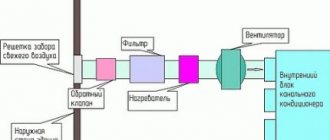
The device and principle of operation of a conventional air conditioner
The air conditioner operates in a closed loop based on two functions:
- the transition of a substance from a gaseous state to a liquid with increasing pressure (and vice versa);
- heat release during condensation (transition from gas to liquid) and cooling during evaporation.
In other words, a compressor is used to transfer heat. It changes the pressure of the refrigerant. Usually freon in various compounds acts in this capacity, for example, “R410”. How to fill the air conditioner with freon - read here.
Here is a diagram of such a system:
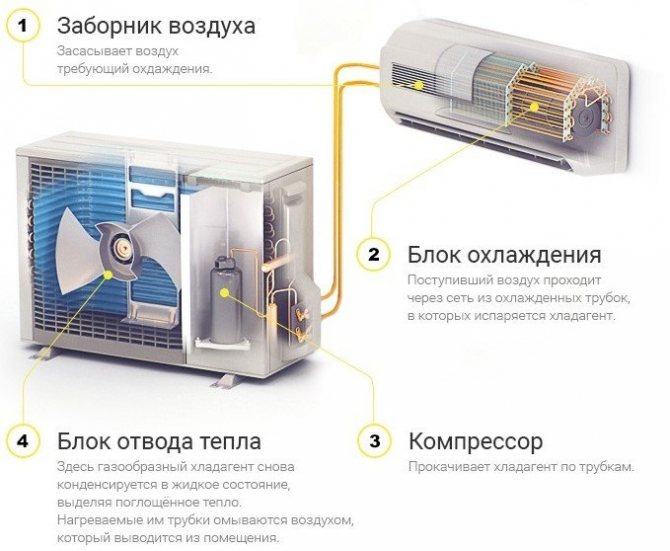
The step-by-step phase of the cycle is as follows:
- A compressor (a small pump with an electric motor) builds up the gas pressure by pumping it from the evaporator (in the room) to the condenser (outside). Due to the increased pressure of the gas, its temperature can rise to 90 degrees Celsius.
When the compressor starts, it runs without lubrication for the first seconds, since oil flows into the crankcase when the engine is not running. Therefore, each next start of the engine increases its overall wear. It is better for the motor if it runs continuously, but this leads to high energy consumption.
- In the condenser, freon begins to give off heat to the environment, because the gas at this moment is hotter than air. The outdoor fan turns on and provides intensive blowing of the heat exchanger, which speeds up the process many times over.
- As a result of cooling, the gas turns into a liquid, but the pressure is still high. The temperature of the liquid is the same, still slightly higher than the ambient temperature.
- Further, the freon passes into a capillary - a thin copper tube wound with a long spiral. Another name for this part is a choke. So the pressure of liquid freon drops to several atmospheres. Part of the liquid immediately turns into a gaseous state.
- Freon ends up in the evaporator. Now the heat exchanger from a liquid state goes into a gaseous state, while the freon is cooled along with the heat exchanger grate in the room. A room fan drives air through a chilled grill, quickly drawing cold into the room.
- Then the cycle repeats again - from phases 1 to 5.
How the air conditioner works in cooling mode is shown in the diagram:
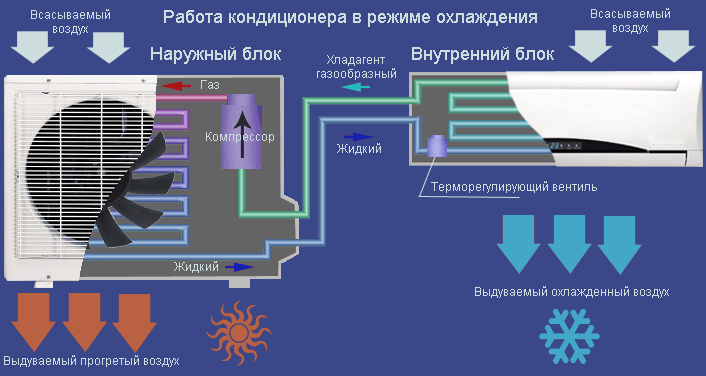

Since the evaporator is very cold and the humidity in the room can be high, drops of water appear on the evaporator - condensation. In fact, it is distilled water. The droplets accumulate and begin to flow down - along the evaporator and below. Of course, water is not needed indoors, so usually a pipe brought out to the street is used to drain the condensate.
The outgoing air flow can be directed with the help of special jalousie planes in the desired direction, both horizontally and vertically. Usually, such control can also be carried out from the remote control. Many models can automatically rotate the louvers to the sides or up and down on a regular basis, pushing cool air through a larger volume.
How to install the air conditioner on your own - read here.
Air conditioner dehumidifier - how it works
This is one of the elements of the system. Its function is to collect the liquid freon flowing out of the condenser and to prevent contamination of the refrigerant. It is located on the freon track, after the condenser and in front of the choke:

Externally, the desiccant looks like a small tube expanding towards the middle and tapering towards the ends. Inside the tube is a moisture-absorbing mineral "zeolite". There are two grids on the path of freon movement:
- One on the inlet side with large openings to prevent the zeolite granules from entering the condenser.
- The second mesh is on the outlet side. The holes in it are relatively small, like in a tea strainer, so as not to let zeolite particles, metal fragments, and so on into the compressor.
An additional hole is usually made in the dryer. It is used in the assembly and repair of the unit in order to quickly create a vacuum in the system. Otherwise, the throttle having a small diameter would slow down the process of evacuating the air conditioner. Do not open this technological hole, otherwise the device will stop working.
Air conditioner device
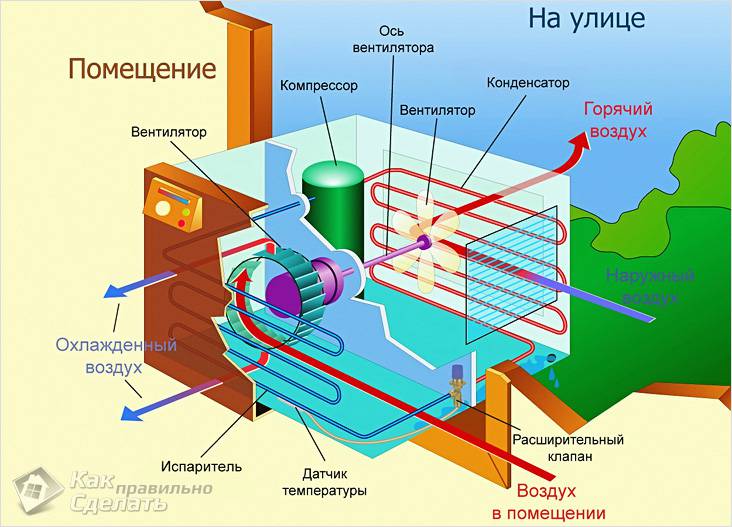

Air conditioner device
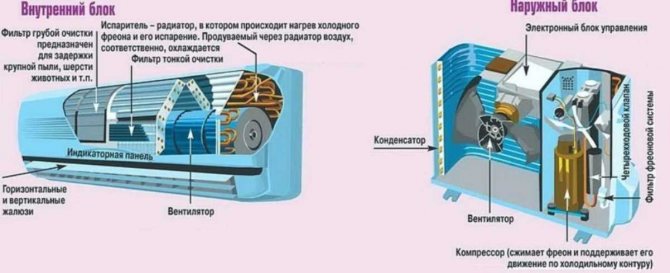
All air conditioners consist of the following parts:
- fan;
- throttle;
- capacitor;
- compressor;
- evaporator.
The compressor compresses the freon and forces it to circulate in the system. The condenser is used to convert freon from gas to liquid. It is usually located in an external unit. The evaporator, on the other hand, causes the liquid freon to turn into gas. Its action is opposite to that of a capacitor. The throttle reduces the freon pressure, and the fans cool the system.
This is how every such device works. At the same time, the principle of operation of a floor air conditioner does not differ from the principle of operation of a wall or ceiling air conditioner.
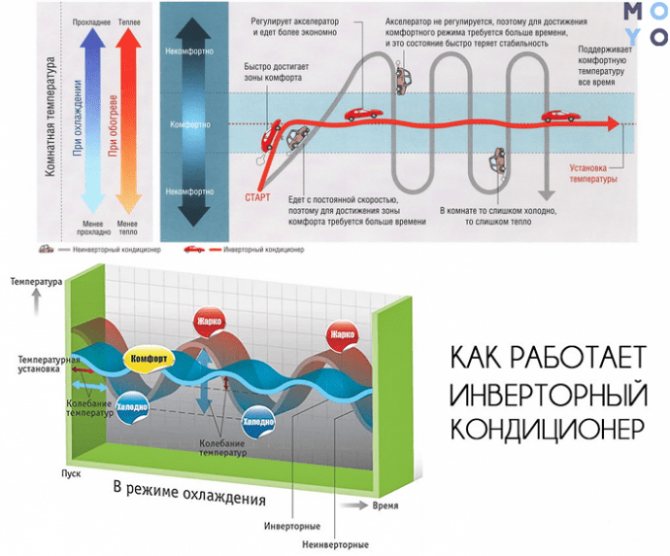
Inverter air conditioner
The main purpose of the inverter air conditioner is to save energy and prolong the operating condition of the compressor. In such systems, work does not take place in jerks "on-off", but with a smooth power control. The air conditioner runs continuously, however, not at full strength. This allows the compressor motor to extend its life. In addition, maintaining a stable temperature in the room requires much less energy consumption than with the "ragged rhythm" of a conventional air conditioner.
Compressor speed control is achieved by converting (inverting) the incoming alternating current into direct current, and then back to alternating current, but with a different frequency. The electronics decide how to change the engine speed - decrease or increase, and the speed changes occur smoothly.
But it is important to understand that an inverter air conditioner is more economical only in those places where a conventional air conditioner is turned on only from time to time. With continuous operation, a conventional air conditioner is much more efficient at the same energy consumption, because it does not waste electricity for conversion. Therefore, if your inverter air conditioner operates at full capacity almost continuously, its capacity was selected incorrectly.
An engineer from Climate-Control will tell you what an inverter air conditioner is and whether it is worth overpaying for it:
Split system
Split means split. In split systems, the condenser and evaporator are not in a single housing, but can be separated, for example, by a wall. However, they are connected by tubes to exchange refrigerant between them. Usually the outer part of the split system is mounted on the outside on the wall of the building. It contains the following elements:
- compressor;
- capacitor;
- throttle;
- external fan, etc.
The outside can generate quite a loud noise during operation (up to 45 decibels), which can displease your neighbors.
The inner part is mounted inside the building, it contains:
- evaporator;
- air purification filter;
- thermostat;
- control electronics.
Usually the interior is very quiet.
When installing a split system, special equipment is required to connect the outer and inner parts with copper pipes. First of all, it is a vacuum pump, without which it will not be possible to assemble a workable system. The manufacturers do not give a guarantee for units installed by non-certified installers.
Modern split systems are equipped with a compressor start-up control system.This system prevents the engine from starting too quickly after the last shutdown so that it does not overheat.
There are multi-split systems in which not one, but two or more indoor units. But such systems are somewhat more expensive than conventional ones, since they require both a more complex system of connection with an outdoor unit, and a more complex control system for each indoor unit (with a separate thermostat, a remote control unit, and so on).
Most split systems are capable of operating not only for cooling, but also for heating.
How the air conditioner performs its function
Thermodynamic processes, which will not be considered in detail in this article, ensure the operability of this type of equipment. In practice, the absorption of heat from the environment by liquids during their evaporation is used. The simplest "cooler" that experienced tourists use if necessary is a dampened cloth. If you wrap a container with a drink, put it in a strong wind, the temperature of the liquid will drop.
This principle is the basis for the functioning of a special group of air conditioners. In these devices, blocks are installed that perform automatic wetting of the working surfaces. The air flow is provided by a built-in fan. The disadvantages of such a system are obvious:
- It is unable to provide high performance.
- The water container must be replenished regularly.
- The unit works only for cooling. For ventilation, heating, it will be necessary to supplement the composition of the equipment with special units.
Modern split systems are much more practical and convenient to operate. Let's consider in more detail the principle of their action. This type of technique uses a closed circuit through which the refrigerant is circulated. Today, freon is very rarely used, since the harm that it can cause to the environment has been discovered.
Attention! In the following discussion, we will use the name of this gas for simplicity. New air conditioners are filled with harmless mixtures that perform the same functions.
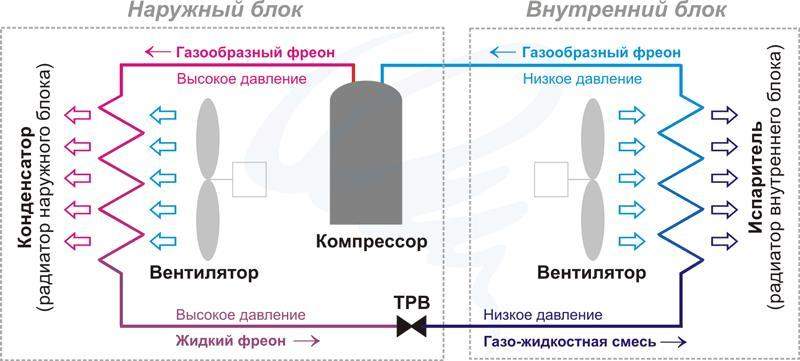

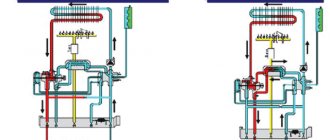
Air conditioner circuit: outdoor and indoor units
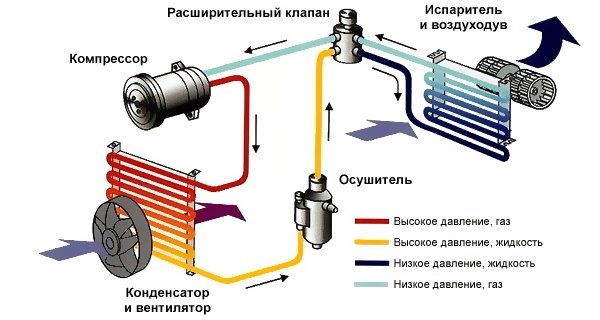
The following duty cycle is used in this type of air conditioner:
- Freon in a gaseous state enters the compressor. This block increases the pressure in the system, which in turn provides the required speed of movement of the refrigerant in the line and a simultaneous increase in its temperature.
- At the next stage, excess heat is removed and freon is converted into liquid. To do this, the gas is passed through a serpentine system of pipes in the radiator. Forced airflow is provided by a fan.
- Then the pressure is reduced. In household models, appliances are used not a complex, but rather effective solution. Freon enters a special valve. This knot is a thin copper tube twisted into a spiral. In it, the process of liquid evaporation begins, reducing its temperature.
- In the next heatsink, the required conversion is completed. Cooled gas is formed. Reducing the room temperature is performed by forced air flow through this unit.
- Then the freon enters the compressor, the cycle is repeated anew.
The main technical parameters of the standard technology are shown in the table:
| Functional part of the air conditioner | Freon state | Pressure, atm. | Temperature, ° C |
| Compressor inlet | Gas | from 2.5 to 6 | from 8 to 22 |
| Compressor outlet | Gas | from 14 to 26 | up to 75-90 |
| Condenser output | Liquid | from 10 to 20 | about 15 higher than the outside temperature |
| Thermostatic valve outlet | Mixture of gas and liquid | from 3 to 7 | Depends on the type of gas, for some refrigerants the value is set at 7.5 |
| Evaporator outlet | Gas | from 2.5 to 6 | Determined by hardware settings |
Floor air conditioner
Floor air conditioners are used when it is undesirable or impossible to use a conventional wall model, for example, the room is too small, and the flow of cold air from the wall will immediately fall on people.
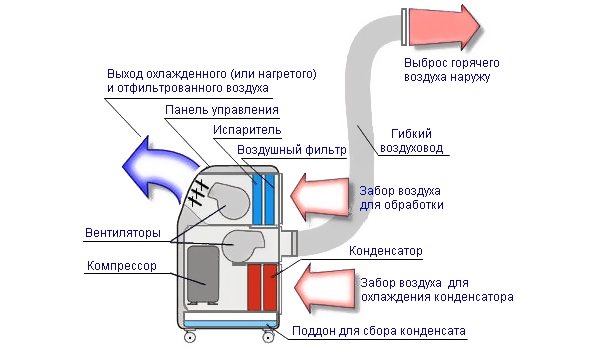

They are of two types: stationary and mobile. And those, and others are not too different from their counterparts on the wall. Stationary floor air conditioner, as a rule, is made according to the "split" scheme. It also needs to exchange heat with the outside world, as the usual one, therefore it is simply fixed at a height of about half a meter from the floor level, and all other elements are the same. A mobile floor air conditioner is most often just a mobile air conditioner.
Mobile air conditioner: features of work
The device of a mobile air conditioner is almost the same as a stationary one. The main difference is that the entire air conditioner is entirely inside the room. In addition, a thick duct pipe is usually required to circulate the outside atmosphere through the condenser. This air duct must be sealed through a window or a special hole in the walls.
The capacity of mobile air conditioners is usually low, since they are designed to cool small rooms. The noisiest part of the air conditioner (condenser + fan + choke) is placed in the dwelling, therefore, with high power of the air conditioner, it will be uncomfortable in the room.
Most of the technical solutions include not only an air cooler, but also a heater. The temperature rise occurs due to the direct heating of the air by heating elements. Moreover, their power can be quite large, so check the power grid for suitability for such loads. Models with the ability to work "on heat", as in split systems (with rearrangement of the duct hose and without heating elements), can also be found.
Mobile air conditioners are often equipped with a powerful fan, which allows not only to cool / heat the air in the room, but also to disperse it throughout the structure.
Distilled water generated during the operation of the unit is most often collected in a special container. In order not to run with it every hour, pouring out the accumulated water, it is better to choose a model with a larger capacity. Also, some models, when filling the water tank, simply stop working, giving signals and demanding to drain the liquid.
Mobile air conditioners are useful where there is no reason to install a stationary one. For example, when renting a house, in a summer cottage or during a long business trip. Often, mobile air coolers are purchased for the kitchen so that in the summer it is not so hot and stuffy during the operation of all kitchen appliances.
You can learn about mobile air conditioners, their pros and cons from the following video, where the mobile air conditioner ТМ Carrier 51AKP series is considered as an example:
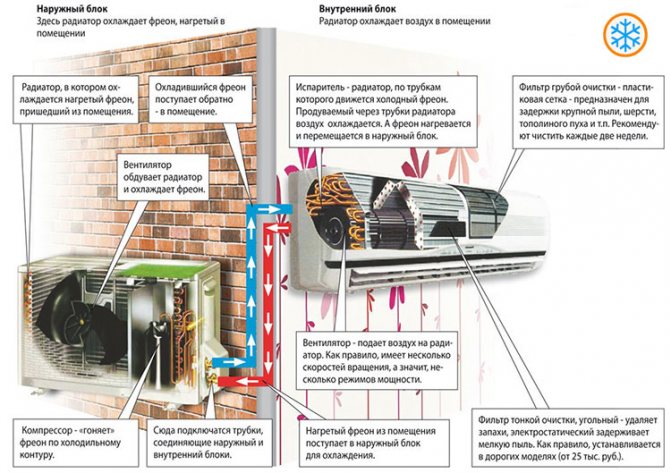

This diagram briefly and clearly shows which processes and in which units of the air conditioner are taking place, making it possible to cool the air in the room.
Of course, not every user is interested in how the air conditioner works. The main thing is to work. But for those who are still interested in this and who are not afraid of a few specific terms, we will briefly tell you.
The principle of operation of air conditioners operating on refrigerant is generally the same (with minor amendments) for all types, be it a split system, window monoblock or mobile air conditioner. The same “heat pump” principle is used in other refrigeration machines (for example, domestic and industrial refrigerators). All air conditioners have three main units - a compressor and two heat exchangers - an evaporator and a condenser. And also on the fan for blowing off the heat exchangers. All other stuffing (electronics, filters, drainage) serves to provide and maintain the operation of these five components. Let's consider the principle of a "heat pump" using the example of a split-system.
So, Air cooling by an air conditioner is based on one interesting physical phenomenon - the absorption of heat from the environment during the phase transition of a substance - from liquid to gas, that is, simply - boiling. But in order to remove this heat from the room, the opposite principle is used - when passing from gas to liquid, the substance, on the contrary, releases heat, releasing it into the environment.
The substance that is used in refrigeration machines is called a refrigerant (freons are just a type of refrigerants, but in everyday life this is generally called the working substance of air conditioners). Boiling takes place in the evaporator - the heat exchanger of the indoor unit, which is a finned coil made of heat-conducting metal (copper or aluminum). Heat is absorbed from the air just as it passes through this coil during the boiling of the refrigerant... The evaporator is blown by the fan (turbine) of the indoor unit.
Further, the refrigerant in the gaseous state (more precisely, in the form of vapor) is sent to the compressor (located in the outdoor unit, outside the refrigerated room), where it is compressed and subsequently condensed into liquid in the second heat exchanger (which is therefore called a condenser). The heat generated during the condensation process is blown out into the atmosphere by the fan of the outdoor unit. The compressor carries out a continuous repetition of this cycle, driving freon along the circuit, and serves as a kind of heart of the air conditioner.
That, in fact, is the whole principle. There are a few more details to add. During cold operation, water constantly condenses on the evaporator. A drainage system serves to drain it. Filters protect the evaporator and turbine from dirt, and at the same time purify the air (as far as possible, of course). Numerous additional functions of course give some effect, but rather it is all more of a marketing nature.
In some models, fresh air is added from the street, and in some, even a semblance of exhaust ventilation is carried out. Of course, this is also more of a marketing than a real replacement for normal ventilation. For work in the winter there are so-called "winter kits", which include heating the compressor crankcase, a winter start device and heating the drain. If the air conditioner is not equipped with such devices, its operation in cold weather threatens to fail quickly. An air conditioner that works in winter without a winter kit is not subject to warranty service, repair or replacement under warranty.
A little about the cooling mode and fan operation. In order to feel comfortable coolness, it is not necessary to put the air conditioner in cooling mode to an extremely low temperature in 30-degree heat. It is enough to cool the air by 2-3 degrees. At the same time, the lower the fan speed, the lower the risk of colds and the quieter the operation of the air conditioner. It is better to direct the air flow parallel to the ceiling. Avoid direct exposure to cold air. Remember that in reality its temperature is much lower than the value that you set on the remote control. On average, it is 15 degrees lower than the original room temperature, so the effect of such a jet is akin to a decent draft.
By the way, the slower the fan speed, the more the air cools and vice versa. But at high rpm, it mixes faster indoors. In general the main idea of air conditioning is not at all rapid cooling, but in MAINTAINING a constant comfortable temperature in the room. This is what the automatic mode is for. Cooling, heating, ventilation and dehumidification are optional functions.
In a simple version of the "auto" mode, the air conditioner automatically turns on in the cold when the temperature exceeds a certain mark and turns off when it reaches a conditionally comfortable temperature (22-25 degrees).In a more advanced version, the temperature can be set arbitrarily, and the air conditioner itself will automatically heat or cool the air, ensuring that the set value is maintained in the room.
There is also a dehumidification mode, in which the air conditioner operates as if it were cold, but does not respond to additional commands - its main task in this mode is to remove moisture from the air and drain it through the drainage channel.
In expensive split systems, there are also different functions such as sensor monitoring of the temperature in different parts of the room and the like, but so far there have been no cases of someone contacting the service complaining about a malfunction of such a sensor).
How does a mobile air conditioner work without an air duct?
A mobile air conditioner without an air duct is actually not an air conditioner, but an air humidifier, and with the need to constantly replenish water supplies. Such a device does not remove heat anywhere, but simply drives the air out of the room through the moist spongy material. Some short-term sensation of coolness is possible in the first minutes of work due to the increase in air humidity.
Compared to a conventional air conditioner, it has the following disadvantages:
- The power of such a device cannot be large - due to the limitation of dimensions and noise, as well as the scope of application in small rooms.
- The humidity in the room becomes very high. Accordingly, mold and so on may appear.
- It is necessary to add water to this device all the time, otherwise it may turn off altogether.
The principle of operation of a window air conditioner
Window air conditioners are popular for the same reason as mobile air conditioners. Usually they do not work all year round, but only in hot weather. This is a very good solution for the kitchen, when you want a little coolness in the summer, and there are no funds to buy an expensive device for cooling a small room.
A similar setup looks like this:
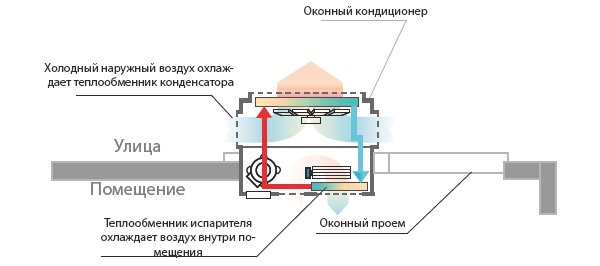

As a rule, they are made according to the "monoblock" scheme and occupy the opening for the window. When choosing a window air conditioner, first check if it is suitable for your particular window (vents). The point is not only in size, but also in the overall strength of the window frame, because the weight of the unit can be considerable, and not every dilapidated window can withstand it.
Keep in mind that most likely there will not be a tight sealed fit of the window air conditioner case, so you will have to solve the issue of insulation from the outside air. Some tenants every summer insert an air conditioner into the window opening and fill the cracks with construction foam, and every autumn they remove the unit to seal the windows for the winter. However, it also happens that the air conditioner is installed, sealed and then takes its place in the window all year round, it just "rests" in winter.
Cheap models may not have a remote control - everything is controlled from the front panel. In this case, this is the right approach - the simpler the better. Less likely to break down complex electronics.
You can clearly see how such an air conditioner works and what happens during its operation in the video:
How does the air conditioner work for heating?
Existing air conditioners, capable of heating in winter, are usually equipped with a four-way valve. This valve, switching, makes the refrigerant heat up from the ambient air, and, on the contrary, give off heat to the room. This is a very economical way of heating a building, since most of the energy is spent not on raising the air temperature itself, but on transferring heat from the street to the house.
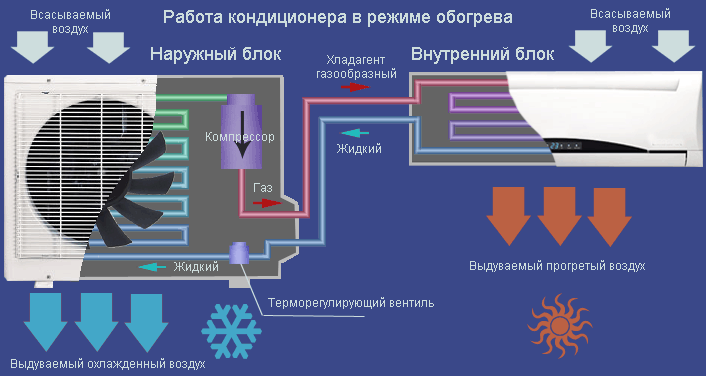

On average, heating a room with an air conditioner is about 3 times more economical than heating a home with electrical appliances that are equipped with heating elements (thermal electric heaters). How to set up the air conditioner for warmth is described here:.
However, it should be borne in mind that the colder it is outside the window and the warmer it should be in your room, the less the air conditioner is suitable for this. At a frost of -15 and below, a household air conditioner usually can no longer provide heat transfer from the street to the house, since:
- The air conditioner is originally intended for cooling, therefore, in the heating mode of the dwelling, its efficiency drops along with the ambient temperature.
- The modern environmentally friendly refrigerant is also not suitable for frost.
- It is difficult for the compressor to operate in cold weather - the lubricant becomes too dense.
Many split-systems have automatic switching between the "cold" - "heat" modes, regularly switching to the room cooling mode (with the general "heat" mode), but without the operation of the fan inside the building. This is done to warm up the radiator in the external block of the system so that it does not get covered with ice from condensate and does not lose its ability to efficiently exchange heat.
In split systems, there is also an unpleasant possibility of the drain hose freezing. The water turns into ice and forms a plug inside the hose. Further flow of water from the air conditioner will no longer take place outside, but into the room.
After getting acquainted with all the variety of types of this climatic technology, it will be much easier for you to choose an air conditioner to suit your needs. Of course, in this case it is worth starting from the type of room that will need to be cooled, as well as from the financial capabilities.
System operation
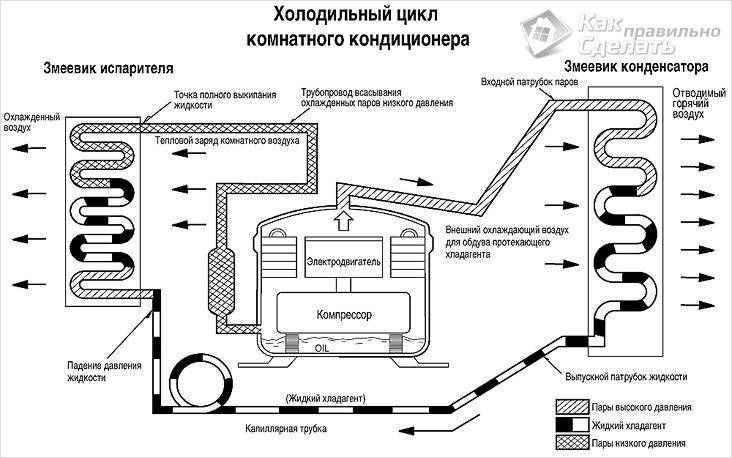

The functioning of the air conditioning system
All parts of the air conditioner (except for the fans) are interconnected with thin copper tubes. In some devices, the tubes are made of aluminum. A coolant circulates through the tubes inside the air conditioner (most often it is freon). The cooler takes either gaseous or liquid form. Fans protect the system from overheating.
When the vaporous freon enters the compression hole, it has a temperature of about 10-15 degrees. In this case, its pressure is 4-5 atmospheres. The refrigerant is compressed in the compressor, the pressure increases 5 times, and the freon temperature rises to 90 degrees.
Very hot freon enters the condenser. There it cools, releasing heat, and smoothly turns into a liquid state. Next, the freon passes the throttle and enters the evaporator. Here, a liquid agent is mixed with a gaseous one. It evaporates and creates cooling. After that, freon enters the compressor again, and the cycle closes. This is how a simple diagram of how an air conditioner works.