Here you will find out:
- What is the calculation of the heating system pump for?
- Selection of a pump according to its main characteristics
- How to calculate the heating circulation pump from the boiler power
- How to choose a circulation pump according to the data obtained
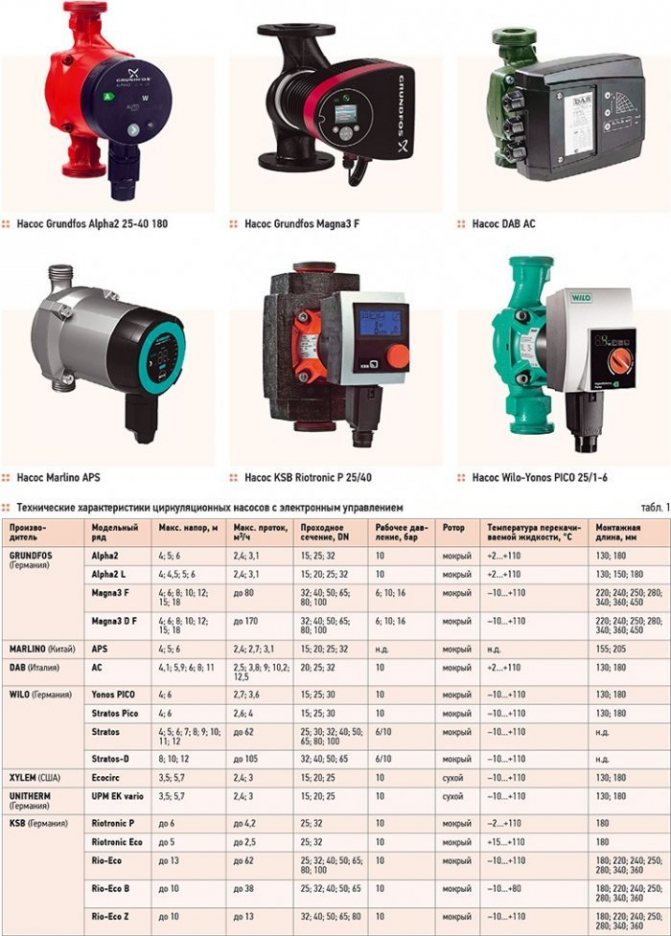
- Empirical pump selection table
- Cavitation in the heating system and in the water supply system
- Pump installation recommendations
The main task of the circulation pump is to improve the circulation of the coolant through the elements of the heating system. The problem of the already cooled water entering the heating radiators is well known to the residents of the upper floors of apartment buildings. Similar situations are associated with the fact that the coolant in such systems moves very slowly and has time to cool down until it reaches the sections of the heating circuit that are at a considerable distance.
When operating autonomous heating systems in country houses, the circulation of water in which is carried out in a natural way, you can also encounter a problem when the radiators installed at the farthest points of the circuit barely heat up. This is also a consequence of insufficient pressure of the coolant and its slow movement through the pipeline. The installation of circulation pumping equipment allows to avoid such situations both in apartment buildings and in private houses. By forcibly creating the required pressure in the pipeline, such pumps provide a high speed of movement of heated water even to the most distant elements of the heating system.
The pump increases the efficiency of the existing heating and allows you to improve the system by adding additional radiators or automation elements
Heating systems with natural circulation of a liquid that transfers thermal energy show their effectiveness when they are used to heat houses of a small area. However, if you equip such systems with a circulation pump, you can not only increase the efficiency of their use, but also save on heating, reducing the amount of energy consumed by the boiler.
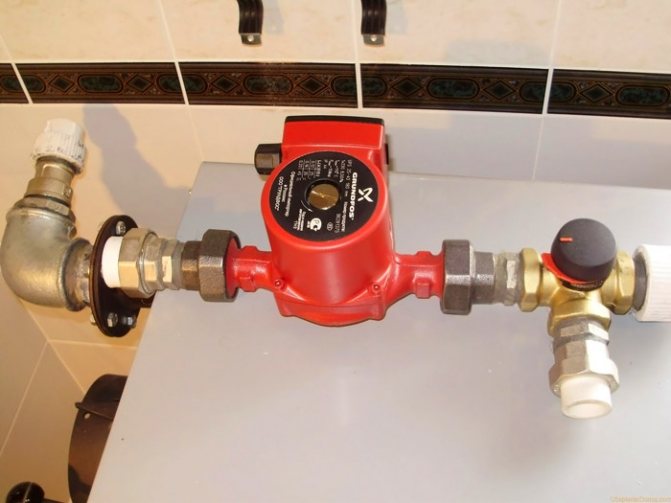
By its design, the circulation pump is a motor, the shaft of which transmits rotation to the rotor. A wheel with blades is installed on the rotor - an impeller. Rotating inside the working chamber of the pump, the impeller pushes the heated liquid entering it into the discharge line, forming a coolant flow with the required pressure. Modern models of circulation pumps can operate in several modes, creating different pressures of the coolant moving through them in heating systems. This option allows you to quickly warm up the house at the onset of cold weather by running the pump at maximum power, and then, when a comfortable air temperature is formed in the whole building, switch the device to an economical mode of operation.
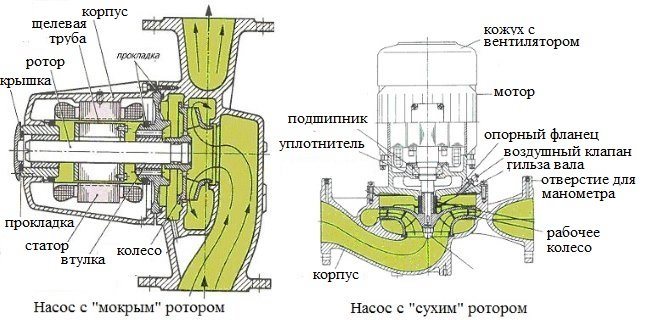
Circulation pump device for heating
All circulation pumps used to equip heating systems are divided into two broad categories: devices with "wet" and "dry" rotor. In pumps of the first type, all rotor elements are constantly in the coolant medium, and in devices with a "dry" rotor, only a part of such elements is in contact with the pumped medium. Pumps with a "dry" rotor differ in greater power and higher efficiency, but they make a lot of noise during operation, which cannot be said about devices with a "wet" rotor, which emit a minimum amount of noise.
What is the calculation of the heating system pump for?
Most modern autonomous heating systems used to maintain a certain temperature in living quarters are equipped with centrifugal pumps that ensure uninterrupted circulation of liquid in the heating circuit.
By increasing the pressure in the system, it is possible to reduce the temperature of the water at the outlet of the heating boiler, thereby reducing the daily consumption of gas consumed by it.
The correct choice of the circulating pump model allows an order of magnitude to increase the level of efficiency of the equipment during the heating season and to provide a comfortable temperature in rooms of any area.


Selection of a pump according to its main characteristics
The main technical characteristics of any pump for heating are:
These parameters must ensure sufficient circulation of the coolant for efficient transfer of thermal energy from the boiler to the radiators, so they must correspond to both the power of the system itself and the hydraulic resistance in it during the circulation of the coolant. Therefore, in order to make the correct selection of a pump for a heating system, it is necessary to know both of these values.
Their exact calculations, which are used by specialists, are rather cumbersome and complicated. Therefore, with self-selection, you can use simplified calculations using the below simple formulas and recommended average indicators that will allow you to select the optimal characteristics of the circulation pump. Moreover, almost everyone can do such calculations.
Three options for calculating thermal power
Difficulties may arise with the determination of the thermal power indicator (R), therefore it is better to focus on generally accepted standards.
Option 1... In European countries, it is customary to take into account the following indicators:
- 100 W / sq. - for private houses of small area;
- 70 W / sq. M. - for high-rise buildings;
- 30-50 W / sq. - for industrial and well-insulated living quarters.
Option 2... European standards are well suited for regions with mild climates. However, in the northern regions, where there are severe frosts, it is better to focus on the norms of SNiP 2.04.07-86 "Heating networks", which take into account the outside temperature up to -30 degrees Celsius:
- 173-177 W / m2 - for small buildings, the number of storeys of which does not exceed two;
- 97-101 W / m2 - for houses from 3-4 floors.
Option 3... Below is a table by which you can independently determine the required thermal power, taking into account the purpose, the degree of wear and tear and thermal insulation of the building.
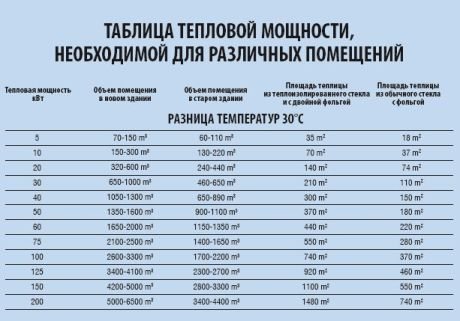

Table: how to determine the required heat output
How to determine the power of the heating system and the required pump flow
The required thermal power of the heating system depends on the amount of heat that is required for comfortable heating of the house and is in direct proportion to its size and the thermal insulation properties of the materials from which its walls, roof, ceiling, floor, windows, doors are made. It is not difficult to calculate the size of a house or part of it heated. A tape measure and a calculator are enough here.
It is more difficult to calculate accurately the heat loss through external structures, since here their material, thickness and design features must be taken into account. Therefore, for a simplified calculation, you can use the recommended average values of 1-1.5 kW of thermal power per 10 m2 of a heated room with a ceiling height of up to 3 m.If the room is well insulated, then you can use a lower value, and if it is not insulated or not enough, then it is better use a larger value.
For example, for a well-insulated house with an area of 120 m2, approximately 12 kW of thermal power will be needed.If the selection of a circulation pump is carried out for an existing natural circulation heating system, then the power of the installed boiler can be taken into account.
Calculation of the required pump capacity
Having decided on the thermal power of heating, you can start calculating the flow (capacity) of the circulation pump. To do this, you can use two simple formulas. The first of them: P = Q / (1.16 x ΔT), (kg / h or l / h) Where:
- Q– previously calculated heating power (W);
- ΔT is the difference between the temperature of the supply pipe and the "return", which for conventional systems, as a rule, is within 20 ° C, and for underfloor heating - about 5 °;
- 1.16 - coefficient taking into account the specific heat of water, W × h / kg × о С (for other coolants (antifreeze, oil) it will be somewhat different and, if necessary, can be found in reference books or on the Internet).
Another formula: P = 3.6 x Q / (s × ΔT), (l / h) Where: s is the heat capacity of the heat carrier (for water 4.2 kJ / kg × ° С). Using any of these formulas, it is possible to determine that, for example, for a two-pipe system with a thermal power of 12 kW, a pump with the following capacity (supply) will be required: P = 12000 / (1.16 × 20) = 517 l / h or 0.5 m3 / h
Calculation of the required head to overcome hydraulic resistance
In order to select a circulation pump for a heating system, in addition to capacity, it is necessary to determine its head (pressure), which it must create in order to overcome the existing hydraulic resistance. But first you need to know the magnitude of this resistance. For a simplified calculation, you can use the formula: J = (F + R × L) / p × g (m) Where:
- L is the length of the pipe line to the most distant radiator (m);
- R is the specific hydraulic resistance of the straight pipe section (Pa / m);
- p is the density of the coolant (for water - 1000 kg / m3);
- F - increase in resistance in connecting and shut-off valves (Pa);
- g - 9.8 m / s 2 (acceleration of gravity).
The exact values of R and F for different pipes, connecting and shut-off valves of different types can be found in the reference literature. For our simplified calculation, you can use the average data of these values obtained experimentally: R - 100-150 Pa / m (the larger the diameter of the pipes and the smoother their inner surface, the less resistance); F can be taken depending on the type of fittings:
- additionally up to 30% of losses in a straight pipe - for each connecting fitting in this section;
- up to 20% - for a three-way mixer or similar devices;
- up to 70% - for the regulator.
You can also use the formula proposed by the specialists of the well-known pump manufacturer Wilo for the calculation: J = R × L × k, m Where: k is the coefficient that takes into account the increase in resistance in the control and shut-off valves:
- 1.3 - simple heating systems with a minimum number of fittings;
- 2.2 - in the presence of control valves;
- 2.6 - for complex systems.
It should be borne in mind that if circulation in a system with two or more wiring circuits (branches) will be provided by only one pump, then their total resistance should be taken into account to select its pressure. If each circuit is provided with a separate pump, then the calculation of the thermal power and resistance of each of them must be performed separately. The number of storeys of a building, when calculating the pressure, does not play a big role. Because in a closed heating system, the liquid column of the supply line is balanced by the “return” column.
Number of speeds of the circulation pump
Most modern models of circulation pumps are equipped with the ability to adjust the speed of the device. Most often these are three-speed models, with which you can adjust the amount of heat entering the room. So, with a sharp cold snap, the pump speed is increased, and in case of warming, it is reduced so that the air temperature in the rooms remains comfortable for living.
For gear shifting, there is a special lever located on the device body. The models of circulation pumps are very popular, equipped with a system of automatic control of the speed of the device, depending on the change in the outside air temperature.
It should be noted that this is just one of the options for this kind of calculations. Some manufacturers use a slightly different calculation method when selecting a pump. You can ask a qualified specialist to carry out all the calculations, informing him of the details of the device of a specific heating system and describing the conditions for its operation. Typically, the maximum load indicators at which the system will operate are calculated. In real conditions, the load on the equipment will be lower, so you can safely purchase a circulation pump, the characteristics of which are slightly lower than the calculated indicators. The purchase of a more powerful pump is not advisable, as this will lead to unnecessary costs, but the system will not improve the performance.
After all the necessary data has been obtained, the pressure-flow characteristics of each model should be studied, taking into account different operating speeds. These characteristics can be presented in the form of a graph. Below is an example of such a graph, in which the calculated characteristics of the device are also marked.
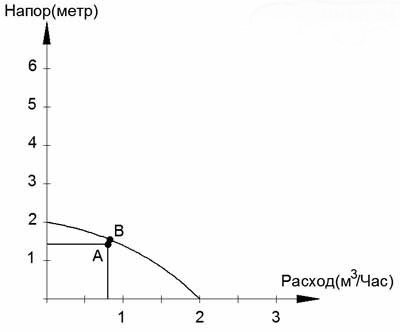

Using this graph, you can select a suitable model of a circulation pump for heating according to the indicators calculated for the system of a particular private house
Point A corresponds to the required indicators, and point B indicates the real data of a specific pump model, as close as possible to theoretical calculations. The smaller the distance between points A and B, the better the pump model is suitable for the specific operating conditions.
Circulation pump speed control
Pump speeds are the ability of the instrument to vary performance. It is easy to find out about the availability of modes - not one power will be indicated in the description, but several (usually three).
Read more: How to calculate a wind generator using the formulas
In the same way, the rotation speed and productivity are indicated in three versions. For example: 70/50/35 W (power), 2200/1900/1450 rpm (rotation speed), head 4/3/2 m.
There are models that automatically change the speed of work (and hence the performance), depending on the ambient temperature.
There is a special switch on the pump body to change the mode. Manual models are advised to set to the maximum power mode and turn it down if necessary. In automatic devices, you just need to remove the regulator from the lock.
The presence of speed modes is not only for increasing comfort. It is also economically justified. Up to 40% of energy can be saved by a mode device versus a conventional one.
Most models of the circulation pump have a function for adjusting the speed of the device. As a rule, these are three-speed devices that allow you to control the amount of heat that is sent to heat the room. In the event of a sharp cold snap, the speed of the device is increased, and when it becomes warmer, it is reduced, while the temperature regime in the rooms remains comfortable for staying in the house.
To change the speed, there is a special lever located on the pump housing. Models of circulation devices with an automatic control system of this parameter depending on the temperature outside the building are in great demand.
To change the speed, there is a special lever located on the pump housing. Models of circulation devices with an automatic control system of this parameter depending on the temperature outside the building are in great demand.
Most models of the circulation pump have a function for adjusting the speed of the device. As a rule, these are three-speed devices that allow you to control the amount of heat that is sent to heat the room.In the event of a sharp cold snap, the speed of the device is increased, and when it becomes warmer, it is reduced, while the temperature regime in the rooms remains comfortable for staying in the house.
How to calculate the heating circulation pump from the boiler power
It often happens that the boiler was purchased in advance, and the remaining elements of the system are selected later, focusing on the power indicators of the heater declared by the manufacturer. Often, a circulation pump is bought for the modernization of natural circulation heating systems in order to provide the possibility of accelerating the movement of the coolant.
If the power of the boiler is known, use the formula: Q = N / (t2-t1)
Q - pump flow rate in cubic meters / h;
N is the boiler power in W;
t2 - water temperature in degrees Celsius at the outlet from the boiler (inlet to the system);
t1 - on the return line.
How to calculate hydraulic resistance?
In order not to count manually, use our calculator.
It has already been discussed that the selection of a circulation pump for the heating system is directly influenced by such an important parameter as the hydraulic resistance, which is created by individual elements of the heating system, allows you to calculate the pump suction height and, as a result, makes it possible to choose a model of equipment in terms of power and the pressure generated. To calculate the suction of the pump (denoted by the letter H), use the following formula:
H = 1.3 x (R1L1 + R2L2 + Z1 …… ..Zn) / 10000
The parameters used in this formula are shown in the table.
| Designation | Parameter | unit of measurement |
| R1, R2 | Pressure loss generated by the circulation pump in the supply line of the pipeline and in the return | Pa / m |
| L1, L2 | Length of the supply part of the pipeline and return | m |
| Z1 ... Zn | Hydraulic resistance, which is created by individual elements of the heating system | Pa |
The R1 and R2 values that apply to this table should be selected from a special information table.
The values of the hydraulic resistance that are created by various devices used to equip heating systems, as a rule, are prescribed in the technical documentation for them. If there is no such information in the passport of the device, then you can take the approximate readings of the hydraulic resistance (see table).
| Heater | Hydraulic resistance, Pa |
| Boiler | 1000–2000 |
| Sanitary mixer | 2000–4000 |
| Thermal valve | 5000–10000 |
| Heat meter | 1000–1500 |
There are special information tables that allow you to find out the hydraulic resistance for almost any element of the heating system equipment.
Knowing the suction lift, for the calculation of which the above formula is used, you can quickly select a circulation pump according to its capacity and find out its required head.
How to choose a circulation pump according to the data obtained
After completing the calculations and determining the main parameters (flow and pressure), we will proceed to the selection of a suitable circulation pump. To do this, we use graphs of their technical characteristics (B), which can be found in the passport or operating instructions. Such a graph should have two axes with the values of head (usually in m) and flow (capacity) in m3 / h, l / h or l / s. On this graph we plot the data obtained during the calculation, in the appropriate dimension and at their intersection we find the point (A). If it is above the pump characteristic curve (A3), then this model does not suit us. If the point falls on the chart (A2) or is below it (A1), then this is a suitable option. But it must be borne in mind that if the point is significantly lower than the graph (A1), then this means that the pump will have an excessive power reserve, which is also impractical, since it will consume more electricity and its cost will also be higher than the model, the characteristic graph which will be as close as possible to our point.
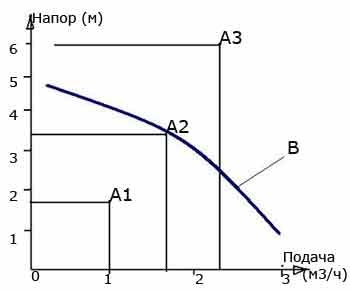

There are models of pumps that have not one, but 2-3 speeds.The graphs of their characteristics will have not one, but, respectively, 2 or 3 lines. In this case, the selection of the pump must be done according to the schedule of the speed that will be used or taking into account all lines if all speeds are used.
What else influences the choice
The selection of a pump for a heating system, in addition to its main parameters (pressure and flow), can be influenced by some other factors, for example, such as: manufacturer, workmanship, durability, maximum operating temperature, cost, etc. Often they are related. Quality pumps of reliable, "Wilo", "DAB", "Lowara", "Ebara" and "Pedrollo" usually have a high price tag. Chinese or domestic models, as a rule, are much cheaper, but there is no guarantee of their reliability and long-term operation. Here it all depends on personal choice: either a high-quality reliable product at a higher price or a cheaper, but less reliable circulation pump, which may soon have to be changed. Sometimes, in order to save money, they buy used Grundfos or Wilo. Often, they normally work longer than new Chinese ones, but if purchased from trusted specialists, who can give a certain guarantee.
Another technical parameter that can be important when choosing a circulation pump is the maximum allowable temperature for its operation, which should also be in its passport or operating instructions. This is especially important if the pump is to be installed in a heating system with a solid fuel boiler on the supply pipe. The maximum permissible operating temperature of it, in this case, must be at least 110 ° C. If, however, it will be installed on the return line, then this parameter is not so important, since the temperature of the coolant in this place rarely exceeds 70 ° C.
Related Videos:
| Next> |
Empirical pump selection table
| Heated area (m2) | Productivity (m3 / hour) | Stamps |
| 80 – 240 | 0.5 to 2.5 | 25 – 40 |
| 100 – 265 | Same | 32 – 40 |
| 140 – 270 | 0.5 to 2.7 | 25 – 60 |
| 165 – 310 | Same | 32 – 60 |
Note: in the third column, the first number is the diameter of the nozzles, the second is the lift height.
Using the given data, you can easily select the right device for stable and long-term operation without much hassle.
Cavitation in the heating system and in the water supply system
Cavitation is a process during which steam molecules are formed in a heating system due to a decrease in pressure. This process takes place if the fluid flow rate decreases or increases in the pipes.
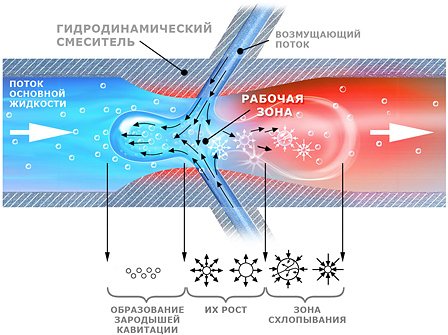

Heating system cavitation
If the heating system is characterized by too low or too high temperatures, then this phenomenon can have a negative effect. The steam that forms collects in bubbles, and if they burst, then, thereby, damage the material from which pipes or other components of the heating system are made.
A correctly selected device and a correctly carried out calculation of the power of the heating circulation pump will guarantee that the operation of the heating system and the water supply system will be most efficient.
If you cannot independently carry out such operations as calculating a pump for heating, or you doubt their correctness, then it is better to entrust this matter to a professional in this field. The specialist will not only help with choosing a pump or making calculations, but will also deal directly with the installation of the pump.