What is a radiator and what is it for?
A radiator is a part of a car that is installed in the engine compartment. It provides constant engine cooling.
How does it work, what is it for, what types of radiators are there, why does it fail, how to care for it and how to choose the best modification? Let's deal with all the nuances in more detail.
General concepts, purpose
During the operation of the car, all its mechanical components heat up. In some compartments, this figure reaches more than one hundred degrees. And the main unit, which will quickly fail due to the high temperature, is the motor.

The moving parts of the engine must be cooled to prevent deterioration. For this, the engineers of each car manufacturer develop and install a cooling system.
_
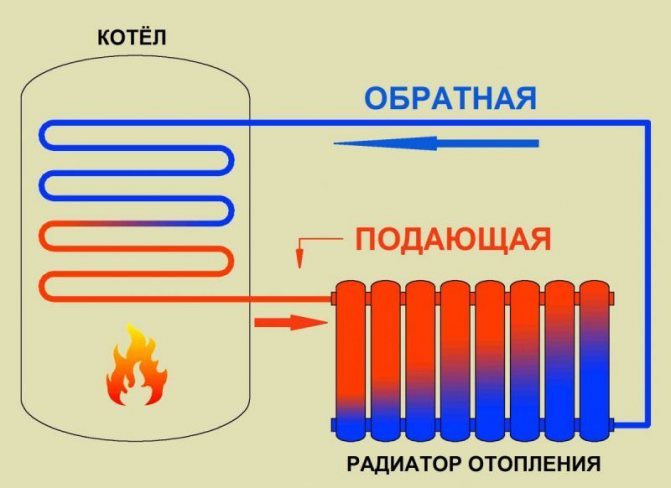
The cooling radiator is a metal heat exchanger filled with antifreeze (or antifreeze) inside. Rubber pipes are connected to it, which are attached to the corresponding motor necks.
The cooling of the motor works according to the following principle. The started internal combustion engine rotates the impeller of the water pump. Thanks to this, antifreeze begins to circulate in the system (in a small circle). When the temperature of the liquid reaches 80-90 degrees, the thermostat is triggered and a large circulation circle opens. This allows the engine to warm up faster to the desired temperature.
The following 3D animation clearly demonstrates how the system works:
Car engine cooling system. General device. 3D animation.
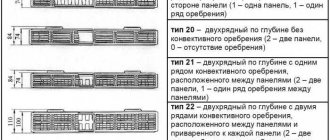
Installation diagrams of an aluminum radiator
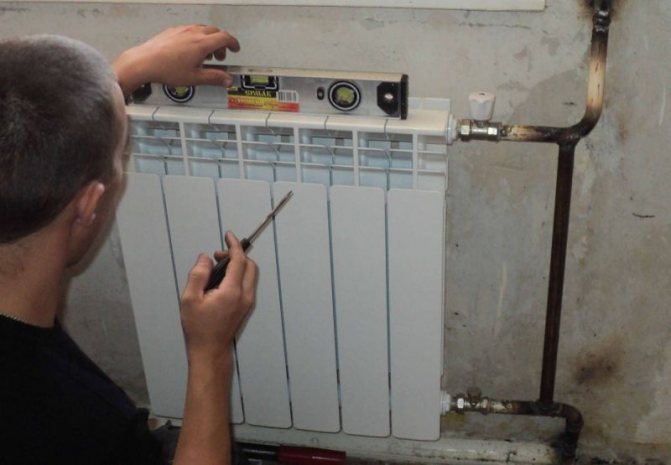
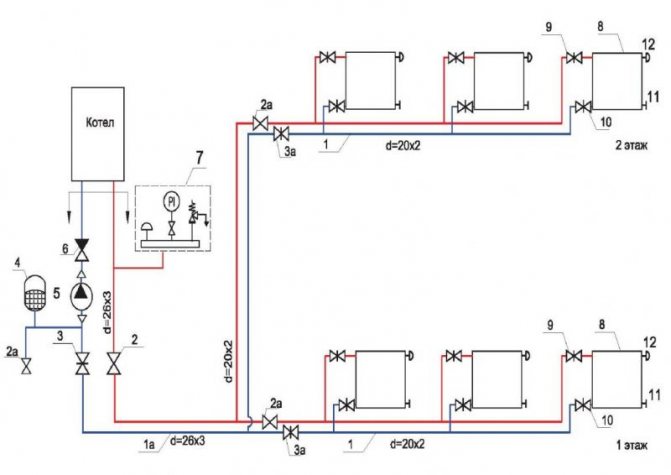
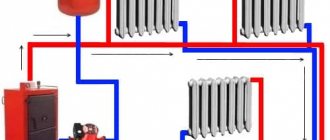
It should be noted that the connection of aluminum heating radiators can be carried out according to different schemes. Aluminum batteries are suitable for one-pipe and two-pipe cabling. In the latter version, the supply and return pipes are connected in parallel, they are connected through the final device of the heating system.
There are such ways to connect aluminum heating radiators: side, diagonal and bottom. Each of the schemes differs not only in the technology of installing the battery, but also in the quality of heat transfer.
Diagonal connection
The most common and effective way is the diagonal connection. In this case, heat loss does not exceed 2%. Ideal for equipment with a large number of sections. The outlet pipeline is connected to the lower one. The supply pipe is connected to the upper branch pipe. This method is used for two-pipe heat supply systems.
Side connection
With lateral connection, the supply pipe is connected from the top, and the outlet pipe is connected from the bottom. Installation is carried out to the branch pipes, which are located on one side. In the lower version, the connection is made to the branch pipes, which are located at the bottom of the battery. True, the heat output in this case is 15% lower than the rated power of the device.
Before connecting an aluminum heating radiator, the device must be properly assembled. The manufacturer describes in detail the installation technology and assembly features in the instructions that are attached to the equipment.
What is it for in the car
The car engine works by burning fuel in the cylinders. As a result, all parts become very hot. When the temperature of the metallic elements rises, they expand. If they are not cooled, this will lead to various problems in the power unit, for example, cracks in the cylinder head, in the cooling jacket, cylinder head deformation, excessive thermal expansion of the pistons, and so on. Ignoring such problems will lead to costly ICE repairs.
In order to stabilize the temperature, all internal combustion engines in their design have a cooling jacket through which fluid circulates with the help of a pump. The heated antifreeze is fed through the highway to the car's radiator. In it, the liquid is cooled, and then flows back to the engine. This process allows you to maintain the operating temperature of the internal combustion engine.
If there was no radiator in the design of the cooling system, the liquid in it would quickly boil. In the car, this part is installed in the front of the engine compartment. This is necessary so that more cold air enters its plane.
The efficiency of heat exchangers depends on the following factors:
- the number of tubes - the more there are, the better the antifreeze will cool;
- cross-section of tubes - oval shape increases the area of contact with air, which increases heat transfer;
- forced airflow - especially useful in urban driving mode;
- cleanliness - the more debris there is between the fins of the heat exchanger, the more difficult it will be for fresh air to get onto the hot pipes.
Internal combustion engine radiators [edit | edit code]
In an internal combustion engine, the radiator is a heat exchanger that integrates the two circuits of the cooling system. Basically, tubular-plate and tubular-tape radiator grilles are used. In the radiator, for the passage of the coolant, seam or solid-drawn tubes made of brass tape with a thickness of up to 0.15 mm are used. Aluminum radiators are also used: they are cheaper and lighter, but the heat exchange properties, all other things being equal (dimensions, heat exchange area, etc.), and the reliability are lower.
On diesel locomotives, a similar device is called a "refrigerator".
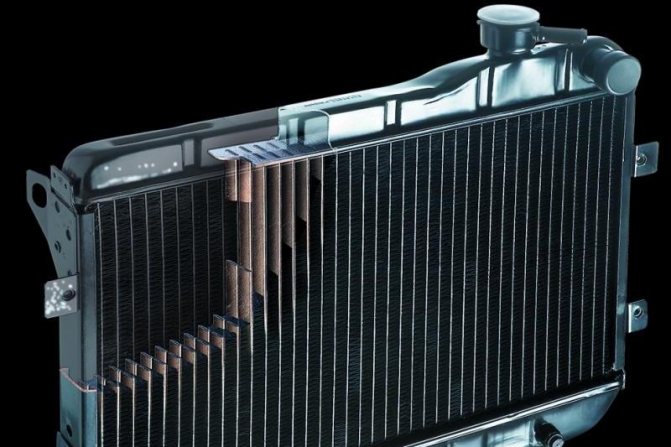
An automobile radiator, the device of which includes two tanks - upper and lower, as well as tubes between them, performs an essential function and is responsible for preventing engine overheating. How this happens, and what types of this node we can find in our machines, we will talk a little below.
Radiator design
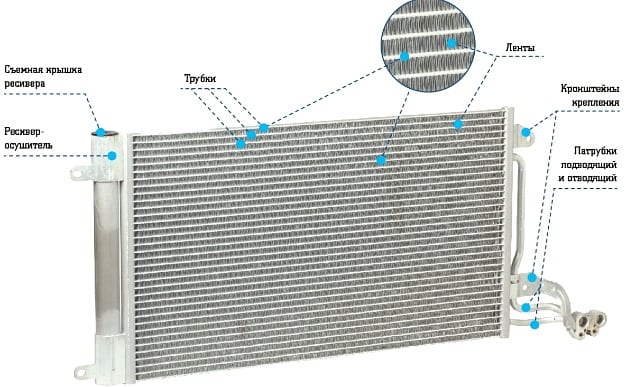

The material from which car radiators are made is metal (aluminum or copper). The walls of the heat exchanger are very thin, due to which the antifreeze quickly gives off its temperature and cools.
The design of the radiator consists of thin tubes welded together in the shape of a rectangle. This element is mounted on two tanks (one at the inlet, the other at the outlet). Additionally, plates are strung on the tubes, which increases the heat transfer area. Air passes between the ribs and quickly cools the surface of the part.
All heat exchangers have two openings: inlet and outlet. The pipes of the system are connected to them. To drain the liquid from the cavity, the heat exchanger is equipped with a plug installed at the bottom of the structure.
If the car is driving on a highway, there is enough air flow to cool the antifreeze naturally (blowing the ribs). In the case of traffic in the city, the air flow is not so intense. For this, a large fan is installed in the cooling system behind the radiator. In older car models, it was directly driven by a motor. Modern machines are equipped with an antifreeze temperature control system and, if necessary, includes forced airflow.
How radiators are made - see the following video:
How car radiators are made
Household oil radiators
An oil-filled (oil-filled) radiator is a mobile heating battery. Device: an electric coil is located inside the sealed casing, the casing is filled with mineral oil. The surface temperature of the oil heater does not exceed 150 ° C. Heat is transferred from the coil to the oil, then from the oil to the body, and from the body to the air.Devices of this type are reliable, durable, quiet, capable of retaining heat for a long time after a power outage, and, moreover, are considered very safe. The main advantages of oil coolers are low price, mobility and low noise level. The disadvantages of a traditional oil-filled heater include long warm-up time (10-20 minutes).
Modern oil heaters have the following set of functions:
- Several operating modes.
- Climate control function
- On / off timer, the radiator will heat up the room by a certain time.
- Overheating protection function.
- Self-twisting wire.
- Remote control for oil heater.
- Hanger for drying things.
Types of radiators
There are several types of heat exchangers. Each of them is designed for its own purpose, but they work according to the same principle - fluid circulates inside them to ensure the exchange of heat. Heat exchangers are used in the following vehicle systems:
- cooling;
- heating;
- climatic.
There are two categories of radiators most commonly used in the automotive industry.
- Tubular lamellar. This is the most common modification found on older cars. The heat exchanger in them consists of horizontally arranged tubes (circular section), on which thin plates are strung. Most often they are made from an aluminum alloy. These modifications were installed on older vehicles. The main disadvantage is poor heat transfer due to the small area of contact with the air flow.
- Tubular tape. They use long tubes (oval section), folded in the form of a coil. The material used for their manufacture is either an alloy of copper and brass, or aluminum. Such modifications are installed in many modern cars. Copper models have excellent thermal conductivity but are very expensive. Therefore, more often the cooling system is equipped with aluminum counterparts.
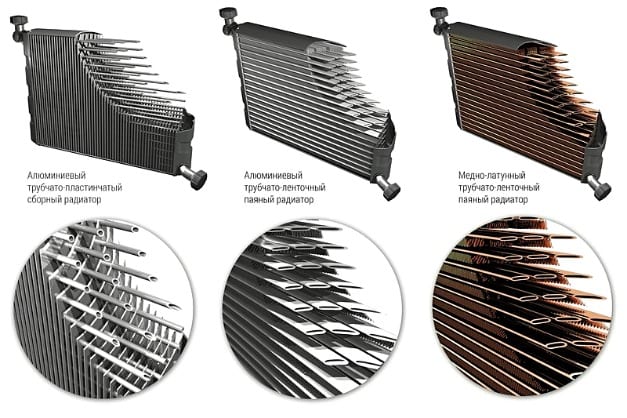

Among the first category, there are two more types of radiators. These are single-pass and multi-pass models. They differ from each other in the principle of circulation.
- One-way. The coolant enters the heat exchanger cavity from one side and is evenly distributed over all tubes. They have a significant drawback: the antifreeze in the cavity is distributed unevenly, due to which the efficiency of heat exchange is lost.
- Multi-pass. The cooling elements are divided into several sections. This design increases the overall length of the line, which improves the heat transfer process.
Radiator device
a - device; b - the steam valve is open; c - the air valve is open.
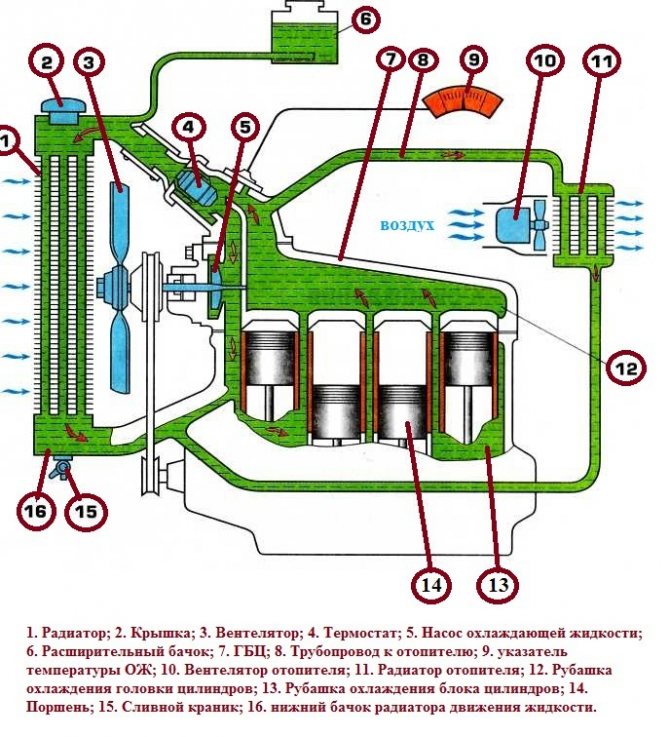
- The radiator structurally has an upper (1) and lower (7) reservoir. These tanks are connected to each other by pipes (5) made of brass or aluminum. Plates (6) are attached to these tubes by soldering, which increase the surface cooling area of the element. Through this surface, heat is removed from the coolant and released into the environment.
- The upper reservoir has a filler neck for filling with coolant. The neck is closed with a plug (3). This plug contains a steam (11) and an air (12) valve.
- The upper reservoir also has a pipe (2) for connecting the radiator to the motor cooling jacket. This connection is realized by means of a rubber hose. Additionally, there is a steam pipe (4) and an electric thermometer sensor (13).
- The lower tank (7) has a branch pipe (8) for connecting the device with a pump (pump). There is also an additional tap that is able to drain the coolant. The radiator is attached to the vehicle frame with special fasteners (9).
Damage to radiators: causes, prevention
Like any part, the radiator in the car can also fail.Here are five main reasons.
- Mechanical damage. Since this part is installed in front of the vehicle, foreign objects often fall on it. For example, it can be stones from a car in front. Even a minor collision from a car can damage the radiator, which will compromise the tightness of the cooling system.
- Oxidation of metal. Although all elements of the heat exchanger are made of stainless materials, the radiators are not protected against scale build-up inside their cavities. Due to the use of low-quality coolant, metal parts of the motor can oxidize, which clogs the line and prevents the free circulation of antifreeze.
- Natural wear and tear. Constant heating and cooling leads to "fatigue" of the metal, which reduces its strength. Vibrations in the engine compartment destroy the connecting seams, which can lead to leakage.
- Excessive line pressure. If a poor-quality plug is installed on the expansion tank, over time, the pressure relief valve stops functioning. Due to the heating of the antifreeze to a temperature above 100 degrees, the volume in the system increases. Most often, seams on plastic elements diverge. But the walls of the old heat exchanger become thinner over time, which leads to depressurization and leaks.
- Coolant freezing. This can happen in the case of using the wrong antifreeze or plain water. In the cold, water crystallizes and expands. From this, cracks appear on the walls of the tubes.


Most of these problems can be prevented by applying preventive methods. To prolong the service of the radiator, the owner of the car can take the following measures.
- Do not fill the system with normal water. In an emergency, you can use distilled, but in the near future you need to change it to antifreeze. This liquid boils at temperatures above 115 degrees. In addition, it contains lubricant, which has a beneficial effect on the pump impeller and other metal parts of the system.
- Change the antifreeze in a timely manner, and when the level decreases, add it. Replacement must be done at least 50-70,000 km. mileage (for antifreeze, this interval is from 150 thousand). But if the coolant has changed its color and turned black, this is a clear signal for system maintenance.
- Install a radiator made for the given car model.
- Perform routine maintenance on the entire cooling system.
- Keep the fins of the heat exchanger clean.
- During the replacement of the antifreeze, periodically flush the inner walls of the coil.
Which is better: repair or change


All motorists can be roughly divided into two categories. The first believe that a failed part needs to be replaced with a new one. The latter are sure that everything can be repaired. And fixing radiators is a frequent topic of controversy.
The Internet is replete with all kinds of advice on how to fix the leak yourself. Some use special compounds. Others fill the system with crack bridging agents. Sometimes some methods help prolong the life of the part for a while. But in most cases, these techniques only clog the cooling system.
It makes sense to repair copper models, because they are easy enough to solder. In the case of aluminum analogs, the situation is different. They can be soldered, but this will involve expensive welding. Therefore, the cost of repairing a leaking radiator will be almost identical to the price of a new part. It makes sense to agree to this procedure only in the case of an expensive heat exchanger model.
In most cases, repairs are only a temporary measure, because high pressure constantly builds up in the cooling system, which will lead to repeated depressurization of the line. If you carry out timely maintenance and cleaning of the system, you will often not need to change the radiator.Therefore, when a part breaks down and precious coolant poured onto the ground, it is better to replace this unit than to constantly throw away money for the purchase of another canister.
How to properly operate?


One of the most important conditions for the correct operation of a radiator is to keep it clean and to prevent excessive pressure in the system. The second factor depends on the expansion tank cap.
The first procedure can extend the life of this component. However, it must be done correctly.
- The manufacturer categorically prohibits the reuse of used coolant. Even if you clean it, it has already lost its properties, and therefore it will already be useless.
- If the antifreeze is very dirty, before pouring a new one into the system, it must be flushed with distilled water (in no case use ordinary water). It does not contain salts and impurities that can build up inside the coil and reduce the cooling efficiency.
- When cleaning the outside, it is important to take into account that the fins of the heat exchanger are very thin and therefore even small forces can bend them. Subsequently, this will interfere with the natural blowing of the radiator pipes. If the procedure is performed using a mini-washer, you need to adjust a small head. The jet should be directed perpendicular to the fins to prevent accumulated dirt from moving into the heat exchanger. Then it cannot be purified in any way.
Which radiator is better?


In most cases, the answer to this question depends on the material capabilities of the motorist. Copper-brass models lend themselves to inexpensive repairs. Compared with aluminum analogs, they have better heat transfer properties (the heat transfer coefficient of copper is 401 W / (m * K), and of aluminum - 202-236). However, the cost of a new part is very high due to the price of copper. And one more drawback - a lot of weight (about 15 kilograms).
Aluminum radiators are cheaper, they are lighter compared to copper versions (around 5 kg), and their service life is longer. But they cannot be properly repaired.
There is another option - to buy a Chinese model. They are much cheaper than the original part for a particular car. Only the main problem with most of them is their short service life. If an aluminum radiator copes with its functions for 10-12 years, the Chinese analogue is three times less (4-5 years).
For details on breakdowns and maintenance of radiators, see the following video:
Engine cooling radiator. Malfunctions. Cleaning.
Rate publication
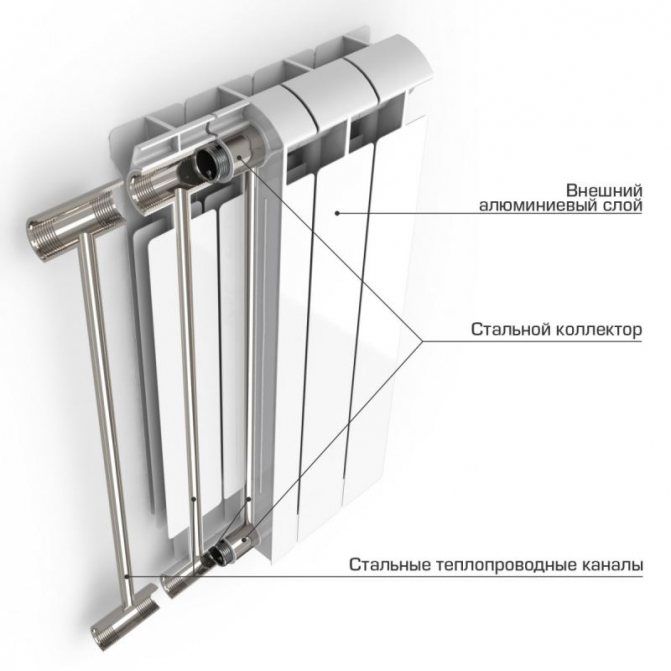
Aluminum battery device
Considering the device of an aluminum heating radiator, it should be noted that the design of the battery can be solid or sectional.
Sectional aluminum heater consists of 3-4 separate sections. As a rule, titanium, silicon, zinc are added to aluminum. These metals make the product more durable and resistant to tearing and corrosion. All sections are connected to each other using a threaded connector. Silicone gaskets are used to seal the connection. The inside of the radiators is polymer coated to prevent the possibility of battery rupture.
Solid aluminum radiators consist of profiles. The profiles are made by extrusion.
No additional metals are added to aluminum radiators.
What gives the material plasticity. The profiles are connected to each other by welding. This connection is highly durable and reliable. Like sectional ones, one-piece models of radiators are covered with a polymer layer inside.
Depending on the production method, there are radiators made by casting, extrusion and anodized products (made of aluminum of a higher purity).
Technical characteristics of aluminum radiators
In view of the high technical characteristics, many decide to buy an aluminum radiator for heating an apartment. The main technical parameters include:
- operating pressure. It is in the range from 10 to 15 atmospheres. In residential apartments, the working pressure can exceed the norm by 3-4 times. In this regard, such radiators are rarely installed in city houses. But for private houses - such a heater would be an ideal solution;
- pressure test. It is in the range from 20 to 50 atmospheres;
- heat transfer coefficient. For the standard section, it is 82-212 W;
- the maximum temperature of the coolant can reach +120 degrees;
- one section can weigh from 1 to 1.5 kg;
- the capacity of each section is from 0.25 to 0.46 l;
- the distance between the axes can be 20, 35, 50 cm. There are models for which this parameter can reach 80 cm.
The manufacturer indicates the parameters for each model of the radiator in the passport of the device. Considering the technical characteristics of aluminum radiators, the price for them is quite reasonable and depends on the type of battery, the number of sections and the manufacturer.
Advantages and disadvantages of aluminum radiators
Before you buy aluminum heating radiators, you need to consider what advantages and disadvantages this device has.
The main advantage of an aluminum battery can be called compactness and much less weight than cast iron systems. You can read more about cast iron heating radiators here. The equipment warms up very quickly and transfers heat to the room perfectly. The service life is quite long. Another advantage is the division into sections - it is possible to choose the required length of the battery. It should be noted that the price for aluminum radiators is indicated per section. This makes it easy to calculate the approximate cost of a sectional device.
Since the equipment is small and lightweight, it is easy to install. Installation can even be carried out on a plasterboard wall. Modern models look aesthetically pleasing and stylish. Aluminum is easy to work with. This allows manufacturers to experiment with battery design. You can choose an option for any interior. Most of all, aluminum radiators are suitable for autonomous heating systems. Despite the high technical characteristics and a lot of advantages, the price for aluminum heating batteries is quite affordable.
The disadvantages of aluminum radiators include low corrosion resistance. This can greatly affect the overall health of the battery. Aluminum is by nature a fairly active metal. If the oxide film covering the surface is damaged, the protective layer will be destroyed due to the release of hydrogen. To improve the anti-corrosion properties, a polymer coating is used. If the battery does not have a polymer coating, then the taps on the supply pipes must not be turned off. Otherwise, the pressure may rupture the battery.
Today, aluminum batteries occupy a leading position in the sales of heating equipment.
Many people prefer to buy this type of heating device and because of the relatively low cost. For aluminum radiators, the average price per section is about 230-300 rubles.