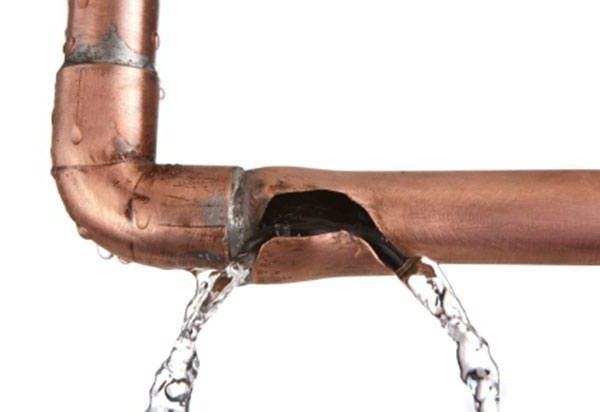
Why is the air in the water supply dangerous?

water hammer effectAir bubbles crush the water flow, causing inconvenience to the consumer. Cranes constantly “spit”, behave unpredictably;
- Air locks accumulate in the same places, causing rapid destruction of pipes and adapters. In danger, turns and bends of pipes, where there is an opportunity for an air bubble to linger;
- Air in the water supply pipes can provoke a water hammer. The unpleasant phenomenon gradually destroys the pipes, causing longitudinal cracks. Over time, the pipe bursts in the damaged area. For a long time, the owner may not notice the destruction, this is the main danger of water hammer.
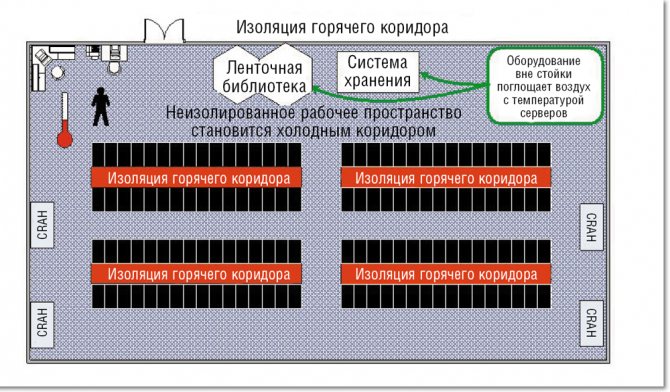
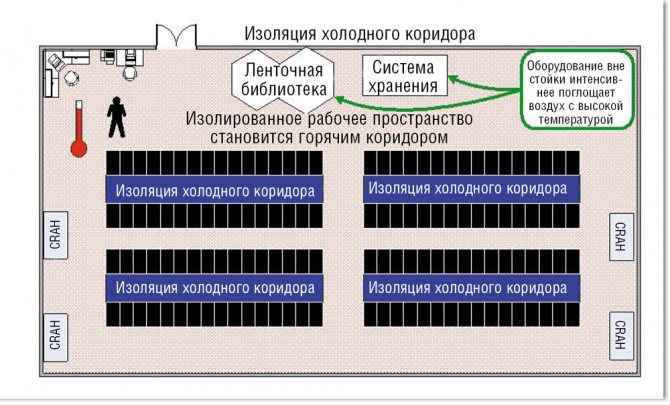
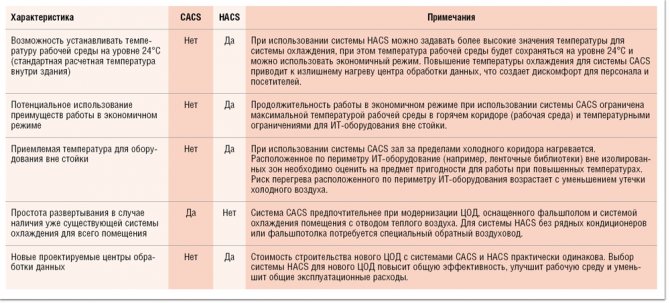
COLD CORRIDOR INSULATION
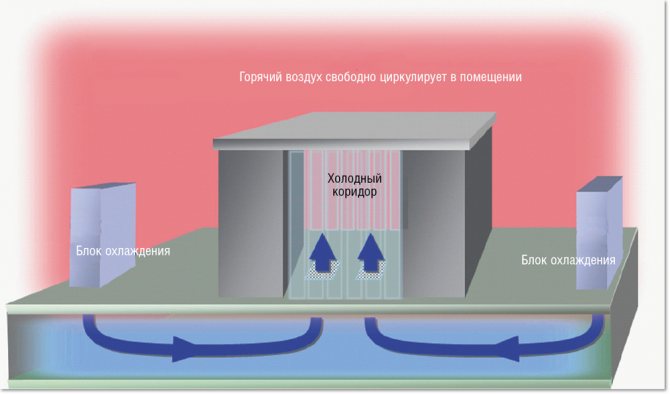
Cold-Aisle Containment Systems (CACS) isolates cold aisles so that the rest of the data center becomes a large ventilation chamber to draw in hot air and separate the hot and cold air streams.
Figure 1 illustrates the basic principles of cold air containment in a raised floor data center with cooling units located around the perimeter. Deploying CACS in this type of data center involves isolating the entry, exit, and ceiling of cold aisles, making this modification suitable for many existing data centers.
|
| Picture 1. Cold aisle insulation system in case of cooling of the entire room. |
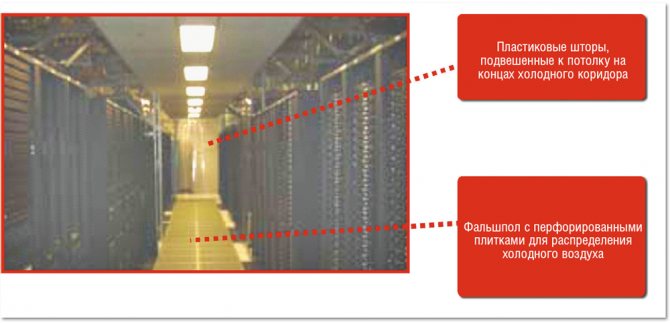
Sometimes data center operators use their own homebrew solutions when various types of plastic curtains are suspended from the ceiling to isolate cold corridors (Figure 2). Some vendors offer ceiling panels and doors that attach to adjoining uprights to separate the cold aisle from the warm air circulating in the room.
|
| Figure 2. An example of a homebrew cold aisle containment system. |
Why does air appear in the water supply system


tap water contains air
There are two reasons for the appearance of air in the water supply system of the house:
- Outside... Air enters the pipes through leaking joints;
- From within... Approximately 30 grams of air per 1 ton of water is dissolved in the stream of water passing through the pipes. Gradually the air is released. The slower the water flows, and the hotter it is, the faster the process goes. That is, in hot water systems, the likelihood of air jams is higher.
In the water supply systems of private houses, air appears for the following reasons:
- when the water level drops, air can be sucked in through the check valve;
- poorly tightened fittings with rubber seals;
- in hot water supply systems, the cavitation process is observed: steam is formed, air bubbles collect in the water, forming voids or caverns;
- the air in the water supply pipes remained from the first start-up of the equipment.
Air bubbles contain 30% more oxygen than atmospheric air. This explains the high oxidizing capacity of air in hot water supply systems. Air bubbles can be of various shapes: spherical - small, no more than 1 millimeter in diameter, mushroom-shaped, oval.
In vertical pipes, bubbles rush upward or are distributed throughout the volume. In horizontal highways, they stop at the highest points where they carry out destructive work.
When the water velocity in the pipes is more than 0.5 meters per second, the bubbles move without lingering. When the speed exceeds 1 meter per second, the bubbles break into very small bubbles. It turns out a semblance of an emulsion of water and air.Air bubbles in the water supply system of a private house begin to collapse at a fluid speed of 0.25 meters per second. If it is lower, traffic jams can stagnate in some places for a long time.
Grill + fan
The grill has a limited frying area, this disadvantage is especially noticeable when you have to cook complex-shaped foods, for example, goose or piglet. And so you want the dish to have a wonderful crust on all sides.
The way out of this situation is obvious - spit. We put it on, periodically (with the help of a motor or manually) turn it and achieve the desired effect. But there is a much simpler way - add fan operation to the grill. It distributes radiation, frying food not only from above, but also from below and from the sides.
It turns out something like a spit, only it is not the product that moves, but the air. At the same time, all the advantages of grilling are preserved - crisp crust, mouth-watering aroma and juicy flesh. The dish will not dry out and will be ready much faster.
For this mode, all dishes that are cooked on a regular grill (except for steaks and toasts) are suitable, and best of all - rolls and poultry.
How to get rid of air in pipes
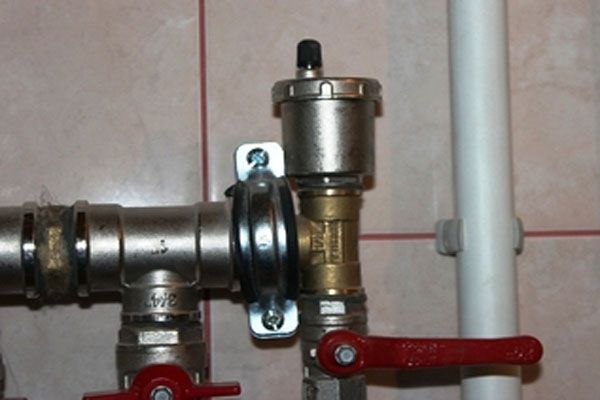


example of installation of a spreader
If there is already air in the water supply system of a private house, but it is not equipped with bleed devices, it is necessary:
- Switch off the pumping station.
- Open all drain taps, drain water and air from the water supply system. Then the pipes are filled again.
You can remove air from the water supply system once and for all with the help of bleed or bleed devices:
- mechanical valves such as the Mayevsky valve;
- automatic air vents;
- ball valves;
- valves.
Mechanical air relief valve device from the water supply system is as follows: a cylindrical box, the top is closed with a lid, from the bottom there is a thread for connecting to the water supply. There is a threaded plug in the middle of the cover. A plastic ball-shaped float is suspended inside the cylinder. If there is no air in the hot water supply system, the ball rises to the hole in the plug and closes it tightly under the pressure of the network. As soon as air enters the device, the ball leaves and the air is discharged. Air can enter the system through the bleed valves, which is useful when repairing or inspecting networks and accelerates the drainage of water.
Air extractors are installed at specific points in the water supply system: at the topmost ends, at bends or bends. That is, where there is an increased likelihood of air accumulation.
Homemade air accumulator
In rural water supply systems, air often flows interspersed with water. It is difficult and inconvenient to use such a water supply system, and automation does not always cope: if there is a lot of air, water overflows with a fountain directly from the valve. Therefore, instead of an automatic bleed device to release air in the water supply system, they install air accumulator... You can do it yourself, this is a tank with a drain pipe and a tap. The diameter of the accumulator must be 5 times the diameter of the water pipe, then it can work efficiently.
The air accumulator is installed at the highest point of the water supply system where it is convenient to manually bleed the air. Air storage tanks are widely used in multi-storey buildings in hot water systems.
Bottom heating + fan
The principle of this mode is the same as when the bottom element is working, only cooking is more rapid. The heat from below rises to the ceiling, is captured by the currents created by the fan and spreads throughout the oven. This setting is often recommended for baking open cakes or quickly finishing baking when a high temperature is required from the bottom, for example for low-rise baked yeast dough.Pros: juiciness inside and even browning on all sides, especially the bottom.
Ecology DIRECTORY
The flow rates of the air and the reactive solution must be constant, the speed of the solution is about 3 ml / min, the speed of the air is 12 l! Min. [...]
A diluting air flow with a small pump 9 (to remove traces of BOg) was drawn through a column 10 with soda lime and fed through a flow rate regulator 8 and a rotameter 7 (with a scale of 0-20 l / min) into chamber 6. In the chamber, a homogeneous, diluted gas mixture, which was supplied to the registering stream. A stable recording of the recording devices was obtained at all dilutions from 0.05 to 2.1 mg / m3 of sulfur dioxide. [...]
The effect of the flow rate on the sorption efficiency of impurities changes with the sorbent. One of the most important characteristics of the concentration column - the ineffective column height - increases with an increase in the air flow rate through the sorbent [68]. Sometimes, when the optimal sampling rate is reached, there is no increase in the volume before breakthrough with a decrease in the flow rate [69]. In other cases, the sorption efficiency increases continuously, as shown in Fig. 11.12. The maximum absorption efficiency of impurities for coal from coconut is achieved at a rate of 100 ml / min, while for Saransk coal, the efficiency is constantly increasing. A very important condition when comparing the results of sorption of impurities obtained on tubes of different sizes is the linearity of the air flow rate under other optimal sampling conditions. In the general case, the adsorption capacity of the tube with coal increases with decreasing linear air velocity [159]. [...]
The volume of the sampled air. The adsorption column acts as a chromatographic column and, under the influence of the air flow, contaminants will move along the column. The volume of air that is passed through the column when the sorbed impurities begin to leave the column corresponds to the volume before breakthrough. This volume is a function of the nature of the adsorbed compound and adsorbent, and usually volatile compounds have a very small volume before breakthrough. [...]
In fig. 2-4 show air flows and their boundaries in the vertical plane when flowing around an obstacle in the form of a free-standing narrow building of infinite length. [...]
The hot auxiliary air flow after the heat exchanger 9 enters the heat exchanger 2 and washes that part of the TT, which in the mode of heating the outside air is the zone of evaporation of the TT working substance. Outside air has a lower temperature and washes in the heat exchanger 2 that part of the TT where the working substance condenses. During condensation, the heat of the phase transition is released, which is perceived by the outside air and ensures an increase in its temperature. [...]
Vertical air movements are usually called air currents or streams. Pilots often talk about updrafts and downdrafts. Vertical air currents are usually quite weak, except for the so-called convective clouds, which look like large white cumulus clouds, often foreshadowing a thunderstorm. During thunderstorms, the speeds of ascending and descending air currents can reach 100 km / h, but in clear weather, as well as inside small, not raining clouds, they do not exceed 1-2 km / h. [...]
After the diffuser, the forced air enters the section of the main heat exchangers, divided by a horizontal partition into the main heating I (upper) and the main cooling 12 (lower) heat exchangers. The transition section 13 has an internal partition 14, which causes separate movement of air flows after the heating and air-cooling heat exchangers.Separated cold and hot air flows enter the section of reciprocal air valves 15, which consists of three independent zones 16. Each zone has a horizontal baffle 17, adjacent through a sealing gasket to the baffle 14 in the transition section 13. [...]
Large droplets lifted by the ascending air flow to the top of the cloud freeze and form hailstones, which grow rapidly as they merge with other supercooled droplets. The part of the cloud where the main growth of hail occurs is called the hail hearth. [...]
The amount of substance supplied to the air stream per unit of time at a certain pressure is set every 2-3 hours, as described on page 42. [...]
Airflow resistance is optional until January 1, 1984 […]
The operation of granulating urea with a stream of air accounts for about 50% of all ammonia losses. In addition, conditions are created for an undesirable dissociation reaction of carbamide to biuret and free ammonia to occur in the granule. One of the possible solutions to this problem is to carry out the granulation process in liquid, inert with respect to urea, solvents with a boiling point and crystallization temperature, respectively, above and below the temperature of the melt and solidification of the urea melt. Fatty alcohols, sulfonated kerosene, diesel fuel, etc. can be used as such solvents. The strength of the granules obtained in this process is 2-2.5 times higher than the strength of the granules obtained in air; the content of organic impurities in the granule is on average 0.01-0.06%, which practically does not affect the agrochemical properties of urea. [...]
It was found54 that when mixtures of air with liquid vapors are obtained, the diffusion time of vapors of a certain amount of liquid from a diffusion vessel does not depend on the air flow rate in the range of 3.5-60 l / h. [...]
The essence of cleaning the air contaminated with paintwork materials sucked from the painting chambers is that the air flow is directed either to a continuous continuously falling film of water, or to a water curtain in the form of the smallest drops of water. A continuous film of water flowing down the screen creates a water curtain in the path of the paint dust, causing coagulation of the carried away paint and varnish material. In the case of using water in the form of an aerosol, capture occurs both due to coagulation and due to complex sorption-kinetic interactions between water and paintwork materials. [...]
So, at the flight speed of the ZM, the temperature of the decelerated air flow at an altitude of 11 km near the streamlined surfaces of the aircraft will reach 330 ° С, at 4М - about 630 ° С. [...]
After 1 min, close the valve of the separating funnel so that the air flow enters the flask through the other funnel. [...]
The following automatic regulation scheme is possible. Two sensors are installed in the air flow after the air conditioner fan assembly. One sensor controls the constancy of the moisture content of the supply air d = dv by correspondingly changing the degree of cooling and dehumidification of the air in the spray chamber t% and d2 = var- This automatic control scheme is often called the variable dew point temperature method. The second sensor controls the receipt of the required supply air temperature t n by acting on the actuator in the bypass channel of the irrigation chamber. [...]
A well-known example of modeling: the flow around an airplane flying in the air is investigated by the flow around its model in a wind tunnel. In this case, the aircraft model is its geometrically similar miniature copy. Only the air flow around the aircraft body is modeled (investigated) and other properties of the aircraft, such as the comfort and safety of the passenger in the seat, are not investigated.To do this, it is necessary to build another model - a separate seat with a dummy on a device that reproduces its possible positions in flight. As you can see, the model takes into account some phenomena (air flow around the aircraft body in one case or the position of a person in a seat in another case when simulating various processes in an aircraft) and process parameters (configuration of wings and body or seat configuration). The phenomena taken into account in the model will be called the components of the model. [...]
The first of them consists in the freezing of NTO vapors by passing an air flow through a refrigerating chamber, in which a temperature reduction is achieved either through the use of a refrigeration unit, or through the use of various cooling mixtures. The disadvantage of this method is that the sampling time is limited, since as the thickness of ice with low thermal conductivity increases, the condensate yield decreases. [...]
Analysis progress. 10-15 ml of benzene is introduced into the tube with the taken sample (against the air flow during sampling). The solution is collected in an evaporation dish and the benzene is evaporated to dryness in a water bath. 0.8 ml of hexane is added to the dry residue. 2 µl of the solution is introduced into the evaporator for separation under the following conditions: column temperature 220 ° С, detector - 230 ° С, evaporator - 250 ° С; flow rate g, pa-carrier 40 ml / min, nitrogen for blowing up the detector - 120 ml / min; chart tape speed 600 mm / h, amplifier scale 2-10 10A; the retention time of the celtan is 2 min 36 s, the retention time of the solvent is 5 s. [...]
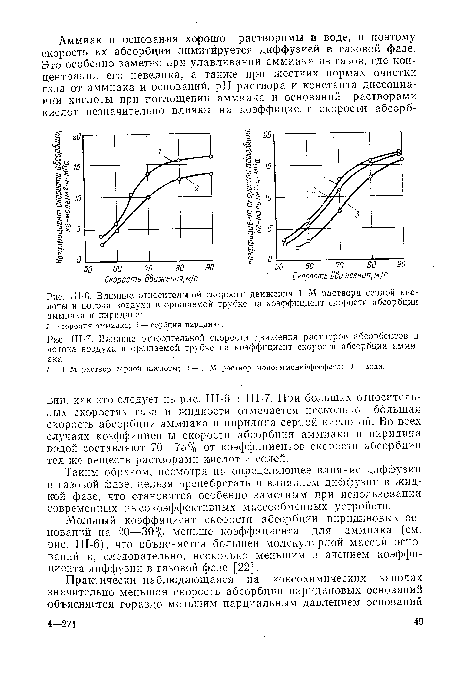
| Sh-7. Influence of the relative velocity of movement of absorbent solutions and air flow in the irrigated tube on the coefficient of the absorption rate of ammonia |
|
From the graph in Fig. 62 it can be seen that the maximum velocities vs of the auxiliary air are values of 8-8.5 m / s, depending on the irrigation density Ht. The final choice of the auxiliary air flow rates and irrigation densities must be made taking into account the provision of sufficient efficiency for cooling the main air flow and, at the same time, the most favorable technical and economic indicators for the power consumption for the recirculation of irrigation water and the movement of air flows in relation to the unit of refrigeration capacity. ...]
The most simple and widespread are devices for dry cleaning of air and gases from coarse non-sticking dust. These include cyclones of various designs, the principle of which is based on the use of centrifugal force acting on dust particles in a rotating air stream (Fig. 15). [...]
Analysis conditions: column temperature 110 ° C; evaporator temperature 200 ° C; carrier gas (nitrogen) flow rate 30 ml / min; hydrogen flow rate 30 ml / min; air flow rate 250 ml / min; the speed of the chart tape is 600 mm / h; sensitivity scale scale 1: 10; retention time of acrylonitrile 2 min 32 s. [...]
The experimental values of / hc on the graph increase with an increase in the mass velocity of the cold air flow in the living section of the condensation zone of the heat exchangers from the TT. Based on the results of processing the experimental data, a power-law dependence for k on (»p) w was established. s with an exponent of 0.65. Line 1 in the graph unites the test results of a six-row heat exchanger in depth with approximately constant initial parameters of hot air flow with = 38.8 ° C and cold air flow with ¿x = 1.5 ° C. Lines 2 and 3 correspond to experiments with a heat exchanger of nine depth rows, but with correspondingly different /, h and tXl. Line 2 unites the experiments at ¿r, = 50 ° C and = 5.5 ° C, and line 3 - at r, = 28.4 ° C = 3.5 ° C. The resulting character of the dependence for kc shows that The intensity of heat transfer to TT is significantly influenced by the temperature difference between the hot and cold streams, as well as the design of the heat exchanger. [...]
Cyclones are characterized by a slow but long (over a number of days) upward movement of air. At the same time, strong clouds and precipitation are common, that is, exactly what is called bad weather, but in terms of atmospheric pollution, it should rather be considered good. The upward flow of air carries pollutants across the atmospheric layer of considerable height. Rain and snow wash out solid and gaseous impurities from the atmosphere, carrying them to the ground. [...]
Coton and Gokhale [272] somewhat modified the method of weighing large droplets in a vertical air stream, developed by Blanchard. They received confirmation of the conclusions of Leonard and Blanchard that in a turbulent air flow the stability limit corresponds to droplets with a diameter of 5.5 mm, and in a laminar flow - 9 mm. Investigations in a wide vertical jet, in which there is no intense turbulence, carried out by Tanaka [546], showed that droplets about 7 mm in diameter tend to split into two relatively large droplets and somewhat smaller ones. A rather strong oscillation of the droplets is observed before destruction. [...]
Terrible devastation is brought by hurricane winds from the region of Iceland, where cold air currents from the shores of Greenland and warm ones accompanying the Gulf Stream mix (Fig. 18.5). […]
The number of samples taken - 40, the number of channels - 5. Duration of sampling - 5 ... 99 min. Air flow rate - 0.1 ... 5 l / min. [...]
If we accept equal operating conditions of heat exchangers with the same values of the velocities of the main flow of air and air-water mixture, then from a comparison of the experimental dependences it can be seen that the highest coefficients k are provided in tubular heat exchangers made of aluminum rolling tubes, in which the values of k for a smooth outer surface area is 3 times higher than that of plate heat exchangers without fins. Consequently, the ribbing of the heat exchanger elements from the side of the auxiliary flow is an effective means of intensifying the processes of heat removal in combined circuits of indirect evaporative air cooling. [...]
The filter medium is the fabric on the frame. Dust collects on the outside of the bag. Cleaning is done with a stream of air or by shaking off the filter bag. These filters remove 99.7% of the particles in the incoming air and are effective at removing small particles. [...]
The cutting unit consists of a system of drive, pressure, transport rollers and guillotine shears. The paper is smoothly moved by a stream of air supplied from the bottom of the sheet from the cross member of the bed. By this flow, the paper web is supported from below in front of the guillotine shears. After cutting, the air supply is interrupted and the cut sheet falls smoothly onto the stack lying on the lifting table (on the pallet). [...]
The primary measuring transducer of the gas analyzer is a flame-ionization chamber, to which two gas streams are supplied: a stream of hydrogen with the analyzed gas and an air stream to maintain the combustion of a hydrogen flame. In the absence of organic substances in the gas streams entering the chamber, the flame in the chamber has low electrical conductivity and the background ionization current arising in the chamber under the influence of an electric field is approximately 10 "" A. The appearance of organic substances in the analyzed gas and their subsequent ionization in a hydrogen flame leads to a sharp an increase in the electrical conductivity of the flame and a corresponding increase in the ionization current between the electrodes. In this case, the ionization current is proportional to the amount of organic substances entering the chamber per unit of time. [...]
A slightly modified design of the diffusion dispenser 53 is shown in Fig. 35. The diffusing liquid is placed in a 13 cm long capillary. The air flow enters from the side into the mixing chamber and goes up. The device is thermostated with an accuracy of ± 0 ° C. [...]
The aerosol method of treatment consists in the fact that in the generator a concentrated solution of pesticides turns into a fog, which is a mixture of air with the smallest droplets of liquid. Artificial fog is formed as follows. The air drawn in from the atmosphere enters the combustion chambers under excess pressure. Some of this air enters the burner and disperses the gasoline. Gasoline flashes in the combustion chamber. Here and in the flame tube, the fuel burns out, and the combustion products are mixed with the excess air supplied. Due to the high temperature, the air increases in volume, and the gas-air mixture at a high speed (250-300 m / sec) exits through a narrow nozzle, dragging the working fluid out of the container located near the generator. The liquid is crushed into small droplets, at a high temperature, a vapor-gas mixture is formed, which is released into the atmosphere. Mixing with relatively cold air, it cools, forming a fog. Fog is carried by air currents over rather long distances - hundreds and thousands of meters, gradually settling on the cultivated vegetation. [...]
With further growth, the croup turns into hail. The conditions favorable for the formation of hail are high water content, higher air temperature and a higher rate of fall of cereals. With a certain combination of these parameters, the heat released during the freezing of droplets does not have time to be released from the surface of the hailstones, and their freezing will be partial. As a result, part of the water will remain in a liquid state and fill the pores, forming the so-called spongy ice [399]. As the pores are filled, excess water will be blown away from the hailstones by a stream of air. Large drops, raised by ascending currents to such a height where they freeze, can also serve as embryos of hailstones. Numerous observations show that the core of the hailstones consists of both snow grains and frozen drops. Ch. Knight and N. Knight [364] obtained from an examination of 400 hailstones that 60% of the embryos had a conical shape (croup), 25% of the embryos were spherical and transparent (drops), 10% were spherical and spongy (croup or drops). […]
The most important for the calculation of indirect evaporative cooling heat exchangers is to determine the values of the heat transfer coefficients from the main air flow through the dividing wall to the water cooled by evaporation. When calculated with respect to a smooth surface, the heat transfer coefficient is determined by the usual expression (1.46). [...]
In contrast to the elements considered above, the determination of the total mercury content by the AAS method is based on measuring the absorption of light by its vapors, which are released by an air flow from an aqueous solution after the reduction of ions to an atomic state, at a wavelength of 253.7 nm in a gas cell at room temperature (“method cold steam ”). Tin chloride, sodium stannite, ascorbic acid, etc. are used as reducing agents [3,8]. The detection limit is 0.2 μg / L, the range of measured concentrations is 0.2 - 10 μg / L [11] To eliminate the interfering effect of organic substances that absorb light at a given wavelength, an acidic solution of potassium permanganate or dichromate is added to the sample. [... ]
There are currently four types of cooling towers in use. The principle of operation of a natural draft cooling tower with a hyperbolic surface (Fig. 1) is that warm air rises up the cooling tower, while the cooling process takes place in the lower section. This creates a natural and continuous flow of air, which rises up the cooling tower and provides cooling the water with a counter flow. This is mainly due to the difference in the density of the incoming cold air and the outgoing warm air. [...]
In the mixed mode of operation, the circulating water first passes completely or partially through the heat exchanger in the dry part and, after being partially cooled, enters the evaporator part, and the air at the exit from the dry part is heated. Subsequently, both air streams from the dry and evaporative parts are mixed. At the same time, the relative humidity of the air leaving the cooling tower decreases, and its temperature rises. In this case, the fog above the exhaust tower either decreases or disappears altogether, depending on the temperature and humidity of the surrounding outdoor air. In winter, when the circulating water consumption is significantly reduced, the dry part of the cooling tower is mainly or even fully functioning, which makes it possible to practically exclude the formation of fog. [...]
The second type of air ion generator consists of a circular electro-effluvial chandelier suspended from glass insulators inside a cylindrical wire cage. An electric fan is placed on top, giving a downward air flow. The dimensions of the chandelier of this model were as follows: diameter 23 cm; the number of points is 14, which is 310 points per 1 m. The protective cage had a diameter of 36.5 cm and a height of 18.5 cm. It consisted of a skeleton made of metal wire, covered with a net of interwoven nickel wire; the size of the cells was taken as 2 × 2 cm.The distance of the chandelier tips from the bottom grid, like other grounded parts of the cage, depends on the voltage applied to the chandelier and is calculated with some excess compared to the distance that corresponds to the spark gap for a given potential. The voltage was applied to the chandelier with a wire insulated with two thick-walled glass tubes inserted into one another. The outer tube was glued over with staniol, connected to the ground. [...]
(Finland) manufactures aspiration devices 8082, 8083, 8077 [37] used in individual samplers. Type 8082 consists of a pump with a regulator for constant air flow. With the help of the clock mechanism, the duration of the pump operation can be set within the range of 10-990 minutes in 10-minute increments. The flow rate is selected using a choke block, without calibration. If the flow rate for any reason (for example, due to blockage) falls below the permissible level, for example, within 30 s, the warning lamp lights up. When the battery voltage drops, the pump warning light also comes on. When sampling gases and vapors, the air flow rate is from 20 ml / min to 0.5 l / min, when taking solid aerosols from 0.5 to 4.0 l / min and from 5 to 500 ml / min. It operates on batteries, the service life of which is 10 hours. The display in the device indicates the recharge time of the used batteries. The instrument is used in conjunction with a flexible hose and a sampling head. The mass of a portable sampler is 0.4 kg, dimensions are 120X73X73 mm. […]
In fig. 26 shows a diagram of a commercial device working on this principle, developed by the firm Maet [312]. In these devices, outside air is captured by a pump and flows through an annular gap that surrounds a glass rod on which a platinum wire winding (cathode) is located. The anode is a platinum ring located at the bottom of the rod.Iodide solution is introduced into the upper part of the rod and, by gravity, flows down the rod in a thin layer, absorbing ozone molecules from the air stream. flowing down from the rod This very sensitive method has an ozone detection threshold of about 2-10 4 ppm. [...]
The first stage of the design consists in determining the concentrations of harmful substances (impurities) in the atmosphere of the adjacent territories and at the industrial site.It is especially important to know the concentration of harmful substances in the places of intake of outdoor air for ventilation of buildings, since this is a decisive factor in its effectiveness. Usually these concentrations are calculated 16]. However, it is very difficult to obtain reliable information by calculation, especially in the surface layers of the atmosphere, where air flows are significantly influenced, in particular, by the development of the territory and vegetation. Therefore, it is better to determine the concentration of impurities in the outdoor air by physical modeling. For this purpose, a wind tunnel is used (an installation that creates a flow of air or gas for the experimental study of the phenomena accompanying the flow of bodies). [...]
In the ecological system, the main source of energy is the Sun, and the secondary source of energy is water, wind, organic matter and geochemical processes. Species specialization contributes to the inclusion of secondary energy flows into the overall system. For example, the plants of some species have long roots that allow them to extract mineral nutrients from great depths (for example, the roots of a camel thorn go 35 m deep). Air currents provide pollination of some plants, leaves in drought use the evaporation of the water contained in them to cool. Thus, they in the best way support the vital activity of the system as a whole. The rest of the species and combinations of species die out in the process of evolution. [...]
The fourth method is probably the most widely used today for suppressing the formation of smoke. This has become particularly justified after the development of the currently used engines with higher pressure and fuel-to-air ratio, as the higher ratio has led to an increase in smoke emissions. However, higher pressure increases the temperature in the combustion zone, although this increases fuel economy. The main effect of increasing the pressure in the chamber is to influence the fuel atomization pattern using conventional mechanical injectors. Atomization occurs closer to the injector nozzle, and less fuel atomized penetrates deeper into the main zone due to the increased air resistance. In order to take advantage of the higher pressure and mixture ratio (such as fuel economy), a different fuel injection system is needed. One approach is to use a pneumatic injector. In its simplest form, liquid flows along the metal plate and drips or splashes at its end. A high-speed air stream is introduced at the end of the plate, and this high-energy air stream atomizes the fuel into tiny droplets. Air speed can reach 120 m / s. [...]
Air separation can in particular be used to separate thermoplastic plastic from the fabric backing. In this process, shredded waste of sheet thermoplastics on a fabric basis (polymer chips, linters, chopped fabric, fabric dust) are separated by an air stream in a cyclone separator and a vortex funnel. The mixture of chips and chopped fabric is fed into a gravity air separator, where the lighter fabric is separated from the chips by a stream of air and discharged into the pipeline, where it is mixed with fabric dust and lint. [...]
In industrial units for the dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene, the thermal efficiency, as a rule, does not exceed 28-33%. Analysis shows that the main reason for the low thermal efficiency is due to the lack of heat recovery from the low temperature contact gas. Indeed, in traditional schemes, the heat of condensation of water vapors and hydrocarbons is not used and is lost into the environment with the air flow in air condensers and with circulating water. The heat flow diagram in the ethylbenzene dehydrogenation unit (Fig.5.16) confirms that a significant proportion of the heat supplied with the fuel is lost to the environment during cooling and condensation of the contact gas in the refrigerator-condenser 7 and separator ¿(Fig. 5.14). [...]
Analysis progress. The sorption tube with the sample is connected to the device through a metering valve, heated in a tubular electric furnace at 150 ° C for 5 minutes. The metering valve at this time is in the "sampling" position. Then the valve is set to the "analysis" position, and the sample is fed with the carrier gas to the chromatographic column for separation under conditions; column oven temperature 110 ° С, evaporator temperature 200 ° С; carrier gas flow rate (nitrogen or helium) 45 ml / min, air flow rate 300 ml / min, hydrogen flow rate 45 ml / min, chart tape speed 600 mm / h; retention times of methylene bromide 1 min 5 s, iodide - 5 min 45 s. [...]
Biofilters are inferior in performance to aerotanks. They are structures filled with a coarse-grained load, on which microorganisms develop, forming a biofilm. Various materials are used as a filler, which must be resistant to destruction and harmless to microorganisms. Distinguish between high-load and low-load biofilters, or drip filters. Highly loaded ones provide for the treatment of large volumes of wastewater with a sufficiently high concentration of contaminants. They are 10-15 times more productive, but they do not provide complete purification of waste liquid. In lightly loaded, complete cleaning is achieved, but their performance is low. These structures are recommended for the treatment of small volumes of wastewater with a low concentration of contaminants. In drip biofilters, natural ventilation is used, which is carried out due to the temperature difference between waste water and outside air. If the temperature inside the filter is higher than outside, the air flow is from bottom to top. At a higher outside temperature, the movement reverses. The height of drip biofilters usually does not exceed two meters, the ratio of the diameter to the height is more than one. The waste liquid is supplied to these filters at such a rate at which the biofilm particles are not washed off, therefore the mineralization of dead cells occurs here, on the filter. The purified water is transparent and can be immediately discharged into the reservoir. [...]
High temperature and heat resistant fan
For saunas, fireplaces and steam rooms or saunas, a high-temperature, heat-resistant fan is better suited. Such equipment is designed to operate at high temperature levels up to 200 degrees Celsius. When choosing a high-temperature fan, you should pay attention to the level of protection.
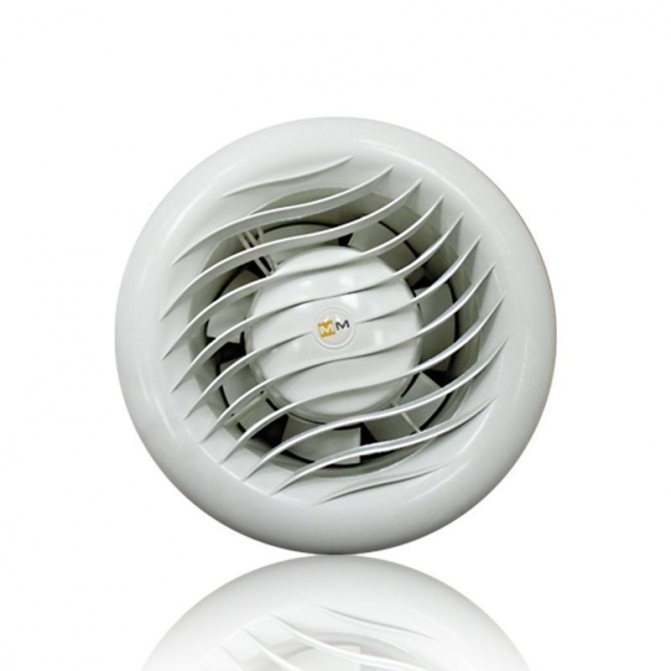


Heat-resistant fan with IP rating is used in saunas, baths
For saunas and baths, a heat-resistant fan is required, a model with IP protection, in which moisture is excluded from the elements of the electrical circuit of the device.
The design of the devices assumes installation on the ceiling (regular, suspended) or on the walls. A fan can be used to regulate the temperature in adjacent rooms.
If the building uses a fireplace heating system, it is rational to operate a heat-resistant fan. The rooms are heated by moving the hot air emitted by the fireplace through the air ducts. The fan in this case must withstand high temperatures and their sudden changes.