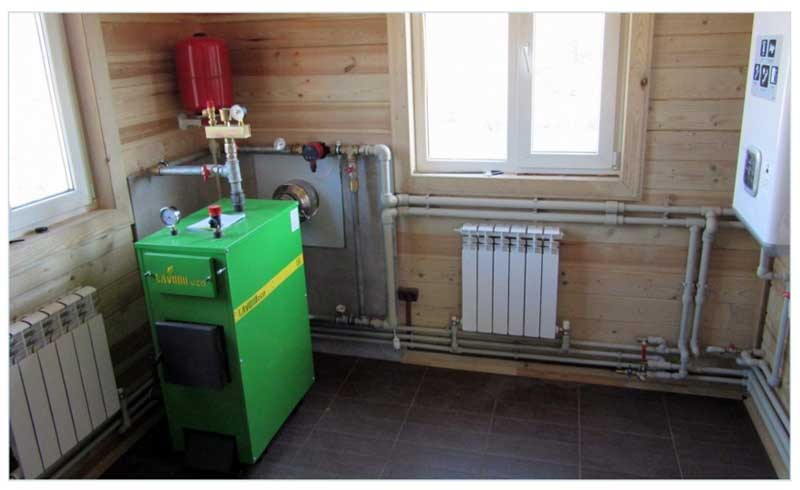
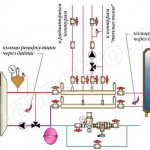
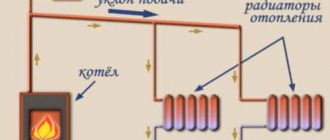
What should be the operating pressure in the heating system
But to answer this question in a nutshell is quite simple. Much depends on which house you live in. For example, for an autonomous or apartment, 0.7-1.5 atm is often considered normal. But again, these are approximate figures, since one boiler is designed to work in a wider range, for example, 0.5-2.0 atm, and the other in a smaller one. This must be seen in the passport of your boiler. If there is none, stick to the golden mean - 1.5 Atm. The situation is quite different in those houses that are connected to central heating. In this case, it is necessary to be guided by the number of storeys. In 9-storey buildings, the ideal pressure is 5-7 atm, and in high-rise buildings - 7-10 atm. As for the pressure under which the carrier is supplied into buildings, it is most often 12 atm. You can reduce the pressure using pressure regulators, and increase it by installing a circulation pump. The latter option is extremely relevant for the upper floors of high-rise buildings.
The advantage of using automatic balancing valves is also the possibility of dividing the system into separate pressure-independent zones and their phased commissioning. The advantages of automatic balance valves include easier and faster system setup, fewer valves and minimal system maintenance. Modern automatic balance valves are characterized by high reliability and improved control characteristics. Some of them are modular as a design, that is, they can be updated or expanded in functionality.
Return in the heating system, its purpose
The return in the heating system is a heat carrier that has passed through all the heating radiators, has lost its own primary temperature and is already cold supplied to the boiler for the next heating. The heat carrier can move both in a two-pipe and in an improved single-pipe heating system.
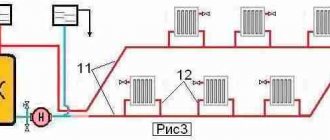
The heating system of Leningrad under itself assumes the sequence of connections of heating radiators. In other words, the supply pipe is led to the first heat exchanger, from which the next pipe goes to another heat exchanger, and so on.
If the heating system with one pipe is improved, then its design will be approximately as follows: along the perimeter of the entire room there is one pipe, into which you can insert the supply and return pipes of each heater. In this case, there is a possibility of installing a control valve for each battery, thanks to which you can very successfully adjust the ambient temperature in this room.
The undoubted advantage of such a heating system is the small number of pipes in it. And minus is the temperature difference between the first heating device from the boiler and the last one. This problem can be removed with the help of a circulation pump, which will become much faster to expel all the water through the system and heat supply, and in this way the heat carrier will not have time to reduce the temperature.
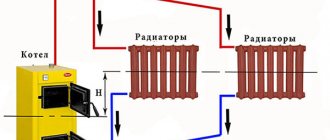
The heating two-pipe system is a wiring of 2 pipes. One pipe is the supply of a hot heat carrier, the second pipe is a return line in the heating system, through which already cooled water from the heating devices enters the boiler. Such a system makes it possible to almost parallel connect all the heating devices, which makes it possible to flexibly adjust each heating device separately, without affecting the operation of others.
Cold return results
Return heating circuit
Sometimes, with an incorrectly designed project, the return flow in the heating system is cool. As practice says, the fact that the room does not receive enough heat with a cold return is still half of the trouble.And the thing is that at different supply and return temperatures, condensate can fall out on the walls of the boiler, which, when interacting with carbon dioxide, which differs during fuel combustion, forms acid. She then can disable the boiler significantly ahead of time.
To prevent this, it is necessary to carefully calculate the project of the heating system, special attention should be paid to such an invisible moment as the return temperature in the heating system. Or include auxiliary devices in the system, for example, a circulation pump or storage water heater, which will compensate for the loss of warm water
Heater connection options
Now we can more than safely say that when designing a heating system, the supply and return must be wonderfully thought out and configured. With the wrong design of the heating system, more than 50% of the heat can be lost.
There are three options for inserting a heater into the heating system:
The diagonal system gives the highest efficiency rate, and due to this it is considered more functional and effective.
The diagram shows a diagonal inset
How to change the temperature in the heating system?
In order to adjust the temperature of the heater and reduce the difference between flow and return temperatures, a heating system temperature controller can be used.
During the installation of this device, you need to remember about the jumper, which must be located in front of the heating device. In the absence of it, you will change the temperature of the batteries not only in your own room, but also throughout the riser. The neighbors are unlikely to be happy with similar actions.
A very simple and inexpensive version of the regulator is the installation of three valves: on the supply, on the return and on the jumper. If you close the valves on the radiator, the jumper must be open.
Where is the return line
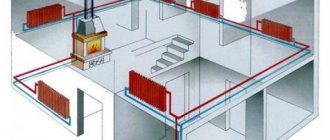
In short, the heating circuit consists of several important elements: a heating boiler, batteries and an expansion tank. In order for the heat to flow through the radiators, a coolant is needed: water or antifreeze. With a competent construction of the circuit, the coolant heats up in the boiler, rises through the pipes, increasing its volume, and all the excess gets into the expansion tank.
Based on the fact that the batteries are filled with liquid, hot water displaces cold water, which, in turn, enters the boiler again for subsequent heating. Gradually, the degree of water increases and reaches the desired temperature. In this case, the circulation of the coolant can be natural or gravitational, carried out using pumps.
Based on this, the coolant can be considered a return flow, which passed through the entire circuit, giving off heat, and already cooled down again entered the boiler for subsequent heating.
Pressure regulator
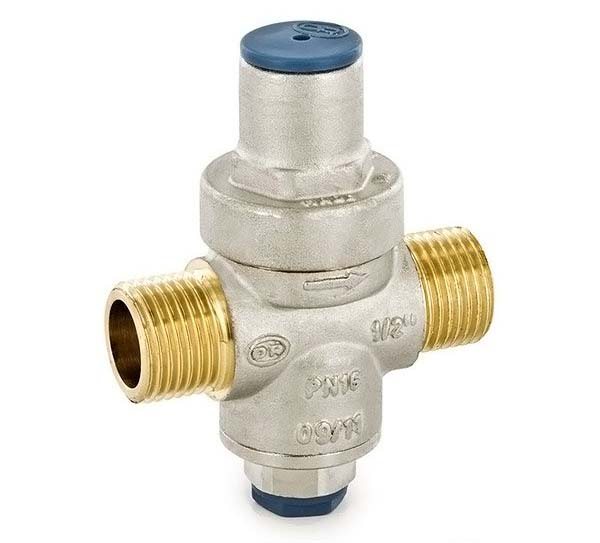


The operation of the batteries and the pump is disrupted due to high or low pressure levels. Correct control in the heating system will help to avoid this negative factor. The pressure in the system plays a significant role, it ensures that water enters the pipes and radiators. Heat loss will be reduced if the pressure is standardized and maintained. This is where water pressure regulators come to the rescue. Their mission is, first of all, to protect the system from too much pressure. The principle of operation of this device is based on the fact that the valve of the heating system, located in the regulator, acts as an equalizer of efforts. Regulators are classified according to the type of pressure: statistical, dynamic. The choice of pressure regulator should be based on the capacity. This is the ability to pass the required volume of the coolant, in the presence of the required constant pressure drop.
DHW circulation
In order for hot water to be available at any point in the system, it is necessary to assemble such a circuit through which it will continuously circulate, coming from a boiler or storage water heater and returning to it if the system is in standby mode. Thanks to this, the water in the pipes never gets cold and is always available to users.
Circulation in the DHW circuit can be natural due to convection. However, greater efficiency can be achieved by using forced circulation with a small pump.
Modern domestic circulation pumps are practically silent and have a capacity of only a few tens of watts. They are easy to operate and require little or no maintenance. However, these are not the same circulating pumps used in heating systems. They are better protected from corrosion, since the water in the DHW circuit is saturated with air, in contrast to closed central heating systems. Thus, the rotor and other elements in contact with water are made of materials that are not sensitive to oxygen.
Experts recommend using circulation if the length of the pipe from the hot water stand to the tapping point exceeds 2 m.If there are two or more hot water circuits in the house located at different distances from the water heater, it is advisable to use special control valves that equalize the pressure in the system. The absence of such valves leads to an imbalance in the system: water begins to circulate in the circuit where the least hydraulic resistance is present.
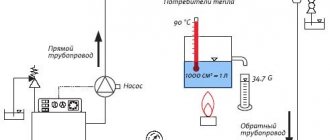
Working pressure in the heating system
The working pressure is the pressure, the value of which ensures the optimal operation of all heating equipment (including the heating source, pump, expansion tank). In this case, it is taken equal to the sum of the pressures:
- static - created by a column of water in the system (in the calculations, the ratio is taken: 1 atmosphere (0.1 MPa) per 10 meters);
- dynamic - due to the operation of the circulation pump and the convective movement of the coolant when it is heated.
It is clear that in different heating schemes the value of the working head will differ. So, if the natural circulation of the coolant is provided for the heat supply of the house (applicable for individual low-rise construction), its value will exceed the static indicator by only a small amount. In compulsory schemes, however, it is taken as the maximum permissible to ensure a higher efficiency.
Numerically, the value of the working head is:
- for one-storey buildings with an open circuit and natural water circulation - 0.1 MPa (1 atmosphere) for every 10 m of the liquid column;
- for low-rise buildings with a closed circuit - 0.2-0.4 MPa;
- for multi-storey buildings - up to 1 MPa.
Features of hot water supply and calculation of the amount of hot water
The calculation of the amount of hot water in the system depends on technical and operational factors:
- Estimated hot water temperature;
- The number of residents in an apartment building;
- The parameters that plumbing fixtures withstand, and the frequency of their operation in the general water supply scheme;
- the number of plumbing fixtures that are connected to the hot water supply.
- A family of four uses a 140 liter bathroom. The bathtub fills up in 10 minutes, the bathroom has a shower with a water consumption of 30 liters.
- Within 10 minutes, the device for heating water must heat it up to the design temperature in the amount of 170 liters.
These theoretical calculations work assuming residents' average water consumption.
Safety valves
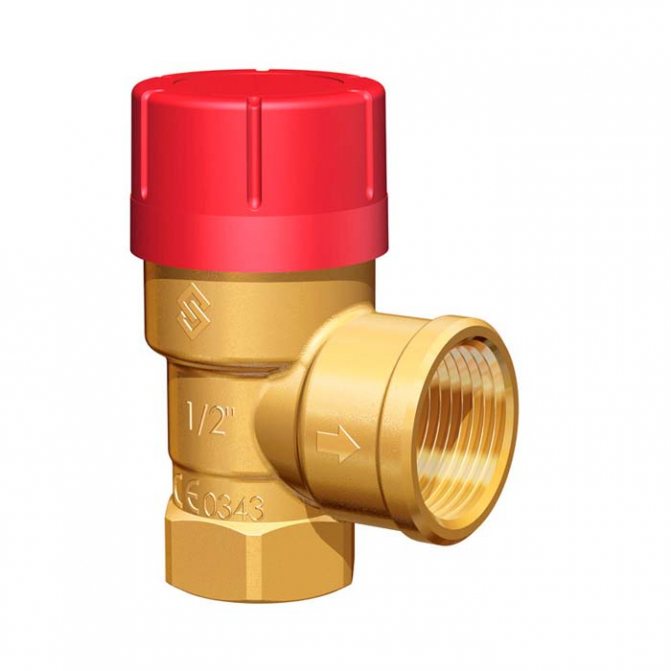


Any boiler equipment is a source of danger. The boilers are considered explosive because they have a water jacket, i.e. pressure vessel. One of the most reliable and common safety devices that minimizes danger is the heating system safety valve.The installation of this device is due to the protection of heating systems from overpressure. Often, this pressure occurs as a result of boiling water in the boiler. The safety valve is installed on the supply line, as close as possible to the boiler. The valve has a fairly simple design. The body is made of good quality brass. The main working element of the valve is the spring. The spring, in turn, acts on the membrane, which closes the passage to the outside. The diaphragm is made of polymer materials, the spring is made of steel. When choosing a safety valve, it should be borne in mind that full opening occurs when the pressure in the heating system rises above the value by 10%, and full closure when the pressure drops below the response by 20%. Due to these characteristics, it is necessary to select a valve with a response pressure higher than 20-30% of the actual one.
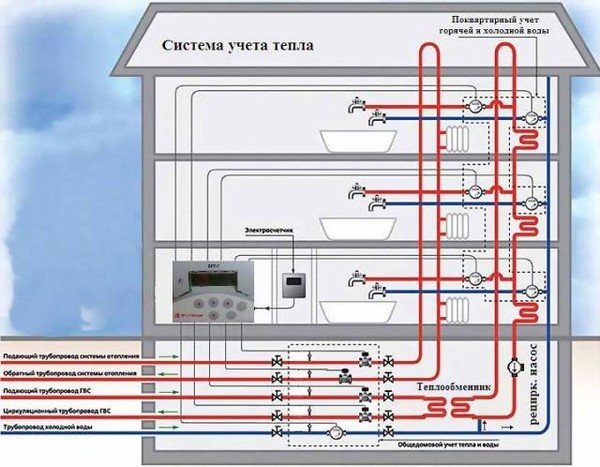
Features of the heating system of apartment buildings
When equipping heating in multi-storey buildings, it is imperative to comply with the requirements established by regulatory documents, which include SNiP and GOST. These documents indicate that the heating structure should provide a constant temperature in apartments within the range of 20-22 degrees, and the humidity should vary from 30 to 45 percent.
To achieve the required parameters, a complex design is used that requires high-quality equipment. When creating a project for a heating system for an apartment building, specialists use all their knowledge to achieve an even distribution of heat in all sections of the heating main and create a comparable pressure on each tier of the building. One of the integral elements of the work of such a structure is work on an overheated coolant, which provides for a heating scheme for a three-story building or other high-rise buildings.
How it works? The water comes directly from the CHP and is heated up to 130-150 degrees. In addition, the pressure is increased to 6-10 atmospheres, so the formation of steam is impossible - high pressure will drive water through all floors of the house without loss. In this case, the temperature of the liquid in the return pipe can reach 60-70 degrees. Of course, at different times of the year, the temperature regime can change, since it is directly tied to the ambient temperature.


Network diagrams
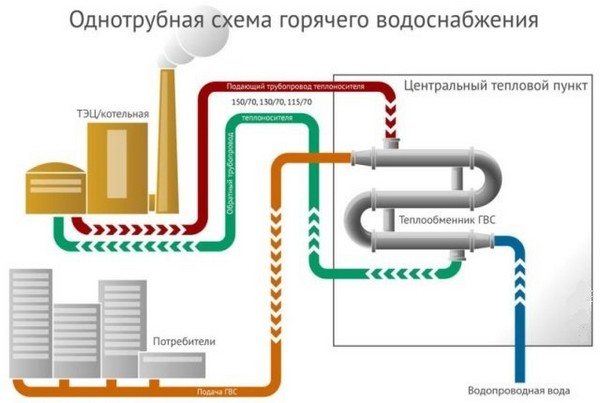
So, let's start with the question of how water enters our homes, I mean hot. It moves from the boiler room to the house, and is driven by pumps installed as boiler equipment. Heated water moves through pipes, which are called heating mains. They can be laid above or below ground. And they are necessarily thermally insulated in order to reduce the heat loss of the coolant itself.
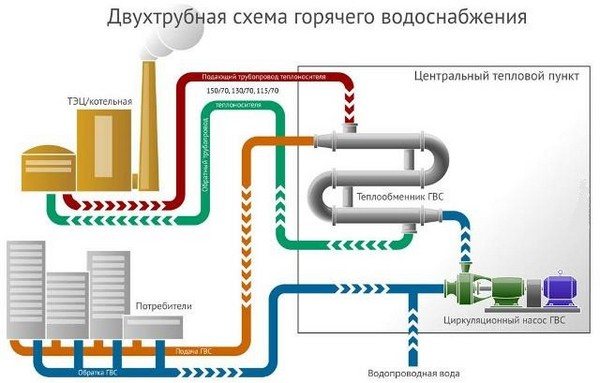

The pipe is brought to the apartment buildings, from where the route is branched into smaller sections, which supply the coolant to each building. A pipe with a smaller diameter enters the basement of the house, where it is divided into sections that deliver water to each floor, and already on the floor to each apartment. It is clear that this amount of water cannot be consumed. That is, all the water pumped into the hot water supply cannot be consumed, especially at night. Therefore, another route is being laid, which is called the return line. Through it, water moves from apartments to the basement, and from there to the boiler room through a separately laid pipeline. True, it should be noted that all pipes (both return lines and feeds) are laid along the same route.
That is, it turns out that the hot water itself inside the house moves around the ring. And she is constantly in motion. In this case, the circulation of hot water in an apartment building is carried out from the bottom up and back.But in order for the temperature of the liquid itself to be constant on all floors (with a slight deviation), it is necessary to create conditions under which its speed was optimal, and it did not affect the decrease in the temperature itself.
It should be noted that today, routes for hot water supply and for heating can be approached separately to apartment buildings. Or one pipe with a certain temperature (up to + 95C) will be supplied, which in the basement of the house will be divided into heating and hot water supply.

DHW wiring diagram
By the way, pay attention to the photo above. A heat exchanger is installed in the basement of the house according to this scheme. That is, the water from the line is not used in the hot water supply system. It just heats up cold water coming from the water supply network. And the DHW system itself at home is a separate line, not connected with the line from the boiler room.
The house network is circulating. And the water supply to the apartments is produced by a pump installed in it. This is by far the most modern scheme. Its positive feature is the ability to control the temperature regime of the liquid. By the way, there are strict standards for hot water temperature in an apartment building. That is, it should not be lower than + 65C, but also not higher than + 75C. In this case, small deviations in one direction or another are allowed, but not more than 3C. At night, deviations can be 5C.
Why this particular temperature
There are two reasons here.
- The higher the water temperature, the faster pathogenic bacteria die in it.
- But we also have to take into account the fact that a high temperature in the hot water system is burns in contact with water or metal parts of pipes or mixers. For example, at a temperature of + 65C, a burn can be obtained in 2 seconds.


Water temperature
By the way, it should be noted that the water temperature in the heating system of an apartment building can be different, it all depends on various factors. But it should not exceed + 95C for two-pipe systems, and + 105C for one-pipe systems.
Attention! According to the legislation, it is determined that if the water temperature in the hot water system is below the norm by 10 degrees, then the payment will also be reduced by 10%. If it is with a temperature of +40 or + 45C, then the payment is reduced to 30%.
That is, it turns out that the water supply system of an apartment building, I mean hot water supply, is an individual approach to payment, depending on the temperature of the coolant itself. True, as practice shows, few people know about this, so disputes usually never arise on this issue.
Dead-end schemes
There are also so-called dead-end schemes in the DHW system. That is, water flows to consumers, where it cools if not used. Therefore, in such systems, there is a very large excess consumption of the coolant. Such wiring is used either in office premises, or in small-sized houses - no more than 4 floors. Although all this is already in the past.
The best option is circulation. And the simplest thing is to enter the pipe into the basement, and from there through the apartments through the riser that runs through all floors. Each entrance has its own riser. Reaching the upper floor, the riser makes a U-turn and already past all the apartments it descends into the basement, through which it is discharged and connected to the return pipeline.

Dead-end scheme
Design features of the heating circuit

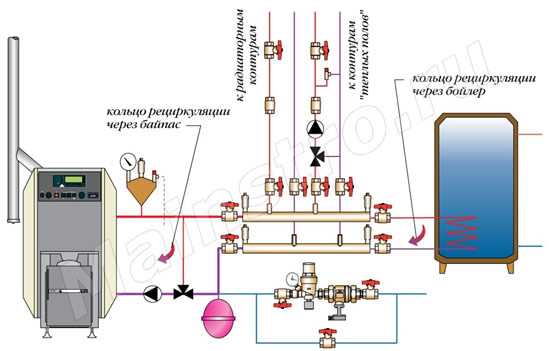
In modern buildings, additional elements are often used, such as collectors, heat meters for batteries and other equipment. In recent years, almost every heating system in high-rise buildings has been equipped with automation in order to minimize human intervention in the work of the structure (read: "Weather-dependent automation of heating systems - about automation and controllers for boilers by examples"). All the details described allow you to achieve better performance, increase efficiency and make it possible to more evenly distribute heat energy across all apartments.
Types of heating systems
The amount of heat that a heating radiator will emit depends not least on the type of heating system and the selected type of connection. To choose the best option, you must first figure out what kind of heating systems are and how they differ.
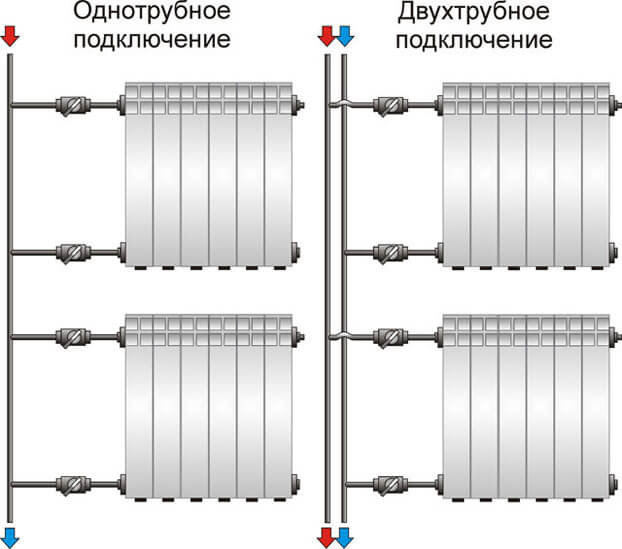
Single pipe
A single pipe heating system is the most economical option in terms of installation costs. Therefore, it is this type of wiring that is preferred in multi-storey buildings, although in private such a system is far from uncommon. With this scheme, the radiators are connected to the line in series and the coolant first passes through one heating part, then enters the inlet of the second, and so on. The output of the last radiator is connected to the inlet of the heating boiler or to the riser in high-rise buildings.
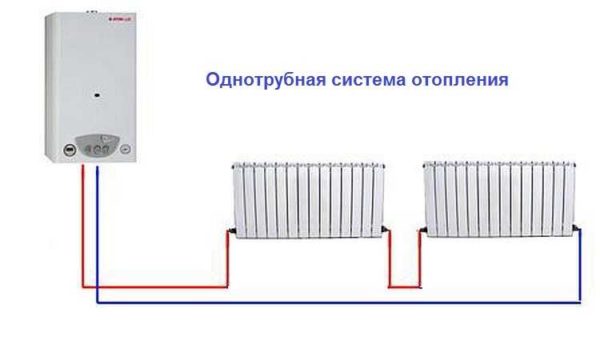

Example of a one-pipe system
The disadvantage of this wiring method is the impossibility of adjusting the heat transfer of the radiators. By installing a regulator on any of the radiators, you will regulate the rest of the system. The second significant drawback is the different temperature of the coolant for different radiators. Those that are closer to the boiler heat up very well, those farther - get colder. This is a consequence of the serial connection of heating radiators.
Two-pipe wiring
The two-pipe heating system differs in that it has two pipelines - supply and return. Each radiator is connected to both, that is, it turns out that all radiators are connected to the system in parallel. This is good because a coolant of the same temperature is supplied to the input of each of them. The second positive point is that a thermostat can be installed on each of the radiators and with its help you can change the amount of heat that it emits.
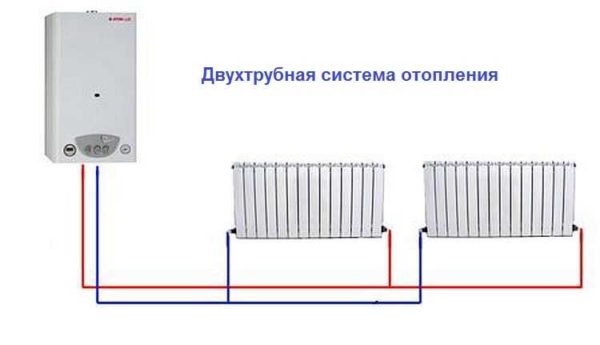

The disadvantage of such a system is that the number of pipes in the wiring of the system is almost twice as large. But the system can be easily balanced.
Traditional DHW wiring
The device of a hot water supply system in stalinkas and early Khrushchev buildings is no different from the distribution of cold water. The only bottling ends with dead-end risers, from which the apartment wiring departs. In the elevator unit, the filling branches into two tie-ins - into the supply and return lines.
DHW switching from flow to return is carried out manually in accordance with the heating temperature schedule:
- At a temperature of technical water at the CHP plant outlet up to 80-90 degrees, DHW is supplied from the supply;
- When 90 ° C is exceeded, the water supply switches to the return water supply.
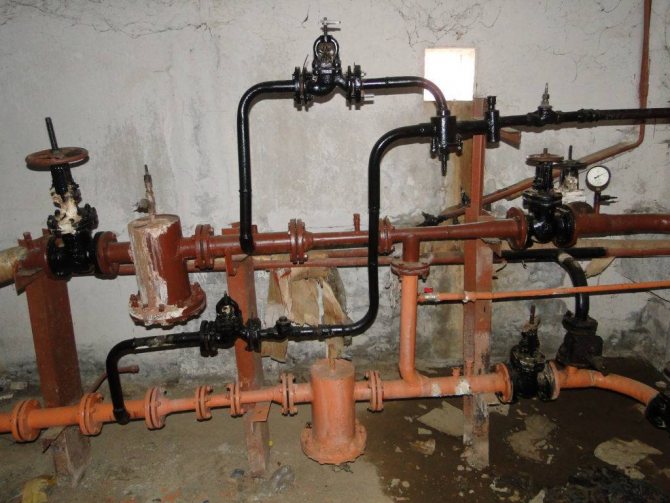


Than it is bad
The advantages of such a scheme are the low cost of implementation and extremely simple maintenance. There are also downsides.
We have already mentioned two of them:
- Without water intake, the water in the risers and liners cools down. To wash or take a shower, it has to be drained down the drain for a long time (up to several minutes). For tenants of an apartment, this means not only a loss of time, but also significant costs: in fact, you drain cold water, but if you have a water meter, you pay for it as if it were hot;

- Heated towel rails that disconnect the domestic hot water supply lines only heat up from the water draw in your apartment. You can forget about high-quality bathroom heating.


Let's throw a handful of little things into the common piggy bank of the solution's shortcomings:
Cold and dampness in the bathroom contributes to the appearance of fungus;
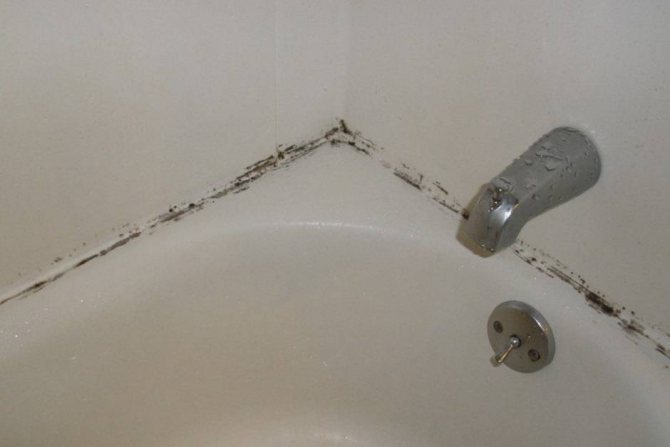


- Towels hung on a cold dryer quickly become musty;
- Cyclic heating and cooling of hot water risers are accompanied by cycles of their lengthening and reduction in size. As a result, the sealing of the risers in the ceiling with cement mortar is gradually destroyed.

All in white and on a white horse
How is the recirculated hot water supply system different from the one described above? It's easy to guess. In it, hot water is continuously circulated through the bottling and (in the case of a multi-storey building) hot water risers.
As a result:
- Instant hot water supply is provided to the point of draw-off at any part of the circuit;
- Towel dryers are transferred from the in-house supply system to the riser (or, in the case of a private house, bottling) hot water. Thanks to continuous circulation, they remain hot around the clock, provide heating of bathrooms and toilets, and at the same time, quick drying of towels;
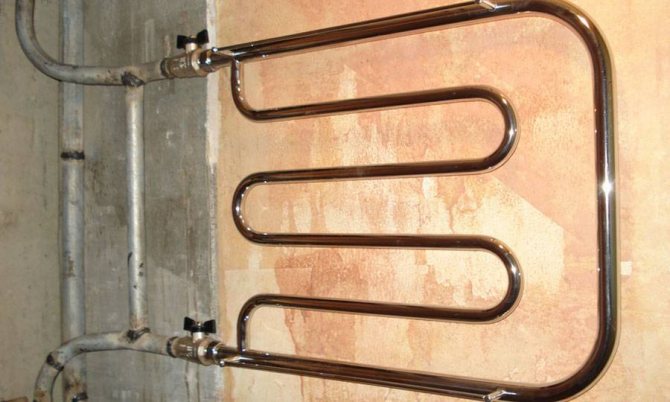


The temperature regime of the DHW system remains stable, without cyclic cooling and heating.
How to fix the situation with a drop
Everything is extremely simple here. First, you need to take a look at the pressure gauge, which has several characteristic zones. If the arrow is in green, then everything is fine, and if it is noticed that the pressure in the heating system is dropping, then the indicator will be in the white zone. There is also a red one, it signals an increase. In most cases, you can handle it on your own. First, you need to find two valves. One of them serves for injection, the second - for bleeding the carrier from the system. Then everything is simple and clear. If there is a lack of media in the system, it is necessary to open the discharge valve and observe the pressure gauge installed on the boiler. When the arrow reaches the required value, close the valve. If bleeding is needed, everything is done in the same way, with the only difference being that you need to take a vessel with you, where the water from the system will drain. When the arrow of the pressure gauge shows the rate, turn on the valve. Often this is how the pressure drop in the heating system is "treated". For now, let's move on.

They are widely used in constant flow systems. The main advantage of manual balance valves is their low cost. As a major disadvantage, it can be noted that every change in the installation must rebuild the system, which is labor intensive and costly.
Automatic balance valves Automatic balance valves allow flexible changes in the parameters of the piping system depending on pressure fluctuations and the flow of the working medium. They are proportional controllers that maintain a constant differential pressure in the system and minimize disturbances caused by control valves. They are characterized by high performance, which allows them to maintain established hydraulic conditions in the systems, compensating for disturbances caused by the control valve.
Implementation
How is the circulation in the hot water supply system of an apartment building implemented?
It is worth making a small lyrical digression here.
The water in the DHW system must have a temperature of at least 60 degrees Celsius. In the presence of central heating, water can be supplied directly from the heating network. Such a heat supply scheme is called open (with coolant withdrawal).


Open heat supply: an elevator unit with outlets through which the domestic hot water supply is supplied
Please note: water from the heating network is usually of a lower quality than drinking water, although formally both cold water supply and hot water supply must meet the requirements of sanitary requirements and standards under number 2.1.4.2496-09. The fact is that additives are introduced into the coolant to prevent corrosion of steel pipelines.
The newest joint venture 30.13330.2016 directly indicates that the withdrawal of hot water from the heating network is undesirable, therefore, modern houses should, if possible, be designed with a closed heat supply (without taking a heat carrier). Water for the needs of hot water supply is taken from the drinking water supply system and is heated in water-to-water, steam-to-water heat exchangers (they utilize the thermal energy of the coolant) or in local water heaters (boilers, water heaters, boilers with an additional heat exchanger, etc.).
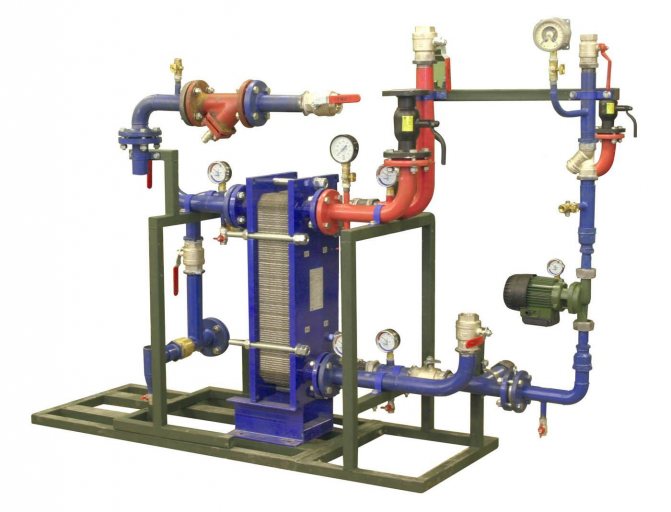


Water-to-water heat exchanger as part of a modern heating station
Open heat supply
Hot water in the system with open heat supply is taken through tie-ins into the direct and return lines of the elevator unit.
Reference: an elevator unit is a heating point that uses partial recirculation of the coolant due to the entrainment of water from the return flow into the fast flow created by the nozzle of the elevator. The nozzle receives hotter and higher pressure water from the supply line. In this case, recirculation ensures the minimum temperature difference between the heating devices throughout the entire circuit with a minimum flow rate of the heating medium from the supply.
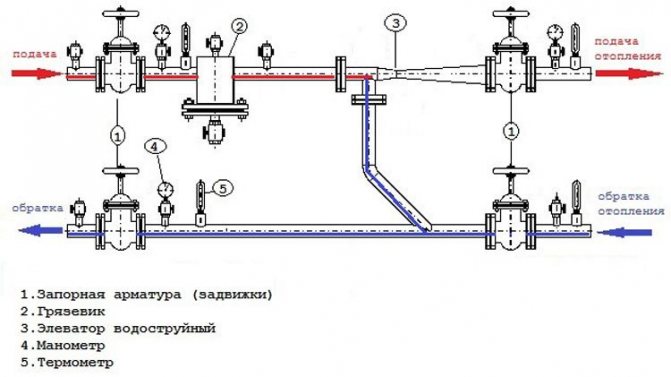

This is how the heating elevator works
Hot water connections are located between the inlet shut-off valves of the elevator unit and the actual water-jet elevator. As a rule, a hot water supply system with circulation in a house with an open heat supply is cut into the elevator unit at four points - two on each line.
Tubes on one thread are separated by throttling ("retaining") washers with a hole, the diameter of which should be approximately one millimeter larger than that of the elevator nozzle.
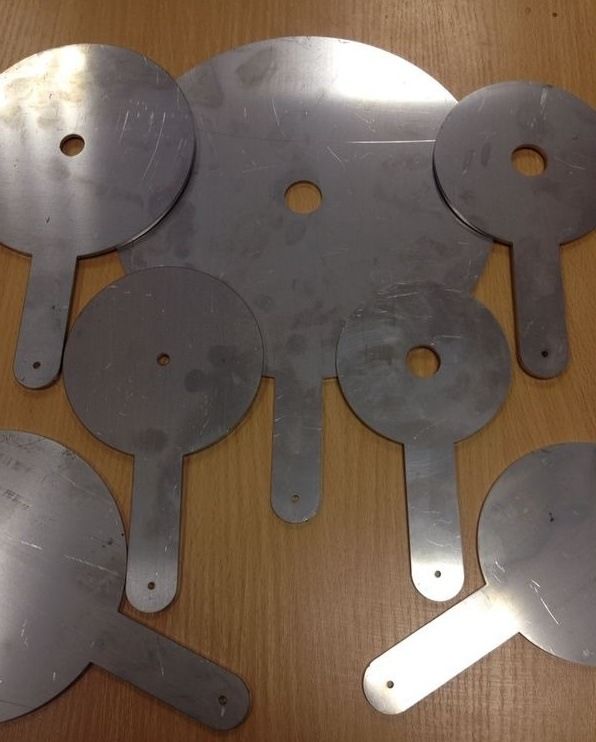


Retaining washers provide a difference between the hot water inlets in one thread of the heating network
Hint: With this hole size, the washer creates a slight drop without interfering with the normal operation of the water jet elevator.
The supply and return temperature changes noticeably throughout the year: it is minimum in summer and maximum at the peak of winter cold.
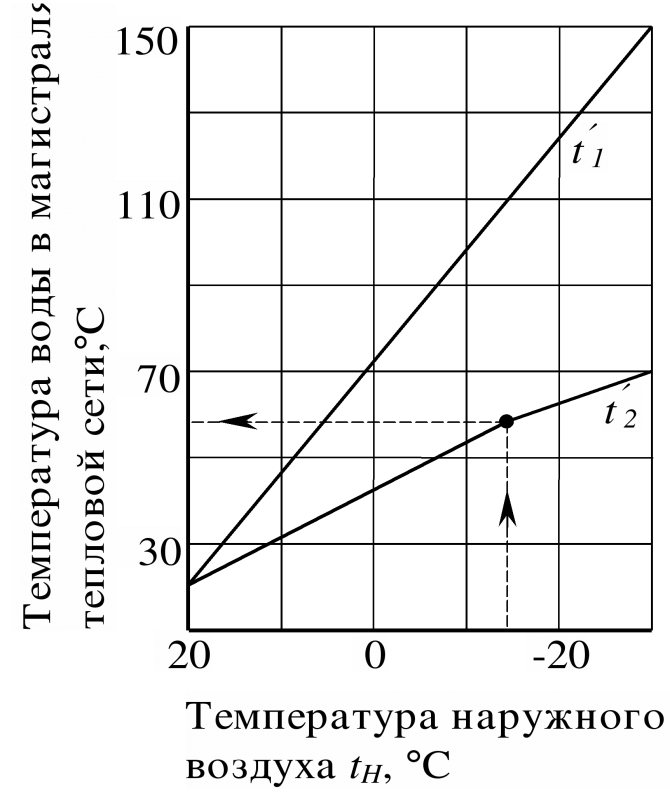

Heating network temperature graph during the heating season
Depending on the season and the current temperature of the coolant, the circulation of hot water in the water supply system can be organized in three ways:
- From straight thread to reverse. This circuit forms a bypass in the elevator unit, which dampens the difference in the elevator, so it is used only outside the heating season;
- From serve to serve. The pressure drop between the inserts (about 0.2 kgf / cm2) is created by a throttling washer. The circuit is assembled in the elevator unit in the off-season, at a sufficiently low supply temperature;
- From return to return. In this mode, DHW operates in the cold season, when the temperature of the coolant on the supply line exceeds 70-75 degrees.
Closed heat supply
The hydrostatic pressure in the DHW circuit of a house with a closed heat supply is always equal to the pressure inside the cold water supply system. The drop that sets the water in motion is simply nowhere to take. That is why such a circulating hot water supply system uses circulating pumps.
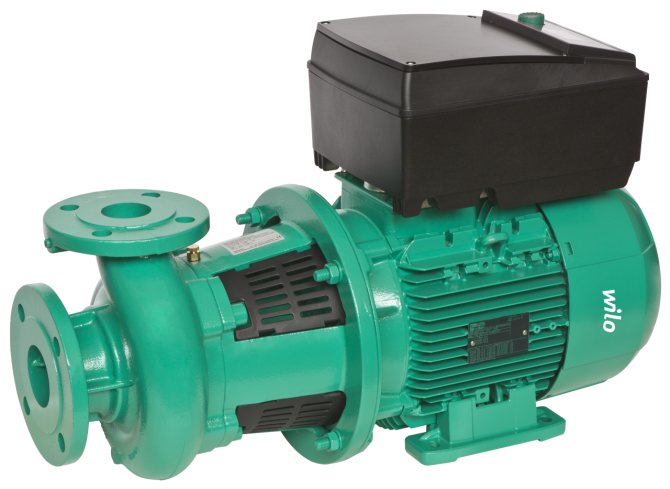


Dry Rotor Water Recirculation Pump
Wiring in an apartment building
How should the hot water supply with circulation in an apartment building be divorced? The answer can be found in the already familiar joint venture 30.13330.2016.
- In a house of five floors and above, the hot water risers should be combined into sections of 3-7 units... In this case, one riser is used as a recirculation pipe, connected to the reverse filling of hot water supply;
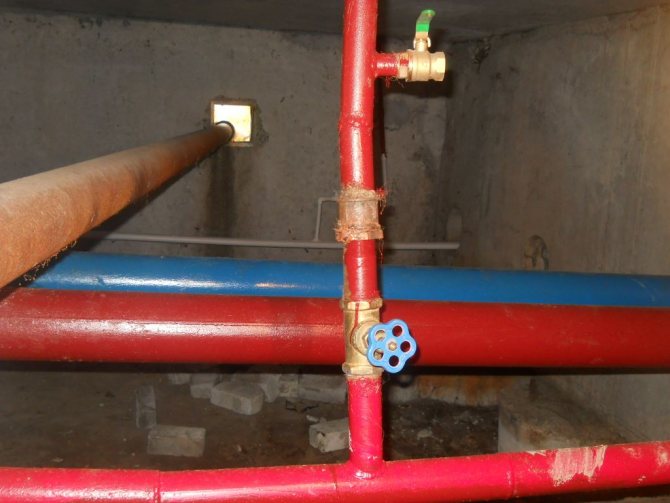


Red pipes - hot water filling, supply and return
However: the author came across hot water circulation schemes in which risers (hot water supply and heated towel rails) passing through one apartment were connected in pairs.
- Horizontal lintels ringing these risers are recommended to be laid on the upper floor of the house (under the ceiling, so as not to create obstacles for free movement around apartments and non-residential areas of the building), in a warm or cold attic (in the latter case, with mandatory thermal insulation in regions with a design temperature of -40 ° C and below) or in the basement (at water supply to risers from the attic);
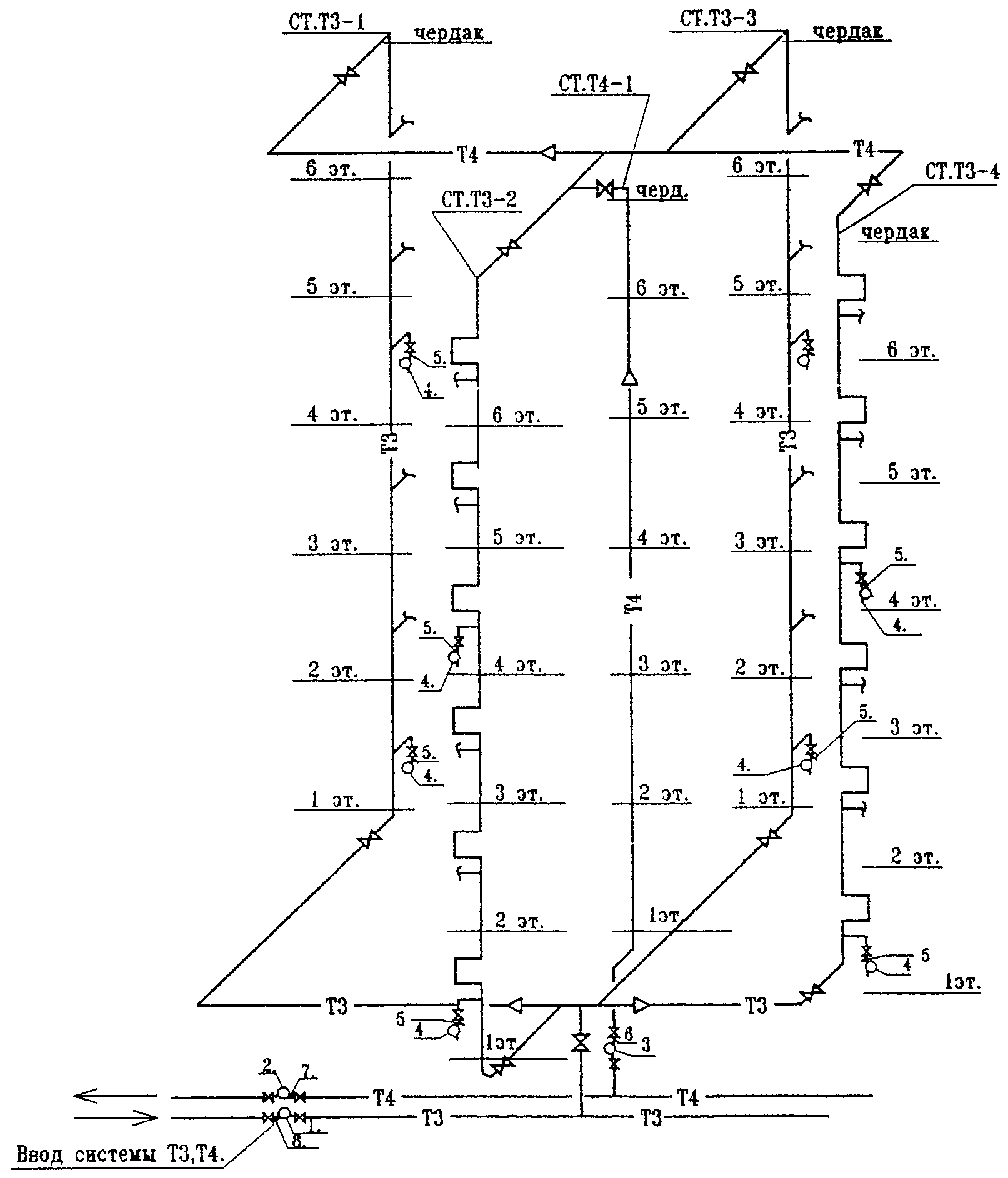

Group of risers with ringed lintels in the attic
Author's note: when installing a circulating hot water supply with your own hands, you should not lay jumpers in a cold attic with your own hands.When the circulation stops (during repair work or in case of an accident), it is easier to freeze such a jumper. When thawing, pipes often break and flood the living quarters under the attic.
- Jumpers are supplied with air vents... These can be both automatic air vents and much cheaper Mayevsky taps;
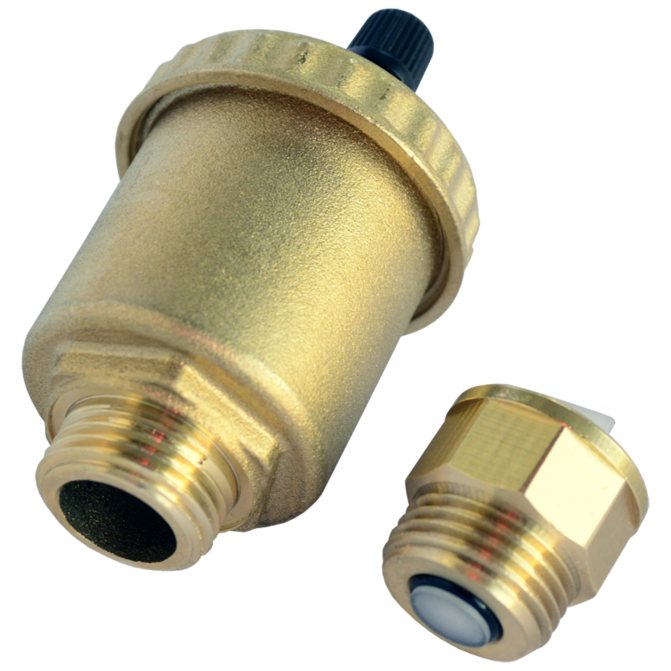


Float automatic air vent and Mayevsky valve
- Each of the looped DHW risers must be equipped with shut-off valves at the base and on the top floor;
- The hot water circulation system allows the connection of heated towel rails to the supply riser (subject to the installation of taps in front of the device and a bypass to the taps) or, with due technical justification, to the circulation riser.
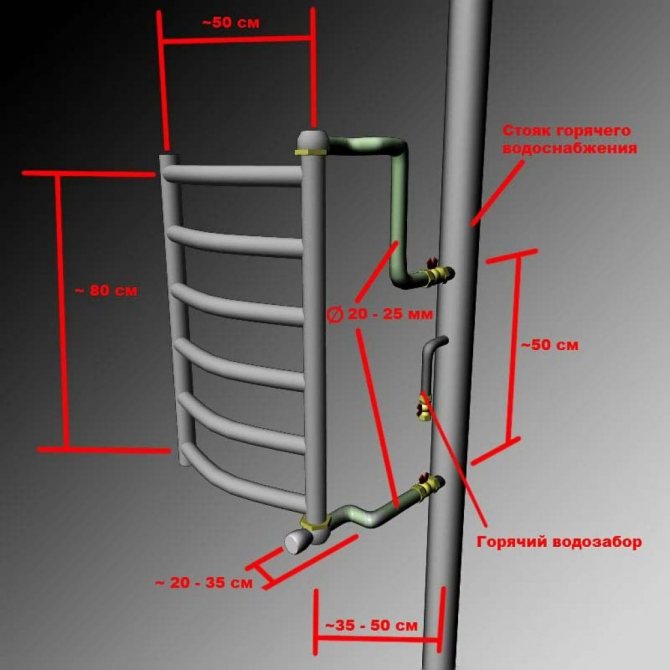

Insert the device into the hot water supply riser
In addition: JV recommends the use of electric heated towel rails. The instruction, frankly, is dubious: with a thermal power of 30-120 watts, such a device will perform its direct functions (drying towels), but heating the bathroom, even a very small one, will in no way provide.


The power consumption of this device is 100 W
Pressure rate
Efficient transfer and uniform distribution of the heat carrier, for the performance of the entire system with minimal heat loss, are possible at normal operating pressure in the pipelines.


The coolant pressure in the system is subdivided according to the mode of action into types:
- Static. The force of action of a stationary coolant per unit area.
- Dynamic. Force of action when moving.
- Ultimate head. Corresponds to the optimal value of the fluid pressure in the pipes and capable of maintaining the operation of all heating devices at a normal level.
According to SNiP, the optimal indicator is 8-9.5 atm, pressure drop to 5-5.5 atm. often leads to interruptions in heating.
For each particular house, the indicator of normal pressure is individual. Its value is influenced by factors:
- power of the pumping system supplying the coolant;
- pipeline diameter;
- remoteness of the premises from the boiler equipment;
- wear of parts;
- pressure.
Pressure can be controlled by pressure gauges mounted directly into the pipeline.
Why the return line does not work
There are many problems associated with the return flow in the heating system.
Squeezes the feed


The water temperature in the return pipe is determined by the heating system device, corresponds to the value in the temperature graph, approved by the service organization.
Often, apartment residents are faced with a problem when the return squeezes the flow.
A common reason is transition of hot coolant from the supply line to the return circuit through all possible parts (for example, jumpers) of the hot water supply pipeline or ventilation. With an automatic control device, as a rule, it is enough to configure it correctly.
The coolant does not come off well
If the circulation of the liquid in the heating circuit is disturbed, the water in the return pipes does not drain well. Initially, the compliance of the circulating pump capacity with the requirements is checked. The reason may be hiding in a banal pipeline leak... A poor circulation situation is typical for apartment buildings located at the end of the heating main. with insufficient pressure drop.
The return is cold, the pipes are clogged
Low return temperature is a serious problem that interferes with ensuring room comfort. The reasons cold return:
- wrong wiring heating;
- air bubble in a system or riser;
- insufficient consumption water through the network;
- underestimated temperature in underwater pipes;
- increased the volume of heat loss;
- inefficiency of pumping equipment, result: poor circulation and insufficient temperature difference between heat supply and return;
- reduced pressure;
- clogged pipes and radiators.
Application Mayevsky cranes allows you to eliminate air locks that impede the movement of the coolant.
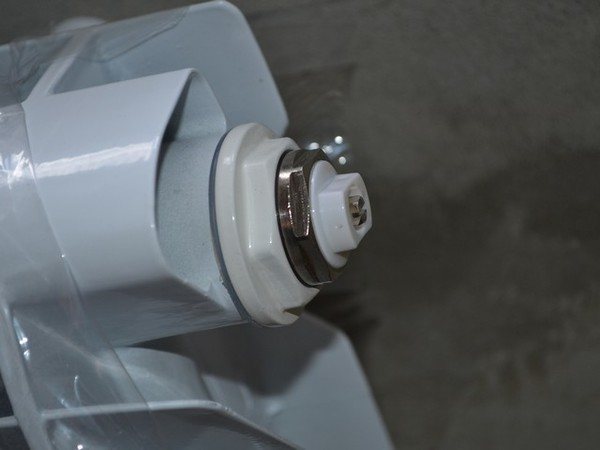


Photo 4. Mayevsky's crane installed on a heating radiator. With it, you can release excess air from the system.
It is important to bleed the air correctly:
- shut-off valves to stop the heat supply;
- open the Mayevsky tap, drain the coolant with air;
- restore the movement of heat by opening the constipation.
Narrow control valve passage often explains the underestimated return temperature, this is a reason to replace it with a new one.
Periodically check the pipeline for clogging, which interferes with the movement of the coolant. Dirt and deposits are removed... If it is not possible to restore the patency of the pipes, the site is replaced with a new pipeline.
Attention! Install exact reason malfunctions are possible after checking the entire heating system.
Diameter of pipes, as well as the degree of their wear
It must be remembered that the pipe size must also be considered. Often, residents set the diameter they need, which is almost always slightly larger than the standard sizes. This leads to the fact that the pressure in the system decreases slightly, which is due to the large amount of coolant that will fit into the system. Do not forget that in corner rooms the pressure in the pipes is always less, since this is the most distant point of the pipeline. The degree of wear of pipes and radiators also affects the pressure in the heating system of the house. As practice shows, the older the battery, the worse. Of course, not everyone can change them every 5-10 years, and it is inappropriate to do this, but from time to time it will not hurt to carry out prevention. If you are moving to a new place of residence and you know that the heating system there is old, then it is better to change it right away, so you will avoid many troubles.
Hydraulic balance of hot water supply systems. The hot water temperature in hot water systems drops significantly with low or no consumption. This leads to several problems: long waiting times for hot water, water overflow and the possibility of unwanted bacteria growing. To maintain the water temperature at the required level, it is usually a constant circulation of water in the systems, through a circulation pump and a circulation pipe. Maintaining the hydraulic balance in these systems is usually done with direct acting temperature controllers.
What elements does the water supply scheme for an apartment building include?
The water meter unit, which organizes the supply of water to the house, is responsible for the operation of several functions:
- It takes into account the consumption of cold water supply, that is, it performs the function of a water meter;
- It can shut off the cold water supply to the house in case of emergency or if it is necessary to repair units and parts, as well as to eliminate leaks;
- Serves as a coarse water filter: such a mud filter should contain any scheme for hot water supply in an apartment building.


The device itself consists of the following components:
- A set of shut-off valves (taps, gate valves and valves) at the inlet and outlet of the device. As a standard, these are gate valves, ball valves, valves;
- Mechanical water meter, which is installed on one of the risers;
- Dirt filter (filter for coarse water purification from large solid particles). This can be a metal mesh in the case, or a container in which solid debris settles to the bottom;
- Pressure gauge or adapter for inserting the pressure gauge into the water supply circuit;
- Bypass (bypass from a pipe segment), which serves to turn off the water meter during repairs or data verification. The bypass is supplied with shut-off valves in the form of a ball valve or a valve.
Heat point
It is also an elevator unit that performs the following functions:
- Provides full and continuous operation of the heating system in an apartment building, and also regulates its parameters;
- Delivers hot water to the house, that is, provides hot water supply (hot water supply operation). The coolant itself in the heating system enters the hot water supply system of an apartment building directly from the centralized heating main;
- The substation can switch the hot water supply between return and supply. This is sometimes necessary in severe frosts, since at this time the temperature of the coolant in the supply pipe can rise to 130-150 0 С, and this despite the fact that the standard indicator of the supply temperature should not exceed 750С.


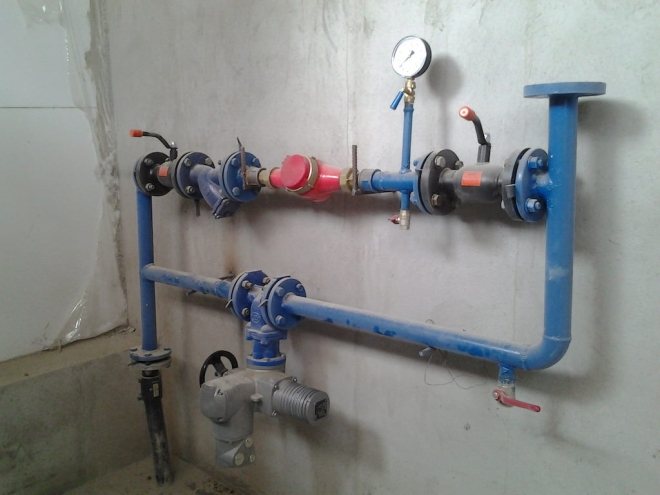
The main element of the substation is a water-jet elevator, where hot water from the working fluid supply pipeline in the house is mixed in a mixing chamber with a return coolant by injection through a special nozzle. Thus, the elevator allows a larger volume of coolant with a low temperature to pass through the heating circuit, and, since the injection is carried out through the nozzle, the supply volume is small.


It is possible to embed adapters for connecting hot water supply between the valves at the inlet of the route and the heating point - this is the most common connection scheme. The number of inserts is two or four (one or two at the supply and return). Two inserts are typical for old houses; in new buildings, four adapters are used.
On the cold-water supply route, a dead-end tie-in scheme with two connections is usually used: the water meter unit is connected to the filling, and the filling itself is connected to the risers through which the pipes are routed to the apartments. Water will move in such a cold water circuit only when parsing, that is, when opening any mixers, taps, valves or gates.
Disadvantages of this connection:
- With a prolonged absence of water intake for a specific riser, the water will be cold for a long time when draining;
- Heated towel rails embedded in hot water supplies from boilers, which simultaneously heat the bathroom or toilet, will be hot only when hot water is drawn from a particular riser of the apartment. That is, they will almost always be cold, which will cause moisture on the walls, mold or fungal diseases of the building materials of the room.
A heating station with four hot water connections in the house makes hot water circulation continuous, and this happens through two filling and risers connected to each other by jumpers.
Important: if mechanical water meters are installed on the DHW sidebars, then the water supply consumption will be taken into account without taking into account the water temperature, which is wrong, since you will have to overpay for hot water that was not in use.
Hot water supply can function in three ways:
- From the supply pipe to the return pipe to the boiler room. Such a DHW system is effective only in the warm season with the heating system turned off;
- From the supply pipe to the supply pipe. Such a connection will bring maximum returns in the demi-season - in autumn and spring, when the coolant temperature is low and far from maximum;
- From the return pipe to the return pipe. This DHW scheme is most efficient in large cold weather, with an increase in the temperature on the supply pipe ≥ 75 0 С.
For the continuous movement of water, a pressure difference is required between the start and end points of the injection into one circuit, and this difference is ensured by the restriction of the flow. Such a limiter is a special retaining washer - a steel pancake with a hole in the middle. Thus, the water that is transported from the inlet to the elevator encounters an obstacle in the form of a washer body, and this obstacle is regulated by a rotation that opens or closes the retaining hole.
Where to install radiators
Traditionally, heating radiators are placed under windows and this is no coincidence.The rising stream of warm air cuts off the cold air that comes from the windows. In addition, warm air heats the glass, preventing condensation from forming on them. Only for this it is necessary that the radiator occupies at least 70% of the width of the window opening. This is the only way the window will not fog up. Therefore, when choosing the power of radiators, select it so that the width of the entire radiator is not less than the specified value.
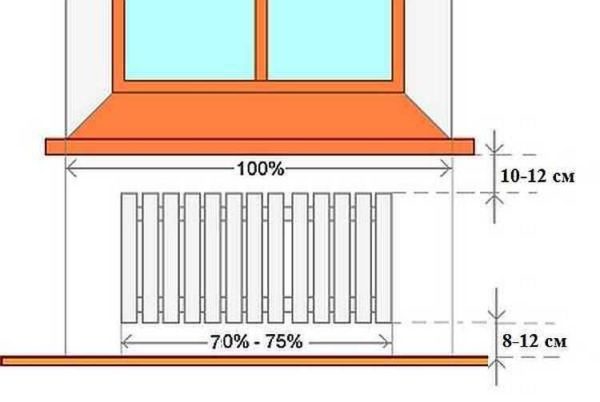

How to position a radiator under a window
In addition, it is necessary to correctly select the height of the radiator and the place for its placement under the window. It must be placed so that the distance to the floor is in the region of 8-12 cm. If it is lowered below, it will be inconvenient to clean, if raised higher, it will be cold for the feet. The distance to the window sill is also regulated - it should be 10-12 cm. In this case, warm air will freely go around the barrier - the window sill - and rise along the window glass.
And the last distance that must be maintained when connecting heating radiators is the distance to the wall. It should be 3-5 cm. In this case, ascending streams of warm air will rise along the rear wall of the radiator, the heating rate of the room will improve.
About Leak Testing
It is imperative to check the system for leaks. This is done to ensure that the heating is efficient and does not fail. In multi-storey buildings with central heating, the cold water test is most often used. In this case, if the heating system drops by more than 0.06 MPa in 30 minutes or 0.02 MPa is lost in 120 minutes, it is necessary to look for places of gusts. If the indicators do not go beyond the norm, then you can start the system and start the heating season. The hot water test is carried out just before the heating season. In this case, the carrier is supplied under pressure, which is the maximum for the equipment.
Their goal is to maintain temperature and minimize water consumption in hot water circulation systems.
An important feature of these valves is the presence of periodic disinfection of the DHW pipeline network. Tags: balancing valves Manual balancing valves
Autonomous heating systems
Today you may not ask for cold, but your heating system will do it for you. If you haven't paid enough attention during the summer season, an unpleasant surprise can be expected at the beginning or during the heating season. Do you have a home in the cold because your radiators are no worse than ever before? A maintenance error or poor tuning of some parts of your heating system could be a malfunction. The summer months are best used to maintain their heating system, but many people will only start taking care of them when they need to flood for the first time.
Return pipeline design and technical parameters
Reverse piping is installed in apartment buildings for the purpose of heating and water supply. This complex design is necessary for the water in the pipes to move in a circular motion and provide the residents with warmth.
Reverse function piping
The installation of the system begins with the heating mains into the house. Branches (there are two of them) are brought along the foundation from the nearest supply chamber. Hot water enters the house through branches. And the reverse, after the heat is released, "goes" to the boiler room or CHP. At the entrance to the building there is a thermal chamber with shut-off valves or taps.
At the heating point (elevator unit), the temperature difference between the supplied and outgoing water is ensured. Also, the supply of hot liquid to the hot water supply is organized there. Provides cleaning of heat transfer agents and water contained in the system, required for hot water supply.
A heating system with a return pipe can be organized in several ways:
- Water supply from the top: under the roof of the building, in the attic or on those floors. A pipeline check valve, on the other hand, is located at the bottom of the house: under the floor or in the basement. The reverse design is also provided: the supply is at the bottom, and the exit is at the top of the house.
- The supply and return water pipe runs inside the basement.
In modern new buildings, heating and water supply is arranged according to the principle of continuous fluid functioning along the contours. This ensures a constant temperature of the pipes in the building and rapid heating of the liquid during withdrawal.
Heating system
A holistic system consists of many elements, without the functioning of which it will not work. Let us consider in more detail what the return water pipeline consists of.
Elevator unit
This is the basis of the return pipe and the entire system as a whole. There is a mixing chamber inside the unit. In it, hot liquid, and also, under high pressure, is poured through a nozzle into cooler water from the return line. At the same time, part of the liquid in the return pipeline enters the system and circulates.
Elevator assembly and location
At different points of the assembly, the pressure is distributed in different ways:
- feed to the node - 6 kgf / cm2;
- to the return flow - 3 kgf / cm2.
Several elevator units in a building can be installed. But only one will have hot water connections.
Heating filling
If the heating and water supply circuit of a house with a return pipe in the basement, heating spills are also located there, their installation takes place without slopes. Fillings are made up to 50 mm in diameter. Risers are connected by welding or threaded connection using tees.
Heating filling
At filling, the top feed is carried out at a constant slope. an expansion tank is placed at the tapping point, which acts as a relief tank.
Heating risers
Risers are supplied to the heating device. They have a size of 25-30 cm. A bypass is always installed between the connections. This is a special jumper. It is slightly smaller than the riser itself. The bypass ensures circulation inside the riser.
If the filling is lower, the jumper is laid in the following ways:
- According to the collector level on the heating loudspeakers.
- by the building, under the ceiling of the last floor.
- In the attic.
DHW
Water supply systems are installed under the floor or in the basement. Domestic hot water filling is installed in the same place. Their functionality can be the same, that is, risers with water intake points are connected to one and to the second. And, separate, when the risers are connected to the filing outlet.
Hot water filling
Hot water risers
Domestic hot water risers are up to 32 mm in diameter. They can be mounted behind the toilet, at the entrance to the toilet or in the kitchen in a closed niche. Modern heated towel rails are connected to hot water circulation systems.
How the design of the return water supply works can be seen in the photo.
Why the pipeline is filled up
Backfilling of the pipeline is carried out after the final installation of the plumbing system. Such backfilling is carried out in order to keep the laid pipes in a stationary position.
Fixation of pipes with backfill is carried out in several stages.
- Manual filling with shovels. This is the initial stage. Carried out from two sides.
- Backfill after ramming and joining pipe joints.
- Sprinkling pipes. Also made from two sides.
What is the temperature in the return pipe system
The return pipe temperature is clearly stated in the building regulations.
Heating should be between 120 and 150 degrees. Most often, the networks work up to 110 degrees, since the pipes in the systems of most buildings are worn out. They simply cannot bear the higher heat and pressure.
Monitoring the operating pressure in heating circuits
For normal trouble-free operation of the heat supply system, it is necessary to regularly monitor the temperature and pressure of the coolant.
To check the latter, strain gauges with a Bourdon tube are usually used. To measure pressures of small magnitude, their varieties can be used - diaphragm instruments.
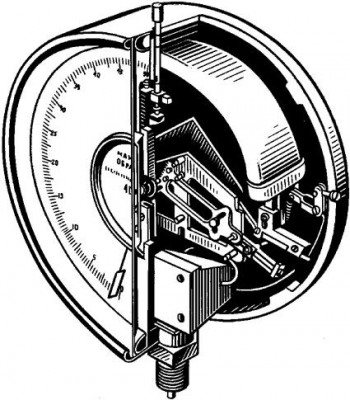

Figure 1 - Bourdon tube strain gauge
In systems where automatic control and regulation of pressure is provided, various types of sensors are additionally used (for example, electrocontact).
- at the inlet and outlet of the heating source;
- before and after the pump, filters, mud collectors, pressure regulators (if any);
- at the outlet of the main line from the CHP or boiler house and at its input into the building (with a centralized scheme).
Figure 2 - Section of the heating circuit with installed pressure gauges
Types of heating schemes
For multi-storey buildings, they are often used one-pipe direct distribution system. It does not have a clear division of pipes into the liquid supply to the radiators and the return line, therefore, the complete circuit is conventionally divided into two equal parts. The riser leaving the boiler is called the supply, and the pipes leaving the last radiator are called the return. Benefits of this circuit:
- saving time and material costs;
- convenience and simplicity of installation work;
- aesthetic appearance;
- the absence of a return riser and a sequential arrangement of radiators (the coolant is supplied on 1st, then 2nd, 3rd and so on).
For a one-pipe system, common vertical layout with vertical outline and heat supply from above.
With two-pipe The wiring system implies the installation of two closed, parallel-connected circuits, one of them provides the function of supplying the coolant to the heating device (radiator), the second - the function of its removal (return).
Radiators are connected in several ways:
- Lower (or saddle, sickle-shaped). Provides for the connection of the supply and return to the lower connecting holes of the radiator. A Mayevsky crane and a plug are installed on the upper holes. They are used for systems in which pipes are hidden under the floor or skirting board. Suitable for multi-section radiators, with a small number of sections, heat losses reach up to 15%.
- Side way, is popular. The pipes are connected to the radiator on one side: the supply of the coolant through the top, the return through the bottom. Not suitable for appliances with a large number of sections.
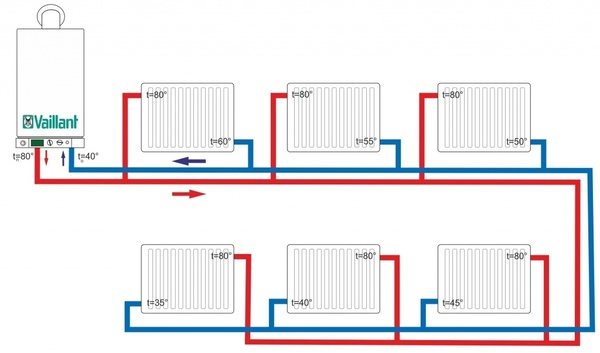

Photo 2. Two-pipe heating scheme with side connection type. The indicated flow and return temperatures.
- Diagonal (or side cross) method involves supplying hot water from above, connecting the return line from below and on the other side. Suitable for radiators with a number of sections not less than 14 pcs.
- The third option the organization of the heating scheme is hybrid way, based on the simultaneous use of one-pipe and two-pipe systems. For example, the collector scheme assumes the supply of the coolant through a single riser, further wiring on site is carried out according to an individual plan.
How it works, how to improve productivity
A single circuit does not provide uniform heating of heating devices, heat transfer decreases with distance from the boiler (the coolant flows into the last radiators colder than the first ones). The disadvantage of such a system is large values of the coolant pressure.
Reference. the performance of the one-pipe system is increased with a circular pump or bypassesformed on each floor.
Advantages of the two-pipe version heating:
- warming up a sufficient number of devices equally, regardless of their distance to the heat source;
- adjusting the temperature regime, carrying out repair measures on a separate device does not affect the work of others.
How to trim heating
How to refuse heating in an apartment building?
Documents
We will only partially touch on the documentary part.The problem is very painful; the permission to disconnect from the DH is given by organizations extremely reluctantly, and often they have to be knocked out through the courts. It is quite possible that in your case it will be much more useful not to have a technical article, but to consult a lawyer who is well versed in the Housing Code.
The main steps are as follows:
- We clarify whether there is a technical possibility to disable it. It is at this stage that most of the friction lies ahead: neither housing and communal services nor heat suppliers like to lose payers.
- Technical conditions are being prepared for an autonomous heating system. You need to calculate the approximate gas consumption (in case you will be heated by it) and show that you are able to provide a safe temperature regime in the apartment for the building structures.
- The act of fire control is signed.
- If you plan to install a boiler with a closed burner and exhaust of combustion products on the facade of the building, you will need a permit signed by the Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision.
- A licensed installer is hired to complete the project. You will need a complete package of documents - from instructions for the boiler to a copy of the installer's license.
- After completion of the installation, a gas service representative is invited to connect the boiler and start it for the first time.
- The last stage: you put the boiler for permanent service and notify the gas supplier of the transition to individual heating.
The technical side
Refusal of heating in an apartment building is due to the fact that you need to dismantle all heating devices without disrupting the operation of the heating system. How it's done?
In houses with a bottom filling, it is worth considering two cases separately:
- If you live on the top floor, you get the consent of the downstairs neighbors and move the jumper between the paired risers to them in the apartment. Thus, you completely isolate yourself from the CO. Of course, you will have to pay for welding, and installation of the air vent, and redecorating the ceiling from your neighbors.
- On the middle floor, only heating devices are dismantled, moreover with welding and cutting off the connections. A jumper of the same diameter as the rest of the pipe is cut into the riser. Then the riser is carefully insulated along its entire length.
Heating check valve
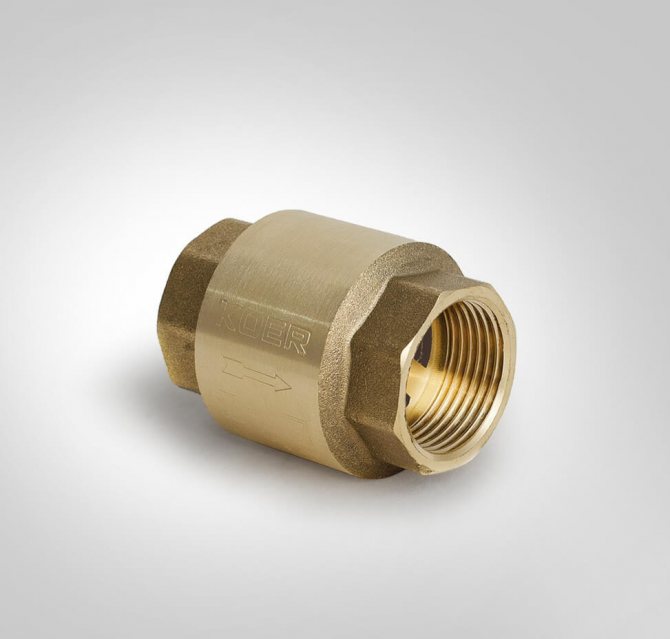


In a complex heating system, there is a fairly large number of auxiliary elements, the task of which is to ensure reliability and uninterrupted operation. One of these elements is the heating system check valve. The check valve is installed so that there is no flow in the opposite direction. Its elements have a very high hydraulic resistance. In this regard, there are restrictions on the use of non-return valves in a natural circulation heating system. In such a system, the pressure is too low. At minimum pressure it is necessary to install gravity valves with butterfly valves, some of them can operate at a pressure of 0.001 bar. The main part of the check valve is the spring, which is used in almost all models. It is the spring that closes the shutter when the normal parameters change. This is the principle of the check valve.
It is necessary to take into account the operating parameters in a particular heating system. In this connection, select the valve of the heating system, which has the necessary spring elasticity. The valves used in heating systems are usually made of the following materials: steel; brass; stainless steel; gray cast iron. Check valves are divided into the following types: poppet; petal; ball; bivalve. These types of valves are distinguished by a locking device.
Layout of the pipeline in a multi-storey building
As a rule, in multi-storey buildings, a one-pipe wiring diagram with an upper or lower filling is used.The location of the straight and return pipe can vary depending on many factors, including even the region where the building is located. For example, a heating scheme in a five-story building will be structurally different from heating in a three-story building.
When designing a heating system, all these factors are taken into account, and the most successful scheme is created that allows you to bring all the parameters to the maximum. The project may involve various options for filling the coolant: from bottom to top or vice versa. In individual houses, universal risers are installed, which provide alternating movement of the coolant.

Heating pipe temperature table
The heating temperature, including the return pipes, directly depends on the indicators of street thermometers. The colder the air outside and the higher the wind speed, the greater the cost of heat.
A regulatory table has been developed that reflects the temperatures at the inlet, supply and outlet of the heat carrier in the heating system. The indicators presented in the table provide comfortable conditions for a person in a living room:
| Pace. external, ° С | +8 | +5 | +1 | -1 | -2 | -5 | -10 | -15 | -20 | -25 | -30 | -35 | |
| Pace. at the entrance | 42 | 47 | 53 | 55 | 56 | 58 | 62 | 69 | 76 | 83 | 90 | 97 | 104 |
| Pace. radiators | 40 | 44 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 54 | 57 | 64 | 70 | 76 | 82 | 88 | 94 |
| Pace. return lines | 34 | 37 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 58 | 62 | 67 | 69 |
Important! the difference between the flow and return temperatures depends on the direction of flow of the heating medium. If the wiring is from above, the drops are no more than 20 ° С, if from below - 30 ° С
Types of radiators for heating apartment buildings
In multi-storey buildings, there is no single rule that allows you to use a specific type of radiator, so the choice is not particularly limited. The heating scheme of a multi-storey building is quite versatile and has a good balance between temperature and pressure.
The main models of radiators used in apartments include the following devices:
- Cast iron batteries
... They are often used even in the most modern buildings. They are cheap and very easy to install: as a rule, apartment owners install this type of radiator on their own. - Steel heaters
... This option is a logical continuation of the development of new heating devices. Being more modern, steel heating panels show good aesthetic qualities, are quite reliable and practical. They are very well combined with the regulating elements of the heating system. Experts agree that it is steel batteries that can be called optimal when used in apartments. - Aluminum and bimetallic batteries
... Products made of aluminum are highly valued by owners of private houses and apartments. Aluminum batteries have the best performance when compared with previous versions: excellent external data, light weight and compactness are perfectly combined with high performance. The only drawback of these devices, which often scares off buyers, is the high cost. Nevertheless, experts do not recommend saving on heating and believe that such an investment will pay off pretty quickly.
Conclusion
The correct choice of batteries for a centralized heating system depends on the performance indicators that are inherent in the coolant in the area. Knowing the cooling rate of the coolant and the themes of its movement, it is possible to calculate the required number of radiator sections, its dimensions and material. Do not forget that when replacing heating devices, it is necessary to ensure compliance with all the rules, since their violation can lead to defects in the system, and then the heating in the wall of a panel house will not perform its functions (read: “Heating pipes in the wall ").
Centralized heating systems demonstrate good qualities, but they need to be constantly maintained in working order, and for this you need to monitor many indicators, including thermal insulation, wear of equipment and regular replacement of used elements.
How is the heating of a residential building arranged? The increase in tariffs prompts the transition to autonomous heating of the apartment; but the rejection of central heating in an apartment building, in addition to the mass of bureaucratic obstacles, also means a number of technical problems. To understand the ways to solve them, you need to imagine the layout of the coolant.