Classification of heat supply systems

In science, there are many options for systematizing communications, depending on the parameter under study. For us, first of all, it is important that there is an open and closed heat supply system. It can also be centralized (within a quarter, district, settlement or even an entire region) and decentralized (individual or local). According to the quality of water supply, systems are divided into municipal and industrial. The total number of classifications is much wider, but they do not apply to the topic under consideration.


Heating system concept
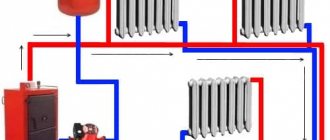
Central heating provides several forms of hot water supply.
The system consists of:
- a device for heating;
- pipes;
- fittings of the water-folding type;
- forced circulation.
The quality of the materials used and the work carried out takes into account the requirements, since water passes through the pipes, heated to 75 C.
If the option of self-installation of the heating system is chosen, the installation rules must be taken into account. This will help reduce the likelihood of injury while using the system.
Heating options
Heat supply schemes can be of several types.
Including:
- centralized;
- decentralized.
The first system is presented in the form of a diagram, which includes boiler room and many consumers heat. It is often used for an apartment building. The decentralized type of hot water supply is characterized by autonomy. The heating of the resource is realized next to the elements of the water-folding type.
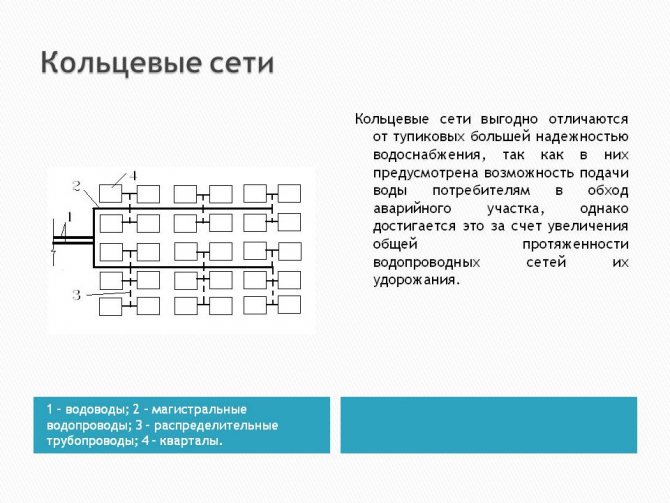
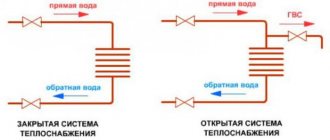
In addition, the system can be open and closed type... In the first case, hot water is drawn from the heating circuit. The closed circuit assumes that cold water drawn from the water supply is heated.
These types of DHW have certain pros and cons. For example, the use of a closed circuit assumes the presence of additional units; in an open system, the quality of water is low.
Features of an open system
It is characterized by the circulation of the coolant obtained from the general communications. An open hot water supply system is when water enters the batteries from the hot water main pipe. From the same source from where the hot water goes to the residents' taps.
The system is based on natural circulation. Due to physical phenomena, the cooling water, acquiring a large mass, will displace the hot stream, giving it acceleration. In some cases (in large systems), the circulation is pumped by means of pumps.
Open type heating is usually installed in high-rise buildings. The main plus here is that there is no need for special mechanisms or devices for heating the coolant. For private households, such a system will be unnecessarily expensive, because the heating pipe will have to be connected to some high-rise building or dig a hole to dock with the highway.
Main advantages
Let's list the main advantages:
- energy independence and centralized supply;
- smooth circulation of the carrier in the system without sudden pressure surges;
- ability to work in case of emergency due to redundant DHW lines.
However, an open heating system is not ideal.
disadvantages
The main disadvantages include:
- high heat loss and, accordingly, unnecessary costs for heating water;
- dependence on the performance of large highways, in the event of an emergency, the supply of hot water supply may stop in a large number of houses;
- water quality decreases due to defects in the mains, in particular, rusty pipes;
- branched open systems require constant monitoring and careful calculations of delivery volumes, heating temperatures and pressures.
Consider an alternative.
Closed DHW system
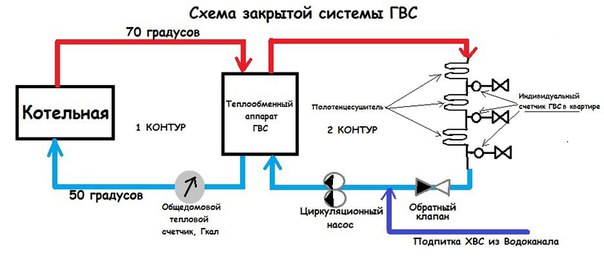

Requires own heater in the apartment. The dead-end DHW system works on the principle of taking cold water from a common pipeline, which then passes through special equipment that carries out heating. A closed hot water system is a more economical solution. The tenant will be able to independently regulate the heating temperature.
What types of heaters are there
The most common are two main options. Consider certain types of water heating equipment.
Flow devices
An example of this type is an ordinary gas water heater. The principle of operation is aimed at instantaneous heating of the water passing through the water heater. The inconvenience of working with such a device is due to the fact that it must be turned on every time you need to use hot water. In this case, the crane should work at this moment. Modern speakers turn on automatically, but the gas wick must burn constantly.
Heating devices
Storage tanks are becoming a more economical solution. Such a device is larger than a column. It contains a container in which volumes of water are accumulated and gradually heated to the desired temperature. At the same time, heating in the tank is maintained with insignificant energy consumption. The downside of the equipment is that it takes a long time to reach an acceptable temperature level. Boilers are usually powered by electricity.
Main menu
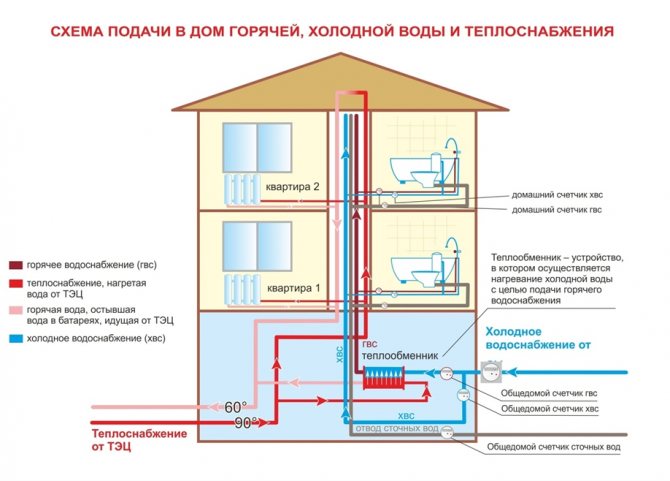
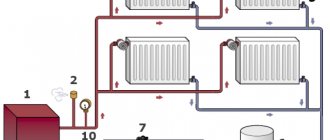
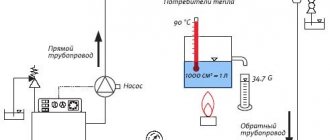
Hi everyone! The hot water supply system for district heating is of two types: open and closed. In this article, we will take a closer look at the open DHW circuit. First of all, what is the fundamental difference between these two schemes. With an open DHW circuit, hot water is drawn directly from the heating network, that is, in simpler terms, the hot water from the mixer tap runs the same as in the heating radiators.
The hot water supply system is connected directly to the heating point of the building. The photo below shows how this happens. One branch is embedded from the supply pipeline,


and the second branch from the return pipeline.
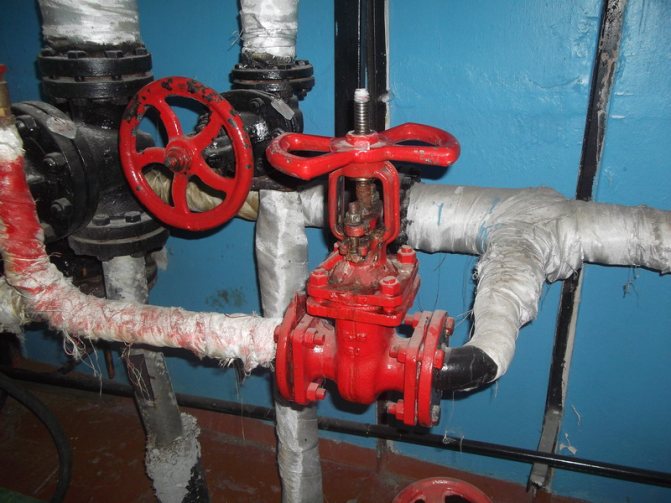


These two branches are mixed in a hot water supply temperature controller, the function of which is to provide the consumer with hot water with the required parameters, namely, not lower than 60 ° C for an open DHW circuit, and not higher than 75 ° C for both a closed and an open circuit in accordance with SNiP 2.04. 01-85 "Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings".
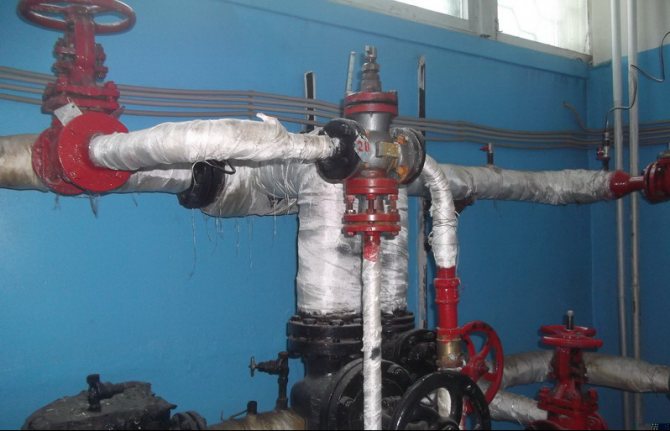


And after the temperature regulator, hot water enters the internal DHW system of the building.
A closed DHW circuit is characterized by the fact that the hot water circuit is separated from the heating circuit. That is, the water through the supply enters the heating circuit, passes through the internal heating system of the building (pipes, radiators) and returns to the return flow, along the way through the heat exchanger heating the hot water supply circuit at the heating point of the building. The hot water supply circulates separately along its own circuit, and the water intake in the building is compensated by the make-up from the cold water supply line. This is the essence and the difference between these two DHW systems.
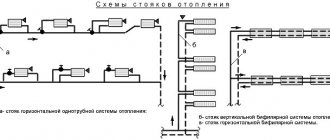
For a closed DHW system, there are several types of circuits - one-stage, two-stage, parallel, sequential. An open DHW system is connected exactly according to the same scheme as in the photo in the article below.
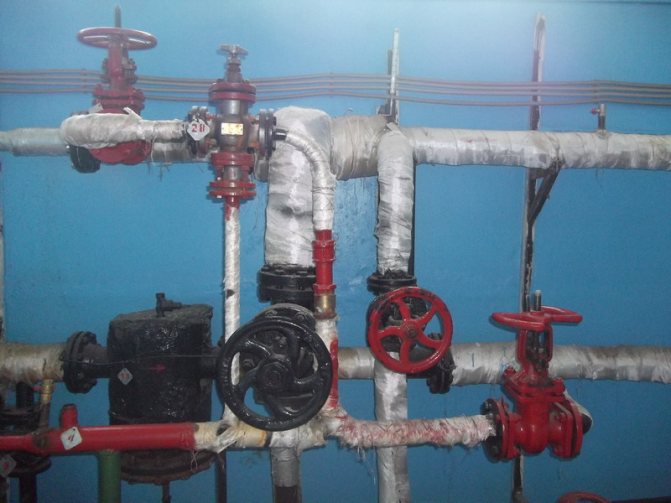


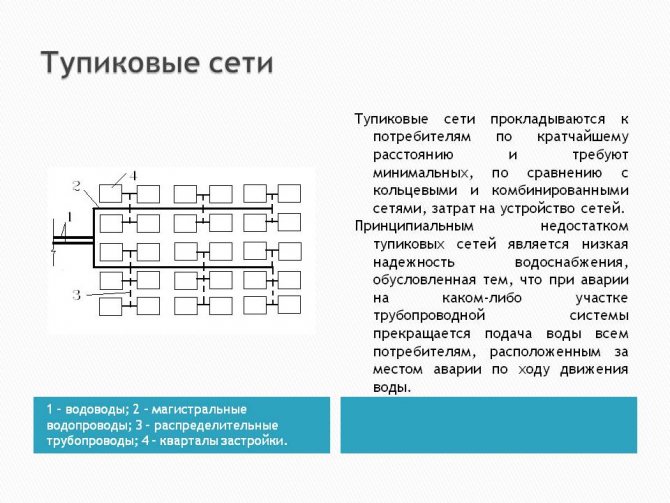
For an open DHW circuit, there are variations - circulation and dead-end wiring.As it becomes clear from the names of these schemes, with a circulation scheme, hot water circulates through the internal DHW system, and ideally, when you open a hot water tap, hot water should run from there almost immediately. But this is ideal, and this is not always the case.
Dead-end scheme - with this scheme, hot water does not circulate in the system, and in order to obtain water of the required temperature, it must be discharged through the tap. That is, you open the tap, wait for the cooled water to drain, then hot water pours out.
An open DHW system is more common in percentage terms, since the installation cost is relatively low (less pipe consumption and no heat exchangers). Personally, in the overwhelming number of serviced buildings, I have come across and are faced with an open DHW system. But besides the advantages (relatively small investment during installation, simplicity of design), such a scheme also has disadvantages.
First of all, the quality of water under such a scheme should correspond to drinking water, that is, oil products should not get into the water, for example, from stuffing box packing on valves of large diameter, rust, scale should not get into the water, there should not be an excessive amount of hardness salts in the water. Unfortunately, this is not always the case. For example, in the city where I live, I practically did not encounter the problem of poor water quality in the hot water supply system. The water in the DHW system complies with the standards. But I know that the situation is not the same everywhere, not in all cities.
And the second misfortune of the open DHW circuit is the frequent failure of the DHW temperature controller, its incorrect operation in the general circuit. I wrote about this in this article.
I would be glad to comment on the article.
Calculation and recirculation procedure
In order for the DHW system to be designed correctly, the following must be borne in mind.
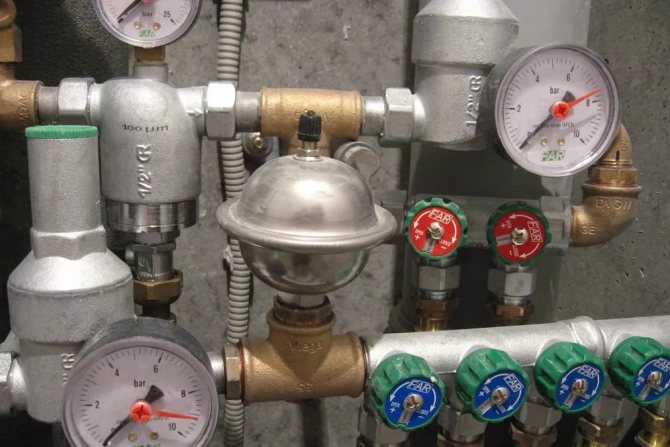
- The drawing indicates the circulation rings. They are closed at the thermal node.
- There are 2 pipelines: supply and circulation.
- On the longest section of the DHW route, zones of maximum circulating heat consumption are noted.
- The diameter of the pipes cannot be less than 1.5 cm. Moreover, they should be 1-2 sizes larger than the diameter of those in the supply section. This is done to avoid air pockets.
When calculating a heating installation, it must be borne in mind that an open system will be effective only with a small distance from the intake point and with frequent opening of the valve supplying boiling water. Otherwise, the consumer will receive cooled water.
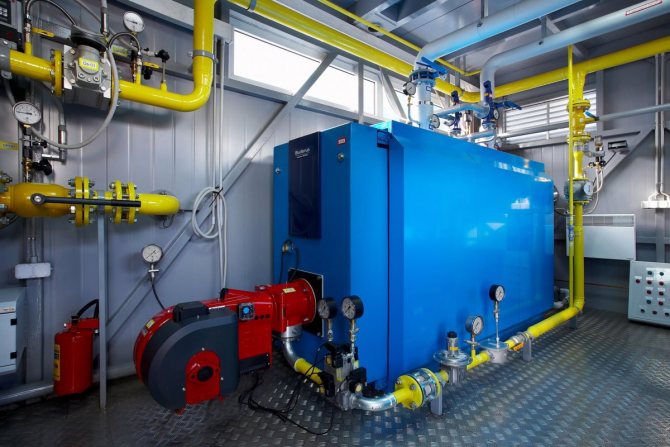
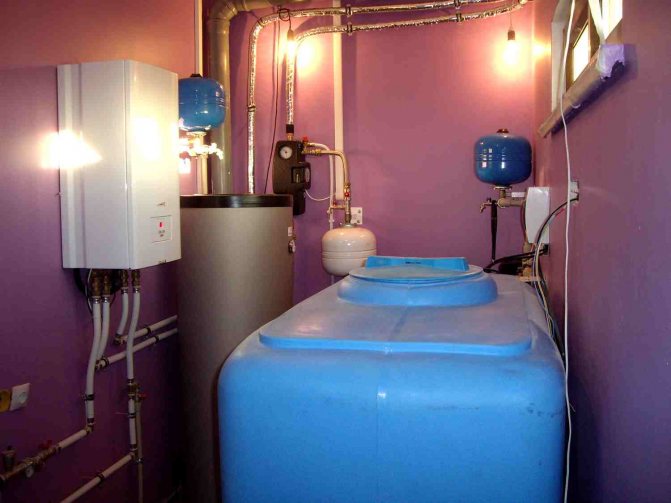
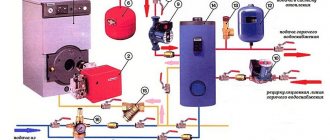
Use of heat points
This is a separate room. It should contain thermal power plants connected to the heating network. Heat exchangers for hot water supply of an apartment building must have tools for regulating consumption, distributing hot water supply to apartments, and setting up the equipment itself.
An individual heating point in an apartment building is usually located in the basement. Previously, the system was installed in attics. In the event of a breakthrough, streams of boiling water spilled over the room and flooded the apartments. If the emergency happened at night, it could lead to serious injury or even death.
An alternative option is to build a heating point in a separate building next to the building. The purpose of the equipment is to transform the coolant, regulate the supply of hot water or heat, distribute the resource among apartments and turn off its supply.
Water heating equipment
A standard water heater can be used for domestic hot water or heating. In the event of equipment breakdown, utility rates will not be reduced. Repair work will also fall on the shoulders of consumers, who are obliged to monitor its good condition.
Thermal energy component
He is responsible for heating cold water. And counters are not installed on the component. Before calculating the heat energy for DHW, the following parameters must be taken into account:
- DHW tariff;
- system operating costs;
- the cost of transferring the heat carrier;
- calculation of heat loss.
The payment for ordinary water supply is also taken into account, calculated on the basis of consumption (RUB / m3).
Main characteristics
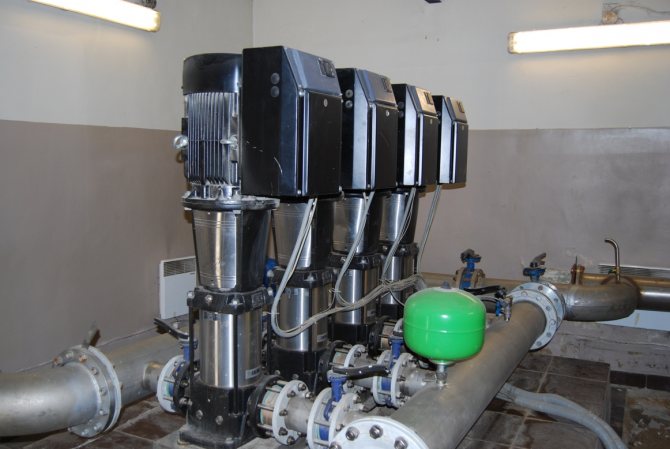
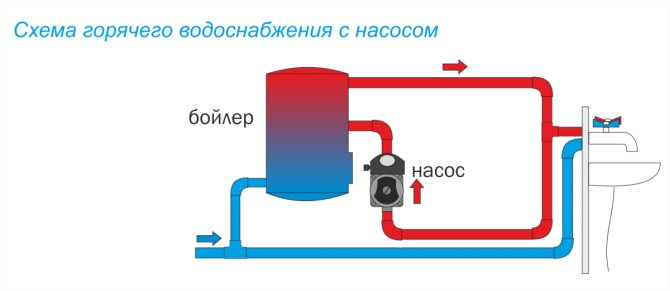
When choosing a circulation pump for DHW or heating, you should pay attention to the following characteristics:
- productivity - the amount of liquid that the recirculation electric pump is capable of pumping per unit of time (m3 / hour or liter / min);
- the head or the pressure of the liquid medium created by the pump (meters of water column or Pa);
- power consumed by the recirculation pump (W);
- way of controlling the device (by means of a timer or temperature sensor).
Since recirculation pumps pump small volumes of liquid, which moves in heating pipes or water pipes at a low speed, high power and performance are not required for such devices. So, to maintain the water temperature in domestic heating and water consumption systems, the length of which does not exceed 40-50 meters, a recirculation pump with a capacity of 0.2-0.6 m3 / hour will be quite sufficient.


Grundfos 3.3cc pump m / hour
In terms of electricity consumption, pumps for the boiler room and hot water supply are also economical, since their power, depending on the model, ranges from 5 to 20 watts. This is quite enough for the electric water pump to be able to provide efficient circulation through the hot water pipes in a private house.
It is very important to choose the right circulation pump for such a parameter as the pressure of the flow of a liquid medium, which it is capable of creating.
In order to choose the right pump for this characteristic, you can be guided by the following recommendations when selecting recirculation equipment for heating and hot water systems of both a small residential building and a large cottage with several floors.
- If the pipes through which the pump must circulate the liquid medium are located at the same level, then we select equipment with a pressure of 0.5–0.8 meters of water column.
- If the house has several floors, DHW recirculation must be provided at several levels of the pipeline, which means that the height to which it is necessary to raise the liquid should be taken into account.
In order to make the recirculation of the liquid medium more efficient in heating and hot water systems, pumps should be selected with a certain margin in terms of the generated pressure.