Refrigerant R404A is a colorless substance in a liquid state of aggregation or in the form of odorless gas. It is non-toxic, insoluble in water, but susceptible to organic solvents. Consists of a mixture of HFC freons R143A, R135A and R125A in the proportion: 4:52:44.
Advantages of R404A refrigerant
Ozone-saving freon R404A is artificially synthesized to replace R502, therefore, in terms of its main qualities, it fully corresponds, and in many respects surpasses its analogue. Freon R404A is characterized by operating parameters similar to those of similar freons, therefore it can be refueled in modern systems. The refrigerant has the following properties:
- low discharge temperature, therefore, prolongs the compressor life;
- easy refueling of the circuit in case of freon leakage;
- low operating costs;
- fire resistance (fire safety);
- acid (oxidant) resistance.
Halon in gaseous and liquid state of aggregation belongs to the class (safety group) A1 / A1. It has a low potential (3750), minimally affecting global warming. The preservation of the ozone layer is ensured by the absence of chlorine in the composition. The exposure limit for the ozone layer (regularly exposed concentration) is 1,000 ppm.
The popularity of R404A freon is due to many advantages over R502:
- a smaller volume of freon is required to ensure proper performance;
- cold productivity increased by 7% is provided;
- does not exceed toxicity standards and is considered a chemically stable composition;
- less greenhouse effect than other refrigerants;
- it is characterized by a constant composition, even in the case of refueling, the stable operation of the refrigeration equipment is ensured;
- due to the stable proportions of the constituent components, when leaking, chemical reactions that are dangerous to people do not occur;
- when stored in a dry place, protected from sunlight, the composition is non-flammable;
- thanks to its low discharge temperature, it has a long service life.
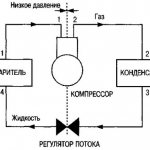
Refrigeration cycle diagram
Air cooling in an air conditioner and other refrigeration equipment is provided by circulation, boiling and condensation of freon in a closed system. Boiling occurs at low pressure and temperature, and condensation at high pressure and temperature.
This mode of operation is called a compression type refrigeration cycle because a compressor is used to move the refrigerant and increase the pressure in the system. Let's consider the scheme of the compression cycle in stages:
- When leaving the evaporator, the substance is in a state of vapor with low pressure and temperature (section 1-1).
- Then the steam enters the compression unit, which increases its pressure to 15-25 atmospheres and the temperature to an average of 80 ° C (section 1-2).
- In the condenser, the refrigerant is cooled and condensed, that is, it turns into a liquid state. Condensation is carried out with air or water cooling, depending on the type of installation (section 2-3).
- When leaving the condenser, freon enters the evaporator (section 3-4), where, as a result of a decrease in pressure, it begins to boil and turns into a gaseous state. In the evaporator, freon takes heat from the air, due to which the air is cooled (section 4-1).
- The refrigerant then flows into the compressor and the cycle resumes (section 1-1).
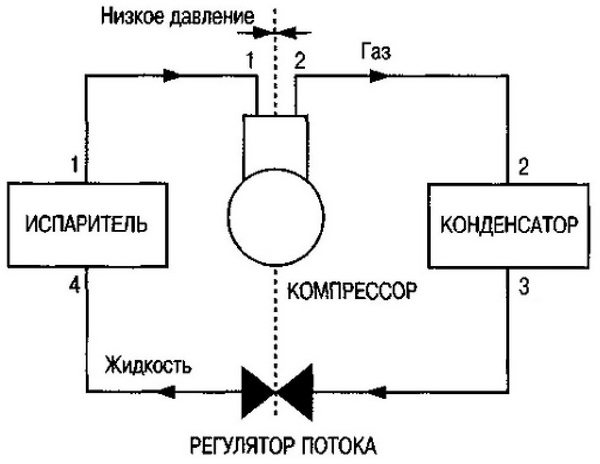
All refrigeration cycles are divided into two areas - low pressure and high pressure. Due to the pressure difference, the freon is converted and moves through the system.Moreover, the higher the pressure level, the higher the boiling point.
The compression refrigeration cycle is used in many refrigeration systems. Although air conditioners and refrigerators differ in design and purpose, they work on a single principle.
Physical properties of ozone-safe freon
Due to the danger of the destruction of the ozone layer of the atmosphere by freons, at first freon R12 and its modifications were completely banned, and now R22 is on the verge of such a ban. New ozone-safe freons are multicomponent mixtures of several freons.
The most common are R407 and R-410A. The first of them was created for the physical characteristics of R22 in order to withstand pressure indicators in the system, however, the different evaporation temperatures of individual components led to the fact that the natural losses of freon became impossible to replenish with refueling. Therefore, when the critical volume is lost, this freon in the system has to be completely changed.
For R-410A freon, the evaporation of components is uniform, but the boiling point is almost twice as high, so the operating pressure of the unit with it increased to 28 atmospheres. The direct dependence of pressure on the temperature of freon means that it cannot be used in air conditioners designed for R22, and in new models it is necessary to increase the compressor power and use more durable, and therefore expensive, materials for the manufacture of the cooling system.

The dependence of pressure on the temperature of freon (enlarge the picture)
Signs of a freon leak
The refrigerant freon in air conditioners is subject to leakage during operation. During the year of use, the amount of freon decreases by 4–7% in a natural way. However, if the air conditioner malfunctions or the indoor unit is damaged, leakage may occur in a new unit as well. It is important to determine it at the initial stage and to top up the device with refrigerant in time.
The main signs of a freon leak:
- Poor room cooling.
- Frost appears on the parts of the indoor and outdoor units.
- Oil leaks under the taps.
- Increased noise and vibration of the device during operation.
- An unpleasant odor appears when the air conditioner is operating.
If the leak is caused by prolonged use, the air conditioner can be restored to its proper functioning by charging it with refrigerant. In case of damage to parts and freon tubes along which the cycle moves, not only refueling will be required, but also the intervention of cooler repair specialists.


What is freon R410a


The information that the refrigerant r 410a has become a replacement for R22 cannot be taken literally. The technical characteristics of freons differ, a split system designed for one type of gas mixture is not filled with a different composition. Freon r 410a was developed in 1991 by Allied Signal. Five years later, the first air conditioners appeared, working with the new freon. The goal of the developers was to replace obsolete gas mixtures containing chlorine. Compounds of the CFC (chlorofluorocarbon) group, when released into the atmosphere, destroyed the ozone layer, increasing the greenhouse effect. The new freon meets all the requirements of the Montreal Protocol. Its influence on the depletion of the protective layer of the Earth is equal to zero.
The composition of freon r410a: R32 + R125. Chemical formulas of the compounds: difluoromethane CF2H2 (difluoromethane) and CF2HCF3 (pentafluoroethane). The ratio of the components is 50% to 50%.
The composition is stable, inert to metals. Has no color, has a slight smell of ether. Under the influence of open fire, it decomposes into toxic components.
Methods for refueling the air conditioner
It is recommended to refuel air conditioners with freon at least once every 1.5-2 years. During this time, there is a natural leak of a significant part of the refrigerant, which must be replenished. Operating the coolers without refueling for 2 years or more may damage the device due to overheating and wear of parts, as well as oil leakage.
Refueling of air conditioning devices is carried out by specialized services.However, if you have the necessary tools, you can do this procedure yourself.


As a rule, an air conditioner does not require a full charge, but only needs to replenish the amount of refrigerant that has evaporated as a result of a leak. Therefore, the most important stage of work is to determine the level of leakage of the substance.
A beginner can do this procedure in two ways:
- By pressure. To find out the amount of freon, you need to look at the air conditioner manual - the pressure level in the system will be indicated there. Then it is necessary to connect a manifold to the device - it will show the real pressure level in the cooler. By subtracting the resulting value from the parameters specified in the documents, it is easy to find out the required amount of substance for refueling.
- By mass. When the air conditioner is fully charged, you can find out the required volume by weight. To do this, you also need to refer to the documentation. When filling the device with freon, the refrigerant bottle for the air conditioner is placed on a precision balance. In the process of pumping, you need to carefully monitor the weight of the cylinder and, when replenishing the lack of substance, immediately turn off the system.
Refueling the air conditioner: the algorithm of actions
Before filling the air conditioning system with freon, you need to select the necessary tools and materials. This will require a pressure gauge, a freon bottle, a vacuum pump, as well as a scale, which will determine the amount of refrigerant in the air conditioner.


Algorithm of actions when refueling the air conditioner:
- First, you need to disconnect the cooler from electricity and determine the amount of freon required for refueling by weight or pressure in the system.
- And also it is necessary to "blow through" the tubes with nitrogen in order to remove excess impurities from the system and to make sure that the system is tight. This is important if there is a suspicion of refrigerant leakage due to system damage.
- Then you need to close the three-way valve clockwise.
- To determine the pressure level and to refuel, you need to connect a gauge manifold to the fitting.
- After that, the three-way valve opens again, a refrigerant cylinder is connected to the manifold and pumped into the system.
Refrigerant Comparison Chart
Previously, in the production of refrigeration units, ammonia was used as a refrigerant. However, this substance has a detrimental effect on the environment and destroys the ozone layer, and in large quantities can create health problems for people. Therefore, scientists and manufacturers began to develop other types of coolants.
Modern types of refrigerants are safe for the environment and people. They are different types of freons. Freon is a substance that contains fluorine and saturated hydrocarbons, which is responsible for heat exchange. Today there are more than forty types of such substances.
Freons are actively used in household and industrial appliances that cool air and liquids:
- As a refrigerant in a refrigerator.
- For cooling the freezer.
- As refrigerants for cooler bags.
- For cooling the air in the air conditioner.
The table of properties allows you to select the optimal type of refrigerant. It reflects the basic properties of freons: boiling point, heat of vaporization, density.
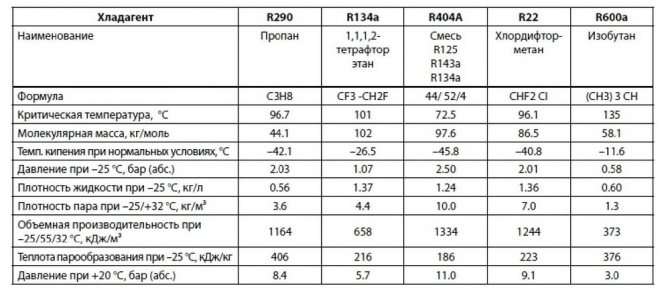

When refueling the air conditioner, you may need comparative tables of freons. They determine the substances with which one or another refrigerant can be replaced if it could not be found on the market. Below is a simplified version of such a table with the most common types of coolers.


CFCs - chlorofluorocarbons, HCFCs - hydrochlorofluorocarbons, HFCs - hydrofluorocarbons
Types of freons (freons)
In accordance with the degree of impact on the ozone layer, freons (freons) are divided into the following groups:
| Group | Connection class | Freons (freons) | Impact on the ozone layer |
| A | Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) | R-11, R-12, R-13, R-111, R-112, R-113, R-113а, R-114, R-115 | Cause ozone depletion |
| Bromofluorocarbons | R-12B1, R-12B2, R-113B2, R-13B2, R-13B1, R-21B1, R-22B1, R-114B2 | ||
| B | Chlorofluorocarbons (HCFC) | R-21, R-22, R-31, R-121, R-122, R-123, R-124, R-131, R-132, R-133, R-141, R-142v, R-151, R-221, R-222, R-223, R-224, R-225, R-231, R-232, R-233 | Causes mild ozone depletion |
| C | Hydrocarbons (HFC) | R-23, R-32, R-41, R-125, R-134, R-143, R-152, R-161, R-227, R-236, R-245, R-254 | Ozone-safe freons (freons) |
| Fluorocarbons (perfluorocarbons) (CF) | R-14, R-116, R-218, R-C318 |
The most common compounds are:
- trichlorofluoromethane (bp 23.8 ° C) - Freon R-11
- difluorodichloromethane (bp −29.8 ° C) - Freon R-12
- trifluorochloromethane (bp −81.5 ° C) - Freon R-13
- tetrafluoromethane (bp −128 ° C) - Freon R-14
- tetrafluoroethane (bp −26.3 ° C) - Freon R-134A
- chlorodifluoromethane (bp −40.8 ° C) - Freon R-22
Application [| ]
- It is used as a working substance - a refrigerant in refrigeration units.
- As a push-off base in gas cartridges.
- It is used in perfumery and medicine to create aerosols.
- It is used in fire extinguishing at hazardous facilities (for example, power plants, ships, etc.).
- As a foaming agent in the production of polyurethane products.
- As a raw material for the industrial production of fluoroolefins [2]: tetrafluoroethylene 2CF2HCl → CF2 = CF2 + 2HCl;
- trifluorochlorethylene CF2ClCFCl2 + Zn → CF2 = CFCl + ZnCl2;
- vinylidene fluoride CF2ClCH3 → CF2 = CH2 + HCl.
Properties [| ]
Physical properties [| ]
Freons are colorless gases or odorless liquids. Well soluble in non-polar organic solvents, very poorly - in water and other polar solvents.
Basic physical properties of methane freons
[2]
| Chemical formula | Name | Technical designation | Melting point, ° C | Evaporating temperature, ° C | Relative molecular weight |
| CFH3 | fluoromethane | R-41 | -141,8 | -79,64 | 34,033 |
| CF2H2 | difluoromethane | R-32 | -136 | -51,7 | 52,024 |
| CF3H | trifluoromethane | R-23 | -155,15 | -82,2 | 70,014 |
| CF4 | tetrafluoromethane | R-14 | -183,6 | -128,0 | 88,005 |
| CFClH2 | fluorochloromethane | R-31 | — | -9 | 68,478 |
| CF2ClH | chlorodifluoromethane | R-22 | -157,4 | -40,85 | 86,468 |
| CF3Cl | trifluorochloromethane | R-13 | -181 | -81,5 | 104,459 |
| CFCl2H | fluorodichloromethane | R-21 | -127 | 8,7 | 102,923 |
| CF2Cl2 | difluorodichloromethane | R-12 | -155,95 | -29,74 | 120,913 |
| CFCl3 | fluorotrichloromethane | R-11 | -110,45 | 23,65 | 137,368 |
| CF3Br | trifluorobromomethane | R-13B1 | -174,7 | -57,77 | 148,910 |
| CF2Br2 | difluorodibromomethane | R-12B2 | -141 | 24,2 | 209,816 |
| CF2ClBr | difluorochlorobromomethane | R-12B1 | -159,5 | -3,83 | 165,364 |
| CF2BrH | difluorobromomethane | R-22B1 | — | -15,7 | 130,920 |
| CFCl2Br | fluorodichlorobromomethane | R-11B1 | — | 51,9 | 181,819 |
| CF3I | trifluoroiodomethane | R-13I1 | — | -22,5 | 195,911 |
Chemical properties [| ]
Freons are relatively inert chemically, therefore they do not burn in air, are not explosive even in contact with an open flame, but actively interact with alkali and alkaline earth metals, pure aluminum, magnesium, magnesium alloys. Formation of mixtures with air or oxygen under pressure and contact with metal heated above 200 ° C is prohibited! When freons are heated above 250 ° C, very toxic products are formed, for example, phosgene COCl2, which was used as a chemical warfare agent during the First World War.
Resistant to acids and alkalis.
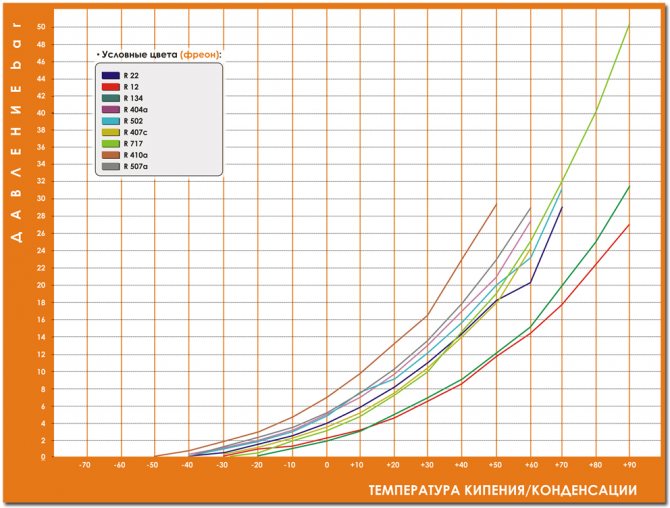
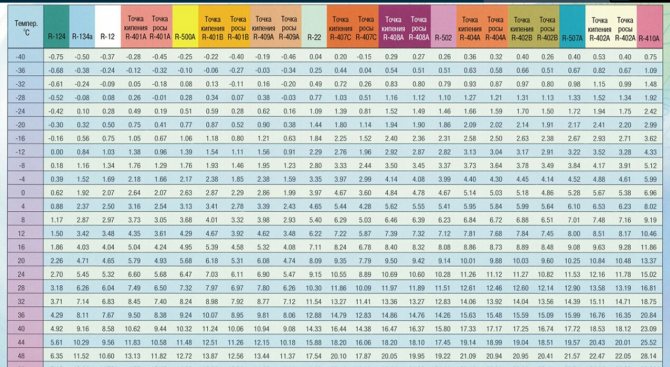
Dependence of the saturation temperature of freon on pressure.
How do I use the table?For example: It is only necessary to measure the condensing pressure after the condenser, before the expansion valve or capillary tube, otherwise it will not correspond to reality. Temperature glideAt the moment, many types of refrigerants have been synthesized (more than 70 types), many of them are multicomponent and consist of parts with different physical properties. For this reason, the temperatures during evaporation and condensation are different. There are two scales for such freons:
For example:
Programs for determining the dependence t / PAt the moment, many manufacturers of refrigeration equipment and refrigerants have released handy applications for phones on different operating systems (including the iPhone). It is more convenient to use them, as they have an interactive scale that imitates the popular "refrigerator ruler" and also allow you to enter the exact value from the keyboard. In their database there are more than 70 types of refrigerants produced at the moment. You can get acquainted with the most popular of them and download it in this article. Pressure temperature table for freons
Self-repair of air conditionersDoes your air conditioner need a voltage stabilizer and how to choose it for the air conditioner? Did you mix up the wires when installing the winter kit? This is easy to fix by repairing the condensation pressure regulator board. Climate news |
masterxoloda.ru
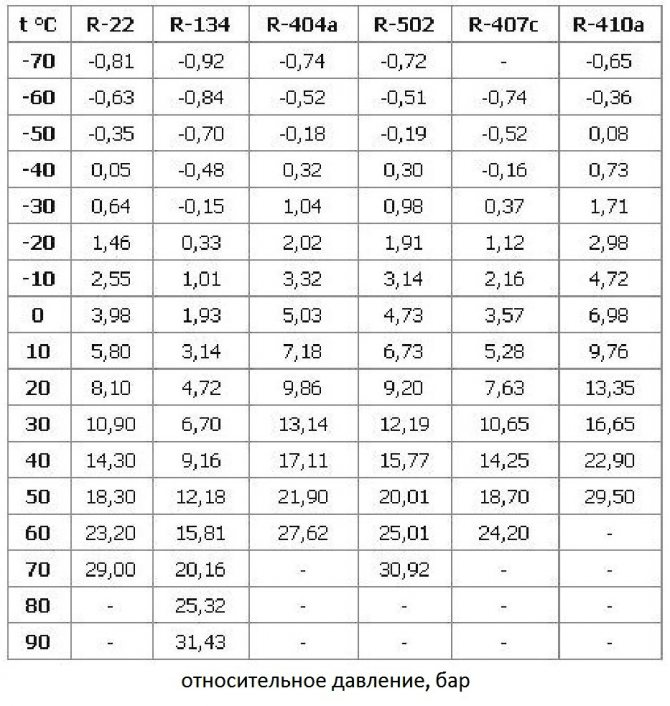
Dependence of the boiling point, condensation of freons on pressure, table
The dependence of the boiling point of freon is the same as its evaporation and condensation. In fact, the value shows at what temperature freon changes its state of aggregation.
In this publication, we have provided two tables for the most common freons: R12, R22, R23, R134a, R142b, R290, R404a, R406a, R407c, R409A, R410a, R502, R507, R600, R717. You can also download the general table of the boiling point of freons from this link.
Boiling point of freons R12, R22, R23, R134, R142b, R290, R404a, R406a
| t, ° C | R12 | R22 | R23 | R134 | R142b | R290 | R404a | R406a |
| 90 | 26.88 | — | — | 31.43 | 16.4 | 35.82 | — | — |
| 80 | 22.04 | — | — | 25.32 | 13.07 | 29.94 | — | 21.5 |
| 70 | 17.85 | 29 | — | 20.16 | 10.23 | 24.72 | — | 17.3 |
| 60 | 14.25 | 23.2 | — | 15.81 | 7.85 | 20.14 | 27.62 | 13.6 |
| 55 | 13.08 | 20.75 | — | 14 | 6.81 | 18.08 | 24.76 | 11.9 |
| 50 | 11.9 | 18.3 | — | 12.18 | 5.87 | 16.16 | 21.9 | 10.4 |
| 45 | 10.25 | 16.3 | — | 10.67 | 5.02 | 14.38 | 19.51 | 9.1 |
| 40 | 8.6 | 14.3 | — | 9.16 | 4.25 | 12.73 | 17.11 | 7.8 |
| 35 | 7.53 | 12.6 | — | 7.93 | 3.55 | 11.21 | 15.13 | 6.7 |
| 30 | 6.45 | 10.9 | — | 6.7 | 2.94 | 9.82 | 13.14 | 5.7 |
| 25 | 5.39 | 9.5 | 45.03 | 5.71 | 2.38 | 8.55 | 11.5 | 4.8 |
| 20 | 4.67 | 8.1 | 40.11 | 4.72 | 1.9 | 7.39 | 9.86 | 4 |
| 15 | 3.95 | 6.95 | 35.56 | 3.93 | 1.46 | 6.33 | 8.52 | 3.3 |
| 10 | 3.23 | 5.8 | 31.37 | 3.14 | 1.08 | 5.38 | 7.18 | 2.6 |
| 5 | 2.66 | 4.89 | 27.54 | 2.54 | 0.75 | 4.52 | 6.11 | 2.1 |
| 2.08 | 3.98 | 24 | 1.93 | 0.47 | 3.75 | 5.03 | 1.6 | |
| -5 | 1.64 | 3.27 | 20.85 | 1.47 | 0.22 | 3.06 | 4.18 | 1.1 |
| -10 | 1.19 | 2.55 | 17.96 | 1.01 | 2.45 | 3.32 | 0.8 | |
| -15 | 0.85 | 2.01 | 15.37 | 0.67 | — | 1.91 | 2.67 | 0.4 |
| -20 | 0.51 | 1.46 | 13.04 | 0.33 | — | 1.44 | 2.02 | 0.2 |
| -25 | 0.26 | 1.05 | 10.96 | -0.06 | — | 1.03 | 1.53 | -0.1 |
| -30 | 0.64 | 9.12 | -0.15 | — | 0.68 | 1.04 | -0.2 | |
| -35 | -0.18 | 0.25 | 7.51 | -0.32 | — | 0.37 | 0.68 | -0.4 |
| -40 | -0.36 | 0.05 | 6.09 | -0.48 | — | 0.12 | 0.32 | -0.62 |
| -45 | -0.49 | -0.2 | 4.86 | -0.59 | — | — | -0.11 | -0.66 |
| -50 | -0.61 | -0.35 | 3.8 | -0.7 | — | — | -0.18 | -0.8 |
| -55 | -0.69 | -0.49 | 2.89 | -0.77 | — | — | -0.35 | -0.83 |
| -60 | -0.77 | -0.63 | 2.12 | -0.84 | — | — | -0.52 | -0.9 |
| -65 | -0.83 | -0.74 | 1.48 | -0.88 | — | — | -0.63 | -0.94 |
| -70 | -0.88 | -0.81 | 0.94 | -0.92 | — | — | -0.74 | — |
Boiling point of freons R407c, R409A, R410a, R502, R507a, R600, R717
| t, ° C | R407c | R409A | R410a | R502 | R507a | R600 | R717 |
| 90 | — | 29.43 | — | — | — | — | 50.14 |
| 80 | — | 23.99 | — | — | — | — | 40.4 |
| 70 | — | 19.26 | — | 30.92 | — | 9.91 | 32.12 |
| 60 | 24.2 | 15.2 | — | 25.01 | 28.85 | 7.72 | 25.14 |
| 55 | 21.45 | 13.41 | — | 22.51 | 25.8 | 6.79 | 22.24 |
| 50 | 18.7 | 11.76 | 29.5 | 20.01 | 22.75 | 5.86 | 19.33 |
| 45 | 16.48 | 10.26 | 26.2 | 17.89 | 20.25 | 5.09 | 16.94 |
| 40 | 14.25 | 8.88 | 22.9 | 15.77 | 17.74 | 4.32 | 14.55 |
| 35 | 12.45 | 7.64 | 19.78 | 13.98 | 15.69 | 3.69 | 12.61 |
| 30 | 10.65 | 6.51 | 16.65 | 12.19 | 13.63 | 3.05 | 10.67 |
| 25 | 9.14 | 5.5 | 15 | 10.7 | 11.94 | 2.54 | 9.12 |
| 20 | 7.63 | 4.59 | 13.35 | 9.2 | 10.25 | 2.02 | 7.57 |
| 15 | 6.46 | 3.78 | 11.56 | 7.97 | 8.88 | 1.62 | 6.36 |
| 10 | 5.28 | 3.07 | 9.76 | 6.73 | 7.51 | 1.21 | 5.15 |
| 5 | 4.43 | 2.43 | 8.37 | 5.73 | 6.4 | 0.89 | 4.22 |
| 3.57 | 1.88 | 6.98 | 4.73 | 5.29 | 0.57 | 3.29 | |
| -5 | 2.87 | 1.4 | 5.85 | 3.94 | 4.42 | 0.33 | 2.6 |
| -10 | 2.16 | 0.98 | 4.72 | 3.14 | 3.54 | 0.09 | 1.91 |
| -15 | 1.64 | 0.62 | 3.85 | 2.53 | 2.86 | -0.18 | 1.41 |
| -20 | 1.12 | 0.32 | 2.98 | 1.91 | 2.18 | -0.27 | 0.9 |
| -25 | 0.75 | 0.06 | 2.35 | 1.45 | 1.67 | -0.38 | 0.55 |
| -30 | 0.37 | — | 1.71 | 0.98 | 1.15 | -0.53 | 0.19 |
| -35 | -0.06 | — | 1.22 | 0.64 | 0.77 | -0.62 | -0.24 |
| -40 | -0.16 | — | 0.73 | 0.3 | 0.39 | -0.71 | -0.28 |
| -45 | -0.34 | — | 0.25 | -0.14 | -0.02 | — | -0.44 |
| -50 | -0.52 | — | 0.08 | -0.19 | -0.14 | — | -0.59 |
| -55 | -0.63 | — | -0.22 | -0.35 | -0.32 | — | -0.69 |
| -60 | -0.74 | — | -0.36 | -0.51 | -0.5 | — | -0.78 |
| -65 | — | — | -0.51 | -0.62 | -0.61 | — | -0.84 |
| -70 | — | — | -0.65 | -0.72 | -0.72 | — | -0.89 |
Did you like the article? Share with friends:
vteple.xyz