ROOM MECHANICAL REGULATOR
A room mechanical thermostat is a device that regulates the operation of climatic equipment, maintaining the set temperature parameters of the room. It can be used both for heating and cooling an apartment or house.
The main difference between room mechanical thermostats and thermostats of another type is that it is a separate, completely independent device, most often made in the form of an external wiring product, intended for indoor installation.
Simply put, a mechanical thermostat, depending on the set program, by turning on or off certain heating or cooling devices, maintains the required temperature in the room.
The main feature of the mechanical thermostat is the complete absence of electrical filling, i.e. no power is required for its operation, not even batteries.
How does a mechanical thermostat work, what exactly allows it to measure the temperature of the surrounding space and control electrical appliances?
Faulty thermostat. What are they?
The thermostat is an important part. It can fail for many reasons, however, corrosion is the most common.
If the thermostat is jammed in the fully closed position, then in any driving mode at any air temperature, the motor may overheat and even in a slight frost. If the thermostat is open, but not completely, then the engine overheats, but at the same time it may not "boil", it all depends on the modes in which the car is operated.
If the thermostat valve "hangs" in a fully open state or partially open, then the engine will warm up to its operating temperature for a long time, and in winter the operating temperature may not be reached at all. So, with a working cooling system and at an air temperature of zero degrees, the power unit should warm up to its operating temperature during movement in five to ten minutes. The engine temperature in the half-open state of the thermostat will not rise above seventy degrees.
How can you tell if a thermostat is working or not?
It is necessary to warm up the engine so that the temperature arrow does not slightly reach the red line. Next, turn off the power unit, open the hood, and check the radiator hose. The top hose is fixed on top of the radiator and is a black rubber hose about five centimeters in diameter. And find the bottom hose, which looks the same as the top one.
Next, touch the hoses, but you should do it carefully, because they may be hot. If the engine temperature sensor shows that the engine has warmed up, and at the same time one hose is hot and the other cold, then most likely the thermostat valve is closed and the "cooling" does not pass through the radiator. In this case, replace the thermostat with a new one.
There is a "popular method" how to test a thermostat for its performance. So, the point is to put the thermostat in a vessel with burning water, at a temperature of about one hundred degrees. After that, look visually, if the valve opens, it means that it is a worker. And if not, then this is a non-working thermostat, and change it to a new one. This method will require removing the thermostat from the car. When updating the thermostat, find out the opening temperature of the valve. The fact is that it can vary over a wide range for different thermostats.And as you understand from what has been said, you cannot put the thermostat with a high temperature when opening it, since in this case the motor may overheat.
- Forward>
OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF THE MECHANICAL THERMOSTAT
A mechanical thermostat is a device that perfectly reflects the principle - “Everything ingenious is simple!”. With all the difference in designs and components used, there is one single principle in the operation of mechanical thermostats, namely the ability of some materials and substances to change their mechanical properties depending on temperature.
As an everyday example, familiar to everyone, that would explain the principle of operation of a mechanical thermostat, we can cite an ordinary mercury thermometer, with which we measure body temperature.
The mercury contained inside the thermometer increases in volume with increasing temperature and enters the graduated capillary, thereby showing the exact temperature.
Roughly the same processes take place in a mechanical thermostat, the only difference is that a change in temperature to a certain level, which is indicated by us separately with a regulating wheel, starts certain processes, most often closes or breaks an electrical circuit, thereby turning on or off heating devices.
To make it clearer how it all works, let's look at the design of a standard room mechanical thermostat.
Types of thermostats
Based on the principle of operation, thermostats are divided into two types:
- mechanical;
- electronic.
In turn, each type is subdivided into subspecies.
Mechanical thermostats
In mechanical thermostats, sensors are used with different actuation technologies, but they are all based on the same principle. To understand how a mechanical thermostat works, one must pay attention to the physical properties of many substances to expand when heated and contract when cooled (water is a notable exception, expanding when cooled). Mechanical thermostats use this property called thermal expansion.
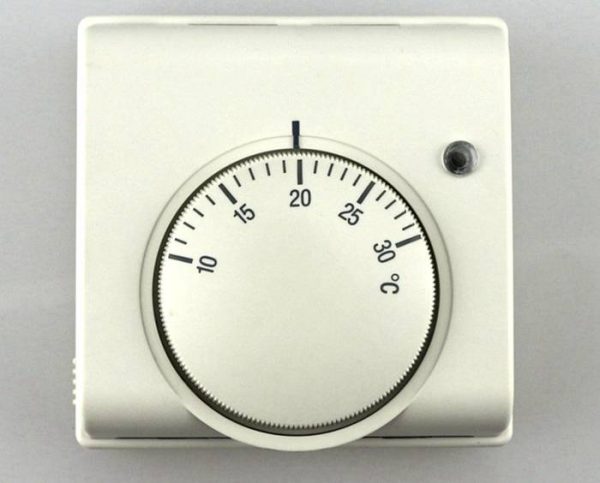

Mechanical thermostat
Bimetallic plates
The principle of operation of the thermostat, the most commonly used, is to use a plate of two strips of different metals, bolted together.
Switching the bimetal thermostat on and off:
- The external drive of the device allows you to set the temperature at which it turns on and off;
- The dial of the disc is connected through a circuit to a temperature sensor - a bimetallic plate that closes and opens an electrical circuit, depending on the greater or lesser bend;
- A bimetallic strip is made up of different metals bonded together;
- One metal expands less than another when heated; therefore, the plate bends inward when the temperature rises;
- The plate is part of an electrical circuit, so when the strip is cold it is straight and the circuit is closed. The system is turned on and warming up. When heated to a certain temperature, the plate bends and breaks the chain. The circuit is disabled.
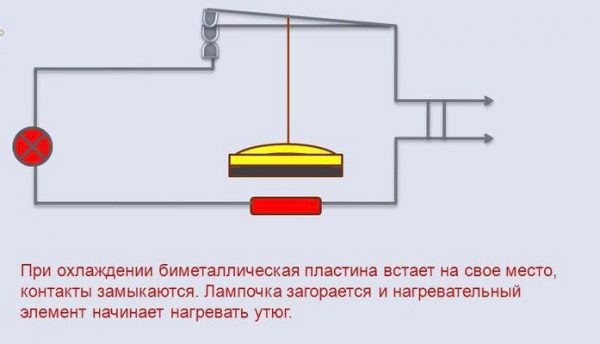

The work of the bimetallic plate
Important! Since the plate takes time to expand and contract, the sensor has a response inertia.
Gas-filled sensors
Due to the slow reaction of metals to temperature changes, alternative designs of thermostats have been developed. One is the use of a gas-filled bellows between a pair of metal discs. The large surface area of these discs allows them to react quickly to heat. In addition, they are resilient and have ridges.


Mechanical thermostat with gas-filled sensor
- As the temperature rises, the gas in the disc space expands and separates the discs.In this case, the one that is inside, presses the microswitch in the middle of the thermostat, opening the circuit. Heating stops;
- When the temperature drops, the gas contracts, again bringing the discs closer to each other. The inner disc moves away from the microswitch. The contact closes, including heating.
Gas-filled thermostats are used for heating systems in homes, they were used in older car models. Sometimes they do not use gases, but volatile liquids with a low boiling point. For example, diluted alcohol.
Important! The specific chemical composition of liquids is selected based on the range of controlled temperatures.
Wax thermostats
This type of thermostat has a sealed chamber with a wax stopper and a free-running metal rod inside. As the temperature rises, the wax melts, expands and pushes the rod out of this chamber. At the same time, the rod acts on the switching on and off of the electrical circuit. The spring returns the mechanism to its place when the wax cools.


Wax thermostat device
Wax thermostats are used in automotive engine cooling control systems, faucets, etc. The simple design thermostat is well suited for the harsh conditions inside the engine and is highly reliable.
Valves are installed on central heating radiators, where wax thermostats are often used. When the radiator heats up to a set level, the wax regulators reduce the flow of water through the radiator.
Electronic thermostats
A digital thermostat is an electronic version of a mechanical thermostat. Instead of a mechanical sensor, a thermistor can be installed - a resistor that changes its resistance with respect to temperature, or a thermocouple. The signal enters the electronic module, where it is processed, and from there commands are sent to turn on and off heating or cooling. The advantage of the electronic thermostat is more precise temperature control.
Digital controllers are:
- Non-programmable. Devices with a simple set of functions, with a digital display and control buttons for setting the selected temperature value;
- Programmable. Mini-computer devices that allow you to set the days of the week, hours, temporary temperature maintenance, manual override, etc.;
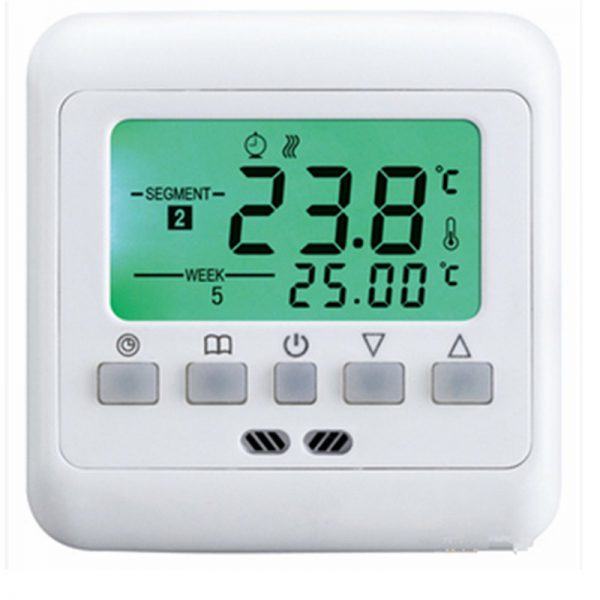


Programmable thermostat
- Wireless. With the development of modern technology, thermostatic devices have become "smarter" and freed from wires. Such devices are linked using various wireless portals such as WiFi or Bluetooth. The most common is WiFi connection. In such connections, the efficiency of the connections is increased and the problems associated with wiring are removed.
Some additional functionalities of electronic devices:
- Integration of window contacts for temperature reduction with open windows;
- Coordination of the work of several radiators;
- Separate mounting of measuring sensors in an optimal place;
- Remote control of the system by phone, internet or smartphone. At a considerable distance from home, you can always make adjustments to the settings;
- Alarm if the temperature is too low or too high. If desired, the owner receives an email message;
- Integration of alarms for smoke detectors and pipe burst detectors.
In addition, the latest generation of wireless thermostats have a pleasant modern look. They can provide detailed energy reports and a voice control system is available.
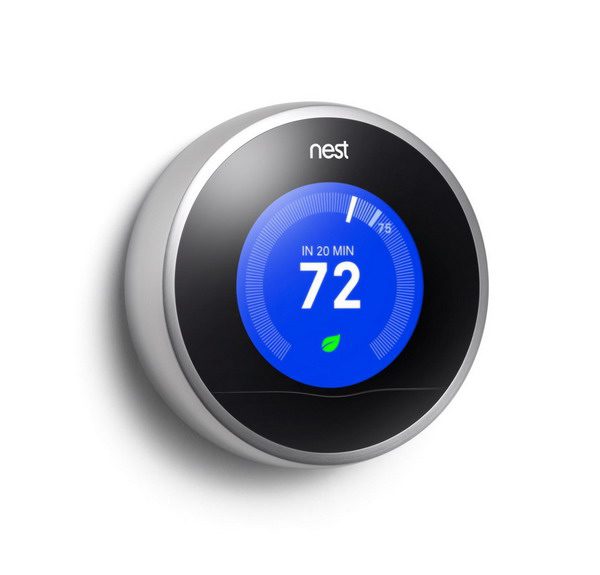


Wireless thermostat
Dual zone thermostats
The dual-zone thermostat allows you to simultaneously control different heating systems and perform programming for two living quarters (for example, a bedroom and a kitchen, a living room and an entrance hall). It is possible to set different levels of the desired temperature in each room or area of the house.
The model of the device usually contains several recorded programs, you can make your own corrections. The commonly used temperature range is 7 to 30 degrees. The regulation step is half a degree.
The two-zone thermostat is suitable for almost all types of heating: electric underfloor and ceiling, gas with water radiators and other systems.
The device consists of several elements:
- electronic programmable module;
- temperature sensors;
The sensors should be installed in places free from drafts and direct sunlight, which can distort the data transmitted to the electronic control module.
In addition to the two-zone thermostats, there are two-stage thermostats used, for example, in air conditioning installations, where automatic control is required in cold and warm cycles with an intermediate dead zone. It consists of a double changeover contact electrically. It can also be used for conventional temperature control using one contact.
Mechanical thermostat device
The main structural element of almost any room mechanical thermostat is a gas membrane. By the way, it is for this that they are often called membrane thermostats.
The special gas inside the membrane, when the temperature changes, changes its volume, thereby affecting the membrane walls. Which, when changing, trigger the mechanism for closing or opening the electrical circuit that feeds the heating or cooling system.
The choice of just such a device method for a room thermostat is due to the possibility of organizing a simple way to adjust its response temperature, as well as the fact that the device responds precisely to changes in the air temperature, and not the surface, which is most important in heating and cooling systems. Therefore, for example, for underfloor heating, it is wiser to use mechanical liquid thermostats with a remote sensor.
Adjustment of the response temperature for a membrane room thermostat is carried out using a control wheel with a scale, which is connected to the membrane mechanism. By turning the wheel, we bring the membrane walls closer or further away from the control mechanism, thereby changing the temperature at which the electrical circuit will close or open. In other words, if the triggering mechanism is closer to the membrane wall, then the gas located in it needs to slightly change the volume for it to trigger; accordingly, a lower temperature is needed and vice versa. This is how the adjusting wheel works.
Let's look at exactly how you can apply a mechanical thermostat to the heating system of a house or apartment.
Thermostat is a popular laboratory equipment
A laboratory thermostat is a device that is used to maintain a constant temperature in a chamber or container for a certain time, regardless of the room temperature. It is in demand in laboratories of various profiles: chemical, medical, biological, research, testing, production. Thermostats are used in industry and agriculture, in microbiology and genetics, bacteriology and pharmaceuticals, in the laboratories of ordinary clinics and in the largest scientific centers. In many studies, the thermostat is a critical piece of equipment that cannot be dispensed with.
Classification of thermostats
Thermostats are available in different designs, functionality and volume.Most often they are usually classified according to the type of "heat carrier": - electric dry-air thermostats; - liquid; - cryogenic.
Electric dry-air thermostat - equipment that supplies warm air into the chamber with the help of a pump. The fans distribute it evenly throughout the chamber.
A cryogenic thermostat is similar in design, with the difference that the pump drives the air entering the chamber not through the heat heater, but through the tubes with the circulating refrigerant. This type of thermostat is also called an "electric cooled thermostat". As well as dry air, cryogenic thermostats are equipped with forced air circulation to maintain a stable temperature at any point in the chamber.
Liquid thermostats are available in different designs and for different purposes. The temperature range and temperature control accuracy depend on the type of heat carrier used. Liquid thermostats can be heating and cooling. The most convenient are thermostats with distilled water: it is easy to change, the viscosity of water does not change when the temperature changes; it is possible to achieve high accuracy of temperature control. The disadvantage of distilled water thermostats is a relatively narrow temperature range: from +5 ° C to +95 ° C. In the widest range of temperatures, a liquid thermostat operates on a special silicone oil: from -80 ° C to +350 ° C. But this oil is expensive and needs to be changed frequently as it quickly oxidizes and polymerizes. When operating in high temperatures, the appliance requires exhaust ventilation. At the same time, one cannot do without an oil thermostat, for example, when checking thermometers with operating temperatures above 300 ° C.
Design features of modern thermostats
Modern temperature control devices are equipped with a microprocessor control with a set of sensors, an information display, a timer, a security and alarm system in case of errors and emergencies, a glass window (glass door) and a backlight for monitoring the processes in the chamber. Electronic control provides high accuracy of temperature control - up to hundredths of a degree. The basis of any modern thermostat, regardless of type and design, is a thermally insulated chamber that provides reliable isolation of objects, samples or materials placed inside from the environment. The chamber, as a rule, is made of stainless steel and contains various sensors to monitor the process. The chamber of dry air thermostats must have fans for even air distribution. In liquid devices, liquid mixing can be solved in different ways.
Thermostat chambers vary greatly in volume.
When choosing a thermostat, one must proceed from its volume, temperature range, and temperature control accuracy. Convenience and operating conditions, functionality, cost also matter.
Laboratory equipment store Prime Chemicals Group offers a dry-air thermostat mc 1 80, thermostat mc 80 spu, other thermostats, thermometers, a wide range of laboratory equipment and chemistry. reagents. We have competitive prices and service, fast delivery in Moscow and the Moscow region.
Using a mechanical thermostat in heating
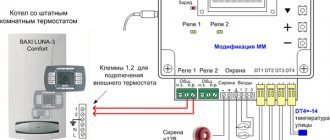
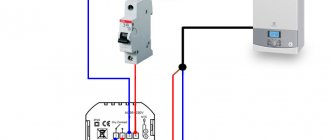
Most often, room mechanical thermostats are used in heating houses, together with gas boilers. Manufacturers quite often in the design of boilers provide for a connection diagram through a mechanical thermostat. The device is installed in a break in the supply wire leading to the boiler and in the case when the air temperature in the room drops below the set threshold value, the circuit closes and the gas boiler starts up, starting to heat the room, maintaining the temperature of the coolant.
The basic diagrams for connecting a mechanical thermostat to heating or cooling are described in our article "Wiring diagram for a mechanical thermostat"
In exactly the same way, home thermostats are connected to any electric heaters in rooms, be they oil heaters, infrared heaters, or any other used for heating indoor air. Thus, the heating process becomes fully automated, requiring almost no human participation in its work, after adjustment.
There are a lot of possible options for using mechanical thermostats; it is simply irreplaceable in heating automation due to its unpretentiousness and reliability. And the simplicity of the design allows manufacturers to produce room mechanical thermostats at a much lower cost than electronic ones, which is an important part of their popularity with the consumer.
The main types and capabilities of thermostats
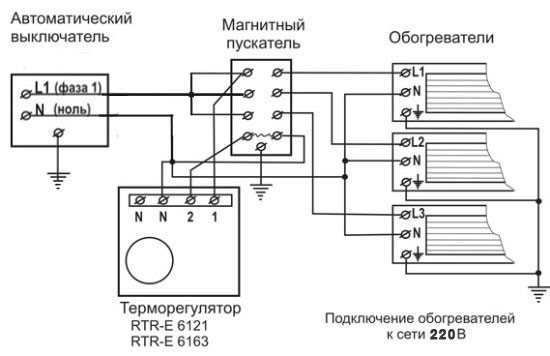

Thermostat connection diagram.
There are two main types of thermostats: gas-floor and liquid.
A gas-floor thermostat, in contrast to a liquid type, is more sensitive to changes in the temperature regime of the environment and has a longer service life - up to 20 years. Gas condensate is used as a heat-sensitive substance.
As for the liquid type, it has more accurate temperature indicators than the gas-floor one. In most cases, paraffin is used to fill it.
Also thermostats are:
- Analog room. Such a device allows you to continuously maintain the selected temperature regime. However, its technical capabilities are somewhat limited. Starting and stopping, as well as changing the operating parameters, occur only manually and completely exclude the programming of the system.
- Digital room. The installation of devices of this type expands the control capabilities, which reduces the load on the heating system. The digital thermostat changes and maintains the temperature according to a preset program. In addition to the simplest functions ("convenience" and "damping"), it allows you to adjust the mode and automatically switch up to 4 times a day.
- Thermostats for an additional "warm floor" system. A feature of the functioning of such a system is its independence from the air temperature, and the room is heated by other heating installations (convector, radiator, etc.) Therefore, the operation of the thermostat is provided by a sensor installed in the floor area.
Related article: How to choose and glue a plinth to the bathroom floor
Sometimes it is not possible or technically difficult to regulate the operation of the heating system in the usual way. Such a situation may arise during the reconstruction of objects or in the case of additional installation of heating devices. Therefore, the optimal control of the heat supply in this case is the installation of a thermostat with a wireless control method.
Selecting a mechanical thermostat (thermostat)
Currently, there are many manufacturers of mechanical thermostats, there are models and famous brands, but, most often, on sale you will find unfamiliar, unknown names. In my practice, I have used a large number of different mechanical thermostats and can advise the following:
- When choosing, be sure to pay attention to the maximum switching power. If it is written that the thermostat is 10 Amperes, it will be possible to connect a load of no more than 2.2-2.3 kW to it. Thermostats with more than 3.6 kW of connected power are rare. If you need to connect more power, you will have to use a contactor, according to the connection diagram, the link to which I gave a little higher.
— Of the inexpensive thermostats, I liked this one - BALLU BMT-1 - you can buy it here. By design, it is completely similar to that described in this article. It will work for you for exactly 3-5 years, and then it depends on the build quality of a particular model and operating conditions. For a summer residence, a garage - that's it!
If you need advice on choosing a mechanical thermostat model - write in the comments, I will try to help with advice!
Classification
Thermostats can be classified according to their operating temperature range:
- High temperature thermostats (300-1200 ° C);
- Medium temperature thermostats (60-500 ° C);
- Low temperature thermostats (less than −60 ° C (200 K)) - cryostats.
Thermostats can be classified according to the working fluid (heat carrier):
- Air;
- Liquid;
- Solid (Peltier and wax elements are usually used).
Thermostats can be classified according to temperature accuracy:
- 5-10 degrees and worse, as a rule, is achieved without stirring, due to natural convection;
- 1-2 degrees (good thermal stability for air, very mediocre for liquid), usually with stirring;
- 0.1 degrees (very good thermal stability for air [1], at the level of the best samples, average for liquid);
- 0.01 degrees (as a rule, it is achieved in liquid thermostats of a special design [2]), it is practically impossible to obtain in an air thermostat with a fan.
Thermostats can be classified by area and application:
- Industrial thermostats; overhead thermostats;
- immersion thermostats;