Water is supplied to boilers for heating by feeding devices: piston pumps with a steam or electric drive, centrifugal pumps with an electric or steam turbine electric motor and injectors (steam jet pumps). Boiler installations must have at least two feed pumps with different drives, this is general information about heating. For uninterrupted supply of water to the boiler in the absence of voltage in the mains, one of the drives must be steam (both are possible). The flow of each pump must be at least 120% of the maximum continuous flow of working boilers.
On hot water boilers operating in the heating system with a total heating surface up to 150 mkvadr, it is necessary to install a second hand pump, on boilers with a heating surface of more than 150 mkvadr - a driven centrifugal pump.
Boilers operating for hot water supply with a total heating surface of up to 25 µvadr must be supplied with a second manual pump with a feed equal to double the boiler output, and with a large heating surface - with a double feed drive pump.
How to choose a circulation pump for heating
For the selection of equipment, taking into account the most suitable parameters, it is necessary use certain formulas
... However, only specialists know which formulas should be used in each specific case. And if the device is selected by an unknowing person, then you should use the following recommendations:
- Circulation pump marking
... For example, Grundfos UPS 25-50 equipment, where the first two digits indicate the diameter of the threads of the nuts - 25 millimeters (1 inch), which are supplied with the device. There are also pumps with nut diameters of 32 millimeters (1.25 inches). The second two digits are the maximum rise height of the coolant in the heating system - 5 meters, that is, with the help of a circulation pump, an excess pressure of no more than 0.5 atmospheres can be created. There are also pumps in which the lift heights are 3, 4, 6 and 8 meters. - Unit performance
... It is the main parameter that determines the operation of the unit. Represented by the volume of the coolant pumped by the pump. For the calculation, the formula is applied:
Q = N: (t2-t1), - where N is the power of the heat source. It can be a boiler or a gas water heater;
- t 1 - shows the temperature of the water in the return pipe. As a rule, it is equal to + 65-70 0 С;
- t 2 - shows the temperature of the water that is in the supply pipeline (comes out of the boiler or gas water heater). Often the boiler maintains + 90-95 0 С.
- The calculation of the heating system and its losses is carried out in order to correctly select the design parameters of the unit that is able to cope with the resistance in the heating system.
... Shows the maximum head that the heating system is capable of. This is the total value of the hydraulic resistance in the heating system. When calculating the hydraulic resistance, the number of storeys of a heated building with a closed heating system is not taken into account. In this case, the average value is taken - 2-4 meters of water column. In low-rise buildings with a traditional heating system, this figure is identical.
This is another parameter that should be considered when choosing a circulation pump, albeit indirectly. This indicator is indicated in the building passport during its design.If these values are missing, they can be calculated. Each country has its own standards for heat per square meter. According to European standards, 100 W is required for heating 1 square meter of a one- or two-family building, and 70 W for an apartment building. The Russian standard is presented in SNiP 2.04.05-91.
... Any heating circulation pump has three positions for connecting to the electrical network. All information about the electric current consumption of the pump is contained in the plate on the unit body (load parameters). Each switch position corresponds to a new pump capacity, that is, the amount of coolant per hour pumped by the device through the heating system. The third position of the switch indicates the maximum performance of this unit, and the maximum current consumption of the pump is indicated on a plate on the pump housing.
Serially produced equipment has average characteristics. Therefore, it is necessary to take into account the individuality of each heating system.
Note! A suitable pump should be chosen taking into account the possibility of the unit operation in several modes, while its power should exceed the design power by 5-10 percent
Purpose of the circulation pump
Open heating systems with a natural type of fluid circulation have been used for many years, even now they can be seen in some houses. They function due to the influence of physical laws. In addition, the pipes in such systems are installed with a certain slope. Those consumers who are just considering options do not always know if a circulation pump is needed for this type of heating.
It should be noted that in the case of competent installation, an open heating system with natural ventilation is quite functional and efficient. However, minor flaws in the assembly process can affect its productivity. The circulation pump allows you to compensate for all the shortcomings and provide the house with heat when needed.

With the help of a circulation pump, it is possible to bypass such important heating conditions with natural ventilation as:
- the presence of a mandatory pipe slope when using a pump for steam heating becomes irrelevant - the equipment will cope with pumping the coolant;
- the cross-section of the pipes may be slightly less than necessary for spontaneous circulation;
- the circulation of the coolant is not blocked by plugs formed due to the difference in water temperature;
- due to the always the same speed of water circulation, the system warms up much faster and more evenly;
- due to the small difference in water temperature, some fuel savings are achieved in the circuit.


It should be noted that maintaining a stable water temperature in the heating circuit not only implies fuel savings, but also allows the boiler to be operated in a gentle mode, while extending its service life. The heat exchanger does not overheat as the liquid always moves at the same speed.
Thus, those heating systems in which a circulation pump is provided use fuel more efficiently and economically.
How to use the heating circuit of the boiler room
The thermal diagram helps to monitor the condition and function. Due to flue gases, the appearance of corrosion of metal coatings of low-temperature or sulfuric acid is not excluded. And so that it does not appear, you should control the temperature of the water. It is noteworthy that at the entrance to the boiler, the optimal temperature will be 60-70 degrees.

And in order to be able to increase the temperature to the desired values, a recirculation pump is installed. Water boilers must be monitored so that their service life is decent, control the constancy of water consumption. Usually the manufacturer sets the minimum data for this indicator.
For boiler rooms to work well, you need to use vacuum deaerators. Typically, a water jet ejector will create a vacuum, and the released steam is used for deaeration. But, the main thing that they are afraid of when installing a boiler room is the constant binding to the place. Modern automation simplifies many processes.
Features of connecting pumping equipment
If a forced circulation system is used to service the house, then when the power supply is cut off, the pump for the boiler must continue to work, receiving energy from a spare source. In this regard, it is best to equip the heating system with a UPS, which will support the operation of the structure for several more hours. External batteries connected to it will help to extend the life of the backup source.
When connecting the pump, avoid the possibility of condensation and moisture getting into the terminals. If the coolant heats up to more than 90 ° C, then a heat-resistant cable is used for connection. You will also need to avoid touching the walls of the pipes and the power cable with the motor and the pump casing. The power cable is connected to the terminal box on the right or left side with a change in the location of the plug. In the case of a lateral terminal box, the cable must only be run from the bottom side. A prerequisite is that the pump must be grounded.
Network pumps are often used to operate in boiler rooms. Such products perform the function of pumping hot water in a heating network system. The temperature of the network water, which the installed unit is able to drive through the pipes, reaches +180 degrees.
At the same time, the device and design of network pumps is relatively simple, and at the same time, the devices show a high level of performance along with reliability.
Types of pumps in the boiler room (5 photos)
Details Section: Heat supply Category: Boiler plants Created on 03/04/2015 19:28 Pumps - devices for the pressure movement of mainly liquids with the transfer of energy to them.


Network pump of the heating and ventilation system. This pump is used to circulate water in the heating network. It is selected according to the flow rate of network water from the calculation of the thermal circuit. Network pumps are installed on the return line of the heating network, where the network water temperature does not exceed 70 ° C.


Recirculation (boiler, anti-condensation, anti-condensation) pumps are installed in boiler rooms with hot water boilers for partial supply of hot network water to the pipeline supplying water to the hot water boiler.
In accordance with SNiP I-35-76 (clause 9.23), the installation of recirculation pumps is carried out if the manufacturers of hot water boilers require a constant temperature of water at the inlet or outlet of the boiler. As a rule, it is necessary to provide common recirculation pumps for all boilers. The number of pumps must be at least two. The capacity of the recirculation pump is determined from the equation for the balance of mixing flows of heating water in the return line and hot water at the outlet of the boiler. The regulation of the temperature of the water entering the water heating boiler and the temperature of the water supplied to consumers is carried out as follows. The amount of water supplied by the recirculation pump is adjusted so as to obtain the required water temperature at the inlet to the boiler. However, in this case, the temperature of the water leaving the boiler may be higher than the temperature required by consumers. To maintain the set temperature of the water supplied to the consumers, part of the water from the return line is directed through the bulkhead to the straight line. The amount of water taken from the return line to the straight line is regulated by the heating water temperature regulator.


Make-up pump. Designed to replenish water leaks from the heating system, the amount of water required to cover the leaks is determined in the calculation of the thermal circuit. The capacity of the make-up pumps is chosen to be equal to the doubled value of the received amount of water to replenish a possible emergency make-up.
The required head of the make-up pumps is determined by the water pressure in the return line and the resistance of pipelines and fittings on the make-up line, the number of make-up pumps must be at least 2, one of which is reserve.


DHW circulation pump. Serves to supply the required flow rate and ensure the required pressure of hot water at the consumer. It is chosen according to the hot water consumption and the required pressure.


Raw water pump. Serves to ensure the required pressure of raw water before the cold water treatment and the supply of chemical. purified water into the deaerator, as well as supplying raw water to the hot water tank.
Random materials:
- Boilers operating on wood, wood chips and wood waste (6 photos) - 05/14/2015 19:41 - Read 3678 times
- Rotary disc shutter (4 photos) - 03/11/2015 20:18 - Read 2400 times
- Roof boiler houses (5 photos) - 02/15/2015 19:28 - Read 2654 times
- Complex testing of boiler room equipment - 11/01/2018 15:20 - Read 3072 times
- Silencers for burners (4 photos) - 03/10/2015 19:55 - Read 3787 times
- Forward>
Boiler feed pump device device
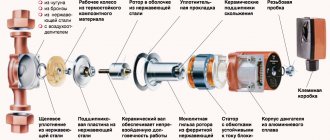
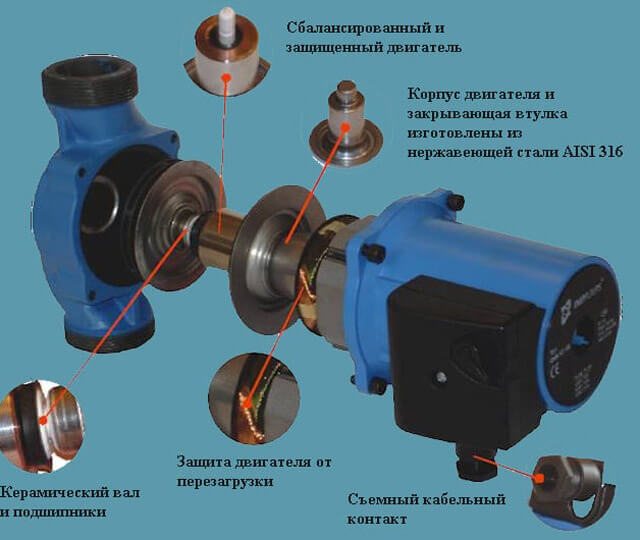
Each pump for a heating boiler performs its own tasks in a closed-loop heating system. The main element of such a pump is the rotor, on which the efficiency of the unit directly depends. When the pump is running, the rotor rotates inside the stator, which is fixedly mounted on a solid base. Some models are equipped with a ceramic stator, which protects the rotor from limestone penetration.


The edges of the rotor are equipped with blades, the rotation of which pushes the coolant further along the pipes. Most of the pumps for boilers are equipped with one rotor, but there are models with several working elements. The rotor is driven by an electric motor. The motors of most pump models are characterized by high power and long service life. All pump elements are housed in a robust aluminum or stainless steel housing.
Centrifugal
The most common type of feeding device in boiler plants is the centrifugal pump. Centrifugal feed pumps are manufactured in single or multi-stage, depending on the flow rate and operating pressure, and are driven by an electric motor or a steam turbine.
The pump consists of impellers rotating on a shaft and a volute casing. Before starting, the pump is filled with water. During the operation of the pump, water enters it through a suction pipeline with a receiving valve and a mesh that protects the valve from clogging. Falling on the impeller blades in the axial direction, water is picked up by the blades and, under the action of centrifugal force, is thrown into the volute-like channel surrounding the rotating impeller, and then into the discharge pipeline.
When water is ejected from the impeller, a vacuum is created in its central part, due to which, under external pressure, water enters the pump through the suction pipe. Thus, with the continuous rotation of the impeller, water flows continuously through the pump.
When leaving the pump, the water speed increases and the pressure decreases. For water to enter the boiler, the discharge pressure must be greater than the steam pressure in the boiler. To reduce the speed of movement and increase the discharge pressure, a guide vane (and here about heat exchangers) is mounted on most pumps, which is a disc with blades bent in the direction opposite to the direction of bending of the impeller blades.The outlet sections of the guide disk blades expand.
To increase the pump flow, the impeller is made with double-sided suction, that is, water is supplied to it from both sides. The head created by one impeller usually does not exceed 50 m. To create high heads, centrifugal pumps are performed with several impellers arranged in series one after the other on one common shaft. Water flows sequentially from one wheel to another. The head generated by a multistage pump is equal to the sum of the heads generated by each impeller.
On the centrifugal pump, manometers and valves are installed on the suction and discharge pipelines, a check valve on the discharge pipelines, air release valves in the upper part of the casing of each stage.
Compared to reciprocating centrifugal pumps have a large flow, smaller overall dimensions, create a more uniform water supply (no jerks).
Disadvantages of centrifugal pumps - obligatory filling of the pump with water before starting, high operating cost at high heads, dependence of the suction height on the water temperature.
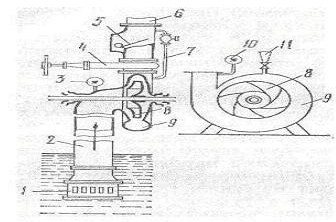

Boiler pump installation rules
Any equipment, be it a unit for a heating system, or a pump for flushing boilers, must be installed strictly in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. One of the most important conditions is choosing the right location for the device. The pump shaft must be perfectly horizontal. Otherwise, air locks will form inside the system, due to which the bearings and other elements of the unit will remain without lubrication. This will result in rapid wear of the device parts.
Another important condition is the correct choice of the place for the pump tapping. The unit must force the liquid to move through the pipeline
The standard installation diagram of the device is shown in the image below.
The main elements in the diagram are shown in this order:
- boiler;
- sleeve connection;
- valves;
- alarm system;
- pump;
- filter;
- membrane type tank;
- heating radiators;
- liquid make-up line;
- Control block;
- temperature sensor;
- emergency sensor;
- grounding.
This scheme ensures the most efficient operation of the pump and heating system. At the same time, energy consumption by each individual element of the system is minimized.
Classification
All pumps are divided into two types:
Dry rotor pump
The working part of the rotor does not have direct contact with water due to the protection of several sealing wheels. These parts are made of carbon agglomerate, high-quality steel or ceramics, aluminum oxide - it all depends on the type of coolant used.
The device is launched due to the movement of the rings in relation to each other. The surfaces of the parts are perfectly polished, in contact with each other, they create a thin layer of water film. As a result, a sealing joint is created. With the help of springs, the rings are pressed against each other, due to which, as they wear out, the parts are independently adjusted to each other.
The service life of the rings is approximately three years, which is much longer than the life of the stuffing box packing, which requires periodic lubrication and cooling. The coefficient of efficiency is 80 percent. The main distinguishing feature of the unit's operation is a high noise level, as a result of which a separate room is required for its installation.
Glandless pump
The working part of the rotor - the impeller - is immersed in the coolant, which simultaneously acts as both a lubricant and an engine cooler. The electrical part of the motor is protected from moisture by means of a sealed stainless steel cup installed between the stator and the rotor.
Typically for the production of a rotor used ceramics
, for bearings - graphite or ceramics, for the body - cast iron, brass or bronze. The main feature of the unit is a low noise level, a long period of use without maintenance, easy and simple adjustments and repairs.
The coefficient of efficiency is 50 percent. This is because the sealing of the metal sleeve that separates the heat carrier and the stator is not possible if the rotor diameter is large. However, for domestic needs, where the circulation of the coolant is ensured in pipelines of short length, it is advisable to use such circulation pumps.
As part of a modular design
modern "wet" type devices include:
- Housing;
- Electric motor with stator;
- Box with terminal blocks;
- Working wheel;
- Cartridge consisting of a shaft with bearings and a rotor.
Modular assembly is convenient because at any time it is possible to replace a failed part of the circulation pump with a new part, and accumulated air is easily removed from the cartridge.
Boiler power supply can be group
with a common feed line for connecting boilers, or
individual
- for one boiler only.
The inclusion of boilers in one power group is allowed provided that the difference in operating pressures in different boilers does not exceed 15%.
Feed pumps that are connected to a common line must have characteristics that allow parallel operation of the pumps.
to supply boilers with water, it is allowed to use:
a) centrifugal and piston pumps with electric drive;
b) steam driven centrifugal and piston pumps;
c) steam injectors;
d) pumps with manual drive;
e) water supply network.
Plumbing use is allowed only on condition that the minimum water pressure in the water supply system in front of the boiler supply regulator will exceed the design or permitted pressure in the boiler by at least 1.5 kgf / cm2
.
Hand pumps can be used for periodic make-up of steam boilers with a working pressure of no more than 4 kgf / cm2
and steam with a productivity no more than 150
kg / hour.
Steam injector equates to a steam driven pump.
A plate must be affixed to the body of each feed pump or injector indicating the following information:
a) the name of the manufacturer or its trademark;
b) serial number;
c) nominal flow at nominal water temperature;
d) the number of revolutions per minute for centrifugal pumps or the number of strokes per minute for piston pumps;
e) nominal water temperature in front of the pump;
f) maximum head at rated flow. After each overhaul of the pump, it is necessary to test it to determine the flow and head.
The results of testing must be documented in an act.
For food steam boilers
at least two electrically driven pumps and one or two steam driven pumps are installed. The total supply of pumps with an electric drive must be at least 110%, and with a steam drive - at least 50% of the nominal capacity of all operating boilers.
With a steam capacity no more than 1 t / hour
one feed pump with an electric drive is allowed if the boiler is equipped with a safety automatics, which excludes the possibility of lowering the water level and increasing the steam pressure above the norm.
For replenishment water heating boilers
with
natural circulation
you need at least two make-up pumps, and with
compulsory
- at least two feed and circulation. Instead of one make-up pump, you can use a water supply system if the pressure in it exceeds the sum of the static and dynamic pressure in the system by at least 1.5
kgf / cm2.
Pumps for water heating boilers with a heating capacity of 4 Gcal / hour
(4,65
MW
) and more must have two independent power supplies.
The pressure that is developed by the circulation and make-up pumps must exclude the possibility of water boiling in the boiler and the system.
Pump classification:
A pump is a machine that converts the mechanical energy of the drive into hydraulic energy of the pumping fluid, thereby making it flow.
Pumps are classified according to many characteristics.
By principle action pumps are divided into positive displacement, dynamic and jet.
In pumps volumetric type a certain volume of liquid that is pumped is cut off and moves from the inlet to the pressure head. In this case, additional energy is imparted to the liquid, mainly in the form of pressure.
Positive displacement pumps are divided into the following groups: piston, rotary (see fig. 42)
(gear, screw), diaphragm.
Fig. 42. Structural diagrams of the pump rotor:
a - gear; b - screw; c - lamellar.
AT dynamic pumps
the increase in energy occurs as a result of the interaction of the fluid flow with the rotating working body. They are divided into two groups:
lobed and vortex.
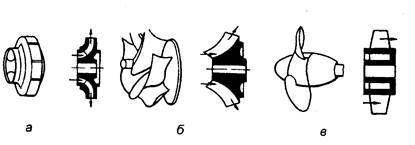

Fig. 43. Diagrams of vane pumps:
a - centrifugal (radial); b - centrifugal (diagonal); in - axial.
Vane pumps (see fig. 43)
in turn are divided into
centrifugal (radial and diagonal) and axial.
AT jet pumps (see fig. 44)
the increase in energy is achieved due to the movement of the flow of the working medium. These pumps are of the following types:
ejectors, injectors and rams.
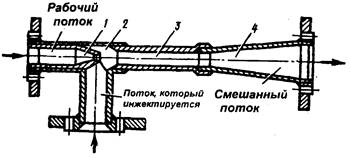

Fig. 44. Water jet pump:
1- pump nozzle; 2- receiving chamber; 3- mixing chamber; 4- diffuser
By fluid properties, which is pumped pumps can be divided into the following groups:
- for clean and slightly dirty neutral liquids;
- for contaminated liquids;
- for aggressive liquids, etc.
Depending on the temperature of the liquid that is pumped over, the pumps are divided into cold (T <373 ° K) and hot (T> 373 ° K).
By appointment pumps are divided into two groups:
thermal circuit pumps - nutritional, condensate, circulation; auxiliary pumps - chemical water treatment pumps, fuel supply, make-up pumps.
Grundfos make-up pumps develop a sufficiently high pressure
How do I get a discount?
Click "I like it"
Print coupon
Get a discount!
- Click the "Like" button on any of the social networks provided.
- In the pop-up window that appears, click the “print coupon” button. A discount coupon will appear in front of you.
- Print a coupon that entitles you to a 5% to 20% discount on goods and services of our company!
Grundfos Authorized Service Partner
Service
warranty and post-warranty
at objects of any complexity
Commissioning
Pumping technology has evolved quite a lot since its introduction into the national economy. At the moment, such devices are often equipped with all kinds of automation. Starting from protection against dry running, mechanical check valves that exclude the return flow of the pumped substance and ending with powerful electronic units that allow you to regulate the rotation speed by changing the frequency of the electric current, measure various characteristics in real time: temperature, current, flow rate, and the like. ...
These processes did not pass by the Grundfos pumps for feeding the heating system and the boiler. These state-of-the-art devices combine excellent quality with the latest advances in science and technology. Despite, at first glance, an auxiliary function, these devices are capable of creating a sufficiently high pressure, which makes it possible to use them even during the initial filling of the system, or during the planned replacement of the coolant.
And for a more detailed acquaintance with the assortment, you can refer to the Grundfos feed pumps catalog, located on the website of the manufacturer's official representative in our country.
Installation of a chiller and air conditioning system in the building of the shopping center on the Kashirskoye highway in Moscow
The employees of the United Service Center CJSC carried out the installation of the chiller and related equipment in the building of the shopping center on the Kashirsky Highway.
Where to buy “Grundfos Booster Pumps”?
Shipment of the goods "Booster pumps Grundfos"
- self-pickup at the address Moscow, 127282, Polyarnaya street, house 31A, building 1. (show the map)
In other cities
Shipping costs in these cities depend on the availability of the goods in the local warehouse. The current availability can be checked by calling our office in your city:
We will be able to offer you the lowest price and shortest delivery times, in comparison with competitors in your region.
The role of Grundfos booster pumps in the heating system
For heating systems, the role of pumping technology is especially important. Firstly, many modern systems require forced circulation of the coolant in the circuit, and secondly, from time to time, the system requires replenishing the volume of the heat-carrying fluid. It is possible to create an absolutely sealed circuit, but this will not become a panacea, because after a certain period of time, a partial or complete replacement of the coolant is required, depending on the technical conditions of the heating system. Also, do not forget about routine maintenance, in which the radiators and the circuit as a whole are flushed, which implies a depressurization of the heating circuit. Therefore, regardless of the geographical location of the owner of the heating system (for example, in Lyubertsy), the Grundfos feed pump will come in handy.
What are the make-up pumping units for?
The answer to this question covers many areas of industrial and domestic applications. We are talking about air conditioning, heating, ventilation and other engineering structures. And the introduction into various auxiliary and main production processes allows the use of Grundfos make-up pumps even for aggressive media and liquids. This will ensure the non-stop operation of the production line, for example, the CIP-washing, which is an essential element in the food industry.
The various design of the units allows them to be used under any environmental conditions: in a living room, in a workshop, in a boiler room, in the open air. After all, the manufacturer has taken care of all possible ways to use this type of equipment. And even a street pump Grundfos has been developed, which is relevant in Korolev and Mytishche.
Now you only need to carefully select the model of the required make-up pump, based on the technical conditions of your system.
Monoblock pump
Previously, pumping units mounted on a foundation or frame, consisting of a pump and a drive, were used as network pumps. Mechanical energy was transferred from the drive to the pump through a group of drive mechanisms. This was primarily due to the need to use powerful drives.
- The modern range of pumping equipment allows the use of monoblock pumps as network pumps.
- The use of monoblock pumps allows, first of all, to significantly save installation space.
- This is especially true when using monoblock pumps with a vertically positioned shaft.
- The use of modern pumping equipment in the modernization of existing boiler houses allows to reduce the required installation area by two or more times.
Buy network monoblock pump from Interpamps
LLC "Interpamps" offers reliable pumping equipment of the Etaline and Etaline-R series, with a capacity of up to 2000 cubic meters per hour, and a pressure of up to 100 meters of water column, designed for operating pressure up to 25 bar and temperatures from -30 to +140 degrees Celsius ... Due to their design and operating parameters, Etaline pumps can be used as network pumps, both in stationary boiler houses and in block-modular ones. Coaxial fittings in Etaline pumps greatly simplify pump piping. Allowing, among other things, to install Etaline pumps directly into the existing pipeline without changing the latter. High efficiency and reliable design of the pumps can significantly reduce the cost of subsequent operation.
The central office of Interpamps LLC is located in Moscow, we offer our partners to buy high-quality pumping equipment inexpensively. We make the selection of pumping equipment at the request of our partners free of charge and in the shortest possible time.
The circulation pump for the boiler of the heating system performs a rather important function - it is he who is responsible for the uninterrupted circulation of the coolant through the pipes and radiators. The efficiency of the heating system and the comfort of living in a private house or apartment largely depend on the choice of the unit.
Scope of application
Distinctive features of circulating network pumps are simple installation and no need for regular maintenance. The equipment is made of high quality materials, which allows for a long service life.
The most common areas of application for such equipment are:
- home heating systems;
- to improve the efficiency of the network boiler;
- supply of fuels and lubricants to bases, industrial enterprises and warehouses;
- pumping chemical reagents to waste water treatment plants;
- pumping water in water supply systems, where there is a drop in the pressure indicator in the line;
- cleaning tanks from contamination and sludge;
- cleaning of oil storages from pollution.
Monoblock pump
Previously, pumping units mounted on a foundation or frame, consisting of a pump and a drive, were used as network pumps. Mechanical energy was transferred from the drive to the pump through a group of drive mechanisms. This was primarily due to the need to use powerful drives.
- The modern range of pumping equipment allows the use of monoblock pumps as network pumps.
- The use of monoblock pumps allows, first of all, to significantly save installation space.
- This is especially true when using monoblock pumps with a vertically positioned shaft.
- The use of modern pumping equipment in the modernization of existing boiler houses allows to reduce the required installation area by two or more times.
Buy network monoblock pump from Interpamps
LLC "Interpamps" offers reliable pumping equipment of the Etaline and Etaline-R series, with a capacity of up to 2000 cubic meters per hour, and a pressure of up to 100 meters of water column, designed for operating pressure up to 25 bar and temperatures from -30 to +140 degrees Celsius ... Due to their design and operating parameters, Etaline pumps can be used as network pumps, both in stationary boiler houses and in block-modular ones. Coaxial fittings in Etaline pumps greatly simplify pump piping. Allowing, among other things, to install Etaline pumps directly into the existing pipeline without changing the latter. High efficiency and reliable design of the pumps can significantly reduce the cost of subsequent operation.
The central office of Interpamps LLC is located in Moscow, we offer our partners to buy high-quality pumping equipment inexpensively. We make the selection of pumping equipment at the request of our partners free of charge and in the shortest possible time.
If the boiler room is designed correctly, then it will serve both heating systems, and ventilation, and the supply of hot and cold water. One might say that no one designs communications on their own. They are guided by at least a typical plan. His choice depends on the type of premises for which it is provided.
The graphic drawing should reflect all mechanisms, apparatus, devices, as well as the pipes connecting them. In standard boiler room schemes, both boilers and pumps (circulation, make-up, recirculation, network), and storage and condensation tanks are included. Also provided are devices for supplying fuel, burning it, as well as devices for deaerating water, heat exchangers, the same fans, heat shields, control panels.

Those heating networks that operate on water are divided into two groups:
- Open (in this case, the liquid is taken in local installations);
- Closed (water returns to the boiler, giving off heat).
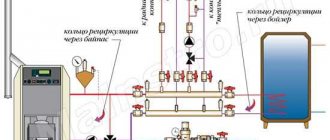
The most popular example of a schematic diagram is an example of an open-type hot water boiler house. The principle is that a circular pump is installed on the return line, it is responsible for delivering water to the boiler, and then throughout the entire system. The supply and return lines will be connected by two types of jumpers - bypass and recirculation.
The technological scheme can be taken from any reliable sources, but it would be good to discuss it with specialists. He will advise you, tell you whether it is suitable in your situation, explain the entire system of action
In any case, this is the most important structure for a private house, therefore attention should be maximized
Pumps
Pumps
According to their purpose, pumps are subdivided into circulation (network), make-up, recirculation (mixing) and feed pumps.
Circulation pumps are designed to move the coolant in a closed loop from a heat source to heating devices. Delivery of pumps D m3 / s. determined by the formula
D = Qcalculated / С∆tcalculated
Qcalculated - maximum heating capacity of the boiler, kW (kcal / h); С - heat capacity of water, kJ / m2-deg (kcal / m3xgrad); ∆tcalc = tcalc (per) -tcalc (arr) is the assumed calculated temperature difference between hot and return water, ° С
The required design set Nsch, m, created by network pumps, is determined by the formula
Nrasch = Nk + Nng + Nns
where Нк is the pressure loss to overcome the resistance of the network in the boiler room, m; Nng - loss of pressure to overcome resistance in external networks, m; Ннс - pressure losses to overcome resistance in the local heating system.
In hot water boilers with closed heat supply systems, two circulation pumps are usually installed: one is working, the other is backup. To replenish leaks in the heat supply system, two make-up pumps are used: one is working, the other is a reserve one (Fig. 45). The feed pump flow is usually equal to 1 - 2% of the hourly flow rate of the heating system. The pressure generated by the make-up pump, depending on the temperature of the water in the system, is within 30-60 m. The make-up pumps are connected to the suction line of the network pumps.
Figure 45. Scheme of installation of pumps and their piping in a hot water boiler room. 1 - circulation and network pumps; 2 - hot water boilers; 3 - mixing or recirculating pumps; 4 - feed pumps; 5 - jumper for cooling water entering the heating network
To avoid dew loss on the convective surfaces of hot water boilers, recirculation (mixing) pumps are installed in heating boiler houses.The performance of recirculation pumps for closed heat supply systems is determined at an ambient temperature of tn = 0 ° C, and the design head is determined depending on the hydraulic resistance of the recirculation ring.
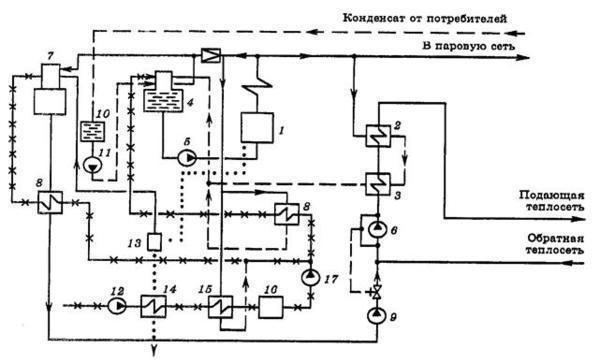
In steam boiler houses of low pressure (P≤0.07 MPa; 0.7 kgf / cm2) feed pumps are installed to power the boilers (Fig. 46), as a rule, two centrifugal ones: one is a working one, the other is a reserve one, which must work under the bay. The flow of each pump must be at least 100% of the maximum flow of the entire boiler room. The design head of the feed pump Hsat, kPa (m), is determined by the empirical formula
Hsat = 1.15P + Hset or Hsat = 1.15x10P + Hset
where P is the operating pressure in boilers, kPa (ati); Нset is the resistance of the suction to discharge pipelines, include the static head between the pump axis and the place where water is injected into the boiler (usually Нset -98-196 kPa; 10-20 m).
When the boiler room steam capacity is less than 0.14 kg / s, one centrifugal and one standby manual feed pump are installed, and for boilers with a steam capacity of up to 4.2 × 10-2 kg / s steam - only one manual pump.
Bulk power of a centrifugal pump N, W, is determined by the formula
N = DнНн / ȵа
where Dn is the calculated pump flow rate, m3 / s; Нн - design head, Pa; ȵа - pump efficiency
Figure 46. Scheme of installation of pumps and their piping in a low-pressure steam boiler room P≤ 0.07 MPa (0.7 kgf / cm2). 1 - condensation tank; 2 - floating wooden covers to reduce the absorption of oxygen from the air; 3 - intermediate partition; 4-feed pump; 5 - hand pump
Centrifugal pumps pump water by centrifugal force as they rotate. The impeller rotation speed is 1500-3000 min-1. Before operation, the centrifugal pump must be filled with water, for which a funnel with a valve is installed on the discharge line.
What you need to know about it
First of all, it is advisable to study the device of the heating system, to understand the essence of its work. To begin with, heating begins with boiler rooms, where some kind of fuel (gas, coal, firewood) is burned, and then heat is transferred through pipes through a coolant. Heat carriers are of several types: air, steam, and the most common is water. But water tends to freeze at low temperatures. Therefore, where necessary, antifreeze diluted with water is used in order to reduce the negative destructive effect on the pipeline. A calculation is made to help determine the correct ratio of water to antifreeze. With central heating, the coolant can be directed through a pumping system or through a conventional one.
The usual, or natural, system is very simple: the water heated in the boiler moves through one pipes, warming up the radiators, and then returns through others to heat up again. There is also an expansion tank and air vents in this simple device. The latter are needed in order to eliminate air bubbles and various gases that can accumulate in the pipes. And excess moisture goes into the expansion tank, which appears when the water expands from heating.
A closed heating system is characterized by a pump. It helps to accelerate the water more than it moves in a conventional pumpless system. A pump is especially needed if the pipes are too narrow, and this interferes with the circulation of the coolant.
What pumps are used for boiler rooms
Network pumps for boiler rooms are most often centrifugal, equipped with an electric motor. By type, they can be divided into: condensate, network, make-up, intended for raw water. You can also find this type of pump as a feed pump.
In boiler water supply systems, it is customary to install several devices at once that have the same characteristics.The pumps are connected in parallel, with one of them being the main one, and the second being the backup one and starts up as needed when the first one fails. However, it is also possible to work with two devices at once. In this case, the water pressure in the pipes remains the same as during the operation of one unit, but the water supply increases, the level of which becomes equal to the sum of the supply of each of the devices.


Boiler room pumps can have enormous weight and dimensions.
For boiler houses, the most optimal option would be to install a centrifugal 1-stage pump of the KM type, a 1-stage unit of the D type with 2-sided suction, or a multistage product of the CNSG type. In addition, many professionals recommend installing condensate type KS in a boiler plant. In this case, the final choice depends on the specific requirements of the buyer, which, as a rule, are determined by the operating conditions of the future equipment.
Selection of the device and calculation of the required pressure
Pumps for boiler rooms are selected strictly based on the requirements of the heating system, or rather, on the required pressure. To understand how much head is required for optimal performance of your system, you can refer to the formula created for this purpose.
At first glance, the formula does not look very simple, but when studying each value, it will not be difficult to calculate the required pressure. The symbols in the formula, which can be used to calculate the required pressure, mean:


Along with the pumps, manometers, taps, filters are installed
- H is the required head pressure in meters of the water column;
- Ltot is the total length of the circuits, taking into account the return and supply pipes. If you use a warm floor, you need to take into account the length of the pipes laid under the floor in the calculation;
- Rsp is the specific resistance level of the pipes of the system. Taking into account the stock, take 150 Pa per 1 running meter;
- r is the total value of the resistance of the pipeline system;
- Pt is the specific density of the heat carrier;
- G is a constant equal to 9.8 meters per square centimeter, or the unit of acceleration due to gravity.
Often there is a difficulty in calculating the total resistance of system elements. However, in this case, the general formula can be simplified by replacing the coefficient k, which is a correction factor, instead of this sum. So, the correction factor of the system in which any thermostats are installed will be 1.7.
For a conventional system with standard fittings and valves without thermostatic control elements, the correction factor is 1.3. The system, which has many branches and valves with high saturation, has this coefficient at the level of 2.2. The calculation according to the final formula, in the case of a correction factor, will look like this: H = (Lsum * Rsp * k) / (Pt * g).
Having made a calculation using this formula, you can understand what parameters and characteristics the pump that you need to purchase owns. We emphasize that it is recommended to choose a pump for boiler rooms, the power of which will not exceed the necessary pressure to create the necessary pressure. By purchasing a pump with a power exceeding the required power to provide the desired head, you will simply be wasting money.
PE feed pumps
Feed pumps for boilers of the PE series are centrifugal, horizontal, sectional, multistage with one-sided arrangement of impellers, one- or two-casing, with a hydraulic heel and end seals of the mechanical type.
They are used to supply water with a temperature of up to 165 ° C to power plants, stationary steam, as well as drum and direct-flow steam boilers of thermal power plants operating on organic fuel (PE 90-180 and PE 90-110 - for supplying feed water to steam generating plants used for the development of oil fields). Cannot be used in explosion and fire hazardous industries.
Features of operation
- PE feed pumps with nominal flow rates of 380 and 580 m³ / h can be operated with or without a hydraulic clutch;
- 600 m³ / h - only with a hydraulic coupling;
- 710 m³ / h - without fluid coupling;
- 780 m³ / h - can be equipped with a synchronous frequency-controlled electric motor.
Structurally, feed pumps of the PE type are horizontal sectional multistage pumps with one-sided arrangement of impellers and are divided into single-casing and double-casing.
Six-stage single-casing feed pumps PE65 / 40, PE65-53, PE150-53 and PE150-63 are designed for boilers with a steam pressure of 40 kgf / cm². The material of the flow path is cast iron SCH20. The ten-stage single-casing feed pump PE270-150-3 is designed for boilers with a pressure of 100 and 140 kgf / cm².
The shaft is supported by two sliding bearings with water cooling chambers. The design of the pumps provides for water cooling of the stuffing boxes. Water is fed into the seal assembly to condense vapors of the pumped liquid, which may leak through the seal. The axial force acting on the pump shaft is taken up by a hydraulic heel cast from modified cast iron. The two-casing design is represented by feed pumps: ten-stage PE380-185-3, PE500-180-3, PE580-195 and eleven-stage PE380-200-3 for boilers with a steam pressure of 140 kgf / cm², seven-stage pump PE600-300-3 for boilers with a steam pressure of 255 kgf / cm².
Designation structure
PE 380 - 185 - 5 UHL3, where:
- PE - Pump type (electric feed pump);
- 380 - Nominal feed, m³ / hour;
- 185 - Head reduced by 10 times;
- m5 - Pump version;
- UHL3 - climatic version and category of placement
Automation and diagram of the boiler plant
Automation makes it possible to use a set of programs that control heat flows. It also depends on the regime of the day, on the weather. Including, this is also needed for heating additional rooms: a playroom, a swimming pool.
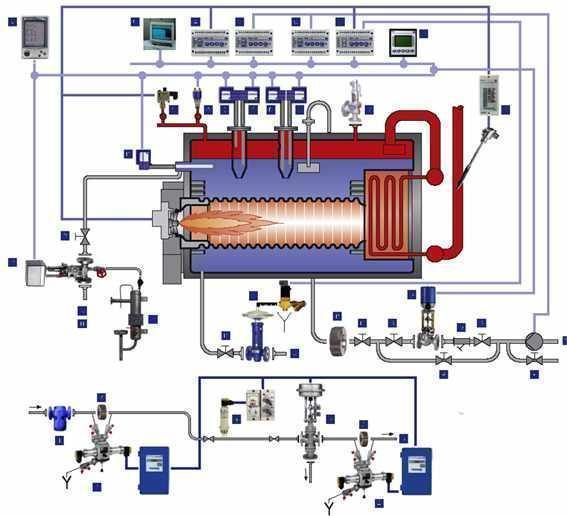

There are some popular custom functions that adapt the operation of the equipment with an eye to the lifestyle of the owners of the house. This is both an ordinary hot water supply system, and a set of some individual options that are convenient for these particular residents, and are economical. In the same way, you can develop a boiler room automation scheme by choosing one of the popular modes.