Why connect batteries
A battery, like a capacitor, can store energy. Unlike a simple galvanic battery, where the chemical reactions that generate electricity are irreversible, the battery can be charged. In doing so, the ions are divorced from each other, and the internal chemistry of the battery is charged like a spring. Subsequently, these ions, due to the "charged" chemical process, will donate their extra electrons to the electrical circuit, themselves striving back to the neutrality of the acidic electrolyte.
All is well, only the amount of energy from the battery that it is able to generate after a full charge depends on its total mass. And the weight depends on the performance - there are standards, and batteries are made according to these standards. It is good when electricity consumption is similarly standardized. For example, when you have a car that takes a certain amount of electricity to start the engine. Well, for their other needs - feeding the automatics in the parking lot, powering locks with anti-theft devices, etc. Battery standards and are designed to power various types of vehicles.
And in other areas where a stable constant voltage is required, the demand for power parameters is much broader and more varied. Therefore, having the same type and strictly identical batteries, you can think about using them in different combinations, and more efficient charging methods than it is banal to charge them all in turn.
Why connect multiple batteries
The main reasons why batteries are combined into assemblies can be summarized as follows:
- Reduce ohmic losses (or heat losses during power transmission) by increasing the system resistance. Current strength and resistance are inversely proportional to each other, and the weaker the current, the lower the loss.
- Assemble a battery suitable for powering devices with higher voltage ranges.
- Increase the battery capacity.
- Increase both power and voltage.
In a word, they create a battery that suits specific needs. It is easier and more convenient to combine the batteries at hand than to buy dozens of different batteries. And in some cases it is trite cheaper.
REFERENCE. The electricity that accumulates in the battery is made up of the energies of the constituent elements. Therefore, with serial, parallel, and combined connection, it will be the same if the same elements are used in the same amount.
Connecting power supplies
Like loads, for example, light bulbs, batteries can be connected both in parallel and in series.
At the same time, as one can immediately suspect, something must be summed up. When the resistors are connected in series, their resistance is summed up, the current on them will decrease, but through each of them it will go the same. Likewise, the current will flow the same through the serial connection of the batteries. And since there are more of them, the voltage at the battery outputs will increase. Consequently, with a constant load, a greater current will flow, which will use up the capacity of the entire battery in the same time as the capacity of one battery connected to this load.
Parallel connection of loads leads to an increase in the total current, while the voltage across each of the resistances will be the same.The same is with batteries: the voltage on a parallel connection will be the same as that of one source, and the current can all together give more. Or, if the load remains what it was, they will be able to supply it with current for as long as their total capacity has increased.
Now, having established that it is possible to connect the batteries in parallel and in series, we will consider in more detail how this works.
Ways to connect devices
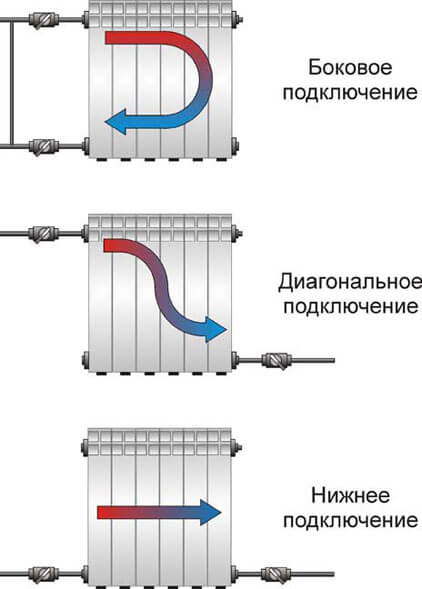
Specialists in the field of design and organization of heating systems distinguish three main types, which differ in the implementation algorithm and efficiency. Each of them has its own advantages, which are manifested in specific operating conditions. Connection happens
Lateral
It assumes that the radiator is connected to the main line from one side. In this case, the water inlet is located at the top, the outlet is at the bottom to ensure the most uniform heating of the sections or panel surface. This installation method is considered effective, since the percentage of uncovered heat exchange area is no more than 10%. Most often, the serial side connection of heating batteries is carried out in apartments of multi-storey buildings that are consumers of a centralized communal network.
Often, such a scheme is supplemented by a bypass - a pipe of a smaller diameter connecting the supply and return lines. This device is complemented by shut-off valves that cut off the device from the system.
Diagonal
Allows you to maximize the heat exchange area of the heater. The resulting power is a reference and is indicated in the passport for the product. To implement this connection diagram, it is necessary to place the entrance to the radiator at the top on one side, the exit at the bottom on the other. Due to this, the flow of the working medium will evenly pass through all internal channels.
This method is ideal for batteries with many sections. It is the diagonal strapping that allows you to fully realize the advantages that the serial connection of heating radiators gives.
Among its shortcomings, it is worth highlighting
- increased costs for building materials compared to lateral connections
- inability to hide communications in the wall or floor
- the complexity of the installation work
Lower
The most aesthetic way of integrating the device into the system is when both the inlet and outlet of the coolant are located in the lower part of the housing from different sides. In this case, the pipes are most often hidden under the flooring and concrete screed. In this regard, the arrangement of such a scheme is possible at the stage of construction and repair.
If the heating batteries are connected in series, at the bottom connection, a loss of up to 15-20% of the system efficiency is possible. This is due to the fact that it is somewhat problematic for water to rise through the internal collectors to the upper part of the device body. As a result, some areas do not warm up enough.
How a chemical power supply works
Food sources based on chemical processes are primary and secondary. Primary sources consist of solid electrodes and electrolytes that connect them chemically and electrically - liquid or solid compounds. The complex of reactions of the entire unit acts in such a way that the chemical imbalance inherent in it is discharged, leading to a certain balance of components. The energy released in this case in the form of charged particles goes out and creates an electric voltage at the terminals. As long as there is no outflow of charged particles outside, the electric field slows down the chemical reactions inside the source. When you connect the terminals of the source with some electrical load, current will run through the circuit, and chemical reactions will resume with renewed vigor, again supplying electrical voltage to the terminals.Thus, the voltage at the source remains unchanged, slowly decreasing, as long as chemical imbalance remains in it. This can be observed by a slow, gradual decrease in voltage across the terminals.
This is called the discharge of a chemical source of electricity. Initially, such a complex was found to react with two different metals (copper and zinc) and an acid. In this case, metals are destroyed in the process of discharging. But then they selected such components and their interaction such that if, after reducing the voltage at the terminals as a result of discharge, it is artificially maintained there, then an electric current will flow back through the source, and chemical reactions can reverse, again creating the previous nonequilibrium state in the complex.
Sources of the first type, in which components are irretrievably destroyed, are called primary, or galvanic cells, after the discoverer of such processes, Luigi Galvani. Sources of the second kind, which, under the action of an external voltage, are capable of reversing the entire mechanism of chemical reactions, and again return to a nonequilibrium state inside the source, are called sources of the second kind, or electric accumulators. From the word "accumulate" - to thicken, to collect. And their main feature, just described, is called charging.
However, with batteries, things are not so simple.
Several such chemical mechanisms have been found. With different substances involved in them. Therefore, there are several types of batteries. And they behave differently, charge and discharge. And in some cases, phenomena arise that are very well known to people who deal with them.
And practically everyone deals with them. Batteries, as autonomous energy sources, are used everywhere, in a wide variety of devices. From small wristwatches to vehicles of various sizes: cars, trolleybuses, diesel locomotives, motor ships.
Battery Design Guidelines
- When connected in series and in parallel, all batteries must be of the same type, age and from the same manufacturer. The capacity of the batteries when connected in series must be the same; in parallel, batteries of different capacities can be connected to each other.
- If, when connected in series, one battery fails, all batteries in the battery must be replaced. If one battery fails when connected in parallel, it is removed, and the remaining ones are used until they are exhausted. The batteries are then replaced.
To avoid premature aging, do not heat batteries. Each 6 ° C rise above 20 ° C reduces the service life by half. Install batteries in a well-ventilated, cool place and leave an air space between them to stimulate heat generation.
- Do not increase the battery capacity with batteries installed in another room. Batteries located in different locations will operate at different ambient temperatures and will not discharge and charge evenly. This will further increase the temperature difference and lead to premature aging and battery failure. If batteries are charged or discharged with high current, thermal runaway and explosion may occur.

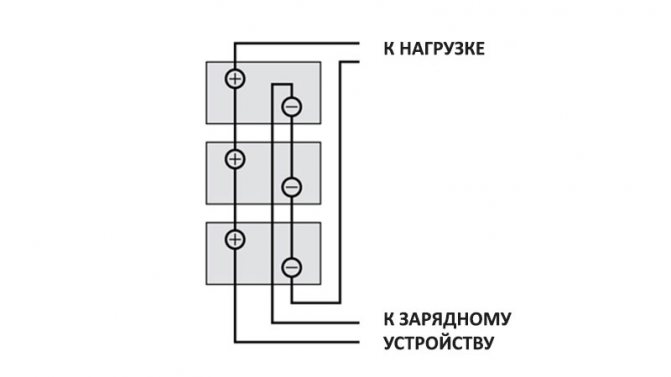
Connecting the charger to a battery of parallel-connected batteries. - If the battery charging or discharging current is 200 A at 12 V (100 A at 24 V) for an extended period of time, significant heat is generated. Use forced ventilation to disperse it.To do this, install a fireproof fan in the air inlet of the battery compartment. The inlet fan reduces the risk of ignition of hydrogen generated by the batteries. (Some standards require forced air ventilation any time batteries are connected to a charger with a power output greater than 2 kW, i.e. 167 amperes at 12 volts or 83 amperes at 24 volts).
- The voltage regulator of any powerful charger must have a temperature sensor that reduces the charging voltage when the batteries are heated.
- Large capacity batteries with high charge and discharge currents are installed in residential compartments only in sealed containers with ventilation brought out.
Some features of batteries
The classic battery is an automotive lead-sulphate battery. It is produced in the form of accumulators connected in series into the battery. Its use and charging / discharging are well known. Dangerous factors in them are corrosive sulfuric acid, which has a concentration of 25-30%, and gases - hydrogen and oxygen - that are released when charging continues after it is chemically finished. A mixture of gases resulting from the dissociation of water is precisely the well-known explosive gas, where hydrogen is exactly twice as much as oxygen. Such a mixture explodes at any opportunity - a spark, a strong blow.
Batteries for modern equipment - mobile phones, computers - are made in a miniature design; chargers of various designs are produced for charging them. Many of them contain control circuits that allow you to track the end of the charging process or charge all the elements in a balanced way, that is, disconnecting those that have already been charged from the device.
Most of these batteries are quite safe and improper discharging / charging can only damage them ("memory effect").
This applies to all, except for batteries based on the metal Li - lithium. It is better not to experiment with them, but to charge only on chargers specially designed for it and work with them only according to the instructions.
The reason is that lithium is very active. It is the third element in the periodic table after hydrogen, a metal that is more active than sodium.
When working with lithium-ion and other batteries based on it, lithium metal can gradually fall out of the electrolyte and once make a short circuit inside the cell. From this it can catch fire, which will lead to disaster. Since it CANNOT be paid off. It burns without oxygen, when it reacts with water. In this case, a large amount of heat is released, and other substances are added to the combustion.
There are known incidents of fire in mobile phones with lithium-ion batteries.
However, engineering thought is moving forward, creating more and more new chargeable cells based on lithium: lithium-polymer, lithium-nanowire. Trying to overcome the disadvantages. And they are very good as batteries. But ... away from sin it is better not to do with them those simple actions that are described below.
Choosing a connection diagram for heating batteries
When the choice of the type of heating boiler is completed, the connection diagram of the heating batteries in the house is determined. It can be one-pipe or two-pipe.
The very connection of the radiators is done in one of three ways:
- bottom;
- lateral;
- diagonal.

If, when deciding how to connect the heating battery, a one-way piping was planned, then the number of sections on one device should not exceed 12 for gravitational heating networks and 24 for systems equipped with a circulation pump.
If it is necessary to install a larger number of sections, you need to use a versatile piping to the heating radiators. When installing heating devices, one should not forget about the throughput of the straight pipe and return pipe, which depends on their diameter and roughness coefficient.
Effective heat transfer can be achieved under the condition of optimal placement of the batteries, or rather, while observing the installation distance of the devices in relation to the walls, flooring, window and window sill.
Installation instructions and how to properly connect a heating radiator provide for the following standards:
- the device should be at a distance of 10 - 12 centimeters from the floor;
- it should be installed no closer than 8-10 centimeters to the windowsill;
- the back panel should not be placed closer than 2 centimeters from the wall;
- when installing batteries, it is necessary to provide for the regulation of the degree of their heating, both in manual and automatic modes. For this, special thermostats are purchased (in more detail: "Control valves for heating radiators, valve installation");
- for the purpose of repairing or replacing the radiator, valves, valves and manual taps should be provided. They will allow you to disconnect the product from the heating system;
- you need to put Mayevsky taps on the devices, such as in the photo. With their help, air trapped in the system is removed.
Serial connection of sources
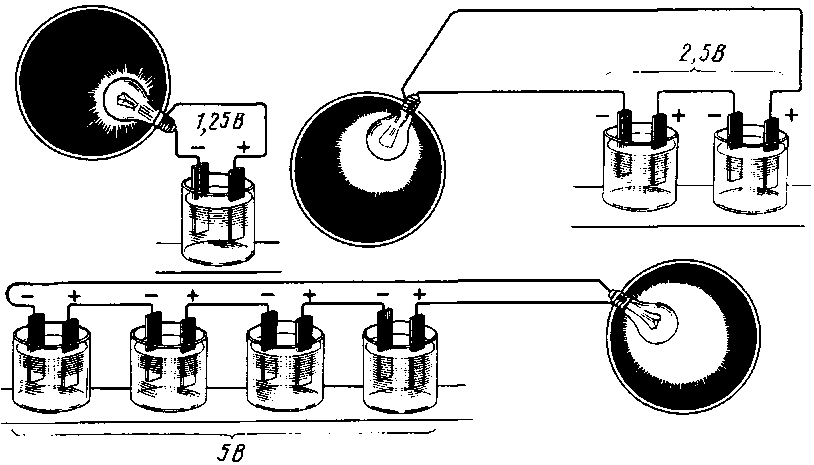
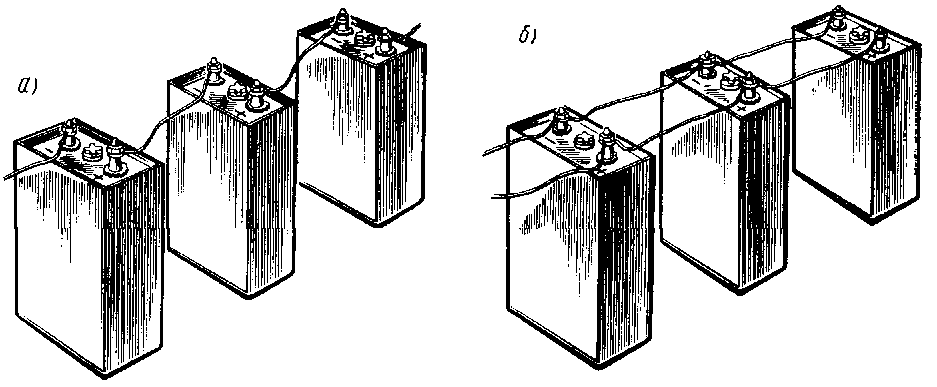
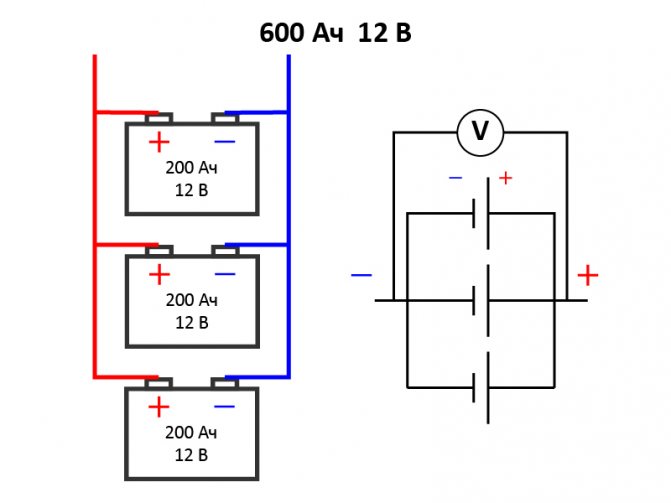
This is a well-known battery of cells, "cans". Consistently - this means that the plus of the first is brought out - there will be a positive terminal of the entire battery, and the minus is connected to the plus of the second. The minus of the second is with the plus of the third. And so on to the last. The minus of the penultimate one is connected to its plus, and its minus is brought out - the second terminal of the battery.
When the batteries are connected in series, the voltage of all the cells is added, and at the output - the plus and minus terminals of the battery - the sum of the voltages will be obtained.
For example, a car battery, having about 2.14 volts in each charged bank, gives a total of 12.84 volts out of six cans. 12 such cans (battery for diesel engines) will give 24 volts.
And the capacity of such a compound remains equal to the capacity of one can. As the output voltage is higher, the rated power of the load will increase and the power consumption will be faster. That is, everyone will be discharged at once together as one element.
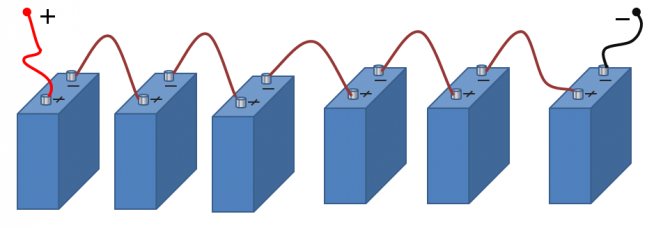

Series connection of batteries
These batteries are also charged in series. The plus of the supply voltage is connected to the plus, the minus to the minus. For normal charging, it is necessary that all banks are the same in parameters, from the same batch and equally discharged.
Otherwise, if they are discharged slightly differently, then when charging, one will finish charging before the others and he will start recharging. And that could end badly for him. The same will be observed with different capacities of the elements, which, strictly speaking, are the same.
The series connection of batteries was tried from the very beginning, almost simultaneously with the invention of electrochemical cells. Alessandro Volta created his famous voltaic pillar from circles of two metals - copper and zinc, which he moved with cloths soaked in acid. The construction turned out to be a successful invention, practical, and even gave a voltage that was quite sufficient for the then daring experiments in the study of electricity - it reached 120 V - and became a reliable source of energy.
Safety engineering
- use dielectric gloves;
- do not touch the terminals with bare hands;
- batteries must be disconnected from loads;
- use tools with insulated handles;
- check the terminals and connection pins before connecting;
- do not use batteries with different parameters and degree of wear;
- be careful with polarity;
- use suitable wires for the connection;
- insulate the assembly from moisture
ATTENTION! The main thing is to protect yourself from electric shock.
Switching errors and their consequences
Switching errors can be divided into errors of the connection itself (mixed up plus and minus) and the wrong choice of batteries and connecting wires.
Parallel connection of batteries
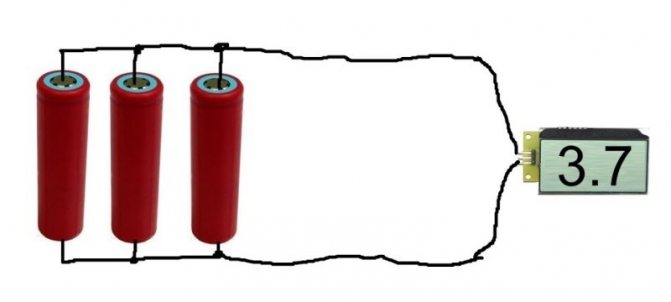
With a parallel connection of power supplies, all the pluses must be connected to one, creating a positive pole of the battery, all the minuses to the other, creating a minus of the battery.
Battery part
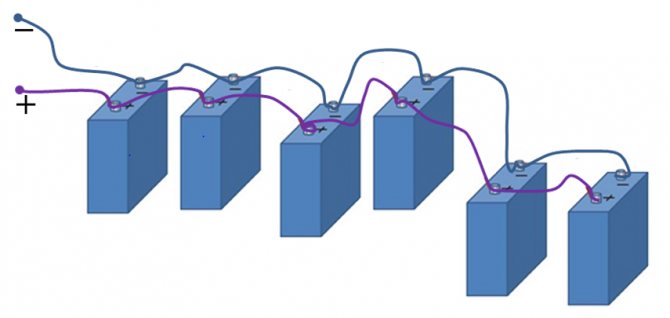

Parallel connection
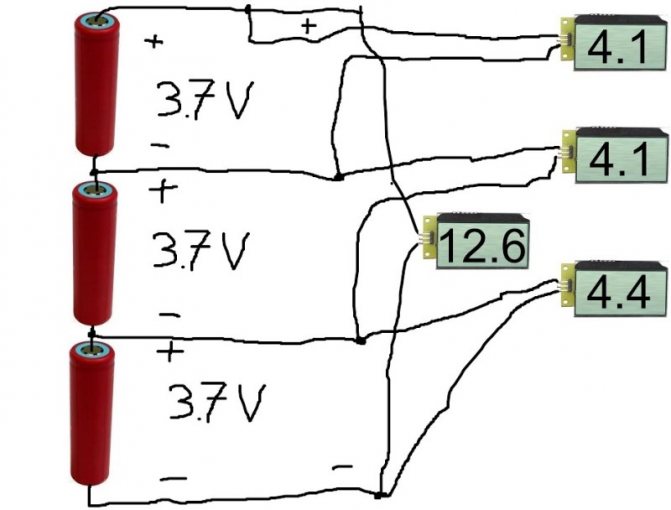
With such a connection, the voltage, as we can see, should be the same on all elements. But what is it? If the batteries have different voltages before connection, then immediately after connection, the process of "equalization" will immediately begin. Those elements with a lower voltage will begin to recharge very intensively, drawing energy from those with a higher voltage. And it's good if the difference in voltages is explained by the different degree of discharge of the same elements. But if they are different, with different voltage ratings, then a recharge will begin, with all the ensuing charms: heating of the charged element, boiling of the electrolyte, loss of the metal of the electrodes, and so on. Therefore, before connecting the elements to each other in a parallel battery, it is necessary to measure the voltage on each of them with a voltmeter to ensure the safety of the upcoming operation.
As we can see, both methods are quite viable - both parallel and serial connection of batteries. In everyday life, we have enough of those elements that are included in our gadgets or cameras: one battery, or two, or four. They are connected the way it is defined by the design, and we do not even think about whether this is a parallel or serial connection.
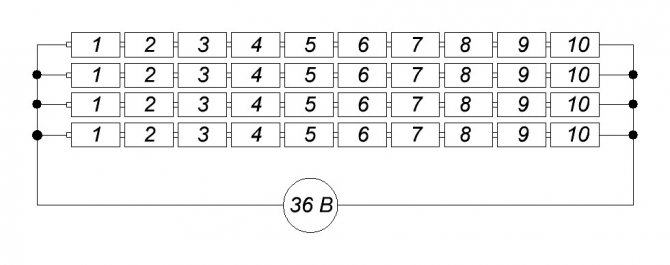
But when in technical practice it is necessary to immediately provide a large voltage, and even for a long period, huge fields of accumulators are built in the premises.
For example, for emergency power supply of a radio relay communication station with a voltage of 220 volts during the period when any failure in the power circuit must be eliminated, it takes 3 hours ... There are a lot of batteries.
Similar articles:
- Methods for converting 220 volts to 380
- Calculation of voltage losses in the cable
- Working with a megohmmeter: what is it for and how to use it?
Factors affecting heating efficiency
The efficiency of the heating structure depends on several factors:
- Layout of heating system elements
... The degree and uniformity of heating the room depends on the correctness of this work, and, accordingly, the amount of money spent on heating a house or apartment. - Selection of heating equipment
... Everything that is needed to create a heating system is acquired on the basis of a professionally performed calculation of technical and financial indicators. The fact is that the decision on how to properly connect heating radiators and the choice of the appropriate equipment contributes to the achievement of maximum heat transfer with minimum fuel consumption.