What is Propylene Glycol
This substance is directly related to the class of dihydric alcohols. The reagent is a liquid substance with a subtle smell and taste. In industry, it is obtained in the process of hydration of propylene oxide at a pressure of 16 megapascals and a temperature range of 160-200 degrees.
The chemical formula of propylene glycol is C3H6 (OH) 2. It is completely safe to use, as it does not contain toxic elements. For heating systems, aqueous solutions are used, which are based on this reagent.
Propylene glycol has a related composition with ethylene glycol - C2H4 (OH) 2. But the last element is not used for heating residential buildings, as it has a fairly high level of toxicity. Moreover, the chemical formula of both substances has a certain similarity.
Heat carrier - glycerin
Glycerin has been used as antifreeze compounds since the end of the last century. The characteristics and properties are rather a cross between ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. The price range is also located in the middle with a bias towards the expensive heat carrier.
Opinions about the advisability of using glycerin in heating systems are often diametrically opposed. We will try to compose SWOT
analysis
based on the arguments of adherents and opponents, since the truth is somewhere in the middle of judgments.

Glycerin - the pros
- Glycerin is a colorless liquid, can be mixed with water in any ratio, absolutely safe for humans and the environment.
- Possesses wide performance characteristics. The lower aisle of the beginning of crystallization is at the point - 30 ºС. The beginning of the boiling stage is comparable to water, or slightly above +110 ºС.
- No expansion when freezing. When thawed, the properties and characteristics are restored in full.
- Does not react with zinc coating.
- Does not damage O-rings and materials, does not provoke leaks in connecting elements.
- Complies with fire safety requirements. Not flammable. Explosion-safe.
- Glycerine coolant does not require flushing the system, after previously using other solutions in it.
- Durability. The warranty periods of operation declared by the manufacturers are from 7 to 10 years.
- Technical characteristics practically correspond to propylene-glycolium, while the price of glycerin coolant is 25% more affordable.
Glycerin - cons
It is worth noting that glycerin in the composition of antifreeze is known and used at the beginning of the 20th century, at the dawn of heating systems. Subsequently, they were replaced by cheaper analogs of glycol coolants. Thus, glycerine antifreeze is not an innovation, but rather a new look at a forgotten past.
- Glycerin has a high density and viscosity. It is necessary to increase the pump rotation speed in order to increase the flow rate additionally loading the heating equipment.
- The heat capacity values are lower than those of water and are inferior to propylene glycol.
- The thermal stability of glycerin leaves much to be desired; even at temperatures of about 90 ° C, foaming of the product can be traced. Of course, the problem is solved by adding additives, but the price goes up.
- Elevated temperature conditions lead to chemical degradation of glycerin. The resulting solid sludge settles on the walls of the system and is difficult to clean.
- A highly volatile tear liquid with a pungent odor, released during decomposition, acrolein, is equated to a carcinogenic substance.
- Evaporated water from the solution leads to the fact that the glycerin thickens with the loss of positive properties. The next step is the formation of a jelly-like substance, already at a temperature of +15 ºС. As a result, the complete exit of the coolant from the performance characteristics, followed by replacement with a new one.
- The production process is not regulated by GOST. There are only technical specifications (TU), which unscrupulous manufacturers interpret based on their capabilities. Warranty obligations are sometimes simply absent. It is not surprising that it is glycerin that acts more often than others as counterfeit products, especially since it is cheaper than propylene glycol.
Summing up, it remains to add that in the European countries of the EU, the production and use of a heat carrier based on ethylene glycol is prohibited by law. At the same time, the development of glycerin-containing products does not occur, since this approach is futile and ineffective. With such an overview, if you have a glycerin-based or propylene glycol-based coolant at hand, it is better to opt for the latter.
Main characteristics
Propylene glycol is a hygroscopic substance that is soluble in water, acetone, ethanol, chloroform and diethyl alcohol. Such a colorless liquid containing a carbon atom has a low degree of volatility. It is non-corrosive and completely safe to use.
Among the characteristics of propylene glycol are:
- density - 1037 kg / m³, which is almost 4 percent more than that of water;
- a fairly high boiling point - 188 degrees above zero;
- thermal conductivity - 0.218 W / (m * K);
- the beginning of crystallization - at -60 degrees;
- specific capacity value - 2483 J / (kg * K).


What propylene glycol looks like
The propylene glycol coolant is an aqueous solution that remains liquid at temperatures ranging from -40 to 100 degrees. The finished substance, in addition to the main component dissolved in distilled water, includes dyes, as well as no more than 5 percent of anti-corrosion, stabilizing, softening additives.
The density of the propylene glycol heating medium depends on the concentration of the main component. The higher its percentage, the higher its maximum boiling point. The density index also increases accordingly. Based on this, percentage markings are indicated on the coolants produced.
Specifications
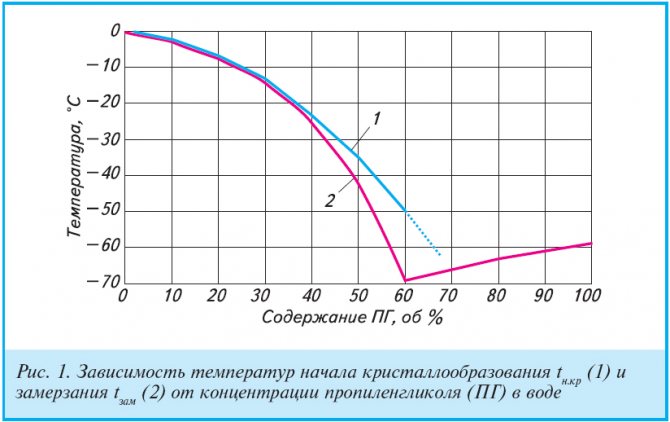

If you add 54% anti-freeze to the coolant, the liquid will begin to freeze at minus 40 degrees
The product is used as a base for an energy carrier with which the system is not afraid of freezing. Inexpensive pipes can be used as the substance contains anti-corrosive components.
Freezing point depending on the concentration of propylene glycol:
- contains 54% of the substance - the energy carrier freezes at -40 ° С;
- 48% - -30 ° C;
- 39% - -20 ° C;
- 25% - -15 ° C;
- 15% - -5 ° C.
In the system with the substance, storage boilers are used; in heating with ethylene glycol, the use of such units according to the instructions is not allowed. The disadvantage of propylene glycol, like ethylene glycol, is considered to be increased fluidity, due to which the liquid penetrates into cracks inaccessible to water. Seams and fittings are welded carefully to prevent leaks.
The propylene glycol heat transfer medium is used only in a system with the appropriate technical characteristics, therefore, changing the water does not always lead to good results. Manufacturers of radiators indicate in the passport the compliance of products with one or another type of energy carrier.
The product is miscible with water, alcohols, ethylene, acids, organics of the carbonyl group, amines and nitrogen-containing solutions.
Advantages and disadvantages
Propylene glycol is one of the most demanded ready-made heat carriers for heating systems. Its main function is to protect the heating equipment from ruptures, which occurs due to the ability to practically not change its volume at low temperatures. Therefore, in severe frosts, when using it, there is no need to drain the system.
The advantages of using a propylene glycol-based coolant include:
- Safety and environmental friendliness. The substance does not contain components of increased toxicity. The reagent does not have a negative effect when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes of the eyes. Its vapors are harmless enough. When the floor finishing material hits the surface, any chemical reactions are excluded.
- Lack of corrosive activity. This property allows the use of this coolant for heating systems with various structural materials.
- High level of thermophysical characteristics. The use of an aqueous solution of propylene glycol for heating circuits promotes rapid and uniform heating of the room. In this case, the heat is retained for a long time.
- Lack of limescale. When heated to high temperatures, this antifreeze does not form any hard deposits. At the same time, propylene glycol has bactericidal and cleaning properties. With its help, various deposits are removed on the internal sections of heating equipment.
The ready-made propylene glycol solution is completely fireproof and its use excludes the possibility of an explosion.
This coolant also has some negative operating points:
- High rate of fluidity. Propylene glycol is able to penetrate the smallest crevices. Its fluidity is slightly higher from water, therefore leaks sometimes occur in places where they should not be. But this property at the same time can be attributed to the positive aspects, since it allows to improve the assembly quality of the heat-conducting structure.
- The possibility of using propylene glycol coolant in the presence of parts containing zinc is excluded. If you do not follow this precaution, then the viscous antifreeze will eventually flake off the zinc, which will lead to blockage of the pipeline.
Also, sometimes the high cost of propylene glycol-based antifreeze is attributed to the negative aspects. At the same time, it must be replaced in the heating system at least after five seasons.
The best coolant propylene glycol
Propylene glycol is more chemically active and reacts quickly with surfaces and other substances. Special functional additives - anti-corrosion, stabilizing, anti-scale and others - help to neutralize such activity. It is strictly forbidden to use propylene glycol coolant in systems with zinc elements. At the same time, no reaction is observed with plastic ones.
Thermagent EKO
Safe heat carrier "THERMAGENT ECO-30" is produced on the basis of DOW pharmacological propylene glycol (Germany) using the "Organic Acid technology" technology. Contains non-toxic, organic (carboxylate) corrosion inhibitors and a package of special additives made in Germany.
Designed for various heating and air conditioning systems as a working fluid that provides operation in the range from -30 ° C to + 106 ° C. The main equipment is double-circuit boilers, refrigeration equipment.
Thermagent EKO
It is forbidden to use THERMAGENT ECO-30 for electrolysis boilers.
It has a greater fluidity than water, therefore, the assembly of all docking assemblies must be extremely careful and the system must be pre-pressurized. It is not recommended to dilute THERMAGENT with water, as this leads to deterioration of anti-corrosion properties.
THERMAGENT-65
Low-freezing liquid intended for use in closed heating systems, in cooling or heat exchangers operating in the range from - 65 to + 112 ° С.
THERMAGENT-65
Designed for use as a low-freezing heat and coolant in closed heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems for residential and industrial buildings, for cooling systems of industrial equipment, chillers, refrigeration units, etc., operating in severe climatic conditions, where steel is used as structural materials , cast iron, aluminum alloys, copper and its alloys. It can work with any type of heating boilers: gas, diesel, electric, however, it is not suitable for electrolysis boilers (Galan type), in which heating occurs by passing an electric current through the coolant.
Warm House ECO-20
Antifreeze made from propylene glycol. Recommended for double-circuit heating devices. Before use, dilute with technical or distilled water. After dilution by 10%, the crystallization temperature increases to - 25 ° С, if it is diluted to 20%, then the characteristics of the solution will change to -20 ° С. After some time of operation, it will begin to become jelly-like. If at this time it is diluted with water, then the solution will restore its characteristics.


Warm House ECO-20
After the end of its service life, the solution still freezes only at low temperatures, but its anti-corrosion properties are significantly deteriorated. It is forbidden to use in electrolysis boilers.
Scope of application
Propylene glycol is in high demand in modern industry. Heat carriers made on its basis are widely used not only for heating systems, but also as antifreeze for ventilation and air conditioning equipment.
The safety of the substance allows it to be used for residential and public buildings. At the same time, antifreeze can be poured into structures made of various materials, including rubber, aluminum, steel, copper or cast iron. An exception is galvanized coating.
The field of application in the industry of propylene glycol is quite extensive:
- pharmaceuticals;
- tobacco production;
- food production;
- automotive and aviation industry;
- Oil and gas industry;
- cosmetology, perfumery;
- medicine.
Propylene glycol uses include livestock and agriculture. It is used to improve the quality of feed, as well as to extend the shelf life of vegetable crops. In the chemical industry, a viscous substance is used in the manufacture of polyurethanes, paint solvents, plastics or polymers.
Varieties of non-freezing coolants
Antifreezes are on sale based on two organic compounds: ethylene glycol and propylene glycol.
Ethylene glycol
Oxygen-containing organic compound, dihydric alcohol. In a purified form, it is a clear, colorless, odorless, oily, odorless liquid. Very toxic. The ingress of ethylene glycol or its solutions into the human body can lead to irreversible changes and death, that is, you can get poisoned, even if it just falls into your hands.
Despite the serious danger, ethylene glycol is very often used as a heat carrier due to its low price. Plus, pure antifreeze is also chemically active, it foams abundantly, and emits toxic fumes.If there is the slightest possibility somewhere, ethylene glycol will definitely leak or, at least, start to release vapors.
Propylene glycol
Dihydric alcohol, a colorless viscous liquid with a weak characteristic odor, sweetish taste, and hygroscopic properties. Chemically inert, safe for humans. Minus - loss of fluidity at high temperatures. It is more expensive than ethylene glycol, but the best option for home heating systems.
An excellent coolant is a special oil, but in our country it is not yet very popular. The advantages of thermal oils compared to antifreezes are quite extensive:
- operate in a wide temperature range from 50 ° C to 410 ° C;
- have a wide range of power: up to 45 MW for one heater;
- distribute heat optimally;
- are characterized by high heat capacity and high heat transfer coefficient;
- prevent corrosion in heating systems, as well as other equipment, etc.
Thermal oils are not used in all systems - only in specially designed ones, which is indicated in the technical passport of heating equipment.
Criterias of choice
The main point that should be considered when choosing a coolant for space heating systems is the manufacturer's recommendation for heating equipment. The instructions for the boiler often indicate the requirements for the liquid with which the water circuit is filled, and sometimes the brand of antifreeze.
The main factors to consider when choosing a propylene glycol solution for heating systems are:
- Climatic conditions of use. The maximum freezing point is indicated on various brands of the product. This indicator depends on the concentration of the solution, the percentage of which is also indicated in the name of the coolant.
- Manufacturer. The efficiency of the heating system depends on the quality of antifreeze. You can buy good products from trusted manufacturers. Quality products do not contain toxic substances and are completely safe to use.
- Characteristics of additives. Propylene glycol-based products in ready-to-use heat transfer fluids can have anti-corrosion properties while providing protection against metal degradation. Softening components are often added to the composition, which protect the rubber elements from deformation. Therefore, when choosing antifreeze, technical and design features of heating equipment are taken into account.


When choosing a propylene glycol-based heat transfer fluid, take into account the characteristics of the additives
Antifreeze with carboxylate type additives is especially popular. Such a coolant can be used for almost any material included in the design of a thermal device.
Propylene glycol intended for heating systems must meet all technical requirements and meet the characteristics of the heating equipment used.
Propylene glycol based heat carrier
Benefits:
- insures the system against rupture;
- the volume during freezing increases by only 0.1%;
- provides the highest level of safety after water;
- not dangerous even with prolonged inhalation of vapors;
- non-corrosive;
- good thermophysical properties;
- possesses bactericidal and sterilizing properties.
Disadvantages:
- high cost (pays off with minimal repair costs, safety and the ability not to be connected to central heating systems).
Features of use for heating
The propylene glycol coolant is poured into the system in accordance with the technical parameters. Before using antifreeze, a number of preparatory steps should be taken:
- drain the liquid from the system, flush all circuits with caustic soda, remove all deposits and rust;
- seal all connections, including tie-ins and bends;
- remove and replace all zinc-containing parts.
The system can then be filled with propylene glycol solution. At the same time, it is recommended to keep the trigger valve open at the lowest point. This action will allow you to immediately see when the heat loops are completely filled. After filling, the system is checked for leaks and a test run of the heating equipment is carried out.
Propylene glycol
This heat carrier is a colorless viscous liquid, which is characterized by a sweetish taste and corresponding odor. And most importantly, it is safe for human health. Propylene glycol is widely used in various sectors of the national economy, including the cosmetic and food industries.
Propylene glycol for heating systems has all the properties of an ideal heat carrier: it boils at a temperature of 187 ° C, and crystallizes at -60 ° C.


Another advantage of propylene glycol is its low corrosiveness, which makes it possible to lower the level of requirements for the quality of steel for heating systems and, accordingly, reduce their cost.
Propylene glycol is excellent for systems that include structural elements made of rubber, plastics, aluminum, copper, cast iron and steel. In addition, when using this substance, scale and sediment do not form on the inner surface of the heating system, which ensures high heat transfer and increases the service life.
Operating moments
Ready-made propylene glycol solution for heating devices has a lower thermal conductivity and heat capacity than water. Therefore, when using a substance, it is often necessary to add the amount of batteries in the room. Replacement of heating equipment may also be required.
In order to productively use polypropylene-based antifreeze for a heating system, some operational recommendations should be taken into account:
- due to the high viscosity of this coolant, it is necessary to install a pipeline with a diameter of at least 25 millimeters, and also select a sufficiently powerful circulating pump;
- for metal pipes, antifreeze with additives that prevent corrosion should be used;
- use an aerometer annually to check the concentration of the main reagent;
- use an expansion tank of at least 10 liters;
- provide free access to all connections of heating equipment in case of eliminating leaks;
- replace the propylene glycol coolant every five operating seasons;
- use and regularly monitor heating dirt traps.
- when replacing antifreeze, completely flush the heating equipment.


The propylene glycol-based coolant must be changed every 5 seasons
If it is necessary to mix this coolant, it must be borne in mind that the solution combines well with a liquid based on glycerin, propylene glycol or ethylene glycol. In this case, the type of additive included in the composition is taken into account, since an incorrect combination of different additives can cause a decrease in the technical characteristics of antifreeze.
Due to its many advantages, propylene glycol is considered one of the best heat transfer fluids for heating equipment. But in order to ensure an effective working process of the heating system for several years in a row, all technical and operational requirements should be observed when using it.
How to use propylene glycol fluids correctly
Propylene glycol-based heat transfer fluids have a similar chemical composition, which differs in the percentage of alcohol. Most often, such compositions are named by the manufacturer's name.
If propylene glycol antifreeze contains about 30%, it freezes at -13 ° C, 35% alcohol solution crystallizes at -20 ° C, 40% at -25 ° C, 75% solution at -65 ° WITH.
When replacing water with a propylene glycol-based composition, it is necessary to take into account some of the properties of antifreeze.
- Lower heat capacity and thermal conductivity. The number of radiators should be increased, as well as a more powerful boiler should be purchased. Heating systems are often installed in private houses that operate at half their capacity - in this case, you can do without replacing the boiler.
- High viscosity. Make sure the pipes have an inner diameter of at least 25 mm and install a larger circulation pump.
- Greater expansion ratio. If the expansion tank is less than 10 liters, then a larger one will need to be replaced.
- High fluidity. It is worth reducing the number of threaded connections, tie-ins and squeegees, and also provide free access to existing connections in case of leaks.
If the technical parameters of the existing heating meet the new requirements, you can proceed to the preparatory work:
- to seal squeegees, connections, tie-ins;
- completely drain the water from the heating system and rinse with caustic soda, it will remove rust and scale;
- remove all zinc parts;
- additives can be added to antifreeze that will protect copper parts;
- check the dirt trap twice as often;
- check the solution every two years for alcohol concentration;
- complete change of antifreeze every five years.
It is always worth flushing the system thoroughly if you are going to switch to another coolant.
Effective use
For effective use of this antifreeze liquid, it should be poured into the heating system circuit after thorough sealing of all components and hydraulic tests. In this case, it is recommended to supplement the system itself with a circulation pump.


By changing the percentage of propylene glycol solution for heating systems, a liquid with a freezing point of -1 ° C to -65 ° C can be obtained.
The service life of propylene glycol without additives is on average 5 years, then it is necessary to either flush with an alkaline solution in the ventilation, cooling or heating system, or completely replace the liquid. With prolonged or frequent exposure to low temperatures (for example, the heating system has not been operated for a long time in winter), it is preferable to change the solution every 3 years.
Application
Before pouring non-freezing liquid into the heating system, it is necessary to carry out hydraulic tests.
The correct choice of antifreeze deserves special attention, it is important to choose one that will fully match the heating system. For these purposes, an analysis of its elements is carried out, and the materials from which it consists are listed. After that, antifreeze is selected, which will not contain additives hazardous to the materials of the system.


For heating systems, the most popular is an anti-freeze liquid with carboxylate additives. As a rule, it has been used for at least 5 years. It is also worth noting that propylene glycol coolant for a heating system without effective additives is especially dangerous for copper heat exchangers and can lead to their unusability after a year of operation.
In the process of use, the coolant becomes contaminated, therefore its quality requires constant monitoring, which is desirable to be carried out in laboratory conditions.
Propylene glycol antifreeze for heating systems should be replaced only after a hydraulic test of the system and flushing it with an alkaline solution.
How to choose antifreeze
Today, the construction market offers a wide range of coolants, which are based on propylene glycol for heating systems (reviews about them are mostly positive). All of them have a different cost, which directly depends on the brand, the country of origin, as well as the performance characteristics of the solution itself.
Some consumers, without special knowledge, use automobile antifreezes (transformer oil, antifreeze, etc.) in their heating systems. However, this is unacceptable, since such solutions contain flammable and unsafe substances for human health. Antifreeze liquid based on propylene glycol is considered the most optimal and versatile in operation. When choosing a heat carrier for a heating system, you should pay attention to the following points:
- Shelf life. Antifreeze can be stored in its original packaging for a long time (even if the period is unlimited, it must be specified by the manufacturer in any case).
- Operating conditions. Non-freezing liquid can be universal, or it can only be suitable for a certain type of equipment.
- Packing material. Typically, antifreeze is sold in plastic cans. In a galvanized container, this substance loses its performance properties.
- Quality certificate. Non-freezing liquid must be manufactured in accordance with technological rules and regulations, tested in laboratory conditions and approved for sale.
- Presence in the composition of refined products.
It is very important to use antifreeze strictly for its intended purpose. Neglecting the rules for choosing an anti-freezing fluid will lead to negative consequences - accidents, water hammer, pipeline ruptures, etc.
Safety engineering
When working with propylene glycol, the following rules must be observed:
- Store the substance in a hermetically sealed container;
- Use protection for the skin of the hands and face;
- Protect eyes and respiratory tract;
- Do not work near electrical appliances;
- Avoid heating the mixture and vapors above 100 ° C;
- Do not use propylene glycol near heat sources;
- Do not expose propylene glycol or its vapors to open flames.
In this article, we examined the characteristics and properties of the coolant (antifreeze) propylene glycol and mixtures based on it. We hope the post was useful to you. You can leave your questions and opinions in the comments. Don't forget to share the article!
Loading ...
Harm and toxicity to the body
According to the international classification, propylene glycol is an E1520 additive. This means that it has been tested for a long time and its harm to the body has not been identified. But this only applies to ingestion.
Propylene glycol is used in the manufacture of cigarettes and e-cigarettes. And smoking and steaming them leads to lung cancer and the development of cardiovascular diseases. Scientists have not figured out which component is causing these diseases.
It is possible that nicotine or other tar substances are to blame. But it may be that inhalation of propylene glycol vapors is a negative factor... Therefore, when working with him and his solutions, it is recommended to observe safety precautions.