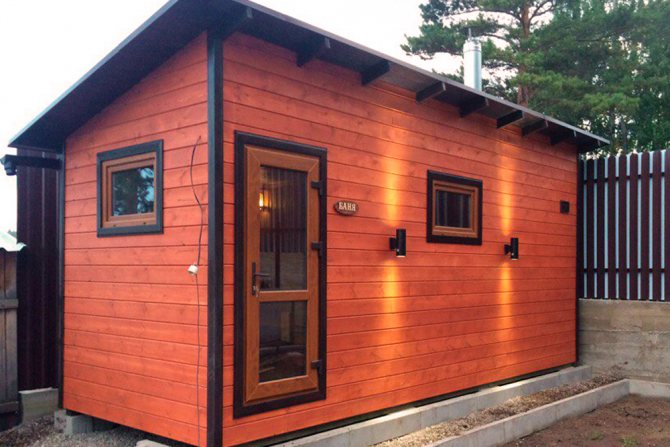
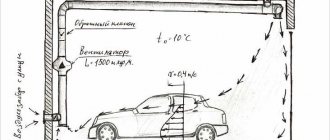
The Russian bath is characterized by the saturation of the air with water vapor, the temperature of which is 40–45 ° C. A summer frame bath made of 55 cm thick boards will keep the bath temperature inside when it is warm outside. If the bath is used only during summer vacations, it is possible not to reduce its useful volume by increasing the thickness of the walls and ceilings.
The energy efficiency of a frame bath for winter use is related to the properties of the heat-insulating elements. The supporting structures of walls, ceilings and roofs - frames made of wooden beams - themselves have a rather low thermal conductivity. But the total area of the frame is small in relation to the entire area of the enclosing structures.
The frame rods (vertical, horizontal and inclined, longitudinal and transverse) only frame the insulation elements, the main heat-insulating load rests on its shoulders. Of course, the work of the insulating layer is impossible by itself:
- without rigid and sealed frame sheathing;
- in the absence of finishing cladding and internal wall cladding;
- high-quality floor and ceiling;
- reliable roof -
insulation is effective when it is dry, clean and retains its original geometric shape.
Construction on a finished foundation
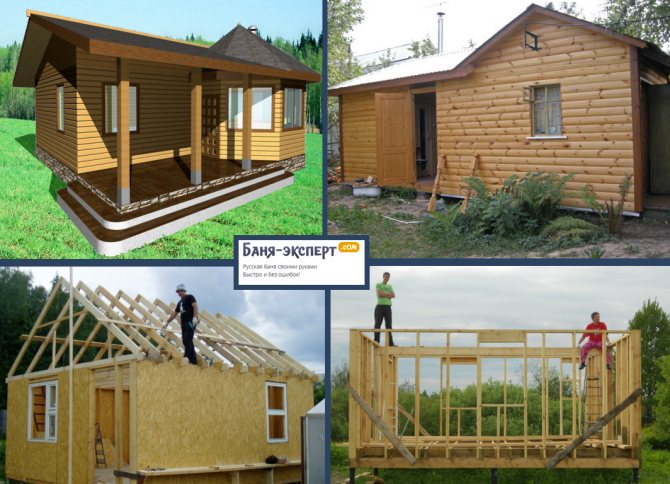
The choice of insulation is possible during the construction of a bath using classical frame technology: a frame-panel bath is created from multilayer panels that are already thermally insulated. They begin to insulate the frame bath when the structure of the structure is assembled on the finished strip foundation, reinforced concrete slab or grillage:
- along the perimeter of the bearing walls, a strapping of wooden beams or spliced boards is laid (along the sheet waterproofing in 2-3 layers);
- on a flat area, the frames of the walls are assembled, stopped for strapping and connected;
- the upper harness is mounted along the perimeter of the power frame;

- horizontal beams are laid on the foundation (the width of the grillage or reinforced concrete contour is calculated on them in advance);
- a frame of floor logs and lathing was mounted;
- the attic floor beams were laid, the rafter system was assembled, the rough attic floor was lined and covered with a vapor barrier;
- all wooden structures are treated with antiseptic and fire retardant.
The further development of events depends on the thickness of the walls of the frame bath, the selected heat-insulating material and the method of its laying.
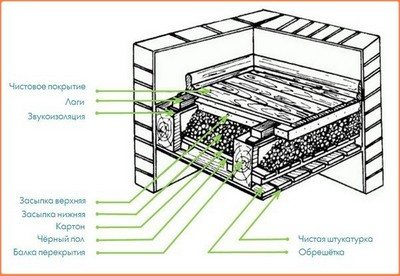
Floor and ceiling insulation
Heat loss in a frame bath can occur not only through the walls, but also through the ceiling and floor. Accordingly, insulation will be required here as well.
Thermal insulation of the floor is carried out at the stage of its arrangement. The sequence of actions here will be as follows:
- a concrete base-screed is poured onto the prepared and carefully compacted soil;
- waterproofing from roofing material or dense polyethylene is laid;
- insulating material is laid;
- a layer of upper waterproofing is lined;
- another layer of concrete screed is poured.
To increase the service life of the rough concrete floor, it is recommended to additionally process it after hardening with some kind of waterproofing solution. This will not allow moisture to penetrate into microcracks in concrete and destroy not only the floor material itself, but also the thermal insulation.
Ceilings are insulated in a way, similar to laying the heat-insulating material in the walls of the frame bath:
- a vapor barrier is fixed on the ceiling;
- insulation is laid;
- another layer of vapor barrier is attached;
- decorative sheathing is stuffed.
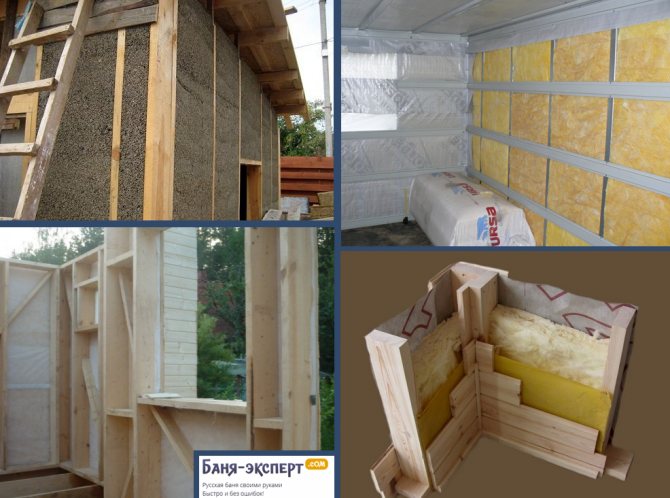
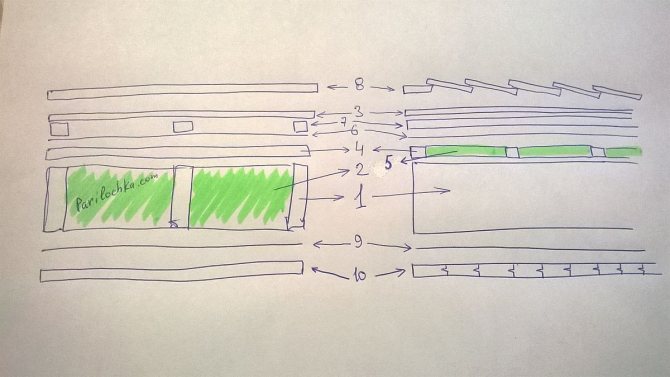
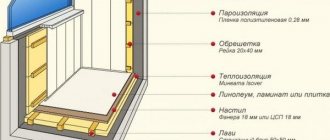
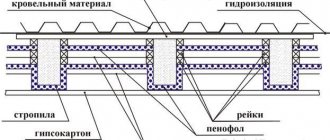
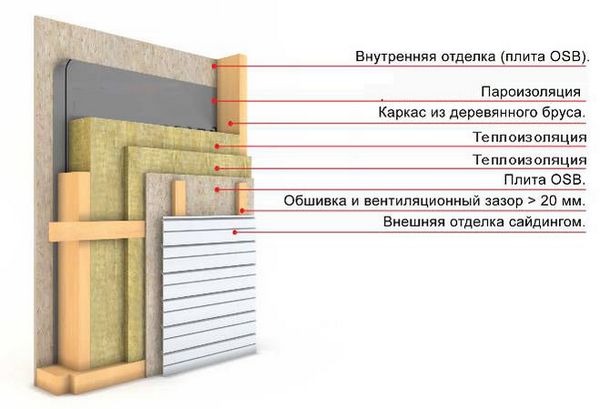
Typical cake of walls, ceilings and roofs
The insulation and the frame for effective and long-term operation require two conditions:
- protection from internal space - in the form of a vapor barrier;
- communication with outside air - through the gap to the wind barrier.
The insulation in the cells of the frame, laid along the floor logs, is covered with a vapor barrier material from above, the power frame - from the side of the frame bath premises, the attic floor frame - from below, the roof insulation - from the attic side.
The next layer behind the vapor barrier (looking outside - inside) is a continuous covering (sub-floor, inner wall cladding, roofs, false ceiling). On the walls and roof slopes, sheathing with profile lumber can also become a finishing interior decoration.
The rough floor is closed with a clean one, the same is done with the attic floor, if it is destined to become an attic floor. In a concrete floor, insulation becomes a layer between two screeds.
On a note. The walls of the bath, which remains closed for a long time in summer and is rarely heated, need to be isolated from steam from the outside as well. The outer vapor barrier membrane stands in the way of air flows from the outside, through the wall - to the inside. This air movement is inevitable if it is warmer outside the building than inside.
Ceiling vapor barrier in residential buildings may be superfluous (if the attic is heated, and small particles do not leave the thickness of the insulation). The attic overlap of the bathhouse needs an obstacle on the way of steam.
Wind protection is needed for the insulation of the outer walls. It is better to place it at some distance from the insulation - after sheathing in front of the cladding. This will help moisture trapped in the porous material to leave it without hindrance.
How to insulate
On horizontal surfaces in a frame bath, roll insulation is laid, in bulk, in the form of a plastic mixture (filler, binder and grout). It is convenient to insulate the roof slopes with roll material.
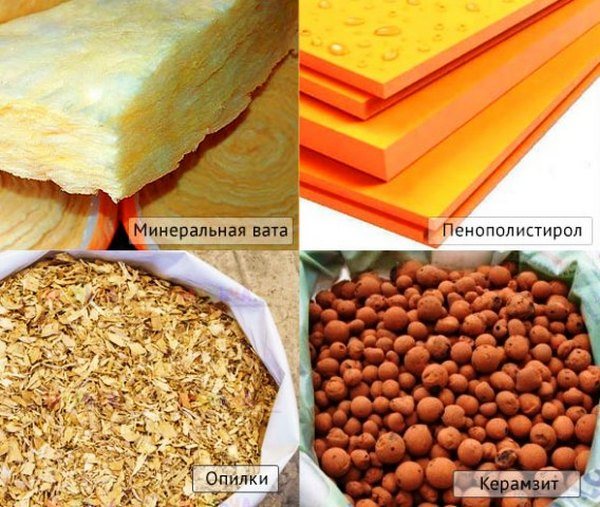


Any porous material can become a heater for a frame bath, as long as it is not flammable, not poisonous and does not create a favorable environment for mold. Everything else is a matter of taste.
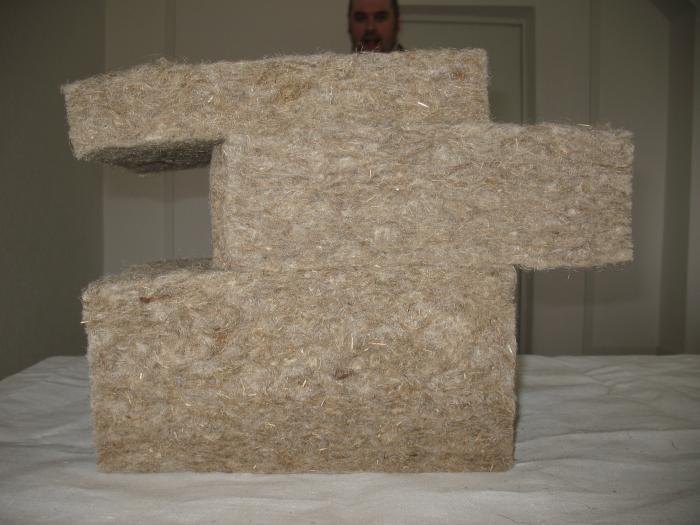
Thermal insulation of a frame bath with mineral wool
In the cells of the frame (walls, floors, roofs), mineral wool is present in the form of slabs:
- compact, ~ 0.6 * 1.2 m - for walls (it is difficult for a flexible flat material of long length to maintain verticality);
- 2 times more wide and 4–8 m long - for floors and roofs (packaged in rolls).
The main share of the volume of mineral wool is air, surrounded by solid thin fibers of inorganic nature. The common thickness of products made of fibrous material is 5, 10, 15, less often 20 cm (suitable for frame beams of appropriate thickness).
An additional element of slab insulation is possible - a covering made of dense thin sheet material. Bonding mineral wool to foil is one of the ways to stiffen a product made of loose material, to reduce the shedding of fiber debris, and to protect it from high temperatures.
Information. The presence of additional materials in the product, including foil, transfers the mineral wool to another flammability group: from “NG” (non-flammable) to “G1” (slightly flammable). The limiting temperature of the product's application drops - to the value of this parameter for the additional material.
The reflective properties of the foil impede the transfer of heat by radiation, but inside the wall - under the cladding - this property is useless. The insulation will almost stop breathing under a thin metal sheet ("almost" - only because not the entire wall will be covered with foil).
Even if a material is glued to the slab to isolate it from steam - it does not allow the smallest particles of water to pass through, but breathes - it is not enough for the vapor barrier of the frame bath structures.
As part of the frame wall, the heat-insulating plates are laid with an intermittent (across the width of the beams) layer, its factory coating will not become a full-fledged vapor barrier - over the entire area of the wall. Therefore, it makes sense to buy mineral wool separately, vapor barrier - separately.


Disadvantages of mineral wool. In order for the mass of fibers to retain a given shape, be suitable for transportation, installation, it is supplemented with a binder:
- bitumen;
- synthetic resins;
- starch.
All additives are flammable. Bitumen is a carcinogen, synthetic resins contain formaldehyde, phenol, which cause serious diseases.
The proportion of the binder in the finished product is small - from 2.5 to 10%.
But if the manufacturer violated the manufacturing technology, used low-quality raw materials, then the sanitary and hygienic safety of the mineral wool slab will be below the permissible level.
(Yes, and norms can undergo changes on any day, following new scientific discoveries).
In any case, it makes sense to be interested in the chemical composition of additives to mineral insulation. There are less hazardous resins available and can be used by the manufacturer.
Information. The shelf life of products made of mineral wool is limited, so the manufacturer puts on the packaging, in addition to other information about the product, the date of its manufacture. Remove the mineral wool boards from the waterproof bag immediately before installation.
Advantages of mineral wool:
- light weight;
- low thermal conductivity;
- not susceptibility to rotting (unless organic dust accumulates in the body of the insulation - due to leaks in the casing);
- durability (half a century);
- vapor permeability (there are no closed pores in cotton wool).
Mineral wool is divided into 3 groups, depending on the nature of the raw materials from which its fibers are made: stone wool, slag, glass.
Stone wool. The source of raw materials for stone wool is basalt volcanic rocks (its second name is basalt). Among the species of this group, basalt wool with a super-thin fiber - BSFF stands out.
STBF boards are free of binders - the fibers "hold" to each other due to their shape. Such a heater is not able to work without a frame, but it is environmentally friendly, withstands the highest temperatures, and has the lowest thermal conductivity.
The properties of other types of stone wool differ, mainly depending on the thickness of the fibers. But any basalt insulation is distinguished by high porosity, fire safety, suitability for residential premises.


Slag wool is not suitable for bath insulation.
Residential buildings are not insulated with metallurgical slag material.
Slag fibers are hygroscopic, do not tolerate strong heat, contain carcinogens (in a safe amount, if the manufacturer is conscientious).
For a frame bath, slag insulation is contraindicated: in the presence of moisture, slag, due to its acidity, will destroy metal corners, nails, staples and other fasteners.
Glass wool Glass batch fibers are long, dense and chemically inert. Among the strengths of glass wool is lack of heat resistance (the fiber melts), but it is good at soundproofing.
Fiberglass insulation is slightly heavier than stone, and manipulations with its mounting elements are especially demanding on personal protective equipment.
The heroes of the following video share the idea of how to make protective clothing in a few minutes:
Organic insulation
Ecowool - fibers made of cellulose, antiseptic and fire retardant. Manufacturers use various protective additives, among them there are more persistent and safe ones, there are short-lived and odorous ones. The main disadvantage of ecowool as a heater is a decrease in volume during operation. Heat-shielding properties also disappear with the volume. The shrinkage of the insulation in the wall frames of the frame bath is fraught with voids.
Ecowool fibers are hygroscopic, this also affects thermal conductivity. Ecowool is chosen because of its environmental friendliness, lack of sharpness, good sound insulation.
Raw sawdust mixture is a good insulation, healthy, inexpensive. Unlike cotton wool, sawdust is heat-intensive - a heated bath will not cool down longer, but it warms up with high fuel consumption. Humidity is contraindicated for sawdust. Flaws in isolation from water and steam will cause rotting.
The fire safety of sawdust is reduced by an enveloping cement, lime mixture, clay, but this is only a reduction in the risk of fire. Laying a mixture of sawdust and binder, or finished cement-sawdust blocks, is more troublesome than installing mineral wool or foam slabs. As part of the structure of a frame bath, organic thermal insulation is rarely chosen.
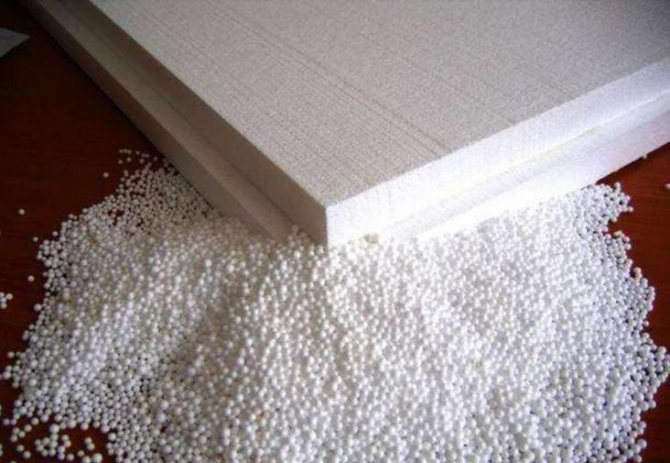
Thermal insulation foam
Polyfoam does not allow steam or air to pass through. The bath from it will be stuffy, and the fire hazard of the foamed polymers is of little concern to anyone.
The savings on the vapor barrier are offset by the cost of the seal between the insulating foam blocks and the frame. Polyfoam does not grow moldy, does not crumble, it is very lightweight, it is simply mounted. But very few risk using it as part of the walls of a wooden building, especially a frame bath.


Backfill insulation: vermiculite, expanded clay
Horizontal structures are especially often insulated with bulk material.
Vermiculite is not toxic, but during extraction it can be contaminated with a dangerous carcinogen - asbestos.
Expanded clay is fireproof, does not emit harmful substances, as insulation is light and heat-absorbing.
It will take longer to warm up a bath with expanded clay inside the walls than with a fibrous insulation, but the room will also cool down more slowly.
Since closed pores prevail in expanded clay, its moisture absorption is negligible. But wet expanded clay dries for a long time.
A layer of expanded clay is thicker and heavier than a layer of mineral wool with the same degree of thermal protection - the frame and foundation will be required more powerful.
Insulation during construction
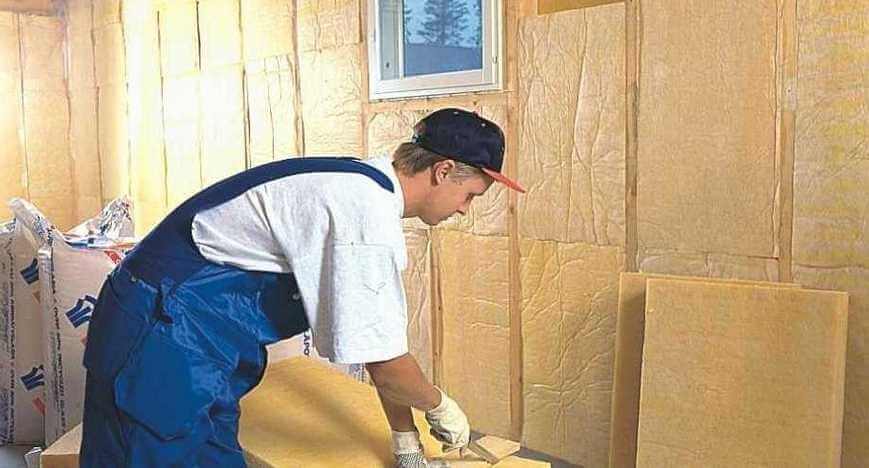
Laying of mineral wool in the cells of the frame's power frame is possible from the outside; it is also permissible to insulate the frame bath from the inside. In the first case, it is more convenient to leave a gap to the outer skin.
When filling the frame from the side of the room, the cotton wool will have to be pressed against the already created external fence. It is good if it is not continuous, and the tightness of the wall will be ensured by wind protection and finishing.
Important! For any method of laying mineral wool, personal protective equipment is required: a respirator, closed clothing with tight cuffs and collars, glasses, seals, a hat.
What is the best way to insulate a frame bath: semi-hard or soft plates? Soft flexible wool will cover the cell area more densely, a semi-rigid plate will be warmer, because there are no areas compacted during laying - with increased thermal conductivity. The elasticity of the material is important, so that the insulation in the cell stands “in the spacer” without leaving any gaps.


Thermal insulation of the attic floor with mineral wool is more convenient and safer to perform from the attic side - fragments of mineral fiber will not fall into the eyes or on the skin.
Not only small and sharp fragments of fibers are dangerous, but also volatile components of binders - vapors of formaldehyde, ammonia, phenol.
This is an additional argument in favor of laying cotton wool outside the frame bath.
In a frame bath, wall insulation with sawdust it is performed from the inside, after the installation of the external cladding (vertical arrangement of the boards is preferable).
Dry backfilling is carried out after impregnation of well-dried sawdust with a fire retardant and antiseptic.
More common is the stacking of sawdust (slightly damp) mixed with cement, sand and tobacco, lime, clay and cement. The maximum permissible sawdust layer thickness is 30 cm.
The floor of the bath is not insulated with sawdust.The cells of the attic floor frame are filled with a sawdust-containing mixture over a vapor barrier, without ramming, allowed to dry, covered with kraft paper and board flooring.
The mixture is poured into the walls in layers of 20 cm, with ramming, in parallel building up the inner lining and waterproofing material. It will take several weeks to dry.
Expanded clay in a wooden frame is covered with dry (while it is dusty, you will need a respirator), ram as intensely as the rigidity of the structure allows. Subsidence of expanded clay is inevitable over time, therefore, it should be possible to add insulation - at the top of the walls, under window openings.
A video about the advantages of insulating an attic floor with expanded clay, laid on glassine:
Ecowool installation is mechanized, after its completion it takes several days to dry the created layer. Dry installation is accompanied by intense dust formation.
Ecowool should not be placed near stoves and chimneys. At a certain temperature, ecowool begins to smolder. Salvation - asbestos-cement slabs, fire-resistant mats based on basalt. (The same protection is required for wooden structures and other insulation materials).
Basic rules for warming a frame bath
Thermal insulation of a bath of this type should take place according to its own rules. For example, it is advisable to insulate a brick steam room only from the inside. A bath from a bar, it is reasonable to simply dig in and that's enough. In the baths from SIP panels, the walls are already finished and well insulated. But, if the construction is carried out with your own hands and a wooden frame is first assembled, then the frame bath should be insulated in a comprehensive manner.
What does it mean? As already mentioned, the main task of the frame is to keep heat and water vapor inside the room and prevent them from penetrating inside the wall and going outside. This means that it is necessary not only to make good thermal insulation of the walls, ceiling and floor, but also to provide a reliable steam and water barrier for all elements of the bath.
All these three tasks: vapor barrier, thermal insulation and waterproofing, are extremely relevant for a frame bath. Imagine this moment: the vapor barrier of the walls or ceiling (which is even worse) is poorly done or is completely absent. At the same time, the insulation is done with mineral insulation (mineral wool).
Over time, water vapor will saturate this insulation, especially on the ceiling, and it will simply cease to perform its functions. From above, in the literal sense, water drips. The walls and ceiling will simply be open to the cold. And high humidity will negatively affect the wooden frame. Mold, mildew and rot will be provided.
What conclusion do we draw? It is imperative to do a vapor barrier. For these purposes, it is best to use Penopremium, Penotherm or their analogue. This foil insulation on a polypropylene foam backing copes with the function of a steam and thermal barrier. Creates a good thermos effect inside the steam room and does not allow water vapor to pass through. When buying, you should choose a thicker foil - 50-100 microns, and the thickness of the substrate - 4-6 mm.
During installation, the foil is aimed from the side of the steam room on the walls and ceiling, and better - on small bars 15-20mm thick. furniture stapler, 8-10 cm overlap. All joints must be glued with special foil tape. If possible, it is necessary to achieve the smallest loss of heat and moisture, that is, to exclude the smallest gaps in the vapor barrier layer.
Do not forget about the protection of the wooden frame. It is quite possible that accidental moisture will appear inside the walls: contrasting temperature, poorly made vapor barrier, etc. To exclude decay and mold of wood, it should be treated with protective hydrophobic impregnations. It is not for nothing that you can see the pinkish or greenish wooden frame of such buildings. This is exactly the result of impregnation with protective antiseptics. Such a protective procedure should be carried out without fail, so as not to “warm your head” later on about replacing rotten parts of the frame.
The waterproofing layer is also important for the frame bath. If we do vapor barrier from the side of the steam room and do not allow steam to penetrate the walls and ceiling, then waterproofing plays a slightly different role. It is mounted on the frame from the outside and does not allow atmospheric moisture to penetrate from the outside. Using special diffusion films such as Yutafol or its analog, you can achieve an interesting and desired effect.
Moisture that accidentally gets into the insulation can evaporate over time without problems and escape through this diffusion membrane. And precipitation or humidity will no longer be able to pass from the street to the inside of the walls. Such waterproofing is very convenient and practical. And in general, if you are wondering how to insulate a bath (frame), then it is necessary to take it as a rule that films and membranes of this type are just as important and necessary attribute in frame construction as the insulation itself. But now a little about something else ...
Is it possible to insulate the finished

Wood will add warmth to the finished building: an additional layer of boards or replacing the existing cladding with a thicker one. What to do if the thickness of the insulation for the frame bath turned out to be insufficient?
The roof will have to be “insulated” from the inside. Remove the inner lining and vapor barrier, nail horizontal bars to the rafters, put an additional layer of cotton wool in the cells formed by them, across the existing, vertically located slabs.
The new insulation is closed with a vapor barrier membrane, sewn up with boards, sheets of drywall.
The walls of the finished frame bath are insulated from the outside - the useful volume of the premises will not suffer.
You will have to remove the cladding, sheathing and windscreen. What to do if it is decided to supplement the frame bath cake with a different insulation? The second layer of insulation, located outside, must be no less porous than the inner one. Otherwise, the imaginary plane with the dew point will shift towards the room.

It is believed that frame walls, the bulk of the body of which is fibrous insulation, will not suffer from condensation - it will not have time to form.
But, firstly, not everyone shares this opinion, and secondly, in addition to the cell filler, there is a frame body, metal connecting parts (corners, brackets, screws, nails).
The windscreen is removed. The frame is extended or supplemented with a crate, the rods of which are deliberately placed in a gap with the elements of the main frame.
Under the second layer of expanded clay or sawdust, you will have to increase the foundation and create an additional frame. If it is decided to strengthen the insulation with mineral wool with expanded clay, then you will have to find a way to place it inside.
A slab-shaped foundation will reduce the difficulty of creating a new frame inside the bath to a minimum, but the internal area will noticeably decrease.
Insulation of the main elements of the frame bath
What can be attributed to the main elements of the bath? These are the ceiling, walls, foundation and, as a consequence of the foundation, floors. For example, insulating the ceiling of a bathhouse is a very important point. If it is enough to insulate the walls to a thickness of 10-15 centimeters, then the ceiling should already have a large insulation thickness. Here the thickness of 15-20 cm is already relevant. In this case, we are talking about mineral insulation, since penoplex can be used with parameters half as much as that of mineral wool (thickness).
Why is the ceiling given so much attention? Here are the simple laws of physics. All the heat tends upward, in this case, toward the ceiling. And here it is important not to release the heat into the ceiling and the open spaces of the street, but to keep it in the steam room. Therefore, the layer of thermal insulation on the ceiling is made slightly larger than in the walls.