General concept of a conditioning device

This is an electrical device, the list of the main tasks of which includes maintaining comfortable climatic conditions in rooms for various purposes. In addition, there are small-sized air conditioners for vehicles and production equipment. The bulk of these devices is a class of household and industrial models. In the second case, the intended use has a slightly different nature than in the household segment. But in both categories, the basic concept of an air conditioner can be represented as follows: an electrical appliance whose work is aimed at regulating the temperature regime in a certain range. According to the standards, climatic equipment must provide the ability to regulate temperature in the range of 17-25 ° C. At the same time, modern devices are able to maintain modes in the range from -5 to 40 ° C. In addition, multifunctional devices also regulate humidity (coefficient - 50-60%), air mass mobility (up to 0.15 m / s) and even the content of some gases (for example, oxygen).
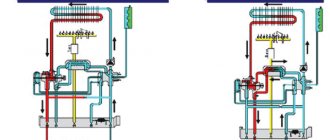
What does a split system consist of?
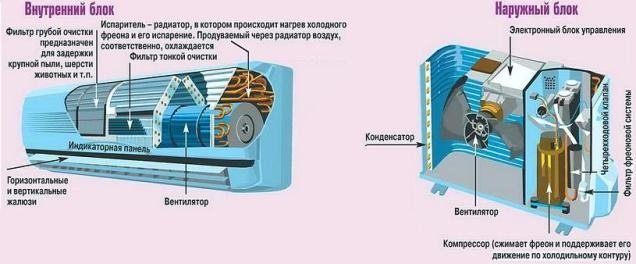
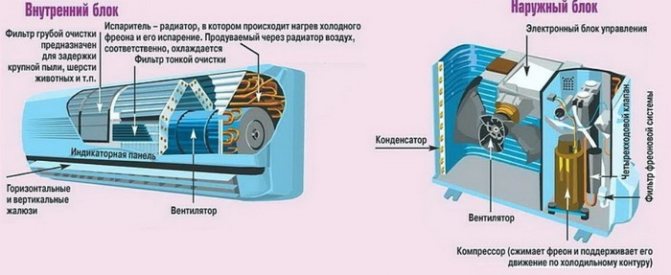
The unit consists of two blocks. It is an internal (evaporative) one, which is a panel, filters, a turbine, an evaporator tray and a control panel, installed in the room on the wall. And the outdoor (compressor-condensing unit), which is installed on the walls from the street side, it houses the compressor, fan, valves, and condenser.

Purpose of the air conditioner
Most often, the equipment is designed for the task of lowering the temperature with the function of humidifying the air. In the summer, the cooling mode is especially in demand, but recently models have appeared that provide heating due to a heat pump. Although there is no question of a full-fledged heating function even at the level of a household heater. In the definition of industrial air conditioners, it is fundamentally important to note their multifunctionality - these are devices that, in addition to temperature control tasks, also purify the air. This function is required in enterprises whose activities are related to the processing of materials and various kinds of raw materials, during which fine dust particles are emitted. To maintain sanitary standards at production sites and the comfort of workers, for example, in wood processing factories, an industrial air conditioner is used. In addition to extended functionality, it is also distinguished by its high power, which allows it to constantly serve premises with an area of up to 250-300 m2.
How does a split system work?
The operation of a split system is based on fundamental laws of physics, in particular on the following: when a liquid evaporates, the hottest molecules disappear first. It is for this reason that people, for example, blow on hot soup, trying to cool it down.
The internal block contains a tube with freon - a boiling liquid. The evaporation of freon leads to the cooling of the vessels, which in this case are the tubes of the heat exchanger. Air masses pass through the fan and are continuously cooled.
However, what happens when the freon runs out? Is the device interrupted? The split system is formed so that the freon does not run out - it moves in a cycle. A compressor is operating, which compresses the vapors and transfers them to the outdoor unit of the device. In the outdoor unit, freon is compressed to a liquid state, after which the freon goes back to the indoor unit, where it continues to perform its function.
After getting acquainted with the principle of operation of the split system, it becomes completely clear why exactly two blocks are needed. Device manufacturers place a fan in the indoor unit, which accelerates the compression of boiling freon, and in the external condenser, compressor and fan - a device that performs the function of converting freon back into liquid.
Compressor models device


It is this type of air conditioners that can work both for cooling and for heating the air, which largely determines its widespread use. The basic set of components in the internal structure of a compressor-type air conditioner can be represented as follows:
- The condenser is a compact radiator module in a block designed for outdoor installation (from the street side). This unit ensures the process of condensation, that is, the transition of gas into a liquid state. Usually radiators are made of aluminum or copper.
- The compressor performs the function of compressing the refrigerant (a working medium like freon) and maintains its circulation in the refrigeration circuit.
- The evaporative radiator is located in the indoor unit (indoors). Provides a process opposite to condensation, that is, with a sharp drop in pressure, the refrigerant already passes from a liquid state to a gaseous state.
- Regulating valves - a throttle that reduces the pressure in the area in front of the evaporator.
- The fans circulate the air flow, thereby blowing the condenser with the evaporator block.
Device and technical points
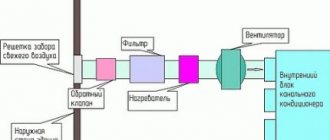
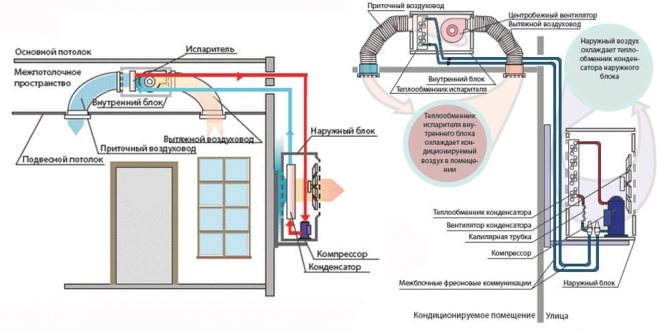
For reliable, safe and efficient operation of the ducted air conditioner, the outdoor unit also has auxiliary equipment - filling fittings, an automation system, various kinds of measuring sensors, an electronic warning system about air conditioner malfunctions. The outdoor unit is located in the open air, preferably from the side less accessible to sunlight. Most often, it is mounted on the wall, but installation on the ground or in other convenient places is possible.
When installing, take into account the technical characteristics and the recommended height differences and distances between the outdoor and indoor units. The indoor unit contains a minimum of refrigeration circuit elements and other elements, based on the fact that the indoor unit is installed inside the room where there are people and the noise from the operation of such an air conditioner should be minimal. Therefore, as few elements as possible are located in the housing of the ducted indoor unit - these are the evaporator heat exchanger and the fan that blows this heat exchanger. It can also contain: a coarse air filter, one or more temperature sensors, a block for receiving a control signal from an infrared control panel (for some models as an option).

Evaporative models device
A simpler design device that performs the tasks of cooling and ventilation. Its advantages include the absence of technological processes associated with the processing of harmful substances like freon in the course of work. The air conditioner device of this type is formed by the following elements:
- Electric motor - controls the operation of the fan, which, in turn, provides the supply of air masses.
- Pipeline infrastructure. Formed by a pump with valves to control the processes of supply and discharge of the aqueous medium.
- Evaporative Filters - Purify water by preventing harmful particles from entering the air. They are usually made of cellulose and have a honeycomb structure.
- The water pan is made of high-strength plastic or metal resistant to temperature extremes and water environments.
Modern models of evaporative air conditioners with the possibility of indirect evaporation have the advantage of eliminating the penetration of moisture into the room.
Split system device
The main difference between a split system and an air conditioner having one monoblock is two interconnected blocks:
External block - it is located outside the house, mounted on an external wall. It is necessary that it be in the fresh air, because it contains a fan, compressor and condenser.
Indoor unit - mounted inside the room. This part of the air conditioning system includes a filter, elements for cooling and heating the air.

These parts are interconnected by copper pipes with a heat-insulating coating. Indoors, they are removed inside the walls or hidden behind decorative panels or suspended ceilings. The interior of modern models of this type is made of durable and lightweight materials. The case looks laconic and fits well into any interior, regardless of the design style. All devices work silently and do not cause any inconvenience.
The second important difference between a split system and a monoblock air conditioner - this is the presence of the function of heating the room with warm air (winter equipment).
The principle of operation of a compressor air conditioner


The operation of the device is based on the circulation of refrigerant (freon) along the contour of pipelines with technological points of its processing. Refrigerant is supplied to the inlet of the compressor unit under low pressure, followed by the process of its compression and heating. Further, freon is sent to the condenser, where, due to intensive blowing, its temperature decreases, and the medium itself turns into a liquid state, while releasing heat. As a result, the air heats up. At the next stage, the principle of operation and the device of the compressor-type air conditioner will have several similarities with the models of the evaporative type, which is expressed by the function of the thermostatic expansion valve. The fact is that after leaving the compressor, freon enters this valve and some of it evaporates under conditions of decreasing temperature and pressure. In the evaporator, the refrigerant takes on a gaseous form, absorbs warm air and cools. This cycle is repeated several times until the set microclimatic indicators are reached.
The principle of operation of the air conditioner
- The principles of the refrigeration machine - a detailed article for specialists in the magazine "Climate World"
The operation of any air conditioner is based on the property of liquids to absorb heat during evaporation and release it during condensation. Let's see how this process takes place in a split system:
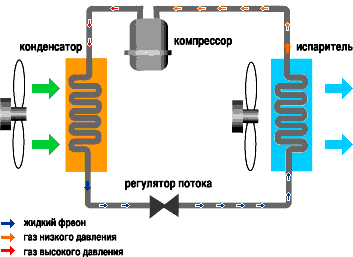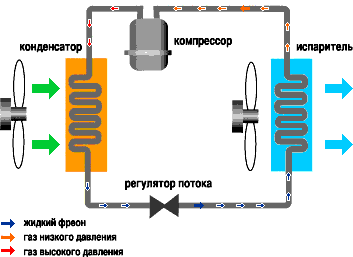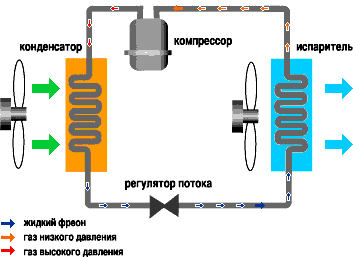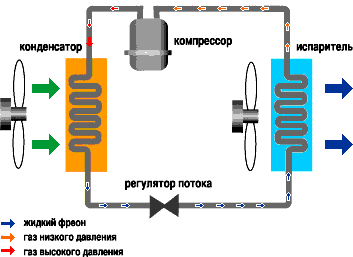
The main components of any air conditioner are:
- Compressor
- compresses freon and maintains its movement along the refrigeration circuit. - Capacitor
- a radiator located in the external block. The name reflects the process that occurs during the operation of the air conditioner - the transition of freon from the gaseous phase to the liquid (condensation). - Evaporator
- a radiator located in the indoor unit. In the evaporator, freon passes from the liquid phase to the gaseous phase (evaporation). - TRV (thermostatic expansion valve)
- lowers the freon pressure in front of the evaporator. - Fans
- create a stream of air blowing over the evaporator and condenser. They are used for more intense heat exchange with the ambient air.For details on the air conditioner design, see the next section - Air conditioner design.
The compressor, condenser, expansion valve and evaporator are connected by copper pipes and form a refrigeration circuit, inside which a mixture of freon and a small amount of compressor oil circulates. During the operation of the air conditioner, the following process occurs:
- Gaseous freon is supplied to the compressor from the evaporator at a low pressure of 3 - 5 atmospheres and a temperature of 10 - 20 ° C.
- The compressor compresses the freon to a pressure of 15 - 25 atmospheres, as a result of which the freon heats up to 70 - 90 ° C and enters the condenser.
- The condenser is blown with air having a temperature below the freon temperature, as a result, freon cools down and passes from the gaseous phase to the liquid phase with the release of additional heat. This heats up the air passing through the condenser. At the exit from the condenser, freon is in a liquid state, under high pressure, the freon temperature is 10 - 20 ° C higher than the ambient air temperature.
- From the condenser, warm freon enters the thermostatic expansion valve (TRV), which in domestic air conditioners is made in the form of a capillary (a long thin copper tube twisted into a spiral). As a result of passing through the capillary, the freon pressure drops to 3 - 5 atmospheres and the freon cools down, part of the freon can evaporate at the same time.
- After the expansion valve, a mixture of liquid and gaseous freon with low pressure and low temperature enters the evaporator, which is blown by room air. In the evaporator, freon completely turns into a gaseous state, taking heat from the air, as a result, the air in the room is cooled. Then gaseous freon with low pressure enters the compressor inlet and the whole cycle is repeated.
This process underlies the operation of any air conditioner and does not depend on its type, model or manufacturer. In "warm" air conditioners, a four-way valve (not shown in the diagram) is additionally installed in the refrigeration circuit, which allows you to change the direction of movement of freon, changing the evaporator and condenser in places. In this case, the indoor unit of the air conditioner heats the air, and the outdoor unit cools it.
Note that one of the most serious problems during the operation of an air conditioner arises if the freon in the evaporator does not have time to completely go into a gaseous state. Then a liquid enters the compressor inlet, which, unlike gas, is incompressible. As a result, a water hammer occurs and the compressor breaks down. There may be several reasons why freon may not have time to evaporate. The most common are dirty filters (this impairs the airflow to the evaporator and heat exchange) and the operation of the air conditioner at low outside temperatures (in this case, supercooled freon enters the evaporator).
| Where to place blocks | To the top | Air conditioner design |
The principle of operation of the evaporative air conditioner
The cooling process as a result of the evaporation of the aqueous medium can be implemented in different ways, which is why direct and indirect regulation of the microclimate is distinguished. In the first case, cooling is based on an isenthalpic process and is recommended for cold weather applications. In summer, air conditioners with direct evaporation can be effective only with an insignificant humidity coefficient. The principle of an air conditioner with indirect cooling involves the use of a surface heat exchanger with an air cooler. Cooled air circulates through the channels connecting them, the temperature regulation of which will depend on external irrigation with water flowing into the sump. Indirect evaporation reduces the performance of the air conditioner, but expands the functionality of regulation due to the reduced moisture content of the supply air.
The principle of operation of the split system

The principle of operation of all cooling units is based on freon. Freon is a mixture of ethane and methane. Freon can be in liquid and gaseous form.
By turning on the cooling or heating function, the system picks up the desired temperature, after which it switches to fan mode. When the target is reached (depending on which mode is selected), the cooling (heating) system will turn on again. Split - the system is equipped with a night mode. The principle is the same.The advantage is that the integrated program raises the temperature by 1 degree every 2 hours to avoid hypothermia.
In heating mode, the equipment can be used if outside the window is not lower than - 8 degrees Celsius.
Varieties of air conditioners in terms of installation


- Mobile air conditioners. The smallest models that can be carried from place to place by plugging into a power outlet in any accessible place.
- Wall appliances. This is the classic and most common form factor, which is divided into two units - indoor and outdoor.
- Channel models. They are integrated into the main duct system - as a rule, they are placed in an overhead recess with the working part exit to the room.
- Cassette models. Also a kind of ceiling air conditioner, but which is not built into the ventilation channel, but communicates with it through the pipes.
- Floor and ceiling devices. Placed on the principle of conventional heaters - convectors or radiators. They have low performance, but due to their compact size and stylish design they are in high demand.
- Column models. The form factor, as the name implies, is presented in the form of a column. That is, the installation is carried out on the floor, however, unlike mobile air conditioners, such devices are mainly stationary and provide for communication with an external unit that works for cooling.
Air conditioning systems
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMS (SCR)
Air conditioning systems are a general concept that unites all systems designed to maintain the specified climatic parameters of indoor air.
What is the air conditioning system for?
An air conditioning system for a home solves many problems, without which there can be no talk of normal living conditions with a good level of comfort.
- Humidify or dry the air.
- Maintain a certain temperature in the house.
- Purify the air that is supplied to our homes.
- Maintain air circulation and air exchange.
The air conditioning system, in contrast to the ventilation system, provides not only the change of air in the room according to the principle of general ventilation, but also automatically maintains the necessary meteorological conditions in it, regardless of the season and the variable supply of heat and moisture into the room.
An air conditioning system can provide clean air in a room, its gas composition, aromatic odors, the content of light ions, and in some cases a certain air pressure.
For small premises, such as an apartment or a separate office, air conditioning systems are used in the form of air conditioners of various modifications or split systems.
Not everyone knows that the purpose of the air conditioning system is also to maintain an acceptable level of carbon dioxide in the room.
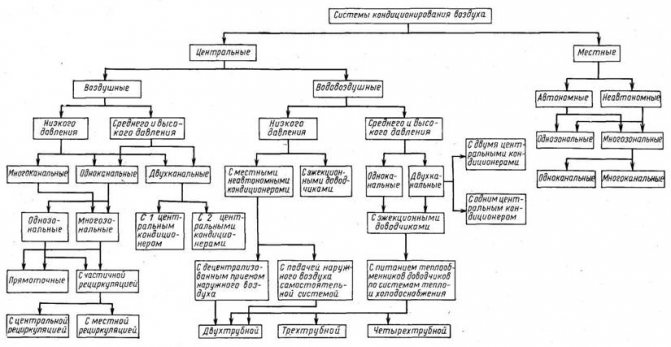
Modern air conditioning systems can be classified according to the following criteria:
- for the main purpose (object of application): to create comfortable conditions for people or technological (to maintain the temperature regime in production);
- according to the principle of the location of the air conditioner in relation to the manned room: central (designed for several rooms and located outside the operated room) or local (located directly in the operated room);
- by the presence of its own (included in the design of the air conditioner) source of heat and cold: autonomous and non-autonomous;
- according to the principle of operation: direct-flow, recirculation and combined;
- according to the method of regulating the output parameters of conditioned air: with qualitative (one-pipe) and quantitative (two-pipe) regulation;
- according to the degree of provision of meteorological conditions in the serviced room: first, second and third class;
- by the number of rooms served (local zones): single-zone and multi-zone;
- by the pressure developed by the fans of air conditioners: low, medium and high pressure.
Types of air conditioners
Currently, there are several types of air conditioners in use:
Window air conditioner - all its parts are located in one body (monoblock type), installed in the window so that part of the body is located outside, and the other is inside the room. A window air conditioner is practically out of use, since during operation it creates a high level of noise and violates the thermal insulation of the room.
Split system - consists of 2 blocks, interconnected by copper pipes, through which freon circulates. Noisy and most of them are located outside the room, and from the inside there is a wall, ceiling, duct or column unit with a good design.
Mobile air conditioner - there are two types - mobile monoblocks or mobile split systems. They can be quickly and easily mounted and dismantled, can be transported from place to place, taken with you to the dacha, etc.
Central air conditioning system - is completed from several units and usually serves for air conditioning of several rooms. Central air conditioning systems can not only cool or heat the air, but also ventilate, humidify and purify it.
Air conditioning systems with chillers and fan coil units - cool the heat transfer fluid that is supplied to the ventilation system and cools the room.
VRF multi-zone air conditioning systems - the main difference from split systems is the multi-zone use and the distribution of the cooler among the blocks as required.
If we talk about the types of air conditioning systems, then there is a great variety, since there are devices for an apartment, and devices for office buildings, and units for industrial premises.
Automation of air conditioning systems in this case is achieved by using additional equipment.
They can be made in the form of a monoblock or a two-component device - a split system.
- The first ones have in one case all the elements that ensure the movement of freon along the refrigeration circuit.
- In the latter, the noisier parts are taken out into the outdoor unit, which is located outdoors, and in the internal (room) unit there are filters, a fan, an evaporative radiator, sometimes a control board and other quiet parts.
The air conditioning system consists of an installation in which the heat and humidity treatment of the air (the air conditioner itself) is carried out, a source of cold supply, devices for automatically maintaining the specified air parameters in the room and a duct system.
The device of any SCR running on freon assumes the presence of such important elements as:
- a compressor that compresses and sucks the refrigerant;
- evaporative and condenser type heat exchangers, through which heat energy is transferred from freon to the environment;
- fans that provide blowing of heat exchangers;
- mechanical cleaning filters + often fine filters;
- control board responsible for the operation of all electronics;
- flow regulator (expansion valve or capillary tube) for dosing liquid refrigerant from the condenser to the evaporator;
- 4-way valve in "warm" air conditioners, redirecting the refrigerant in the other direction.
The device of the air conditioning system assumes the presence of a compressor in its composition.
It is the compressor, by creating a reduced pressure, that causes the evaporation of freon, while absorbing heat from the room. Entering the external unit, freon vapors turn into liquid again, emitting heat.If the blocks are "swapped", then the air conditioner will work in the opposite direction, heating the room.

Features of large ventilation and air conditioning systems
• versatility of the units. Almost all of them perform several functions concurrently.
• modularity of all elements of the system, that is, all units are a constructor. For a specific building and specific premises, the ventilation and air conditioning system is always selected individually. And components such as control and automation cabinets and air ducts are always made individually, to order.
• water is used to transfer both heat and cold. In some cases, not pure water is used as a refrigerant, but, to increase the cooling capacity, an ethylene glycol solution is used. That is, in general, a large air conditioning and ventilation system is water-based.
What ventilation and air conditioning systems are made of
Refrigeration machines
They serve as a source of cold for central air conditioners and fan coil units - fan coil units. The chiller can be reversible, that is, it can work as a heat pump and serve as a heat source in the off-season.
Heat point
It is traditionally not referred to as an air conditioning and ventilation system, since the heating point is naturally already present in the building. It is simply a hot water connection point, which serves as a heat source for air heating. Hot water is supplied to the heating sections of central air conditioners and air supply units, as well as to those fan coil units that must work for heating.
Electric boilers
Or other types of boilers. An alternative source of heat in the off-season, when the central heating system is not working, and it is often necessary to heat the premises in spring and autumn anyway.
Central air conditioners
Serve for centralized air conditioning, which is then distributed to the premises through ventilation ducts.
Supply units
“Stripped down” central air conditioner, with fan, heating and filtration sections, but no cooling section. The main task of the air handling unit is to supply fresh air to the premises, additional ones are to heat and filter it.
Fan coil units (fan coil units)
A fan coil unit is the same split-type air conditioner, only cold water from a chiller and / or hot water, which can come from a substation, boiler or chiller, serves as a refrigerant for it.
They can also be wall, floor, ceiling, cassette, duct, etc.
The main burden of creating a microclimate in the premises does not fall on them. Fan coil units serve precisely for precise adjustment of air parameters in each room individually, because it is inconvenient to do this with the help of a centralized air conditioning and ventilation system.
Precision air conditioners
That is, air conditioners precisely control the parameters of the air environment. As a rule, they are not part of the general air conditioning and ventilation system. These are separate monoblock air conditioners (cabinet type) that are installed in separate isolated rooms, such as server rooms, laboratories, etc.
Piping system and pumps
They serve to transfer cold and heat in the air conditioning, ventilation, air heating systems. Collected individually for a specific object.
Duct system
Air supply to the premises from central air conditioners and supply units. It is also made and assembled individually.
Fans
As a rule, in the air conditioning and ventilation system, separate fans are either exhaust or smoke exhaust. Supply ventilation is carried out by central air conditioners and supply units.
Automation system
Control cabinets, computerized dispatcher's workstation, indoor sensor system, etc.
Various additional equipment
Tasks performed by the mentioned system components
Cold supply - chillers
Heat supply - heating point, less often boilers and reversible chillers
Conditioning - central air conditioners, precise finishing with fan coils
Forced ventilation - supply units, less often central air conditioners
Exhaust ventilation - separate exhaust fans
Air heating - supply units, less often central air conditioners
All this is connected together by a system of pipelines, air ducts, and is controlled by a single automation system.
These are the components of air conditioning, ventilation and air heating systems, i.e. a system for providing a comfortable microclimate.
Features of split systems
This group includes all models of air conditioners that are divided into two blocks, one of which is taken out into the street, and the other is mounted indoors. A typical split air conditioner device provides for the presence of a compressor, condenser, filters, fans and a connecting line. Actually, the main working processes take place in the external unit, and the internal module only provides communication with it, being also responsible for regulating the microclimate parameters. This separation reduces the harmful effects of the refrigerant and completely eliminates the noise in the room from the working compressor.


As a result of the technological improvement of the two-block design, the concept of a multi-split system has appeared and is successfully applied. The air conditioning device of this type differs in that several compressors with condensers and multi-way valves can be involved in one working infrastructure. Multi-component systems allow control from one indoor unit, while controlling the operation of several outdoor modules.
Types of air conditioners, their pros and cons


Household air conditioners are divided into three groups:
- stationary monoblocks;
- split systems (used most often);
- mobile monoblocks.
Air conditioner with split air system (split system)
The design of such a unit is quite simple. The main elements are two blocks. They are interconnected by wires and tubes. Freon is transmitted through the latter.
Outdoor unit - it is he who performs all the key tasks. Inside there is a condenser and refrigerant refrigerant, which is circulated by the compressor.
The indoor unit houses the evaporator - an element whose function is to cool the air flow before supplying it to the room. The housing also includes integrated flow control louvers and a filter system.
Advantages of this type of device:
- lack of noise during operation;
- the ability to set the desired temperature;
- the ability to regulate the air flow.
The disadvantages include:
- labor intensity and high cost of installation (for installation, you need to contact the master);
- high risk of damage to the outdoor unit by residents of the lower floors.
A multi split system is the same. The difference lies in the fact that such equipment provides for several indoor units with one external one.
Monoblock mobile air conditioner
Installation of a monoblock can be done by hand. The key element of the unit is the body. Installation is most often done in the opening of either a window or a door. Dignity is mobility. Disadvantages:
- low efficiency, since the body is not sealed;
- noisy work.
Nowadays, mainly silent operating devices are in demand. Therefore, this type of device has practically disappeared from the market.
Stationary monoblock
Stationary devices have the lowest price. Installed in window openings or cuts into supporting structures. Disadvantages:
- make a lot of noise;
- in winter, cold air will be passed through the building into the room.
This is a great option for a country cottage. The only advantage is cheapness. In stores today are rare.
Possibilities of modern air conditioners
Regardless of the form factor and principle of operation, most of the new generation models provide enhanced control over the processes of microclimate regulation. What is a modern air conditioner in terms of user control? This is an ergonomic device that, through remote control, provides opportunities for informing about temperature, humidity and even the composition of the air environment. The remote control usually has a digital display with control elements (sometimes touch-sensitive). Also, some devices integrate a Wi-Fi module to implement remote control at a remote distance via mobile devices.
Air conditioner operation
After installation, in addition to using the device for its intended purpose, the owner is required to perform a number of preventive maintenance operations. For example, the device of an air conditioning system with a compressor block provides for the presence of a special infrastructure for convenient measurement of performance indicators, by which it is possible to monitor the state of the refrigerant that periodically requires replacement. As for the evaporative systems, they need constant renewal of the aquatic environment with topping up. Also, to maintain the operating condition, it is recommended to regularly purge the communication channels, clean the blocks and the drainage system.


What is an inverter split system: differences and features
In some cases, this kind of low-capacity duct air conditioners can be used for domestic use, but not for all premises. A feature of the location of indoor units is the mandatory presence of space between the main ceiling and the suspended ceiling. It is in this free space that the ducted indoor unit and air ducts are located, through which air is distributed to the room / rooms and, accordingly, is taken from them. If there is an inflow of fresh air, then there must be a special air duct through which such air is supplied for processing to the indoor unit. It is for this reason that ducted air conditioners are used in office, industrial and other premises, where the ceiling height is large enough, which makes it possible to make their use available in such cases.
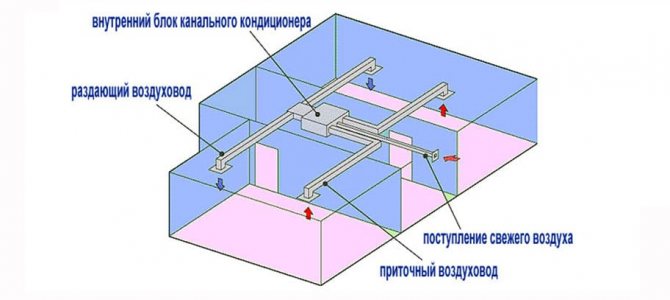

In modern cottages, if the height of the ceilings allows, it is also possible to use channel air conditioners, and in this case they act as household equipment.
Main advantages
:
- installation of one indoor unit can provide air preparation in several rooms;
- possible admixture of fresh air, which allows to ensure the flow of oxygen-enriched air;
- hidden installation of all equipment, inlet and outlet ducts, which does not in any way affect the external interior of the room;
- operation control is possible both with a wired and with an infrared control panel.
Negative aspects
:
- if one indoor unit provides air handling in several rooms, then the same temperature will be maintained in all rooms. This is not always convenient;
- use is possible only for rooms with high ceilings;
- complex selection, calculation and routing of air ducts in rooms. You should not entrust such work to unqualified specialists.
Pros of the air conditioner
Each type of this device has its own advantages and weaknesses, but, in principle, they are the optimal solution for fulfilling the tasks of regulating microclimatic parameters. For example, compressor models benefit from power and versatility of application, while evaporative models are distinguished by energy efficiency and ventilation capabilities. For industrial applications, a split air conditioner with a multi-component connection of operating modules is optimally suited. In this case, with a small amount of installation activities, it is possible to provide many rooms with effective high-power microclimate controllers.
Cons of the air conditioner
The main complaints about this equipment, in addition to the need for maintenance and their structural complexity, relate to harm to health. Moreover, this also applies to devices that do not provide for the use of refrigerants. After all, what is an air conditioner as a regulator of microclimatic parameters? This is a tool that theoretically allows you to change the temperature, humidity and air flow rates in an accelerated mode. If, however, the process of changing these indicators is incorrectly approached, sharply adjusting their values, then the risk of diseases and, above all, colds, increases.
Cleaning
The conditioner is beneficial as long as it is clean. It is very important to carry out preventive procedures. If you do not follow the rules of operation and hygiene, this can lead to rapid wear of the device, excessive energy consumption, as well as health problems. Cleaning can be carried out both independently and with the help of specialists. The recommended frequency of cleaning is at least once a month, and the filters (nets) in the indoor unit are twice a week.