In what cases is it compiled
The act is required for:
- Commissioning of new equipment. The act will be a confirmation that each element is in its place, the installation was carried out responsibly, the system is working.
- The onset of the heating season. After a summer break in operation, the pipes could fail. After checking their capacity, an act is drawn up.
- Already carried out repair work.
- The emergence of docked emergency situations on the pipeline. In this way, specialists identify the amount of work required, the weak points of the existing heating network.
For the smooth operation of the heating system, preventive control checks are necessary, reliable information about the high-quality functioning of the system at startup.
Heat circulation rules in the house
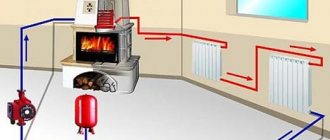
In fact, the pump is required mainly to compensate for losses during the movement of the coolant through the pipes. That is why circulating pumps for domestic heating systems have a relatively low power and rather low energy consumption (about 100 W), like a conventional lamp.
The circulating pump consists of a cast-iron body, inside which there is a rotor (rotating part) and an impeller mounted on it. The rotor spins - the impeller pushes the water. One of the basic rules for installing a pump in a system: the rotor axis must be positioned horizontally. When properly installed, circulating pumps are virtually silent. The operation of the pump can only be checked by slight vibration by touching it with your hand.
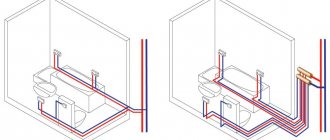
Indoor temperatures are easier to control and adjust if you use two-pipe wiring. At the same time, two pipes are connected to each heating device: direct and reverse. Then the temperature of the coolant at the inlet of all devices will be the same. Two-pipe wiring is similar to the parallel connection of electrical appliances, when "plus" and "minus" are connected to each from a common source. But the methods of performing two-pipe wiring in the house may be different. The pipes can be “starred” when two pipes are drawn to each radiator. In a wiring in the form of a "loop", two pipes, supply and return, sequentially bypass a number of devices.
Place the distributor comb so that the distances from it to the radiators are approximately the same. The length of the pipeline to different heating devices should not differ greatly, in any case, dozens of times. Otherwise, the pressure drop of the coolant on a long section will be much greater than on a short one. In this case, it will be almost impossible to adjust the system normally.
As a rule, a modern house has a rather complex heating system that combines several independent circuits. The ideal solution in this case is the use of special fast assembly systems, or, as they are also called, pumping groups. Such devices have all the elements necessary to connect the entire range of possible equipment to the boiler. The pumping groups themselves are designed for solving specific problems, so it remains only to choose the desired modification.
The essence and types of crimping
Nowadays, heating is most often carried out by the "water circuit" system. In this case, the heated water circulates through the labors, imparting its thermal energy to the premises. Leaks are unacceptable, the pipeline must be completely sealed for normal operation.Pressing, on the other hand, deliberately creates a volume in the pipe that is greater than normal.
When this is done with air, it is called pneumatic pressing.
When using water, then hydro-pressing. The latter method is considered safer and therefore more popular. For this reason, an example of hydraulic pressing is given as a blank.
When testing, it is recommended not to exceed the pressure inside the pipe by more than 15 MPa. When it comes to raising pressure with water, then there are limitations. The maximum possible pressure should not exceed the normal operating pressure by more than 30%.
In multi-storey buildings, they resort to pneumatic pressing if the pipes are very old and there is a possibility of flooding. But then a level of risk arises and all residents must be notified of the tests being carried out.
The work process is simple, but multi-stage. The algorithm looks like this:
- The necessary materials and equipment are being prepared.
- Draining the liquid that was in the heating system earlier.
- Uploading a new one.
- Create the highest possible test pressure.
- Taking control measurements after 10 minutes.
- Flushing, adjusting the heating system to normal pressure values inside.
- Documentary registration of the work performed, the formation of reports and acts.
But this is how the list of procedures looks only if there are no "thin spots" in the heating system and, accordingly, the tightness in it is not violated. If the pressure drops quickly, does not hold, then the system needs repair work. In such a situation, the specialist performs the necessary actions (pipe replacement, sealing of connections, cleaning, etc.), and then starts pressure testing from the very beginning. Only a heating system that has passed the test is approved for the heating season.
An important nuance! Pressure testing should be carried out after cleaning and flushing the pipes. Otherwise, salt and other deposits inside them can mask possible external damage and breakouts.
If there are deposits of the order of 1 cm on the inner surface, then this reduces the overall heat transfer and efficiency by 15 percent or more of the total indicators. For documentary confirmation of cleaning, a special act is also drawn up.
Heating system connection
H2_2
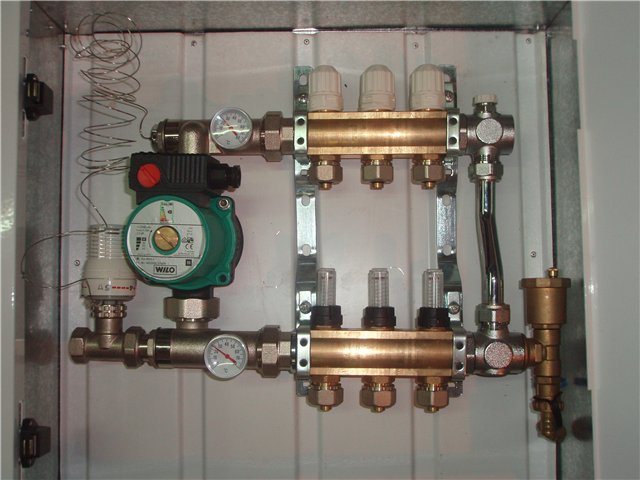

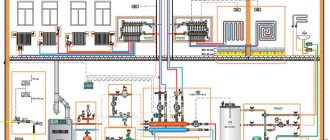
The order of connecting all elements of the system to each other includes three main stages. The work consists of installing a boiler, a tank, a pump, laying highways and installing heating radiators. After that, commissioning works are carried out, and only then the system will be ready for operation.
The first stage in the installation of the system is to install the boiler as the center of all heating circuits. The installation site should be well ventilated, with a natural light source and a gas leak detector. The gas boiler is installed in the place where gas, water and electricity are supplied. After connecting the heating device, it will also be necessary to run the main pipes for supplying water to the heating and hot water supply circuit, as well as the coolant drain line. Water shut off valves are connected to these pipes.
Laying of main pipes and installation of radiators
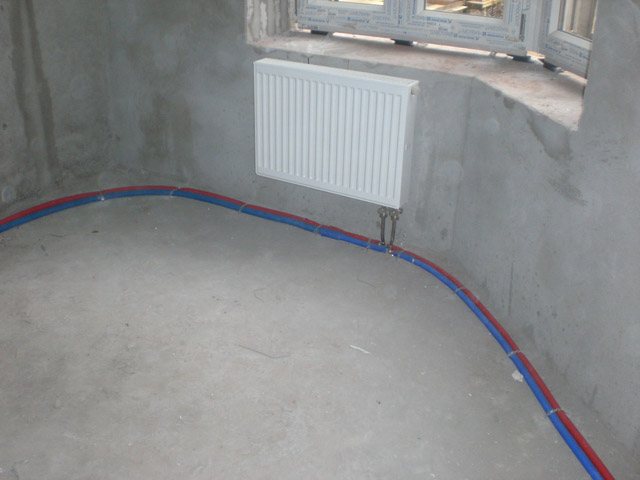


For systems with not too high working pressure, it is best to choose pipes made of XLPE, polypropylene or metal-reinforced plastic, which are connected either by soldering or using fittings. The installation process is not too complicated, the main thing is to correctly connect all the pipes and carefully check all the connection points. For open systems, it is important to ensure the design angle of inclination of the pipes during operation.
Ensuring the most efficient heat transfer from radiators involves connecting them at certain distances from adjacent surfaces. The installation rules are as follows: from the window sill, the batteries should lag by 100 mm, from the floor - by 120 mm, and from the wall - by 20 mm.Radiators are connected to the mains supplied from the boiler - either one, with a serial connection, or two, with an additional pipe for removing the water that has given off heat. The connection diagram is selected depending on the operating conditions of the heating system and the length of the circuits.
Advice! Additionally, temperature regulators can be installed on the batteries.
Testing and acceptance of heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems into operation
Reliable and efficient operation of heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems depends on the quality of the project, installation and operation. The presence of errors at any stage of the life cycle of systems can significantly affect the parameters of the microclimate in the premises and, as a result, on the well-being and performance of a person.
In the operation of HVAC systems, the main stages can be distinguished:
- commissioning, adjustment and adjustment of operating modes;
- acceptance into operation;
- Maintenance.
They can be conditionally divided into documentary and technical (practical) parts (Table 1). That is, this is the maintenance of documents that allow you to identify and delimit the areas of responsibility of performers, and the actual work associated with adjustment, adjustment, repair, etc. The documents increase the level of responsibility of the contractors.


In this article, we will talk about the process of accepting heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems into operation.
Commissioning of HVAC systems, as a rule, is carried out after completion of installation or overhaul. Actually, the acceptance process is the transfer of the heating system to the customer by the installation contractor. This process is similar to buying any thing, all the details are important here: quality, price, appearance, etc.
Also, when accepting HVAC systems, it is important:
- availability of technical and operational documentation (approved projects with working drawings, an explanatory note with changes adopted during installation, acts and protocols justifying the adopted changes, acts of hidden work, acts of pre-launch tests and system adjustments);
- the quality of the work performed;
- compliance of the installed system with the project;
- system performance (indoor climate).
If changes were made during the installation work, then it is advisable to coordinate them with the design organization and the customer.
Before the representative of the customer and the contractor get together and sign the acceptance certificates, it is necessary to carry out all the necessary measures. The main activities related to the adjustment and adjustment of heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems are: comparison of design and actual indicators; tests; adjustment; setting of operating modes; control of microclimate parameters in the room.
So, let us summarize the intermediate result when accepting HVAC systems into operation and note the important actions.
1. Necessary tests and adjustments of systems. They will provide a uniform and required microclimate in the premises, which means good health and mood of the customer.
2. Checking the quality of the installation. Poor-quality installation can be seen at once by a number of signs: it is impossible to establish the system, bring it to operating mode, it is inoperative, looks terrible and naturally causes aesthetic discomfort. If initially the assembly "bloopers" did not give themselves out, then problems will appear in the future, for example, the presence of leaks.
Bad installation means inoperability or poor performance of the system and guarantees the dissatisfaction of the customer who spent the money and, in the most unfavorable set of circumstances, will want to return it.
3. Registration of the process of putting HVAC systems into operation.The signing of the acceptance certificate, which is a borderline, after which the contractor receives money and the burden of responsibility for the system's performance.
Tests of ventilation and air conditioning systems are carried out when they are put into operation, after installation, overhaul and during the operation of these systems. The frequency of periodic testing depends on the purpose of the premises (and the requirements for them) that serve these systems.
The purpose of any test is to test something under "extreme" conditions - increased load, pressure, temperature, flow, etc. The minimum goal of this activity is to determine if the system under test is working. With regard to heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems, a check is carried out in order to assess their parameters. And from the point of view of operation, the main quality is work efficiency. For example, in heating systems, efficiency is determined by the comfortable temperature, in ventilation systems - by the purity of the air and its normalized mobility. The criteria for evaluating air conditioning systems are comfortable temperature, relative humidity, cleanliness and normalized air mobility. If these parameters do not correspond to the comfortable ones, then the system is ineffective or ineffective.
Table 2 shows a generalized classification of tests for HVAC systems.
In accordance with [1, 2], tests are classified according to the following main features:
- by appointment - pre-launch, acceptance, operational;
- content - technical and efficiency;
- by volume - individual, autonomous and complex.
Pre-start tests precede the start-up of systems and are required primarily to check the system's operability, to match the actual operating modes with the design ones, and to set up the systems. These include: hydraulic, thermal tests of heat exchange equipment (air heaters and air coolers), individual equipment tests, etc.
Acceptance tests are needed to verify the operation and efficiency of systems. They are conducted by a special commission. Based on the test results, an acceptance certificate is drawn up.
Performance tests are carried out primarily to check and monitor the status of systems. Based on the results of these tests, an operational adjustment of the system can be carried out.
Technical tests are aimed at the removal and control of the main indicators of the system.
Efficiency tests are the verification of the conformity of the actual and required parameters of the microclimate.
Individual tests are a verification of the technical characteristics of a piece of equipment.
Autonomous tests verify the performance of the system.
Comprehensive tests are carried out to check the efficiency of the entire complex of systems. Technical tests of HVAC systems include:
- hydraulic (hydrostatic) heating systems and other piping systems; the purpose of these tests is to control the tightness;
- thermal testing of heating systems is the control of the uniformity of heating of heating devices and the temperature drop of the coolant;
- aerodynamic testing of ventilation and air conditioning systems - a test directly for the ability to provide the required air distribution in the premises and for the tightness of air ducts.
The presented list is far from complete - measurements of other parameters of the system (temperature, pressure, flow rate, speed, concentration) were “left out of brackets”.
We will provide a detailed description of these and other tests in subsequent articles. As you can see, the process of accepting systems into operation is important for both the customer and the contractor.After all, a well-performed work on setting up systems is the key to the success of people in the room, the customer, as well as the success of the performers of design and installation work.