What is a condensing gas boiler?
Gas condensing boilers are gaining more and more popularity in the market as they have proven to be very efficient devices. Condensing boilers have a fairly serious efficiency factor. It is almost 96%. While in conventional boilers, the efficiency hardly reaches 85%. Condensing boilers are very economical. These boilers are very popular in Europe, since the Europeans have a rather acute issue of fuel economy. Despite the slightly higher cost of a condensing boiler compared to a conventional boiler, condensing gas heating units pay off rather quickly. Boilers of this type are confidently looking into the future, because the principle of their operation is the most promising today.
Who should choose a condensing boiler for heating?
This device will be appreciated by owners who show concern for the environment and do not forget about the rational use of their own funds. Due to the processing of condensate, the boiler emits a minimum amount of harmful substances into the environment, therefore it is one of the most environmentally friendly heaters on the market by leading brands.
The rationality of devices is that they are able to more efficiently use energy from the combustion of fuel, such as gas or liquid fuel. A diesel or gas condensing boiler, which can be bought in a specialized service, collects some of the heat from the recycled gases and uses it to heat water from the return line of the heating system. Thus, the device requires less fuel to operate the burner and opens up resources for savings.
The history of the appearance of the condensing gas boiler
In the distant fifties, models of condensing-type boilers began to appear for the first time. These models were not perfect as they are today, and have undergone numerous changes during their evolution. Well, already in those distant years, boilers of this type showed quite serious indicators of fuel economy. This important factor is still the main one that makes air-conditioning boilers very attractive to buyers.
In those years, heat exchangers made of cast iron or steel were used, which made them short-lived. Under the influence of condensate, the boilers quickly failed due to severe corrosion. Only in the seventies did new materials and technologies replace cast iron from steel. Many boiler elements, including heat exchangers, began to be made of stainless steel. Such modernization significantly extended the service life of the condensing boiler. Many experts agree that boilers of this type in their modern form are reliable, very environmentally friendly, and very efficient heating devices in terms of efficiency. Experts also believe that air conditioning boilers have a very promising future. In the USSR, research was also carried out in this direction, but this technology did not receive any serious development.
High reliability of condensing boilers
In the previous section, the main requirements for heat exchangers for condensing boilers were briefly indicated. Here we will consider the main consequences of taking these requirements into account in the design of boilers.
Materials used for the heat exchanger
The chemical formula given above in the paragraph "condensing boilers operating principle" took into account only the main components of the combustion process.Now is the time to remember other components, primarily nitrogen in the air and sulfur compounds that are present in fuel. As a result of the participation of these elements in the combustion process, acids are formed on their basis - sulfuric, sulfurous, nitric and nitrogenous. Accordingly, these acids are contained in the condensate. Thus, the materials used for the manufacture of the condensing boiler heat exchanger must be resistant to acidic environments. The most common metals used are aluminum silicate alloys (silumin) and high quality stainless steels.

Silumin heat exchangers are made by casting with, possibly, subsequent milling. In the manufacture of stainless steel, pre-formed parts are welded. Due to the lower cost of the material as such and the cheaper production technology for ready-made molds for casting, silumin heat exchangers are usually somewhat cheaper, but they have significantly lower long-term resistance to acid condensate.
Heat exchangers made of suitable stainless steel are not chemically attacked by acids. As an additional consequence of the use of these materials, we get an increase in the overall reliability of the product, including in relation to the quality and type of heat carrier used.
Variable and critical modes of operation
Due to the fact that the heat exchangers of condensing boilers are initially designed based on a wide range of coolant temperatures (the lower temperature is not limited) and high values of temperature tensions in the heat exchanger firebox, at the output we get equipment that is resistant to abrupt changes in operating modes and outputs of various parameters (temperatures , coolant flow rates, pressure) beyond the permissible limits. Undoubtedly, the safety components of the equipment, electronic and mechanical, without fail provide for control over these parameters, but the design of the boilers provides an additional guarantee of the durability of the installation.
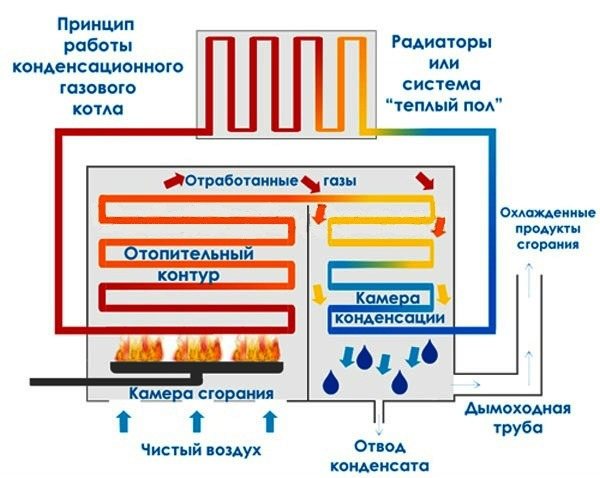
Condensing boiler working principle

Condensing boiler working principle
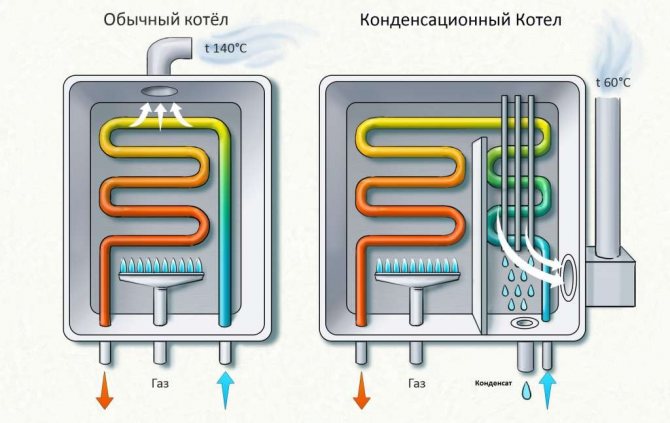
The principle by which many heating boilers work is very simple. It includes only one action - fuel combustion. As you know, when fuel is burned, a certain amount of thermal energy is released. With the help of a heat exchanger, heat energy is transferred to the coolant, and then, with the help of circulation, it enters the heating system. Circulation can be carried out both forcibly and by gravity. The vast majority of modern boilers use forced circulation of the coolant.
In a conventional boiler, a certain amount of heat energy goes out through the chimney. This heat can be removed and reused. Simply, a conventional boiler partially heats the atmosphere with water vapor, which is formed when the gas is burned. The most important feature is hidden here. According to the principle of their work, condensing gas boilers are able to store and direct again into the heating system that steam energy, which in an ordinary boiler simply goes into the chimney. The whole trick of a condensing-type boiler lies in its heat exchanger.
The condensing boiler is focused on absorbing the energy that is released when steam condenses. The same heat energy is absorbed by the water that comes in the return line, and which pre-cools the steam to the dew point temperature, thus releasing thermal energy. This heat energy must be returned to the heating system, thereby increasing the efficiency of the condensing boiler.
Currently, all heat exchangers for condensing boilers are made of anti-corrosion materials. These include silumin or stainless steel. A special container is provided for collecting condensate in condensing boilers.Excess condensate is discharged into the sewerage system.
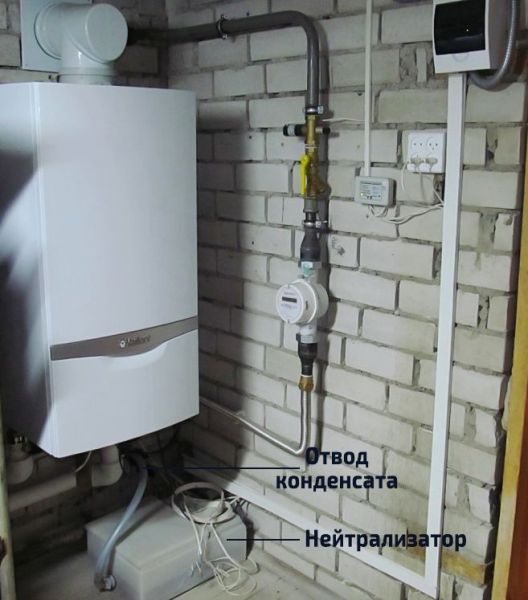
Condensate is considered to be a rather corrosive liquid. Therefore, in some countries, condensate must be neutralized before being discharged down the drain. There are neutralizers for this procedure. A neutralizer is a kind of container that is filled with special granules. These granules can contain magnesium or calcium.
Gas condensing boiler
The high efficiency of the condensing gas heat generator is ensured by the presence of an additional heat exchanger in its design. The first heat exchange unit, standard for all heating boilers, transfers the energy of the combusted fuel to the heat carrier. And the second adds to this also the heat from the exhaust gas recovery.
Condensing boilers operate on "blue fuel":
- main (gas mixture with a predominance of methane);
- gasholder or balloon (mixture of propane with butane with a predominance of either the first or second component).
Any gas option can be used. The main thing is that the burner is designed to work with one or another type of fuel.

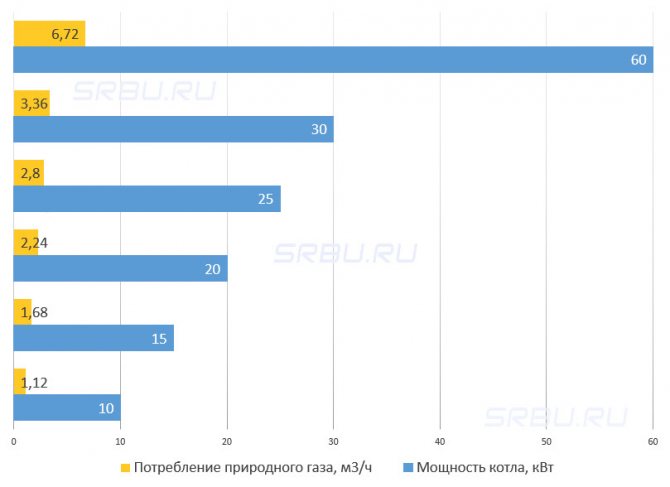
Condensing gas boilers are more expensive than conventional convection models, but they outperform them in terms of fuel costs by reducing gas consumption by 20-30%
The condensing heat generator shows the best efficiency when burning methane. The propane-butane mixture is slightly inferior here. Moreover, the greater the proportion of propane, the better.
In this respect, the “winter” gas for the gasholder gives a slightly higher efficiency at the outlet than the “summer” one, since the propane component is higher in the first case.
Unlike a condensing gas boiler in a convection boiler, part of the thermal energy goes into the chimney together with the combustion products. Therefore, for classical designs, the efficiency is in the region of 90%. You can raise it higher, but technically too difficult.
This is not economically justified. But in condensates, the heat obtained from gas combustion is used more rationally and fully, since the heat released during the processing of steam is accumulated and transferred to the heating system. In this way, the coolant is additionally heated, which makes it possible to reduce fuel consumption per 1 kW of heat received.
Device and principle of operation
By design, a condensing boiler is in many ways similar to a convection analogue with a closed combustion chamber. Only inside it is supplemented with a secondary heat exchanger and a recuperation unit.

The main features of the condensing heat generator device are the presence of a second heat exchanger and a closed combustion chamber with a fan
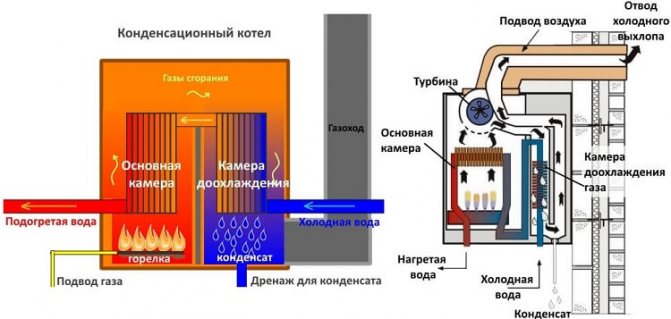
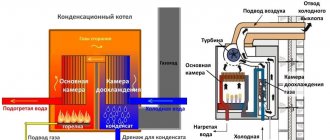
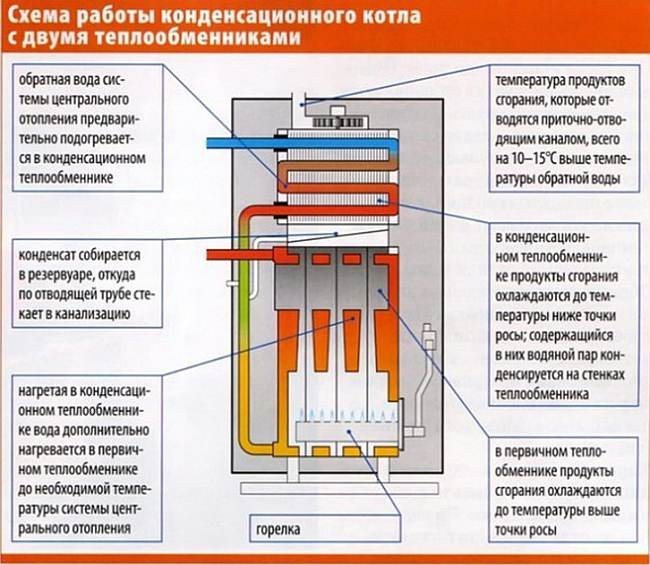
The gas condensing boiler consists of:
- closed combustion chambers with modulating burner;
- primary heat exchanger No. 1;
- exhaust gas cooling chambers up to + 56-57 0С (dew point);
- secondary condensing heat exchanger # 2;
- chimney;
- air supply fan;
- condensate tank and drainage system.
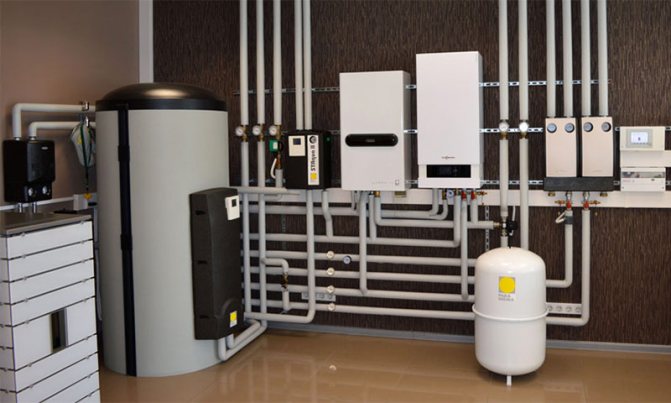
The equipment in question is almost always equipped with a built-in circulation pump for the coolant. The usual version with a natural flow of water through the heating pipes is of little use here. If there is no pump in the kit, then it will definitely need to be provided when preparing a boiler piping project.

Additional percentages of efficiency for a condensing boiler are formed as a result of heating the return line by cooling the exhaust gases in the chimney
Condensing boilers on sale are single-circuit and double-circuit, as well as in floor and wall versions. In this they do not differ from classical convection models.
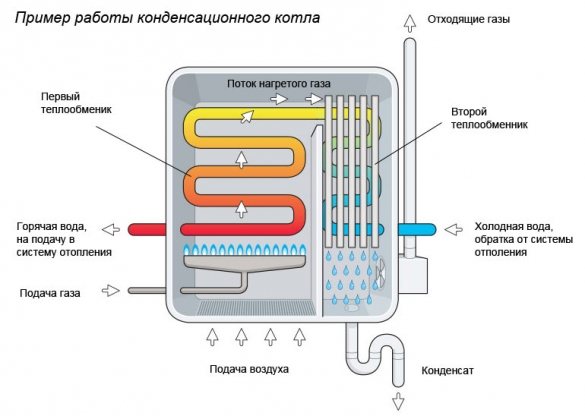
The principle of operation of a condensing gas boiler is as follows:
- The heated water receives the main heat in heat exchanger No. 1 from gas combustion.
- Then the coolant passes through the heating circuit, cools down and enters the secondary heat exchange unit.
- As a result of condensation of combustion products in heat exchanger No. 2, the cooled water is heated by recovered heat (saving up to 30% of fuel) and goes back to No. 1 in a new circulation cycle.
In order to accurately control the flue gas temperature, condensing boilers are always equipped with a modulating burner with an output of 20 to 100% and an air supply fan.
Nuances of operation: condensate and chimney
In a convection boiler, the combustion products of natural gas CO2, nitrogen oxides and steam are cooled only to 140–160 ° C. If you cool them below, then the draft in the chimney will drop, aggressive condensate will begin to form and the burner will go out.
All classic gas heat generators [/ anchor] strive to avoid such a development of the situation in order to maximize the safety of work, as well as extend the service life of their equipment.
In a condensing boiler, the temperature of the gases in the chimney fluctuates around 40 ° C. On the one hand, this reduces the requirements for heat resistance of the chimney material, but on the other hand, it imposes restrictions on its choice in terms of resistance to acids.

Exhaust gases from a gas boiler during cooling form an aggressive, highly acidic condensate that easily corrodes even steel
Heat exchangers in condensing heat generators are made from:
- stainless steel;
- silumin (aluminum with silicon).
Both of these materials have enhanced acid resistance properties. Cast iron and common steel are completely unsuitable for condensers.
The chimney for a condensing boiler may only be installed from stainless steel or acid-resistant plastic. Brick, iron and other chimneys are not suitable for such equipment.


During recuperation, condensate forms in the secondary heat exchanger, which is a weak acidic solution and must be removed from the water heater
When operating a condensing boiler with a capacity of 35–40 kW, about 4–6 liters of condensate are formed. Simplified, it comes out about 0.14-0.15 liters per 1 kW of thermal energy.
In fact, this is a weak acid, which is forbidden to be discharged into an autonomous sewage system, since it will destroy the bacteria involved in waste processing. Yes, and before dumping into a centralized system, it is recommended to first dilute with water in a ratio of up to 25: 1. And then you can already remove it without fear of destroying the pipe.
If the boiler is installed in a cottage with a septic tank or VOC, then the condensate must first be neutralized. Otherwise, it will kill all microflora in an autonomous purification system.
"Neutralizer" is made in the form of a container with marble chips with a total weight of 20-40 kg. As it passes through the marble, the condensate from the boiler increases the pH. The liquid becomes neutral or low alkaline, no longer dangerous for bacteria in the septic tank and for the material of the sump itself. It is required to change the filler in such a neutralizer every 4–6 months.
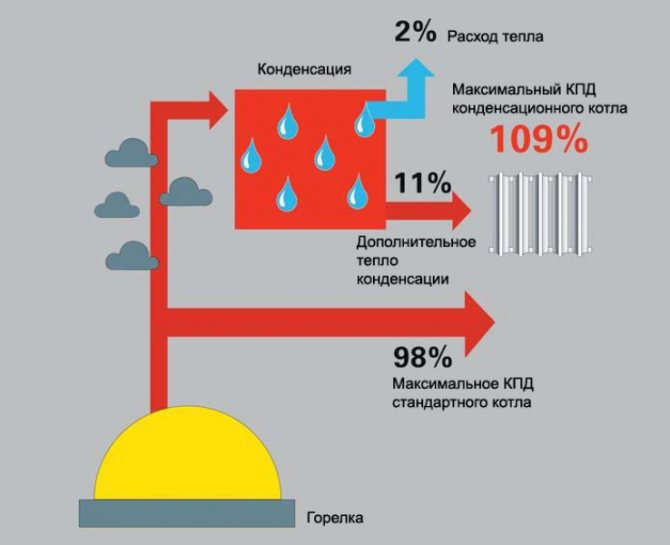
Where does the efficiency come from above 100%?
When indicating the efficiency of a gas boiler, manufacturers take as a basis the indicator of the lowest calorific value of gas without taking into account the heat generated during condensation of water vapor. In a convection heat generator, the latter, together with approximately 10% of the heat energy, completely goes into the chimney, therefore, it is not taken into account.
However, if you add the condensation secondary heat and the main one from the burnt natural gas, then more than 100% efficiency will come out. No scams, just a little trick in the numbers.


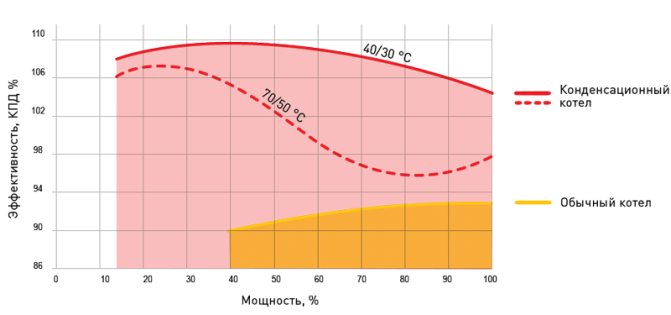
When calculating the efficiency for the highest heat of combustion for a convection boiler, it will be in the region of 83-85%, and for a condensing boiler - about 95-97%
In fact, the "wrong" efficiency above 100% arises from the desire of heat generating equipment manufacturers to compare the compared indicators.
It's just that in a convection device "water vapor" is not considered at all, but in a condensation device it must be taken into account. Hence, there are small discrepancies with the logic of basic physics, which is taught at school.
How to determine the efficiency of a condensing boiler
Today there are low temperature and traditional heating systems. Low-temperature systems include, say, underfloor heating. Condensing devices integrate very well into these heating systems and show high efficiency results in such systems. This is because these heating systems provide very good conditions for the best condensation. If you correctly mount a tandem from a condensing boiler plus a warm floor, then in this case you can not use radiators at all. "Warm floor" will perfectly cope with the task of heating a room, no worse than a system that uses radiators. All this thanks to the high efficiency of the condensing boiler.
It is often believed that condensing gas boilers have incredible efficiency, which even goes beyond 100%. Of course it is not. The well-known laws of physics work everywhere and no one has canceled them yet. Therefore, such statements from manufacturers are nothing more than marketing.
If, however, to approach the issue of evaluating the efficiency with all objectivity condensing gas boiler, then we get somewhere around 95% efficiency. This indicator largely depends on the conditions of use of this equipment. Also, efficiency can be increased by using "weather-dependent" automation. With this equipment, it is possible to achieve differentiated boiler control based on the average daily temperature.

Arrangement of the main units of the condensing boiler
From a structural point of view, a condensing boiler is not very much, but still differs from a conventional gas boiler. Its main elements are:
- a combustion chamber equipped with a burner, a fuel supply system and an air blower;
- heat exchanger No. 1 (primary heat exchanger);
- aftercooling chamber of the steam-gas mixture to a temperature as close as possible to 56-57 ° C;
- heat exchanger No. 2 (condensing heat exchanger);
- condensate collection tank;
- chimney for removing cold flue gases;
- pump that circulates water in the system.
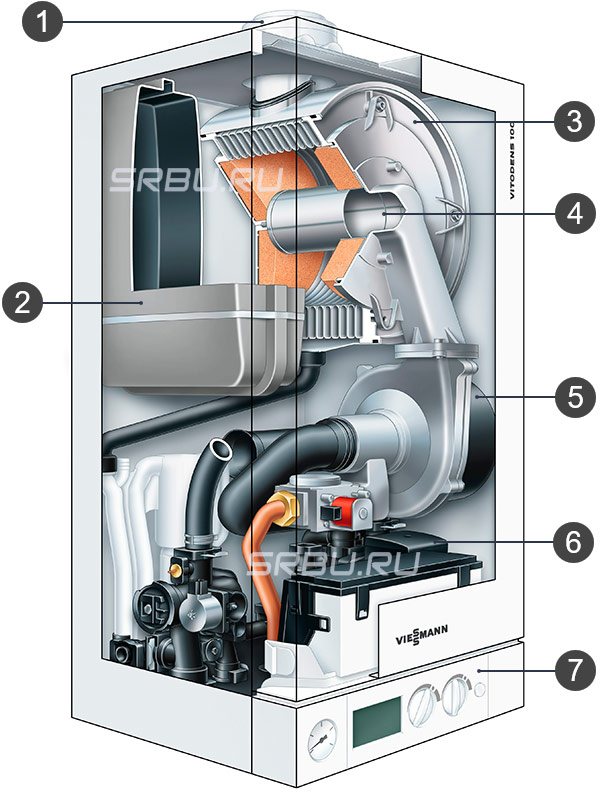

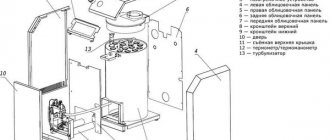
1. Chimney. 2. Expansion tank.
3. Heat transfer surfaces. 4. Modulating burner.
5. Burner fan. 6. Pump. 7. Control Panel.
In the primary heat exchanger, coupled with the combustion chamber, the evolved gases are cooled to a temperature significantly higher than the dew point (in fact, this is how conventional convection gas boilers look like). Then the flue mixture is forcibly directed to the condensing heat exchanger, where it is further cooled to a temperature below the dew point, i.e. below 56 ° C. In this case, water vapor condenses on the walls of the heat exchanger, "giving up the latter." The condensate is collected in a special tank, from where it flows down the drain pipe into the sewer.
Water acting as a heat carrier moves in the direction opposite to the movement of the vapor-gas mixture. The cold water (return water from the heating system) is pre-heated in the condensing heat exchanger. It then enters the primary heat exchanger where it is heated to a higher user-specified temperature.
Condensate - alas, not pure water, as many believe, but a mixture of dilute inorganic acids. The concentration of acids in the condensate is low, but taking into account the fact that the temperature in the system is always high, it can be considered an aggressive liquid.That is why, in the production of such boilers (and primarily condensing heat exchangers), acid-resistant materials are used - stainless steel or silumin (aluminum-silicon alloy). The heat exchanger, as a rule, is made cast, since the welded seams are a vulnerable spot - it is there that the process of corrosion destruction of the material first begins.
The steam must be condensed on the condensing heat exchanger. Everything that passed further into the chimney, on the one hand, is lost for heating, on the other hand, it has a destructive effect on the material of the chimney. It is for the latter reason that the chimney is made of acid-resistant stainless steel or plastic, and its horizontal sections are given a slight slope so that the water formed during the condensation of small amounts of steam, which nevertheless got into the chimney, is drained back into the boiler. It should be borne in mind that the flue gases leaving the condenser are very cooled, and everything that has not condensed in the boiler will certainly condense in the chimney.
At different times of the day, a different amount of heat is required from a heating boiler, which can be regulated using a burner. The burner for a condensing boiler can be either modulating, i.e. with the ability to smoothly change the power during operation, or non-simulated - with a fixed power. In the latter case, the boiler adapts to the owner's requirements by changing the frequency of the burner switching on. Most modern boilers designed for heating private houses are equipped with simulated burners.
So, we hope you got a general idea of what a condensing boiler is, how it works and how it works. However, most likely, this information will not be enough to understand whether it is worthwhile for you to personally purchase such equipment. To help you make this or that decision, we will tell you about all the advantages and disadvantages, pros and cons of a condensing boiler, comparing it with a traditional convection boiler.
Chimney
The removal of exhaust gases and the supply of air to the combustion chamber in a condensing boiler is carried out forcibly, since boilers of this type have a closed combustion chamber. Condensers are quite safe because they don't need a traditional chimney to use them. Boilers of this type use a coaxial or two-pipe flue system. These systems are made of plastic, as the condensation tank has a negligible flue gas temperature. The use of cheap materials in the manufacture of smoke removal systems can significantly reduce the cost of the boiler.
Principle of operation
This unit is designed on the basis of a conventional (convection) heat generator. The energy carrier for both types of boilers is natural or liquefied gas.
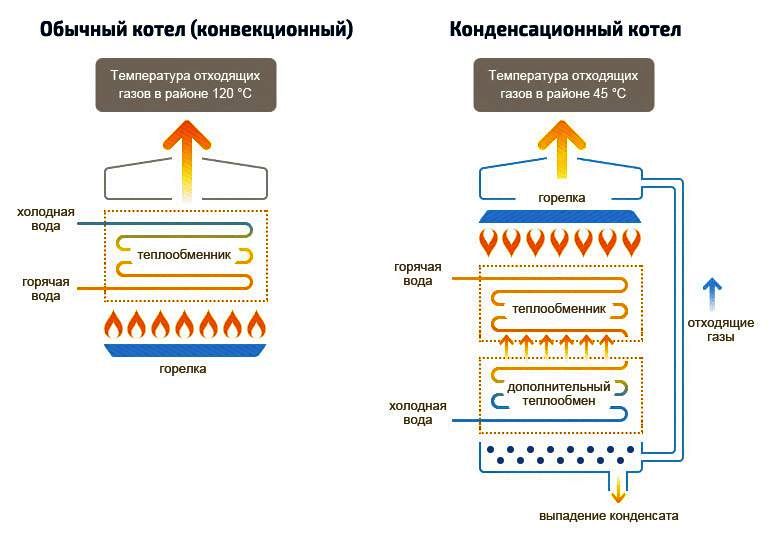
The principle of operation of a convection boiler is extremely simple. Fuel, burning, through a heat exchanger transfers energy to the coolant (most often ordinary water). The heated water circulates through the heating system, heating the home.
Combustion products with a temperature of 140–150 ° C, consisting of carbon dioxide and water vapor, are removed through the chimney. As a result, the efficiency of this heat generator ranges from 90 to 93%, the remaining 7-10% of the unused energy escapes into the atmosphere.
It is important! At a flue gas temperature below 140 ° C, condensation forms on the walls of the chimney, which, when it enters the boiler, negatively affects the metal components, reducing the durability of the unit itself.
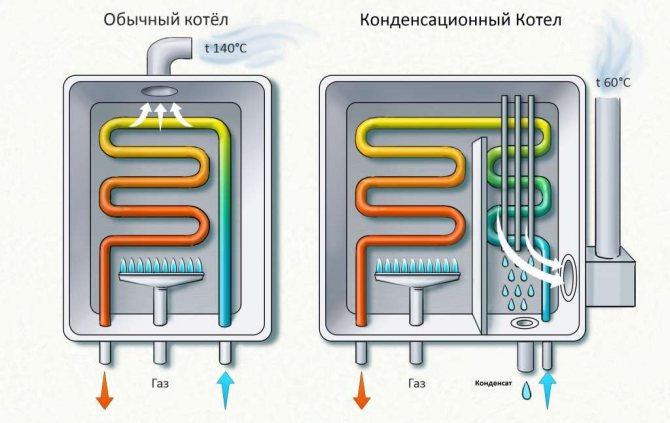

Differences in the operation of conventional and condensing boilers
In a condensing boiler, combustion products, passing through the main heat exchanger, enter the aftercooling chamber with a secondary (condensation) heat exchanger, through which cooled water flows (return flow). Passing through this heat exchanger, the gases cool down.At temperatures below 56 ° C (dew point - vapor condensation temperature), water vapor is converted to condensation. The heat energy released in this case is used for preheating the "return". The temperature of gases entering the atmosphere through the chimney is reduced to 40–60 ° C.
Thus, slightly warmed water enters the main heat exchanger. As a result, the boiler needs to consume less fuel to heat the coolant to the required value.
Manufacturers claim that the efficiency of these units reaches 104-108%. From the point of view of physics, this is impossible. This meaning is arbitrary and is a marketing gimmick. In this case, the energy released during fuel combustion is taken as 100% efficiency.
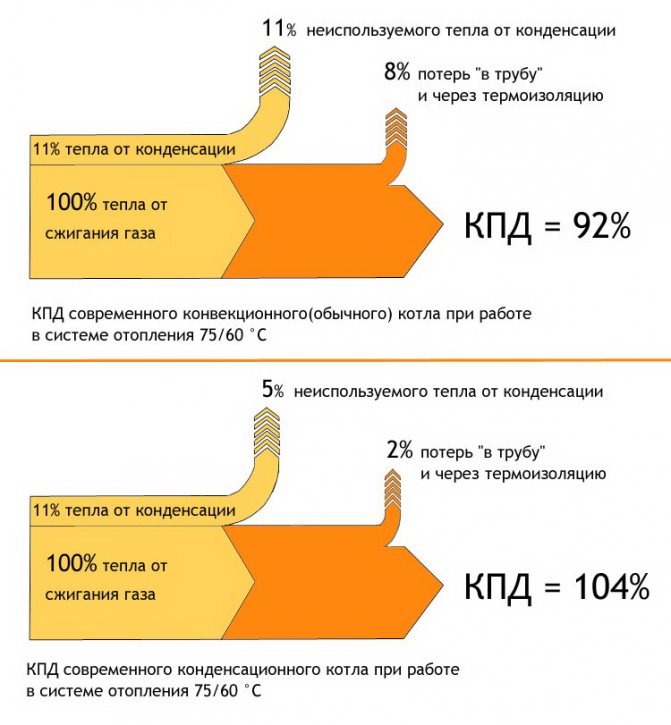

Efficiency formation scheme in gas boilers.
Unused energy is taken away from a convection (conventional) boiler in the form of hot flue gases escaping through the chimney (6–8%) and losses of heat radiation (1–2%). The result is an efficiency of 90–94%.
When calculating the efficiency of condensing boilers, 11% of the heat released during condensation of water is added to 100%. Heat loss is 1–5% of unused heat during condensation and 1–2% through thermal insulation. Hence the efficiency of more than 100%, advertised by the manufacturer, appears.
It is important! With objective calculations, the efficiency of convection boilers is 83–87%, condensing (under ideal operating conditions) - 95–97%.
The maximum efficiency of a convection boiler is achieved when operating in a high-temperature mode 80–75 / 60, where the first digit is the temperature of the coolant leaving the unit, the second is that entering it (return flow). With a decrease in the second parameter, condensate forms in the boiler, which negatively affects the functioning and durability of the apparatus.
For condensing boilers, the most suitable low temperature setting is 50/30.
The ideal conditions for the use of condensing boilers is a return temperature not exceeding 35 ° C. Exactly then:
- The largest amount of condensate is formed;
- The maximum primary heating of the coolant occurs;
- Fuel economy reaches 30–35%.
This is possible when installing a heating system with "warm floors".
When using radiators in the heating system in severe frosts, the temperature of the coolant must be increased. If the boiler receives a "return" above 60 ° C, condensate will not be produced. In this case, the unit operates in the mode of a conventional convection boiler with an efficiency not higher than 90%. Fuel savings are reduced by up to 5%.
Video: how a condensing boiler works
Comparative table of different types of boilers
| Boiler type / Parameter | Condensing gas | Convection gas | Liquid fuel | Solid fuel | Electric |
| Unit cost | The tallest | High | High | Low | Average |
| Operating costs | Lowest | Low | High | Low | The highest |
| Ease of use | High | High | Average, complexity of operation | Low, requires constant monitoring | The highest |
| Reliability | High | High | High | High | High |
| The amount of emissions into the environment | Very low | Low | The highest | Average | Absent |
Do I need to buy a condensing boiler?
Like traditional gas boilers, there are several types of condensers:
- The first type is floor-standing boilers. "Napolniki" have a higher power, which sometimes reaches 320 kW and more.
- The second type is wall-mounted boilers, the power of which is up to 120 kW.
If it becomes necessary to increase the capacity, then several heating boilers can be combined into a single heating cluster. Condensing gas units have different purposes, and therefore they are double-circuit or single-circuit. In addition to heating, double-circuit condensing boilers are also engaged in the preparation of hot water, while single-circuit condensing boilers are engaged only in heating the premises.
Boilers of this type have very high performance, which fully comply with all the most serious requirements imposed by the relevant authorities on heating boilers. Condensing boilers are very popular in resort areas, holiday homes and other tourist destinations. It's all about efficiency and sustainability.
A condensing gas boiler has much less harmful emissions, almost 10 times less than a conventional gas boiler.
Advantages of condensing boilers
- Very compact;
- They are lightweight;
- Boilers of this type are highly efficient;
- Capacitors have a fairly deep modulation;
- Equipped with an inexpensive smoke exhaust system;
- Boilers of this type have very good environmental performance and do not pollute the environment;
- These boilers have practically no vibration;
- Low noise, and this property makes them very comfortable to use;
- Condensing boilers are very economical. Fuel economy is sometimes up to 40%, which will greatly delight potential buyers.