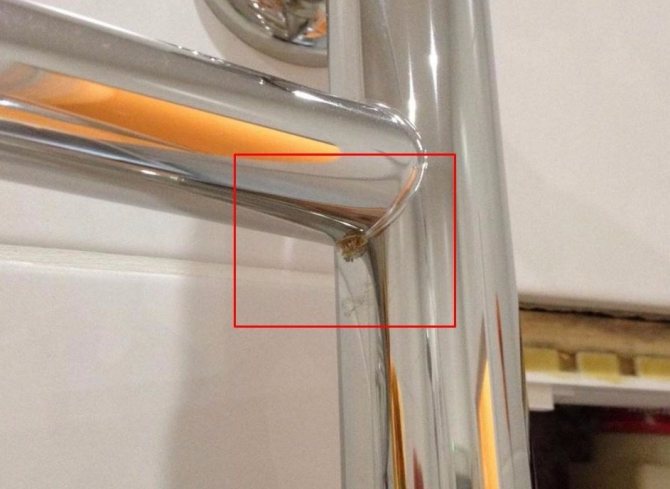
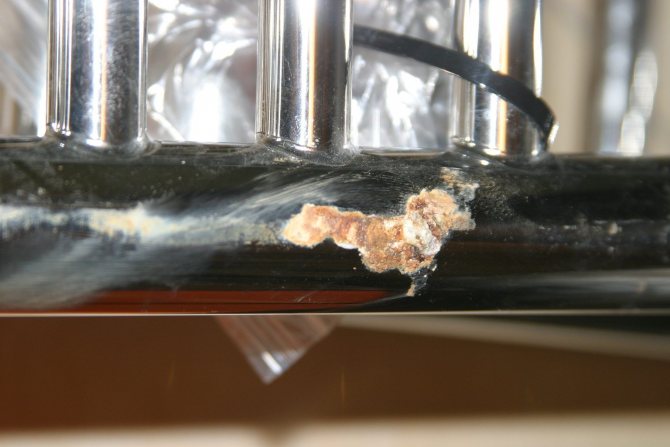
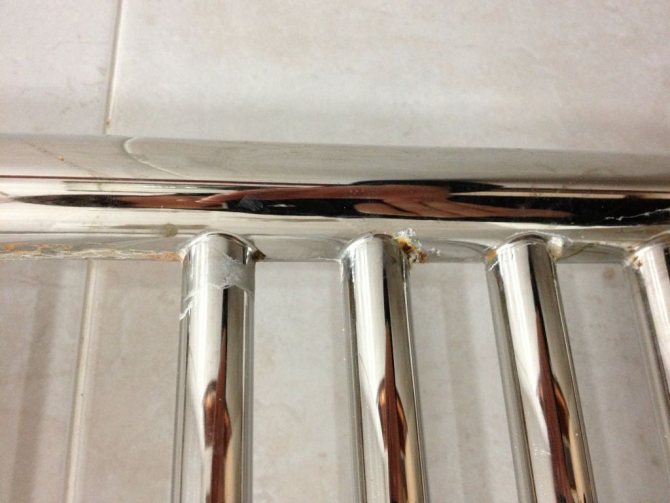
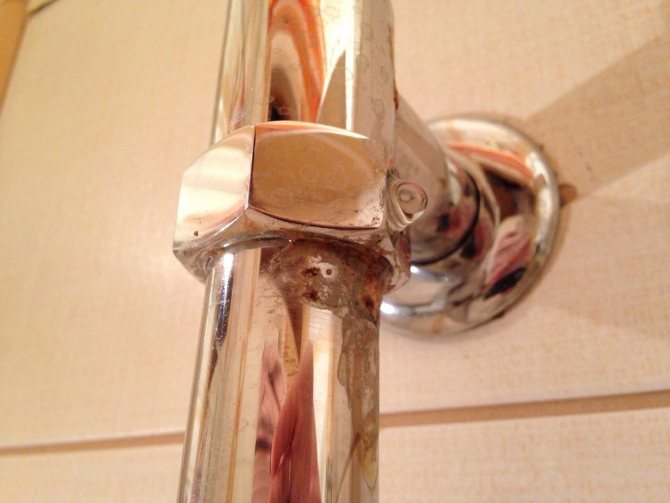
First signs of corrosion
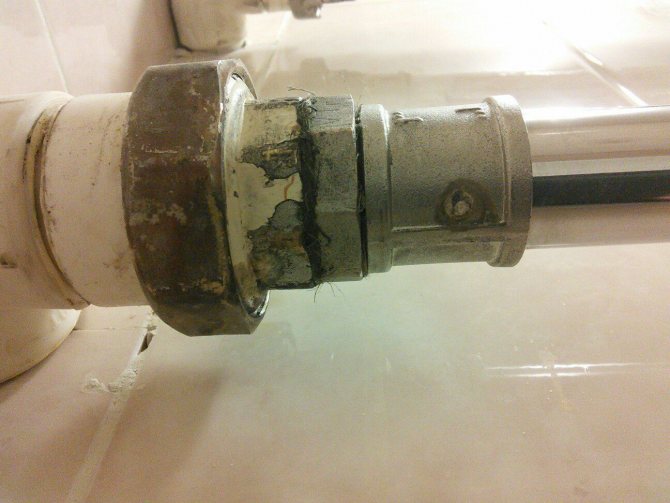
You can determine that your heated towel rail has become a "victim" of corrosive processes by the appearance of the equipment. The first signs of metal destruction are:
- swelling of the decorative layer (paint) - first this occurs at the joints and on the sharp edges of the structure;
- the appearance on the affected surface of a noticeable whitish coating, resembling a fine powder;
- the formation of small dents and depressions in the damaged areas - it seems that the metal has been eaten by a bug.
Minor damage is usually the result of galvanic corrosion caused by electrical potential differences between dissimilar metals, one of which acts as the cathode and the other as the anode. And if you add wandering currents to this, the destruction will be much more serious.
A little about the nature of stray currents and their danger
The reason for the appearance of stray currents acting on your heated towel rail is the potential difference between grounded structures. And in order to equalize the potentials, it is necessary to create a system in which all metal elements will be in contact with the neutral conductor in the existing input-distribution device.
Such a system will maximize the safety of the user (if you grasp the pipe and grounded equipment with your hand, you will not get a fatal discharge). And this is very important, because the greater the potential difference, the more serious danger threatens a person. For example:
- If this value is 4 or 6V, you may receive a 5mA shock. It will be sensitive, but not fatal.
- If its strength is 50 mA, cardiac fibrillation may develop.
- And when the human body is exposed to a current of 100 mA, death occurs.
But there are cases when even a small potential difference in 4B became the cause of death.
Description of the phenomenon
Stray currents are those that appear in the ground when it is used as a conductive medium.They create corrosion of metal, which is wholly or partly below the surface of the earth, and sometimes only comes into contact with land plots. Observed on tram and railway tracks, electrified roads. Sometimes they become the cause of a short circuit and an emergency.
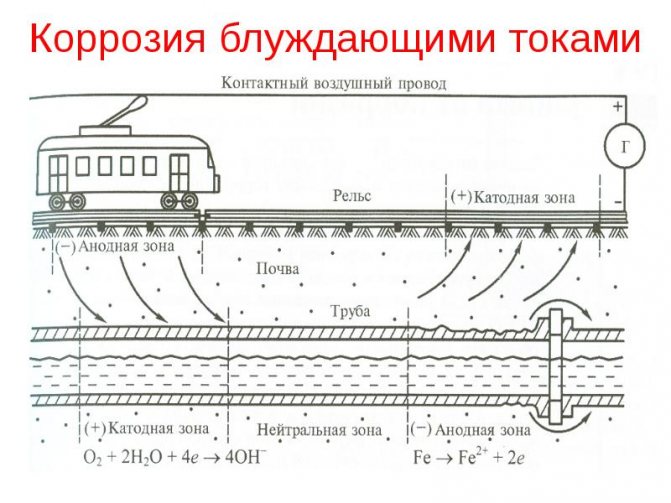

Destructive phenomenon
They differ from ordinary stationary electric currents in that they appear suddenly and in the most unpredictable area. The process occurring on the object through which the electric current begins to flow depends on which direction they have. If the object has a positive potential relative to another object, upon contact with it, an electric current appears with corrosion and oxidation of the wires. If the object has a negative potential, then the parameters of the substance that is in the liquid of the composition of the medium where the electric current flows are restored on it.
Note! Since the reactivity of elements that come into contact with a liquid medium or electrolyte is not clear, it is difficult to predict the time with the place of the appearance of a wandering type of electric current. At present, its presence leads to corrosion of an object with a positive potential.
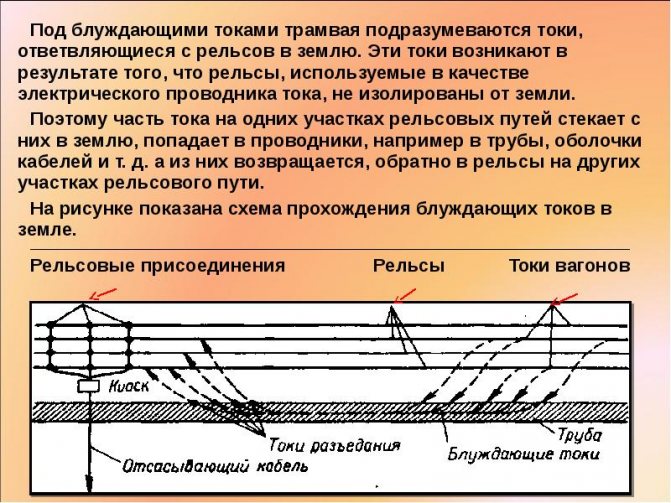

Full definition
Potential difference: causes of
But where does the potential difference come from, if the house is built taking into account all applicable norms? In theory, if the building rules are followed, there should be no potential difference. But in practice, it often happens that when assembling structures and engineering systems, welded joints are replaced with squeegees. Another common option is to integrate additional resistors or metal parts into the circuit. Both can cause a potential difference at opposite ends of the pipe and, accordingly, initiate metal corrosion.
Do not forget about the "conflict" between metal and plastic, which also plays an important role in the destruction of various peripheral devices (these include heated towel rails). Due to the fact that plastic pipes are often placed between stainless steel plumbing equipment and a metal riser (they are used to perform wiring around the apartment), the connection between these parts of the system is broken. And although the riser will be grounded in any case (in new high-rise buildings this is done through the equalization system, and in the houses of the old fund - through the ground loop located in the basement of the building), the potential difference is still formed. And when water moves through pipes, which demonstrates excellent conductivity, micro friction also occurs, which is guaranteed to lead to the appearance of stray currents. And they, in turn, provoke corrosion. The circle is complete!
Innovative technology to protect heated towel rails
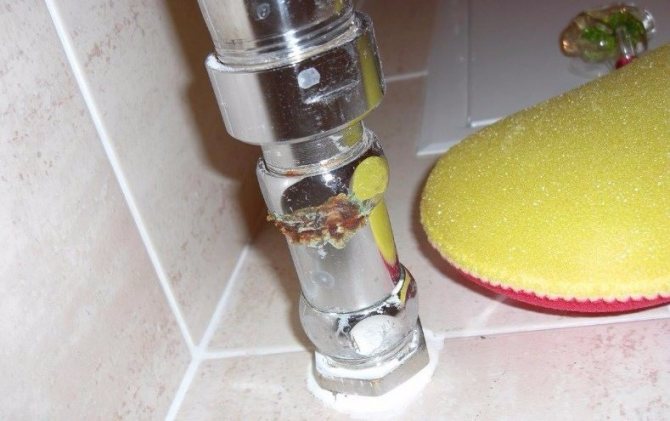
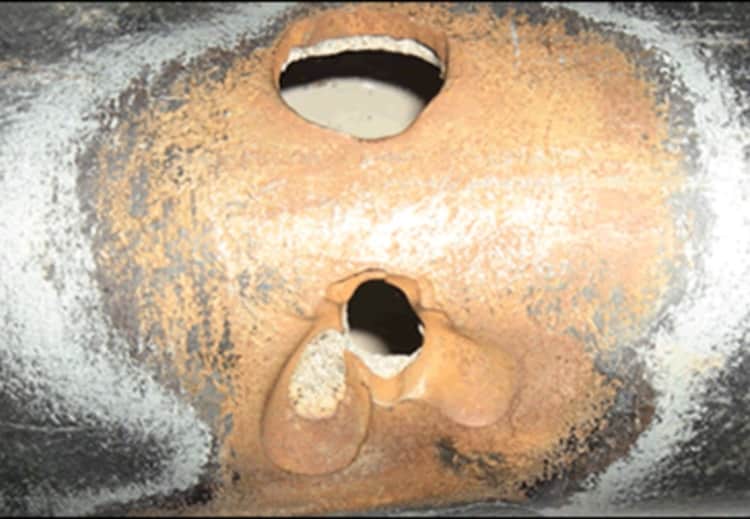
The biggest problem with stray currents is electrocorrosion. The heated towel rail is already subject to a fairly high degree of risk. Due to the fact that hot water passes through the pipes, salts accumulate on the inner walls, which interfere with the passage of the coolant. Due to the effect of electricity on water, the effect of galvanic corrosion occurs, when the precipitation and deposition of salts is accelerated, as well as the corrosion processes of the metal, in other words, rust begins to affect the pipe many times more strongly.
Taken together, all these factors lead to the rapid failure of the heated towel rail. Usually the manufacturer speaks of 5 years of service, but a stainless steel heated towel rail is in fact capable of withstanding 20-30 years of use.
In the case of stray currents, electrocorrosion will destroy the metal in 2-3 years and will not find fault with the manufacturer. Incorrect installation is to blame for everything.
However, manufacturers of heated towel rails have tried to foresee this fact and make more expensive products with corrosion protection.This tool is presented in advertising as protection aimed specifically at electrocorrosion, but in fact the innovation also protects against salt precipitation.
To save a heated towel rail, the manufacturer covers the inner surface of the pipe with a special polymer. Thus, the electricity from the pipe cannot affect the water. At the same time, the inner surface becomes smooth, which prevents the deposition of salts, which means that such a coating protects the pipes from overgrowing.
But don't think that such an innovation is a panacea. We must not forget that stray currents are not only electrocorrosion, but also the danger of electric shock. In terms of corrosiveness, the coating will really protect the heated towel rail. But for your own safety, it is better to ground the heated towel rail.
Why haven't there been such difficulties before?
Strange as it may sound, but the reason for the emergence of such a problem as the potential difference in engineering systems was progress. Namely, the widespread replacement of metal pipes with plastic ones. While the hot water supply, cold water supply and heating pipelines were completely metal, there were no difficulties. And there was no need to separately ground each radiator, mixer or heated towel rail - all pipes were grounded centrally in the basement of the house, in two places. And all metal appliances in bathrooms and toilets automatically became safe and protected from stray currents.
The transition to plastic changed everything: on the one hand, pipelines began to serve longer, and on the other hand, there was a need for additional protection of plumbing equipment. And here the point is not only in the pipes themselves, because in terms of conductivity, metal-plastic is close to traditional metal, but also in fittings - connecting elements. More precisely, in the materials from which they are made and which cannot provide electrical contact with the aluminum "core" of the metal-plastic pipe.
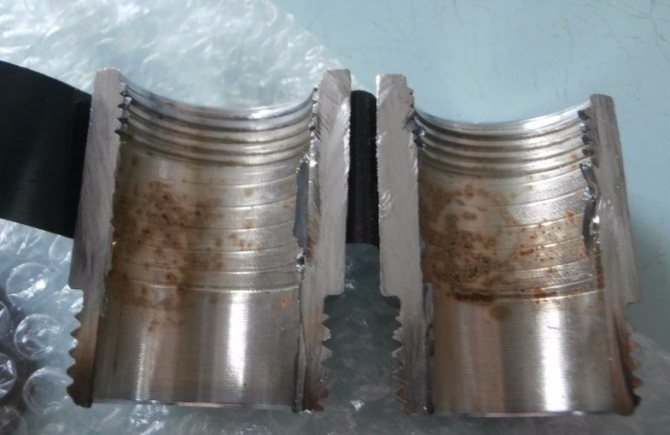
Impact on plumbing
The wandering electric current destroys the water supply as the particles of electricity eat up the metal molecules. When pipes are constantly exposed to energy, their walls become thinner. As a result, damage appears, which leads to the need to make a complete replacement of the water supply system. To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to choose the right way to protect the products.
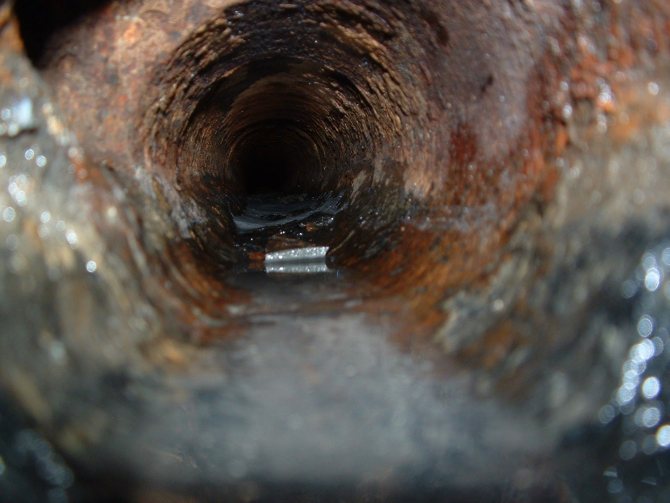


Thinning of water supply walls as a factor of current exposure
Grounding as protection against electrical corrosion
To prevent the occurrence of stray currents in the system and to protect the heated towel rail from electrochemical corrosion, it is necessary to recreate a stable connection between it and the riser pipe. In other words, you just need to ground the peripheral device by connecting the heated towel rail with a wire to a metal riser, or mount a potential equalization system.
It is also important to do this because some unscrupulous residents of apartment buildings, wanting to save money, put bugs on their electricity meters, and use heating or water supply pipelines as grounding. And then their neighbors are in real danger, because even a simple touch to a metal battery will give a person a "chance" to receive a fatal electric shock.
Ways to ground a heated towel rail
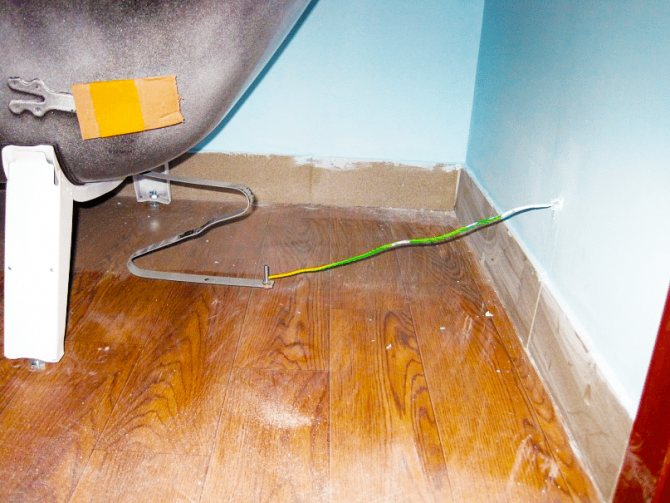
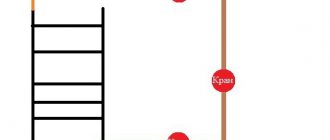
There is actually only one way to ground a heated towel rail: using a ground wire connected to the ground loop in the electrical panel. When using plastic in the installation of a heated towel rail, each metal element of the system is grounded. For this:
- The wire must be stripped, and then bent in the form of a loop
- The paint is cleaned from the pipe, after which the stripped part of the wire is leaned against the metal part of the pipe.
- The loop is secured with a metal clip.
- All metal parts of the structure are bypassed with such loops.
- The wire is brought out to the electrical panel at the entrance and connected to the grounding loop.


There is only one way to ground a heated towel rail
In old houses, where the ground loop is not provided, you will have to do with metal pipes so as not to break the loop that equalizes the potentials of metal structures.
Polymer processing - the solution to the problem without grounding
But you can solve the problem in another way by treating the inner surface of a stainless steel water heated towel rail with a special polymer composition. It will create an insulating coating that will effectively “work” against potential differences and corrosion.
Polymer processing of water heated towel rails is an additional service that is performed by our company at the request of the buyer. And you can order it online on the ZIGZAG website.
Go to