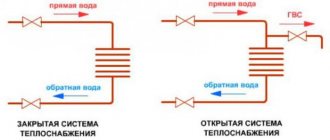
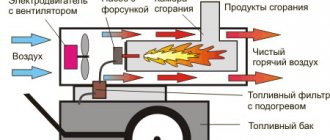
Here you will find out:
- How air-to-water heat pumps work
- Specificity of application and work
- Advantages and disadvantages of air source heat pumps
- Top 5 Benefits for Plant Owners
- How to choose an air-to-water heat heating pump
- Algorithm for assembling a homemade unit
- Features of unit maintenance
An air-to-water heat pump is used for heating domestic and industrial premises in the southern regions and central Russia. You can buy such a device or make it yourself, for example, from an air conditioner.
What do you need to know?
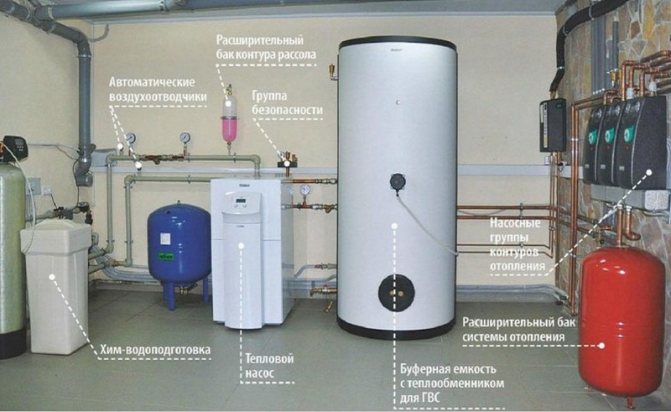
You can say that since heat pumps are so efficient, why are they so poorly used. The whole point is the high cost of equipment and installation. It is for this simple reason that many refuse this solution and choose, say, electric or coal-fired boilers. Nevertheless, it is not worth discarding this option for many reasons, which we will definitely mention in this article. Heat pumps, once installed, become very economical as they use the energy of the ground. The ground source pump is a 3 in 1. It combines not only a heating boiler and a DHW system, but also an air conditioner. Let's take a closer look at this equipment and consider all its strengths and weaknesses.
Principle of operation
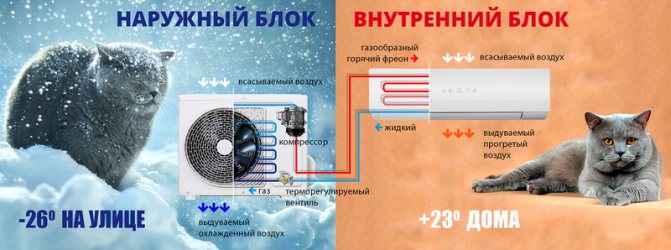
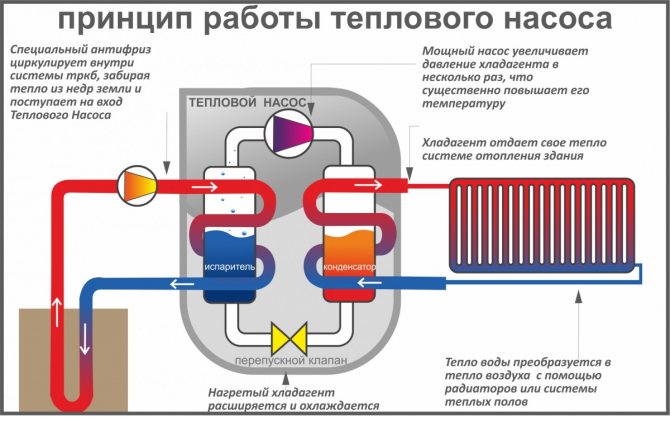
For those who do not quite understand the topic, it is worth explaining what an air-to-water heat pump is. In fact, it is a "reverse refrigerator" - a device that cools the air outside and heats the water in the tank. Then this water can be used for hot water supply or heating the house.

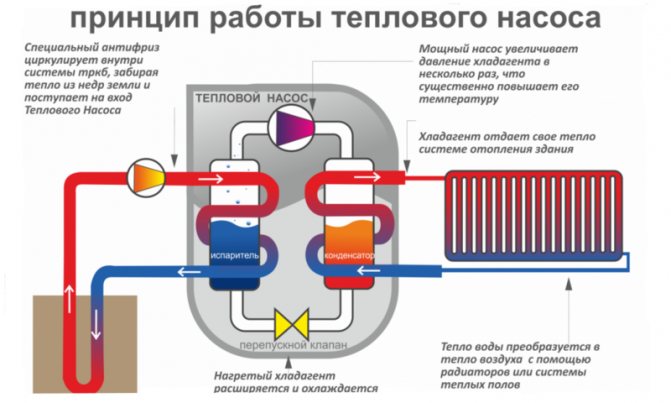
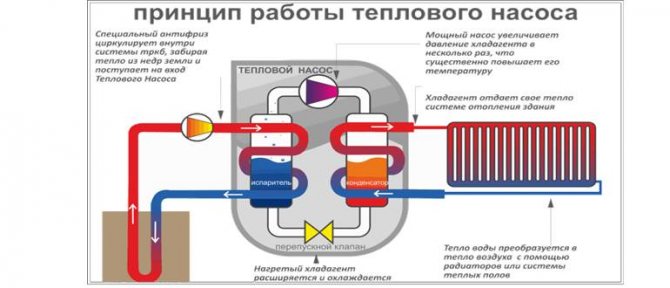
Internal arrangement of an air-to-water heat pump schematically
The heat pump uses a closed cycle and only consumes electricity. Its efficiency is measured as the ratio of the consumed electrical energy to the received thermal energy. The efficiency of heat pumps is also measured in COP (Coefficient of performance). COP 2 corresponds to an efficiency of 200% and means that for 1 kW of electricity it will give 2 kW of heat.
The principle of the unit
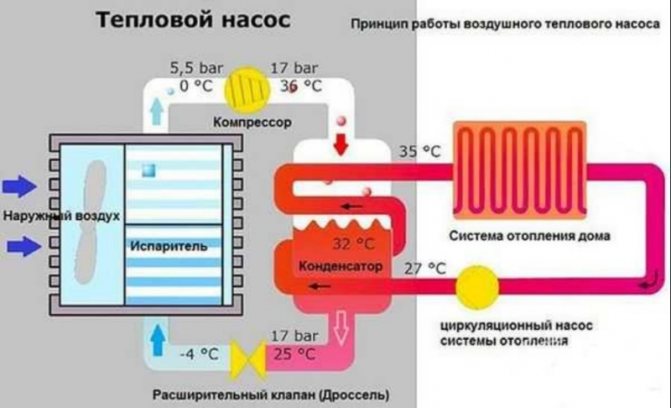
The principle of operation of a heat pump for heating is to use the potential difference of thermal energy. That is why such equipment can be used in any environment. The main thing is that its temperature is at least 1 degree Celsius.
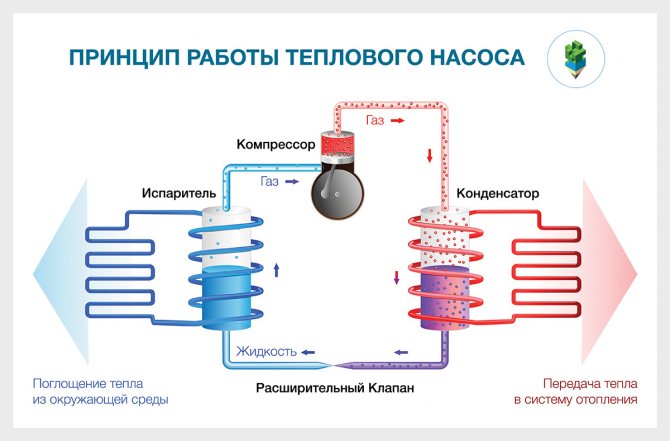
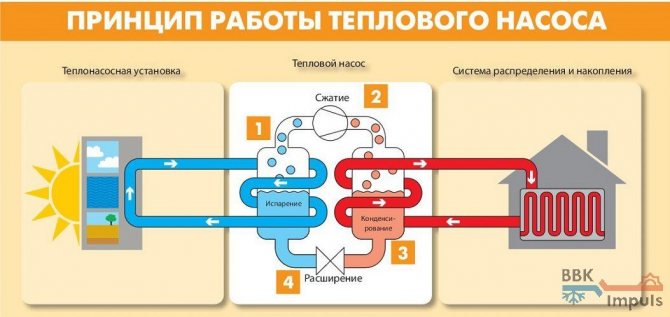
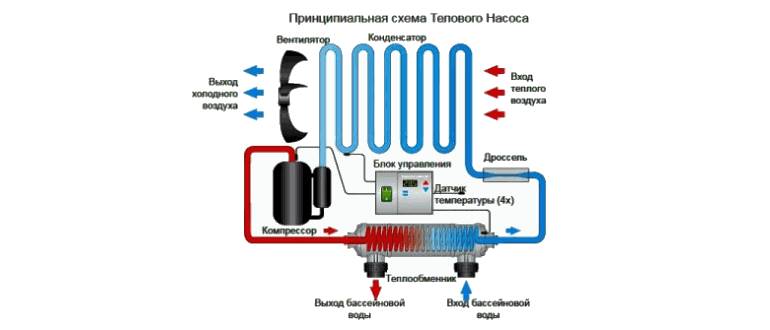
We have a coolant that moves through the pipeline, where, in fact, it heats up by 2-5 degrees. After that, the coolant enters the heat exchanger (internal circuit), where it gives off the collected energy. At this time, there is a refrigerant in the external circuit, which has a low boiling point. Accordingly, it turns into gas. As it enters the compressor, the gas is compressed, as a result of which its temperature becomes even higher. Then the gas goes to the condenser, where it loses its heat, giving it to the heating system. The refrigerant becomes liquid and flows back to the external circuit.


Advantages and disadvantages of heat pumps
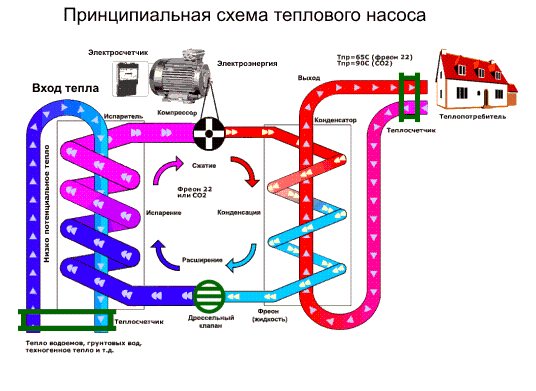

Heat pumps for home heating can be controlled by specially installed thermostats. The pump automatically turns on when the temperature of the medium falls below the set value and turns off if the temperature exceeds the set point. Thus, the device maintains a constant temperature in the room - this is one of the advantages of the devices.
The advantages of the device are its economy - the pump consumes a small amount of electricity and environmental friendliness, or absolute safety for the environment. The main advantages of the device:
- Reliability.The service life exceeds 15 years, all parts of the system have a high working resource, energy drops do not harm the system.
- Security. No soot, no exhaust, no open flame, no gas leakage.
- Comfort. The operation of the pump is silent, coziness and comfort in the house help to create climate control and an automatic system, the operation of which depends on weather conditions.
- Flexibility. The device has a modern stylish design and can be combined with every heating system in the house.
- Versatility. It is used in private, civil construction. Since it has a wide power range. Due to this, it can provide warmth to rooms of any area - from a small house to a cottage.
The complex structure of the pump determines its main disadvantage - the high cost of equipment and its installation. To install the device, it is necessary to carry out excavation work in large volumes.
Briefly about the types of heat pumps
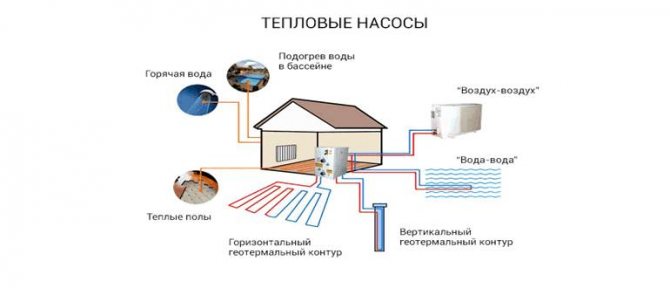
Several popular geothermal pump designs are known today. But in any case, their principle of operation can be compared with the work of refrigeration equipment. That is why, regardless of the type, the pump can be used as an air conditioner in the summer. So, heat pumps are classified according to where they can extract heat from:
- From the ground;
- From the reservoir;
- Out of thin air.
The first type is most preferable in cold regions. The fact is that the air temperature often drops to -20 and below (for example, the Russian Federation), but the depth of soil freezing is usually insignificant. As for reservoirs, they are not everywhere, and it is not very advisable to use them. In any case, it is better to choose a ground source heat pump for home heating. We examined the principle of operation of the unit a little, so we go further.


How does a ground source heat pump work? Principle of operation.
To obtain heat from the ground, a ground heat exchanger is needed. To do this, a pipe is simply placed in the ground, forming a loop in which liquid circulates - it is popularly called brine. The loop (in practice there are several) passes through the evaporator of the heat pump, where the temperature of the brine drops and becomes lower than the temperature of the ground. Passing further along the pipe in the ground, the brine gradually heats up. At the end, it again enters the evaporator, where it gives off heat.

Thus, the brine mediates the temperature difference between the soil and the pump evaporator.
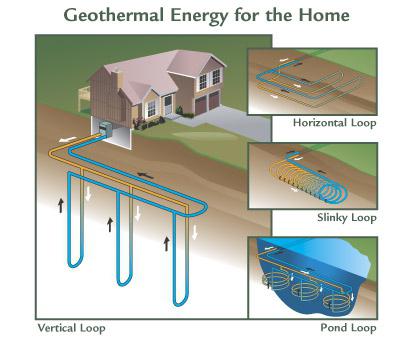
The heat exchanger can be horizontal or vertical. The size of the land plot helps in choosing a solution - several hundred square meters are required for the manufacture of a horizontal heat exchanger, and several dozen are enough for vertical probes.


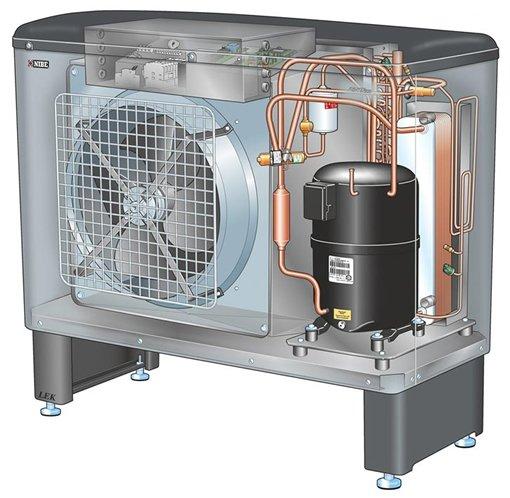
It is important that the volume of the heat exchanger is large - for the entire heating season, the pump receives several megawatt-hours of heat from the ground. If it is too small, it is exposed to excessive cooling and, as a result, the pump cannot work properly. The control system of a ground source heat pump, as a rule, turns it off when the brine temperature drops to -7 ° C, because below this value, the course of processes in the circuit is excessively disturbed.
Ground source heat pump with horizontal heat exchanger.
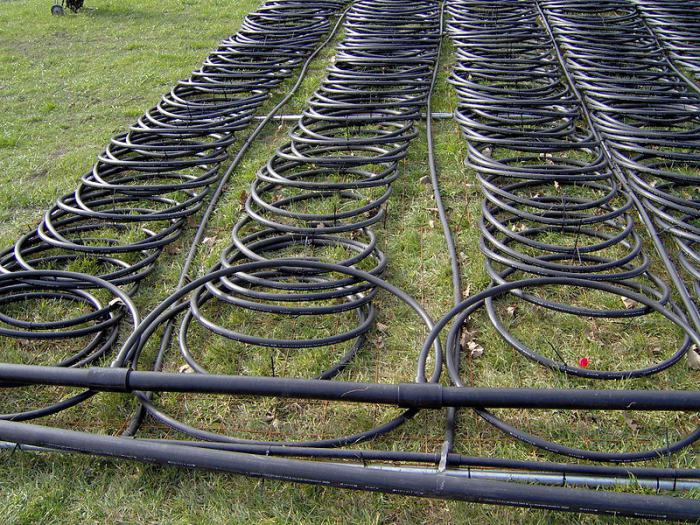
In the case of a heat exchanger made of pipes located horizontally, the optimal depth is 0.2 - 0.5 m below the freezing line. However, if there is a watercourse at a relatively shallow depth, then the best solution is to place pipes in it. Then the heat pump achieves a higher efficiency factor Kp.
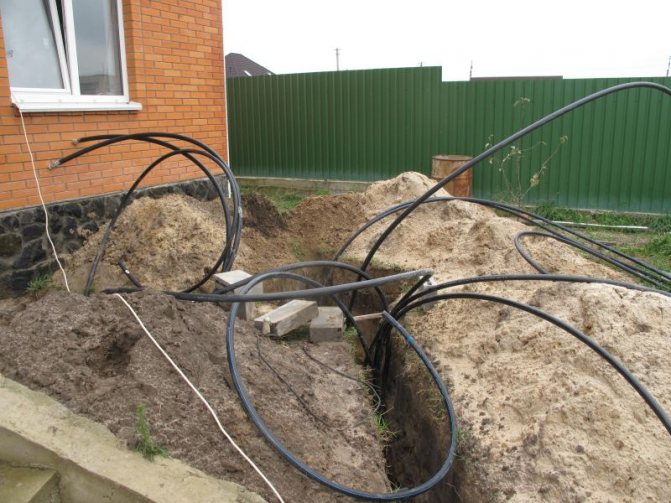


Pipes of a horizontal heat exchanger are laid in a pre-prepared pit with dimensions corresponding to the required surface of the heat exchanger. They are led in the form of a coil (bends) over the entire surface of the pit, observing certain intervals between adjacent sections.The intervals should not be less than 0.4 m and not more than 1.2 m, taking into account the type of soil, from which its ability to "regenerate" (adding heat) follows. The longer the ground surface is frozen, the greater the interval should be.
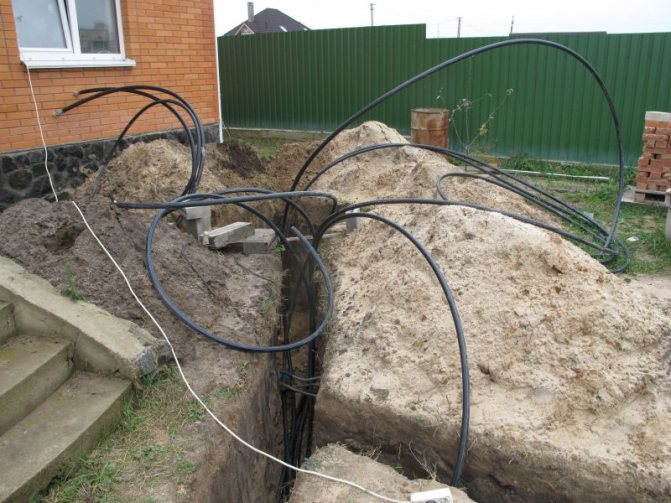


It must be remembered that the heat output of the heat exchanger does not flow from the length of the pipe, only from the surface of the ground on which it is laid. Small gaps do not allow receiving more heat from it, due to the need to use a long pipe. This translates into a higher investment and operating cost, because to pump brine through a long pipe, a circulation pump with a higher capacity is needed. Due to this too large gap between the pipes, it happens that the heat does not enter in the designed amount, so that the power of the heat exchanger is less.
Ground heat exchanger project.
Designing an appropriately sized ground heat exchanger is the key to the correct operation of a heat pump. To calculate the required value, information on the required power of the heat pump is required. If it is not in the technical characteristics of the device, then it is enough to know that it corresponds to the thermal power reduced by the compressor power. If we do not know what capacity the compressor has, but we have information about the capacity factor Kp, then the cooling power is calculated with sufficient accuracy by the formula:
Qcool = (Kp - 1) / Kp • Qtopl.
It is necessary to pay attention that the substituted values are reached at a temperature corresponding to that which reigns both in the soil and in the heating system during the operation of the pump at full capacity (for example, 0/35 - brine temperature 0 degrees Celsius, heating system 35 degrees Celsius).
Calculation of the surface of the heat exchanger of a horizontal ground source heat pump.
The strength with which a ground heat exchanger transfers heat depends on the type of soil, namely its moisture content. Depending on this, to calculate the surface of a horizontal heat exchanger, the following values of the thermal power of the soil are taken qg (for polyethylene pipes):
- sandy dry - 10 W / m2
- sandy, wet - 15-20 W / m2
- clayey dry - 20-25 W / m2
- clayey, wet - 25-30 W / m2
- wet (aquifer) - 35-40 W / m2.
Of course, these are indicative values.
It is difficult to assess whether the soil is the same over the entire area intended for the heat exchanger until they start building it, so it is better to take a lower value for the calculation. In a properly made system, the compressor of the heat pump runs from 1800 to 2400 hours per year, the heat output of the soil leads to lengthening the working time.
The surface of the heat exchanger is calculated by the formula:
A = Q / qg
Example: the home's energy demand for heating is 14 kW, and the pump will satisfy them in full (must work in a monovalent system). The selected device receives a thermal power (heating) of 14 kW for parameters 0/35, while achieving an efficiency coefficient Kp = 4.5. The cooling power is, therefore, Qcool = (4.5-1) / 4.5 • 14 = 10.9 kW, that is, 10900 W. The heat exchanger must be made in dry clay soil, therefore its area must be A = 10 900/20 = 545 m2. Attention is drawn to the fact that in the case of an aquiferous soil, the heat exchanger can be two times smaller, but if the soil is sandy, then its area will occupy more than 1000 m2. In such a situation, the best solution is to place the pipes vertically.
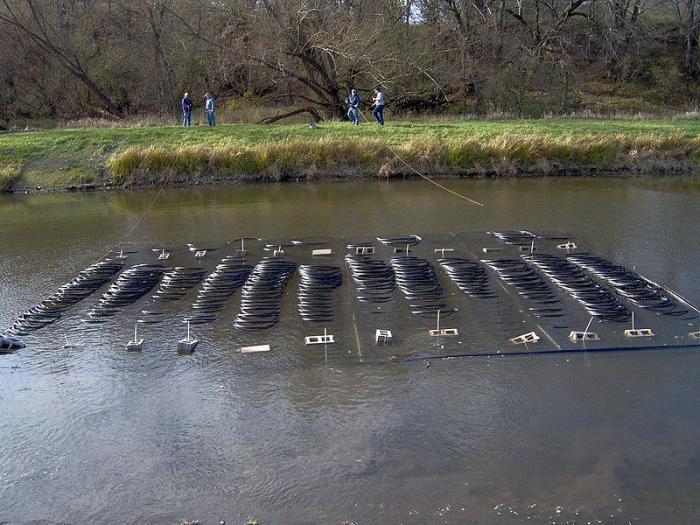
Heat exchanger of a vertical ground source heat pump.
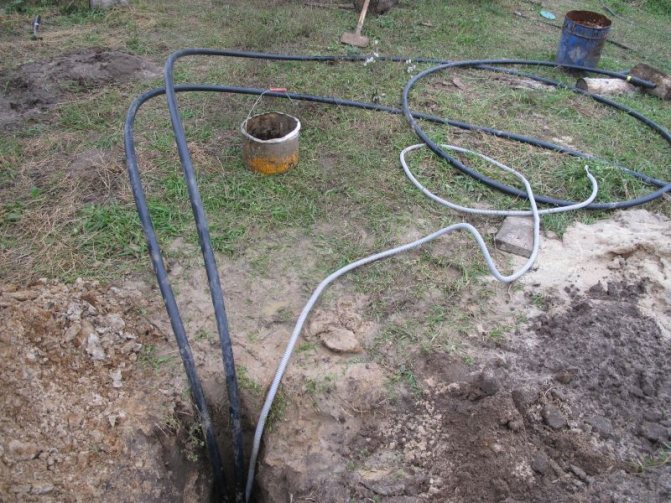
The heat pump achieves a higher efficiency factor Kp when the heat exchanger tubes are positioned vertically in the ground - at a depth of 40-150 m.This is due to the fact that at a depth below 10 m, the temperature of the ground is about 10 degrees Celsius all year round - that is, in winter it is almost ten more than at a depth of 1.5 meters.


The vertical heat exchanger, however, is clearly more expensive than the horizontal one. These are vertical sections of a pipe that forms a loop (the pipe goes down through the holes, at the bottom it turns and goes up). They are called geothermal probes. In this case, they are calculated not by area, but by the total length of the heat exchanger, usually consisting of more than one probe.


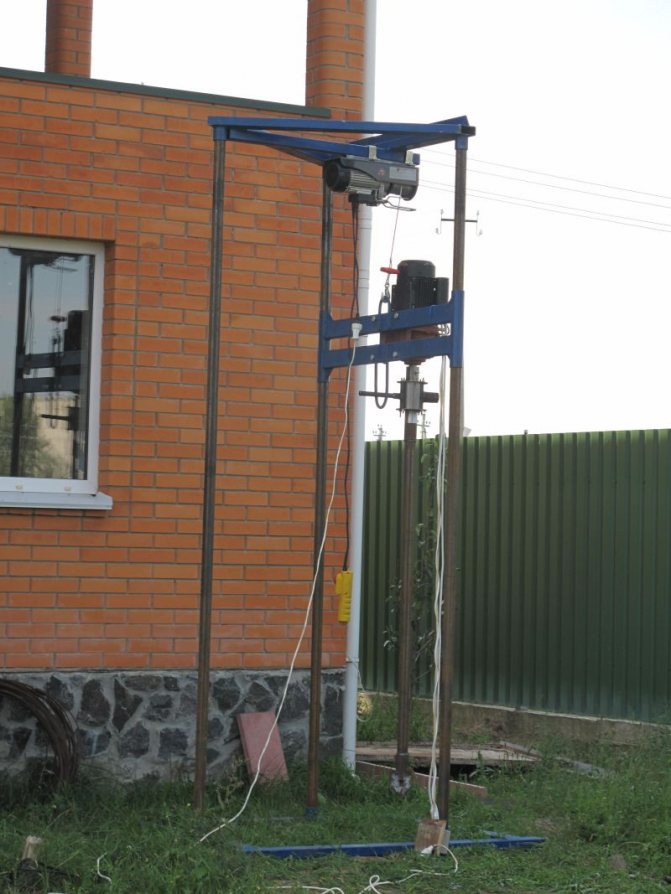
In vertical wells, one or two pairs of pipes (U or Y probe) are placed. Insertion of the well pipe is facilitated by the head, an element connecting the risers that can be adapted to accommodate an additional filling pipe. The head is pushed into the holes, and with it the heat exchanger pipes. Then liquid concrete is poured into the well.


In a Y-type heat exchanger, liquid flows down to the head in one tube and returns from the head in the other. In a double U type heat exchanger, it flows with two pipes down and two up.
The distance between drilling points up to 50 m deep should not be less than 5 m, and in the case of deeper ones from 8 to 15 meters. Must be located on a line perpendicular to the direction of water flow.
Calculation of the length of the heat exchanger of the vertical ground heat pump.
In this case, it is important how the properties of the soil change with depth. Information can be provided by geological maps and documentation of wells previously made in the vicinity. On this basis, it is possible to estimate the thickness of the individual soil layers and calculate the average value of the thermal conductivity coefficient for the area in which the heat exchanger tubes are to be placed.


Calculations, however, are not able to take into account all movements of groundwater and in practice it often happens that the result obtained is significantly different from reality. To be sure that the vertical heat exchanger will work properly, it is necessary to carry out a survey of the soil in the place where the drilling is to be done. In this case, the productivity of the heat of the soil qg also depends on its type.
For PE80 pipes it is:
- dry sandy soil - 10-12 W / m;
- sandy wet - 12-16 W / m;
- medium clay dry - 16-18 W / m;
- medium clay wet - 19-21 W / m;
- heavy clayey dry - 18-19 W / m;
- heavy clay wet - 20-22 W / m;
- wet (aquifer) - 25-30 W / m.
It is necessary to take into account the thickness of individual layers of a certain type of soil and, on this basis, calculate the overall performance of each probe.


The heat output of the soil, in which both layers are dry, like the aquifers, when using double U probes (four pipes in the well), averages about 50 W / m. It can be tentatively assumed that in the case of the applicants' heat pump, in the example of calculating a horizontal heat exchanger (cooling capacity 10.9 kW), holes with a total length of L = 10,900/50 = 218 m are required, that is, for example, four of 55 meters each.
"Ground-water": how best to place it?
Getting heat from the ground is considered the most appropriate and rational. This is due to the fact that there are practically no temperature fluctuations at a depth of 5 meters. A special fluid is used as a heat carrier. It is commonly called brine. It is completely environmentally friendly.
As for the placement method, that is, horizontal and vertical. The first type is characterized by the fact that plastic pipes, representing the outer contour, are laid horizontally on the square. This is very problematic, since the laying work must be carried out on an area of 25-50 square meters. In the case of vertical wells, vertical wells are drilled with a depth of 50-150 meters.The deeper the probes are placed, the more efficient the geothermal heat pump will work. We have already considered the principle of operation, and now we will talk about important details.
Heat pump "Water-to-water": principle of operation
Also, do not immediately discard the possibility of using the kinetic energy of water. The fact is that at great depths, the temperature remains quite high and varies in small ranges, if this happens at all. You can go several ways and use:
- Open bodies of water such as rivers and lakes.
- Groundwater (well, well).
- Waste water from industrial cycles (return water supply).
From an economic and technical point of view, the easiest way is to set up the operation of a geothermal pump in an open reservoir. At the same time, there are no significant structural differences between the pumps "soil-water" and "water-water". In the latter case, pipes immersed in an open reservoir are supplied with a load. With regard to the use of groundwater, the design and installation are more complex. It is necessary to allocate a separate well for water discharge.
The principle of operation of the air-to-water heat pump
This type of pump is considered one of the least efficient for a variety of reasons. First, in the cold season, the temperature of the air masses drops significantly. Ultimately, this leads to a decrease in pump power. It may not be able to cope with the heating of a large house. Secondly, the design is more complex and less reliable. However, installation and maintenance costs are significantly reduced. This is due to the fact that you do not need a reservoir, a well, and you do not need to dig trenches for pipes at your summer cottage.
The system is placed on the roof of the building or in another suitable place. It is worth noting that this design has one significant plus. It consists in the possibility of using exhaust gases, air that leaves the room again. This can compensate for the insufficient capacity of the equipment in the winter.


Air-to-air pumps and more
Such installations are even less common than "Air-Water", for a number of reasons. As you may have guessed, in our case, air is used as a heat carrier, which heats up from a warmer air mass from the environment. There are a large number of disadvantages of such a system, ranging from low productivity to high cost. An air-to-air heat pump, the principle of which you know, is not bad only in warm regions.
There are strengths here as well. First, the low cost of the coolant. Chances are, you will not encounter an air line leak. Secondly, the effectiveness of such a solution is extremely high in the spring-autumn period. In winter, it is impractical to use an air heat pump, the operating principle of which we have considered.
DIY air heat pump: assembly diagram
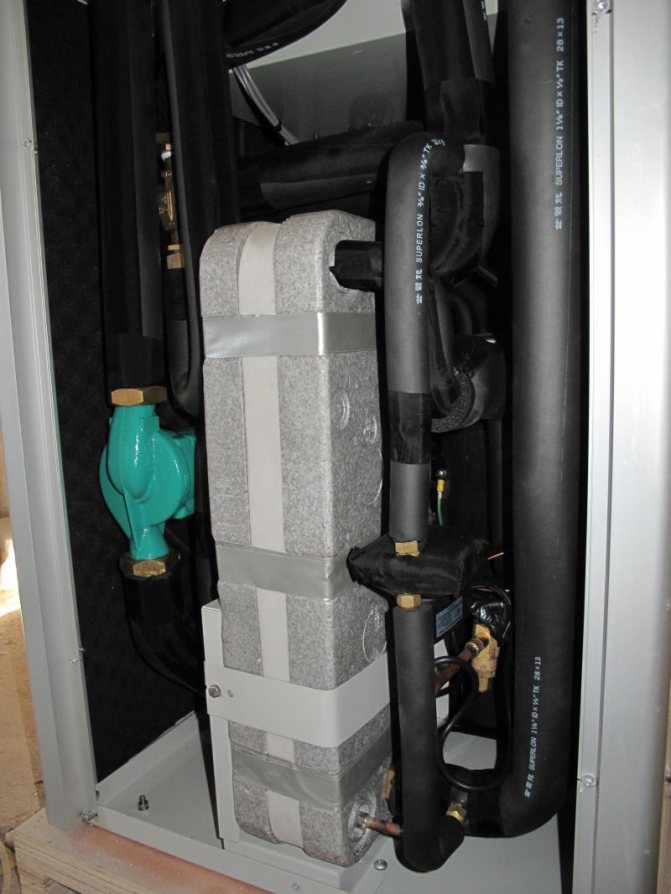
Unlike rather complex geothermal and hydrothermal systems, an air-to-water heat pump is available for manufacturing even on its own.
Moreover, for the manufacture of an air system, we need a relatively cheap set, consisting of the following parts and assemblies:
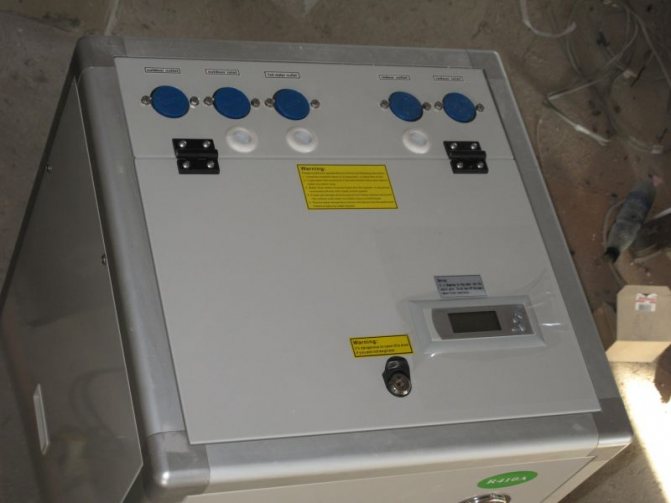
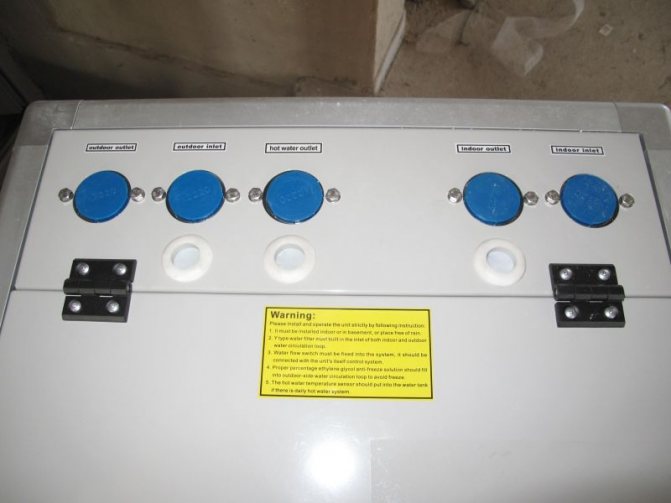
External air-to-water heat pump unit
- Split system compressor - it can be purchased at a service center or in a repair shop
- 100-liter stainless steel tank - can be removed from any old washing machine
- A polymeric container with a wide mouth - a regular can or polypropylene will do.
- Copper pipes with a throughput diameter of more than 1 millimeter. You will have to buy them, but this is the only expensive purchase in the entire project.
- A set of shut-off and control valves, which will include a drain cock, an air etching valve, a safety valve.
- Fasteners - brackets, pipe clips, clamps and others.
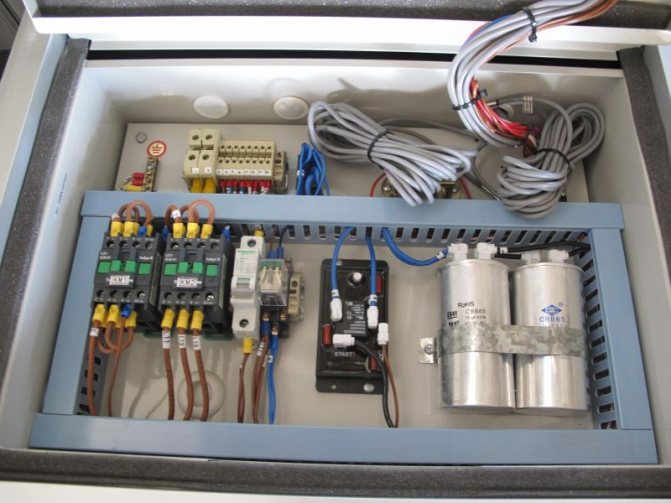
In addition, we will need the cheapest refrigerant - freon and at least the simplest control unit, without which the use of heat pumps will be very difficult, due to the need to synchronize the operation of the compressor with the temperature on the surface of the evaporator and condenser.
Assembly of the unit
Well, the build process itself is as follows:
- We make a coil from a copper pipe, the dimensions of which must correspond to the cross section and height of the steel tank.
- We mount the coil in the tank, leaving the copper pipe outlets outside of it. Next, we seal the tank and equip it with an inlet (bottom) and outlet (top) fitting. As a result, the first element of the system is obtained - the condenser - with ready-made taps for the direct heating pipe (upper fitting) and return (lower fitting)
- We mount the compressor on the wall (using the bracket). We connect the pressure connection of the compressor to the upper outlet of the copper pipe.
- We make a second coil from a copper pipe, the dimensions of which coincide with the cross section and height of the polymer can.
- We mount the coil in the can, installing a fan on its end, which blows air onto the coil. Moreover, two issues should come out of the can. As a result, this whole structure, which is the evaporator of the system, is mounted on the facade or in the ventilation shaft.
- We connect the lower outlet of the tank (condenser) with the lower outlet of the can (evaporator) by cutting a control choke into this pipeline.
- We connect the upper outlet of the can with the suction pipe of the compressor.
That's basically it. The system based on the principle of air heat pump operation is almost complete. It remains only to pour refrigerant into the compressor and connect the throttle valve to the control unit.
Homemade heat pump
Studies have shown that the payback period of the equipment directly depends on the heated area. If we are talking about a house of 400 square meters, then this is approximately 2-2.5 years. But for those who have a smaller housing, it is quite possible to use homemade pumps. It may seem that it is difficult to make such equipment, but in fact it is somewhat not so. It is enough to purchase the necessary components, and you can proceed with the installation.
The first step is to purchase a compressor. You can take the one on the air conditioner. Mount it in the same way on the wall of the building. In addition, a capacitor is needed. You can build it yourself or buy it. If you go with the first method, you will need a copper coil with a thickness of at least 1 mm, it is placed in the case. It can be a tank of a suitable size. After installation, the tank is welded and the necessary threaded connections are made.


Power and efficiency
If the efficiency of geothermal and water heat pumps practically does not depend on the season, then the situation is different with air heat pumps. Performance directly depends on the outdoor temperature, the colder it is, the lower the COP (efficiency).
Many people believe that how much heat it can produce depends on the power of a heat pump, but this is not the case. It characterizes the energy consumption, and the amount of heat generated depends on the efficiency. Accordingly - from the air temperature outside the house.
The final part of the work
In any case, at the final stage, you will need to hire a specialist. It is a knowledgeable person who must solder copper pipes, pump freon, and also start the compressor for the first time. After assembling the entire structure, it is connected to the internal heating system. The outdoor circuit is installed last, and its features depend on the type of heat pump used.
Do not overlook such an important point as replacing outdated or damaged wiring in the house. Experts recommend installing a meter with a capacity of at least 40 amperes, which should be quite enough for the operation of a heat pump.It will not be superfluous to note that in some cases such equipment does not live up to expectations. This is due, in particular, to inaccurate thermodynamic calculations. So that it does not happen that you spent a lot of money on heating, and in the winter you had to install a coal boiler, contact trusted organizations with positive reviews.

Safety and environmental friendliness above all
Heating with the pumps described in this article is one of the most environmentally friendly methods. This is mainly due to the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere, as well as the conservation of non-renewable energy resources. By the way, in our case, renewable resources are used, so there is no need to be afraid that the heat will suddenly end. Thanks to the use of a substance that boils at low temperatures, it became possible to realize the reverse thermodynamic cycle and, with less energy, get a sufficient amount of heat into the house. As for fire safety, then everything is clear. There is no possibility of gas or fuel oil leakage, explosion, no dangerous places for storing flammable materials and much more. In this regard, heat pumps are very good.