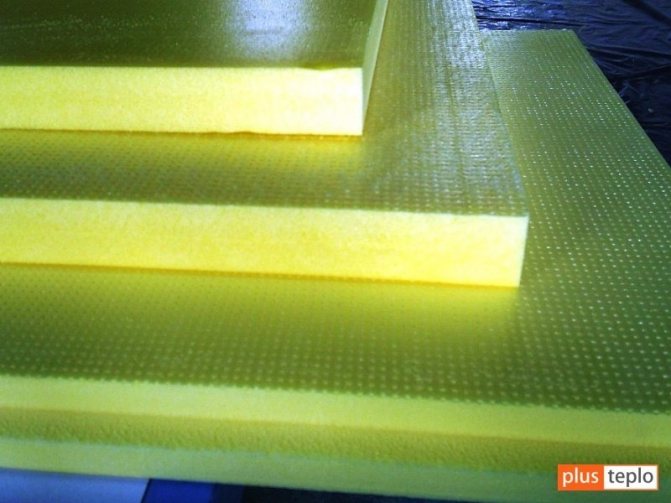
What is foam made of?
Polyfoam can be made from any polymers (plastics). The most famous raw materials are polyurethane, polyvinyl chloride, phenol-formaldehyde, polystyrene and others. But what kind of plastic the material would not be made of, there is only 2% of it in the material, the rest is atmospheric air. Domestic building material is produced in accordance with GOST 15588-2014 and is indicated by the general marking of PSB, to which numbers and letters are added, which indicate additional properties: low density, self-extinguishing, universal and others. Raw materials for expanded polystyrene look like translucent beads with a diameter of 0.2 to 3.7 mm. The material is produced in several stages:
- Foaming.
- Drying.
- Stabilization.
- Cutting.
- Maturation.
- Baking.
One of the methods assumes, after stabilization, the transition to baking, bypassing the 2 previous stages. Not so long ago, a modern version of the material appeared on the market - extruded foam. It differs from the classical one in the smaller size of the cells and their complete closure. Such material was recognized as more technological, but ordinary polystyrene foam is still the most in demand, it can be used as a wall insulation from any material: wall blocks, concrete monolith, wood, brick and much more.

https://youtu.be/8HqSQaYZsqA
Is foam "harmful"? ..
Surrounding ourselves in modern life with synthetic materials, we do not always think about whether this familiar object is dangerous for our health?
Regarding high-quality foam under normal conditions of its use, you can be calm, since it does not emit substances harmful to humans in dangerous concentrations.
Polyfoam also has a beneficial effect on the ecological balance in the construction theme, since it is recyclable as a thermal insulating filler for concrete mixtures, blocks with internal voids. It can also be used to improve soil structure.
The use of foam crumbs for looseness of the soil
Important! Use quality material from trusted certified manufacturers.
Specifications
| Options | The values | Comments (1) |
| Compressive strength at 10% linear deformation | 0.05 to 0.16 MPa | Strength indicators directly depend on the polymer from which the foam is made. For example, phenol-formaldehyde have higher strength values. |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.038 to 0.043 W / mGrad | The parameter also depends on the brand of building material. |
| Frost resistance | Up to 200 cycles - normal Up to 500 cycles - extruded | The characteristic values depend on the brand |
| Water absorption | 1% per day | Tests have shown: 3% of the volume for 1 month of full immersion in water. The parameters are insignificant, however, if moisture gets into the expanded polystyrene, then it can subsequently freeze when the cold weather sets in. |
| Water vapor permeability, coefficient | 0.03mg / mchPa | This building material does not form natural air exchange between premises and streets. |
| Fire resistance | Flammability G3-G4 Flammability B2-B3 Smoke formation D3 | Expanded polystyrene is considered a difficult flammable material |
| Foam cost | On average, 3 thousand rubles per 1 m3. | Styrofoam is quite available, the price depends on the brand and thickness. |
| Soundproofing | Depending on the thickness, it can increase the protection up to 32 dB | Expanded polystyrene is characterized by high performance, but inferior to other materials, for example, mineral wool |
| Environmental friendliness | Safe | It does not have radioactivity, it is completely utilized, since no toxic raw materials are used in the production and a minimum of energy is expended. |
| Life time | 13 to 80 years old | The value of the indicator depends on the manufacturer, production technology and raw materials. |
| Foam density | 11 to 40 kg / m3 | The characteristic depends on the brand. |
Standard foam sizes - thickness varies from 20 to 100 mm, length and width: 1000 * 1000, 1000 * 1200, 1200 * 1200. How much the foam costs depends on the size parameters.
Types of foam
It is subdivided into the following types:
- polystyrene;
- polyethylene;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- polyurethane.
Polystyrene
There are two ways to produce this type of foam:
- Pressless... This variety is familiar to every person. When buying home appliances, you can pay attention to the fact that it is packed in foam, consisting of small balls fastened together. It is very fragile, it can be crumbled and broken by hand.
- Press... But this species will be much more difficult to crumble. The granules of such foam are more tightly adhered to each other. The production technology is much more complicated and more expensive than that of the pressless one, so it is much less common.
There is such a variety as extruded foam, it is practically no different from non-press.


Polystyrene foam varieties have one significant drawback -
high hygroscopicity.
We recommend: Which polypropylene pipes are better for heating and water supply? How to solder with your own hands
Water vapor enters the cavities between the “balls” and granules.
This material “does not breathe”, so the steam does not go anywhere and, when exposed to subzero temperatures, it can freeze, destroying the structure.
Even in the absence of exposure to cold, the accumulated steam degrades the thermal insulation properties of the foam and increases the humidity in the room.
Extrusion foam is devoid of such disadvantages, since homogeneous in structure... It is common in the production of disposable cutlery, tableware, food packaging.
About the durability of polystyrene foam, we can say that in a press-free one it will be from 10 to 35 years old... Extrusion will last much longer, about 50-70 years old... Of course, the service life directly depends on the manufacturer of the material and the impact of destructive factors at the installation site.
Polyurethane
One example of polyurethane foam is foam rubber... It has a porous structure, good air and steam permeability, high elasticity. It is used in furniture production, both as upholstery and filler.
Many household items are made on its basis. Highly flammable and releases hazardous substances that are more toxic than polystyrene foam. The reason for this is hydrocyanic acid in the composition. It is extremely short-lived, turns yellow and collapses when exposed to external factors such as ultraviolet light.
PVC
By itself, polyvinyl chloride is a thermoplastic polymer that contains up to 56.8% combined chlorinewhich makes it difficult to burn. It can be manufactured both by pressing and non-pressing methods. Its properties are similar to extruded polyethylene foam.


There are no toxic substances in it. When burning, the polyvinyl chloride foam decays on its own.
It has high elasticity, but it can corrode the metal structures next to it.
Polyethylene
It is quite common in everyday life. Looks like like a translucent filmconsisting of air pimples.
It is used to wrap fragile things and easily damaged equipment in it, it does an excellent job of protecting it from damage.
Polyethylene foam is very flexible and has different thicknesses, from a few millimeters to several centimeters. It is similar in strength to extruded polystyrene foam, but its distinctive feature is its non-toxicity. It is considered an environmentally friendly material with a long service life. Flammable.
We advise you to read: Do-it-yourself insulation of the foundation of a private house
Features of the
This building material is widely used due to the following qualities:
- ease of processing of building materials allows you to create structures of any geometry, even the most complex;
- low strength and high compression density;
- it maintains the stability of the structure in a wide temperature range: from -170 to +80 degrees;
- high resistance to many chemicals and biological factors;
- high thermal insulation allows us to consider foam insulation as an excellent building material, for example, for the construction of modern multi-layer house structures;
- environmentally friendly building material, since it does not contain substances from a series that is toxic and harmful to human health;
- easy to handle and install, also with conventional building adhesives.
- the price of non-extruded foam is lower than that of EPS.
What is Styrofoam?
Styrofoam is special class materials, which are plastics with a foamed structure, white.
Structure
Most of the foam volume is gas... Its density is much lower than that of the material on the basis of which it is made - polymer. Heat passes only in individual cells, thanks to which it has good thermal insulation qualities.
High quality noise suppression due to the fact that the thin partitions of the cells are a poor conductor for sound. Foams are made from almost all well-known polymers... The density and mechanical strength of the foam varies depending on production and processing technologies and on the composition of the original raw materials.
What is it made of?
Usually, in a domestic environment, we most often come across pressless expanded polystyrene. Styrofoam granules (PSV / EPS) are produced by polymerizing styrene and adding pentane to it, which forms the pores. Expanded polystyrene is a very popular thermal insulation material, which is 98% gas enclosed in microscopic thin-walled polystyrene cells.


The procedure for foaming polystyrene is carried out several times and, as a result, the density of the material becomes much less.
Then the resulting mass is dried to remove residual moisture. After drying, the granules are shaped into familiar slabs.
Pressing is done on special machines, after which the foam processed with hot steam.
The thickness of the foam plates can be from twenty to one thousand mm. Below we will take a closer look at the technical characteristics of this material.
Disadvantages:
- limited mechanical strength necessitates the formation of protection after installation;
- collapses on contact with paints and varnishes and nitro paints;
- building material can be damaged by rodents, so it must be covered with substances less attractive to animals;
- the material almost does not allow air to pass through, which makes it necessary to equip the building with ventilation systems;
- Plastering on polystyrene foam requires preliminary preparation to ensure the best adhesion.
Why Styrofoam? So why did the foam deserve such unlimited trust, why exactly is it used as a sound-insulating material, as well as insulation? What is the foam made of? Let's turn to the physical and chemical properties. Expanded polystyrene is a light, biologically safe, white material resistant to external influences.
What are the benefits of Styrofoam? It has an extremely low thermal conductivity, which allows it to maintain the required temperature in all conditions.
How flammable is foam? The fire hazard is not great, polystyrene has the ability to self-extinguish, and, being a combustible material, it still burns weakly, smolders.
Where can you buy equipment that can be used to produce foam? You can buy equipment for the production of foam plastic in Saransk, it works throughout Russia and offers high-quality, certified equipment.
So you can buy polystyrene not only in Saransk? Of course, we work not only in one city, all of Russia uses the products of our company.
Why do people need styrofoam? Do they use it so often at home? But nevertheless, due to its properties, this material is in many respects irreplaceable.
As everyone knows, foam is lighter than water and therefore is always on its surface. It is for this reason that it is very often used for buoys, which indicate the place from which great depth begins.
All materials with a density lower than that of water are in great demand. But is this the only advantage of polystyrene? Of course not. In order to make sure of this, you need to consider polystyrene and expanded polystyrene.
If you read books on chemistry, you can find out that polystyrene is used to create expanded polystyrene on a large scale. Of course, it will be very difficult for a person who has absolutely no knowledge of this industry to understand this. In simple words, polystyrene is better known to all as polystyrene.
Scope of application
This material is widely used in various spheres of human activity: packaging for products, furniture manufacturing, tailoring, outdoor advertising, shipbuilding, electrical engineering and radio. But expanded polystyrene is most in demand in the construction industry:
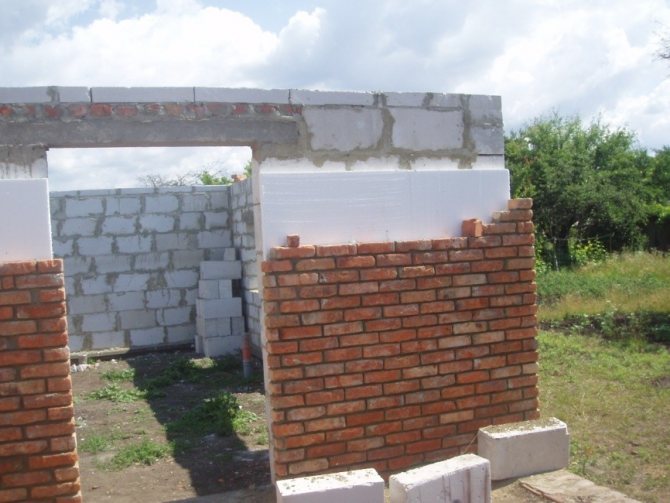


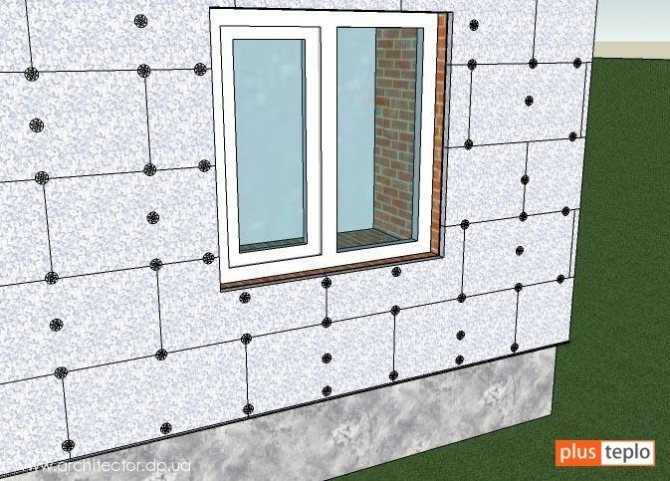
- Polyfoam is a building insulation material that can be used to insulate the walls of a house from the outside.
- Thermal insulation of roofs and floors.
- As an insulation of engineering communications.
- For soundproofing between floors or rooms.
- Polyfoam for insulation is used on the plinth, closing it with cladding, as well as for thermal insulation of the foundation.
Disadvantages of Styrofoam
This material is very popular and is used almost everywhere, it occupies a leading position in the demand for thermal insulation materials. Can be applied both for domestic purposes and in mass construction... For all its popularity, many simply do not know everyone. disadvantages possessed by this product.
High flammability
Despite the many different types of foam, none of them cannot withstand fire for a long time, with prolonged exposure to high temperatures, it ignites and turns into a liquid mass. The smoke emitted during combustion can paralyze the respiratory system of a person.
We recommend: Linoleum flooring, what is it, types, characteristics. How to choose the right one for your home?
It is because of this disadvantage that the material is not suitable for finishing ventilation. There will be a constant flow of oxygen and headspace. In this case, putting out the fire will be very problematic.
Fragility
Correctly mounting this material is quite difficult, it crumbles and breaks... It is very fragile: for example, if the ceiling is insulated with foam plastic, then walking in the attic can damage the thermal insulation.


Hygroscopicity
Hygroscopicity is a property of the material absorb moisture... The use of styrofoam in damp, humid rooms is not recommended. It will not be the best choice for finishing a basement or bathroom, but extruded polystyrene foam will withstand such a test.
High sensitivity to solvents
When gluing foam boards, it is imperative to make sure that the materials are compatible. Some adhesives can corrode styrofoam.
Excellent shelter for mice
This building material has all the properties to make mice want to settle there: it retains heat well, is easy to “gnaw through” and provides reliable protection.
To avoid this, it is required to cover the material with mineral wool, which will scare off rodents with its pungent odor. You can beat the foam with metal inserts - this is laborious, but they will become insurmountable obstacle for mice.
Fragility
Approximately every ten years, the material will have to be changed, and even earlier when exposed to destructive factors.


Toxicity
Polyfoam is dangerous not only when burning. Due to the long exposure of time and the lack of timely replacement, it begins to produce a harmful substance - styrene monomer.
When installed in an unventilated room, there will be a specific smell that has a negative impact on human health.
Vapor barrier
During installation, it should be borne in mind that the foam “does not breathe“Therefore, if you install it in a room without artificial ventilation, it will give high humidity and constant condensation on the glass.
Pros and cons of Styrofoam
As we have already mentioned, the foam is popular material for insulation, while the main advantage here is the low cost, but in addition, such material has its pros and cons. So, let's look at the main ones.
Pros:
- low weight of the plates;
- good strength characteristics: tensile strength - 80 kPa, compression - 130 kPa;
- the price of polystyrene is lower than that of mineral wool;
- ease of processing;
- low weight of the wall after insulation (if the thickness is 100 mm, then the weight is only 11-15 kg);
- moisture does not violate its thermal insulation properties, since the material is not hygroscopic.
Minuses:
- low vapor permeability;
- poor sound insulation properties;
- partial destruction if the temperature is above 80 degrees;
- no resistance to organic solvents;
- restrictions for insulation, since it is used for residential premises, but not suitable for high-rise buildings over 25 m, as well as public buildings.
Building material mythology: Styrofoam
Expanded polystyrene is a widespread thermal insulation material known to everyone as Styrofoam. Its properties to retain heat are determined by still air isolated in closed cells. The material is lightweight, durable, easy to process and does not require special protective equipment when working with it. It would seem - the perfect material ?!
So why don't the controversy around foam insulation not subside? Answers to topical questions of safety, durability, flammability, approval and rules for use in construction, as well as attractiveness to mice - in our review. Stroyka's experts figured it out.


Is it harmful?
Pentane. Expanded polystyrene consists of 98% air and only 2% of polystyrene, which is the initial raw material for its production and obtained by polymerization of styrene. A high percentage of air in the structure of the material is ensured by almost complete (by 80–90% with primary and by 10–20% with secondary foaming) replacement of the blowing agent (pentane), which is initially contained in the granules and, when heated, becomes volatile, expanding itself and expanding (foaming) polystyrene granules. Residues of pentane “volatilize” at the stage of aging of granules and ready-made blocks.By the time the final product is delivered to the consumer, there is either no pentane in foam products at all, or its content is so small that it poses no threat to human health.
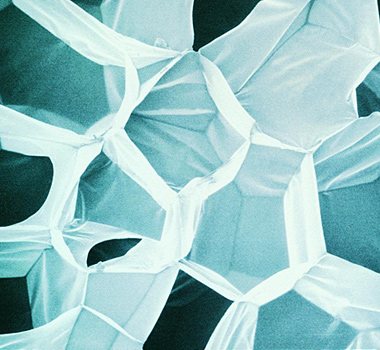

Foamed polystyrene structure - 98% air, 2% polystyrene. The cells are closed
Residual monomer
As you know, complete polymerization of styrene is impossible, as a result of which expanded polystyrene contains in its composition a residual monomer - styrene. Styrene is a toxic substance belonging to the third hazard class. It has an irritating effect on mucous membranes and a harmful effect on the human heart and liver. The percentage of monomer in finished high-quality slabs or blocks is no more than 0.005%. The migration of styrene into the air does not exceed 0.001 mg / m3. The maximum permissible concentration of styrene: in the air of the working area - 30 mg / m3; maximum one-time - 0.04 mg / m3; daily average - 0.002 mg / m3. Thus, the possible percentage and migration of styrene is several times and an order of magnitude less than the maximum permissible concentration of its content.
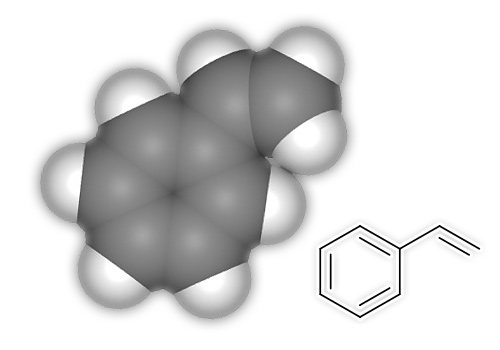

Styrene molecule
Depolymerization
Polystyrene is an equilibrium polymer, that is, it is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its monomer. The depolymerization process begins at a temperature of 320 ° C. The normalized temperature for the use of expanded polystyrene products is from minus 40 ° C to 80 ° C. Thus, styrene precipitates are possible only at temperatures significantly exceeding the limit temperatures. In the temperature range of admission to operation, foam polystyrene insulation does not pose a danger.
Penetration
In any multi-layer wall structure, consisting, for example, of brick, expanded polystyrene and a layer of plaster, the gradient of the partial pressure of the gas mixture is directed from the inside out: the gas always rushes from an area with a high partial pressure to an area with a low one - from warm to cold. Therefore, the migration of any unsafe substances is possible only outward, and not inward.
Moreover, the likelihood of styrene penetrating through 2 cm thick plaster is four times lower than the likelihood of an AIDS virus cell entering through the latex of a contraceptive.
Is it dangerous?
Expanded polystyrene is a combustible material and belongs to the highest flammability group - G4. If exposed to open flames, it is likely to burn.
Fire safety approval for use in construction. Building polystyrene foam is allowed for use at construction sites only when the granules used for its manufacture are added to the composition of fire retardants - special additives that slow down the ignition and impede the combustion of the foam. Under the influence of a flame, such a material melts and loses in volume; in the absence of fire, it quickly dies out.
https://youtu.be/Z-uxTGfVwO8
Ignition open material is possible from the flame of a match, lighter, blowtorch, autogenous welding sparks. Impossible - from a calcined iron wire, a burning cigarette and sparks generated at the point of steel. Self-ignition of expanded polystyrene occurs at temperatures from 460 to 490 ° C.
Application in construction. In the event that expanded polystyrene insulation is used inside a multi-layer structure, it must be protected from all sides with non-combustible materials. Competent thermal rehabilitation of the house with expanded polystyrene plates reduces the likelihood of fire insulation to zero. A layer of plaster a few centimeters thick is able to keep the foam from igniting for 15 minutes. The scheduled time of arrival of the fire brigade is 10 minutes.
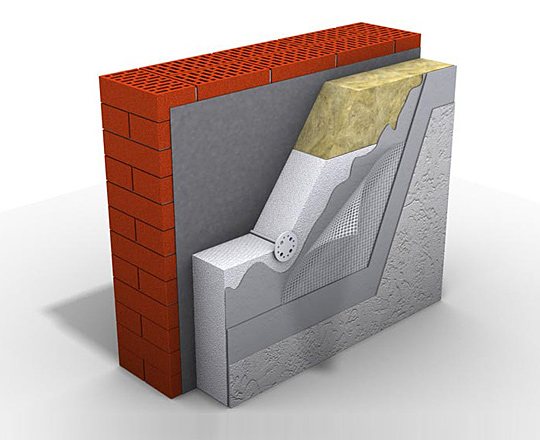

Is it durable?
The durability of the material outside the structure is determined by the quality of the raw materials and the sintering of the granules; in the design - the quality of production and installation of the structure.
Destruction. Expanded polystyrene is not afraid of water, steam, temperature changes, but under the influence of sunlight, slight destruction of the upper layers of the material is possible, the thickness of which is calculated in tenths of a millimeter. Such destruction is manifested in the yellowing of the material.
Expanded polystyrene is afraid of the direct action of organic solvents, gasoline, acetone, white spirit. Under their influence, the foam melts, losing up to 100% of its volume, therefore, the application of chemicals containing solvents in their composition directly on the surface of the foam is prohibited.
Stability of properties. Actual test data of domestic and foreign researchers show that expanded polystyrene does not change its physical, mechanical and thermal properties up to 50–80 years. The material successfully withstands tests by alternate freezing-thawing, while its characteristics do not change significantly, and the material itself does not collapse. In a properly manufactured and installed structure, the durability of the foam is determined by the durability of the structure itself and the materials of which it consists.
Rodents. Research by scientists has proven that expanded polystyrene as a means of food is of no interest to rodents. "Tailed neighbors" show "interest" in the foam only in cases when the latter is an obstacle on their way to food and water, which is excluded by the correct thermal insulation device. There are also cases when mice make holes in foam slabs, or use it as bedding. This happens no more often than rodents use wood, burlap or paper for the same purposes.


How to choose?
The main properties of expanded polystyrene are determined by the raw materials used for its manufacture and the quality of sintering of the foamed granules. Both criteria are easy to evaluate and are available to the average consumer purchasing foam on the market.
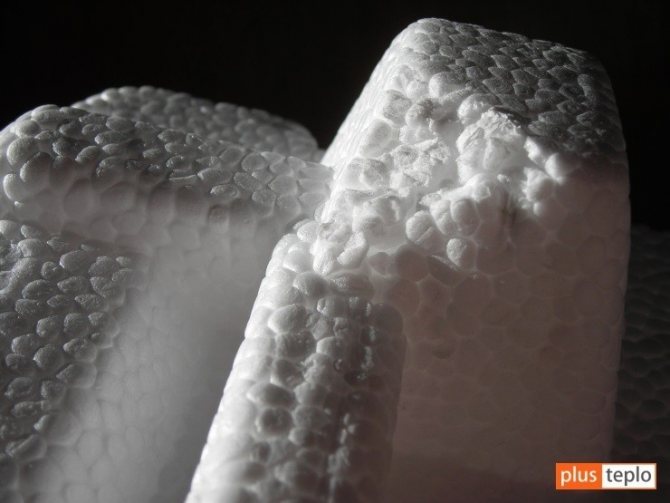
Sieving. A manufacturer who wants to save money knows that polystyrene not dispersed into fractions is cheaper and is a compromise solution both for a consumer who does not delve into quality issues, seeking to save money, and for a manufacturer who is eager to "weld". It is easy to distinguish such foam - the sizes of the balls vary significantly. Expanded polystyrene made from scattered raw materials will differ in the same size of all granules and, as a result, in the stability of the properties of the board or product.


On the picture: on the left - a plate made from non-scattered raw materials, contains granules in the structure that differ significantly in size; on the right is a slab made from scattered raw materials, in which all the granules are approximately the same size.
Sintering of granules. The strength properties of polystyrene, its ability to withstand the effects of frost and water are a direct consequence of the quality of sintering of granules. The larger the surface of the granules in contact with each other, the stronger the bonds between them and the better your insulation. Round balls are a sign of poor sintering. If the granules have the shape of a polyhedron, then the cake is good. If, when touched, the material crumbles into granules, regardless of their shape, the sinter is poor.


On the picture: on the left is an example of good pellet sintering; on the right - a poorly sintered plate crumbles from one touch, all the granules are round.
Exposure and smell, humidity. Smell and touch the expanded polystyrene you are purchasing. Manufactured in compliance with the technological parameters and aged, the foam is practically odorless. If an unpleasant odor emanates from the material, most likely, the manufacturer did not comply with the production regulations, and it is better to refuse to buy such a heater.If it is wet between the plates of the polystyrene offered to you, the foam has not been dried, which means that you will not see the desired thermal conductivity.
Instead of an epilogue
Compliance with technological regulations, the use of high-quality raw materials, correct installation in the structure and protection from external influences can guarantee you durable and safe thermal insulation. It is enough for the consumer not to pursue dubious savings, but to give preference to a large manufacturer; the builder - to skillfully use the material in the structure.