The air exchange rate in the premises of retail trade enterprises (stores)
| № | Premises | Estimated air temperature for the cold season, ° С | The rate of air exchange or the amount of air removed from the premises | |
| inflow | hood | |||
| 1 | Sales areas of shops with an area of 400 m2 or less: | |||
| food | 16 | — | 1 | |
| non-food | 16 | — | 1 | |
| 2 | Sales halls of shops with an area of more than 400 m2: | |||
| food | 16 | By calculation | By calculation | |
| non-food | 16 | By calculation | By calculation | |
| 3 | Cutting | 10 | 3 | 4 |
| 4 | Unloading rooms | 10 | By calculation | By calculation |
| 5 | Premises for preparing goods for sale (when placed in a separate room), picking, acceptance | 16 | 2 | 1 |
| 6 | Pantries (uncooled): | |||
| bread, confectionery; | 16 | — | 0,5 | |
| gastronomy, fish, milk, fruits, vegetables, pickles, wine, beer, drinks; | 8 | — | 1 | |
| footwear, perfumery, household chemical goods, chemicals; | 16 | — | 2 | |
| other goods | 16 | — | 0,5 | |
| 6.1 | Premises for the preparation of goods for sale (when placed in a separate room), picking, acceptance, expeditions | 16 | 2 | 1 |
| 7 | Premises for demonstration of new products (if placed in a separate room) | 16 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | Ironing | 16 | By calculation | By calculation |
| 9 | Waste chambers (unheated) | — | — | — |
| 10 | Room for mechanized pressing of paper waste | 16 | — | 1,5 |
| Storage rooms: | ||||
| 11 | packaging materials and inventory | 16(8) | — | 1 |
| 12 | exchange fund containers | — | — | 1 |
| 13 | containers | 8 | — | 1 |
| 14 | cleaning equipment, detergents | 16 | — | 1,5 |
| 15 | Linen | 18 | — | 0,5 |
| 16 | Workshops, laboratories | 18 | 2 | 3(2) |
| 17 | Refrigerated containment chambers: | |||
| meat, semi-finished products, gastronomy | 0 | — | — | |
| fish | -2 | — | — | |
| vegetables, fruits, confectionery, drinks | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| ice cream, dumplings, etc. | -12 | Periodically | ||
| food waste | 2 | — | 10 | |
| 18 | Air-cooled machine rooms | 5 | By calculation | |
| 19 | Water-cooled chilled chamber machine rooms | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| 20 | Office premises, staff room, main cash desk, security room, ACS strong point | 18 | — | 1 |
| 21 | Dressing rooms, utility room for catering staff, dining room | 16 | — | 1 |
| 22 | Public toilets for shoppers and toilets for staff | 16 | — | 50 m3 / h per toilet |
| 23 | Showers | 25 | — | 5 |
| 24 | Dispensary room (when the store is located in the underground floors) | 20 | — | 60 m3 / h per person |
| 25 | Premises for receiving and issuing orders | 12 | — | 1 |
| 26 | Glass container reception rooms | 16 | — | 1 |
| 27 | Health center | 20 | 1 | 1 |
Estimated air exchange
For the calculated value of air exchange, the maximum value is taken from the calculations for heat input, moisture input, intake of harmful vapors and gases, according to sanitary standards, compensation for local hoods and the standard rate of air exchange.
The air exchange of residential and public premises is usually calculated according to the frequency of air exchange or according to sanitary standards.
After calculating the required air exchange, the air balance of the premises is compiled, the number of air diffusers is selected and the aerodynamic calculation of the system is made. Therefore, we advise you not to neglect calculation of air exchangeif you want to create a comfortable environment for your stay indoors.
Air exchange rate in the premises of public catering establishments
| № | Names of premises | Design air temperature, ° С | Air exchange rate per hour | |
| inflow | hood | |||
| 1 | Hall, dispensing | 16 | According to the calculation, but not less than 30 m3 / h per person. | |
| 2 | Lobby, entrance hall | 16 | 2 | — |
| 3 | Cooking shop | 16 | 3 | 2 |
| 4 | Hot shop, confectionery baking room | 5 | By calculation, but not less than 100 m3 / h per person. | |
| 5 | Workshops: precooking, cold, meat, poultry, fish, processing of greens and vegetables | 18 | 3 | 4 |
| 6 | Premises of the production manager | 18 | 2 | — |
| 7 | Premises for flour products and confectionery finishing, linen | 18 | 1 | 2 |
| 8 | Room for cutting bread, for preparing ice cream, service, utility room | 18 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | Washing room: dining room, kitchen utensils, pans, containers | 18 | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | Director's office, office, main cash desk, rooms of waiters, staff, storekeeper | 18 | 4 | 6 |
| 11 | Pantry for dry products, pantry for inventory, pantry for wine and vodka products, storage room for beer | 12 | — | 1 |
| 12 | Pantry of vegetables, pickles, containers | 5 | — | 2 |
| 13 | Reception | 16 | 3 | — |
| 14 | Engine room for refrigerated chambers with air-cooled units | By calculation | By calculation | By calculation |
| 15 | The same with water-cooled units | — | 3 | 4 |
| 16 | Repair shops | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 17 | Premises of public organizations | 16 | 1 | 1 |
| 18 | Refrigerated storage chambers: | |||
| meat | 0 | — | — | |
| fish | -2 | — | — | |
| dairy products, gastronomy | 2 | — | — | |
| semi-finished products, including a high degree of readiness | 0 | — | — | |
| vegetables, fruits, berries, drinks | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| confectionery | 4 | — | — | |
| wines and drinks | 6 | — | — | |
| ice cream and frozen fruits | -15 | — | — | |
| food waste | 5 | — | 10 | |
| 19 | Smoking room | 16 | — | 10 |
| 20 | Unloading rooms | 10 | By calculation | By calculation |
Notes: 1. The air temperatures in rooms (except for refrigerated chambers) indicated in the table are calculated when designing heating systems.
2. In buffets, bars, cocktail halls, banquet halls located in separate rooms, the air ratio is taken as minus 3.
3. The air temperatures in the refrigerated chambers indicated in the table are maintained around the clock throughout the year. In chambers for the simultaneous storage of meat and fish or meat, fish semi-finished products, take temperatures ± 0 ° C; for vegetable semi-finished products +2 ° С; for storage of all products (1 chamber in the enterprise) ± 2 ° C.
A little about air exchange
As you know, natural ventilation systems are designed in residential buildings.
The places for removing air from the premises are the kitchen, bath, toilet, that is, the most polluted rooms of the apartment. The supplied outside air enters through cracks, windows, doors.
Over time, the materials and construction of windows have improved. The current structures are completely sealed, which does not allow the necessary air exchange and meet the minimum air exchange rate.
Such problems are solved by installing various air supply systems. These are supply valves in the wall and supply valves in windows.
2.Calculation of air exchange
Air exchange - the amount of air required to completely or partially replace the polluted air in the room. Air exchange is measured in cubic meters per hour.
How do they perform calculation of air exchange? In general, air exchange is determined by the type of air pollutants found in a given room.
The main calculations of air exchange are the calculation for the sanitary standards, the calculation for the normalized frequency rate, the calculation for the compensation of local extracts. There is also air exchange for the assimilation of apparent and total heat, for the removal of moisture, for the dilution of harmful substances in the air. Each of these criteria has its own method for calculating air exchange.
Before starting the calculation of air exchange, you need to know the following data:
- the amount of harmful emissions into the room (heat, moisture, gases, vapors) in one hour;
- the amount of harmful substances per cubic meter of indoor air.
Air flow rates for modulated equipment
| № | Equipment | Brand | kw | Air volume, m3 / h | |
| Exhaust | Supply | ||||
| 1 | Electric stove | PE-0.17 | 4 | 250 | 200 |
| 2 | PE-0.17-01 | 4 | 250 | 200 | |
| 3 | Electric stove | PE-0.51 | 12 | 750 | 400 |
| 4 | PE-0.51-01 | 12 | 750 | 400 | |
| 5 | Roasting cabinet | ShZhE-0.51 | 8 | 400 | — |
| 6 | ShZhE-0.51-01 | 8 | 400 | — | |
| 7 | ShZhE-0.85 | 12 | 500 | — | |
| 8 | ShZhE-0.85-1 | 12 | 500 | — | |
| 9 | Electric device, cooking | UEV-60 | 9,45 | 650 | 400 |
| 10 | Mobile boiler | KP-60 | — | — | — |
| 11 | Deep fryer | FE-20 | 7,5 | 350 | 200 |
| 12 | Cooking kettle with a capacity, l: | ||||
| 100 | KE-100 | 18,9 | 550 | 400 | |
| 160 | KE-160 | 24 | 650 | 400 | |
| 250 | KE-250 | 30 | 750 | 400 | |
| 13 | Steam cooking apparatus | APE-0.23A | 7,5 | 650 | 400 |
| APE-0.23A-01 | 7,5 | 650 | 400 | ||
| 14 | Electric frying pan | SE-0.22 | 5 | 450 | 400 |
| SE-0.22-01 | 5 | 450 | 400 | ||
| SE-0.45 | 11,5 | 700 | 400 | ||
| SE-0.45-01 | 11,5 | 700 | 400 | ||
| 15 | Steam table | ITU-0.84 | 2,5 | 300 | 200 |
| ITU-0.84-01 | 2,5 | 300 | 200 | ||
| 16 | Food warmer mobile | MP-28 | 0,63 | — | — |
Source: "Design of public catering establishments" Reference manual to SNiP 2.08.02-89
Application area
1.1. This standard establishes the minimum air exchange rates for outdoor air (outdoor air consumption rates), which ensures the necessary cleanliness (quality) of air in the manned premises and its minimum possible adverse effect on human health. The minimum air exchange rates are not calculated.
1.2. Indoor air quality must be ensured regardless of the adopted ventilation system and air exchange organization scheme.
1.3.This standard applies to all areas that may be occupied by people in residential and public buildings, except for areas for which other regulations or special conditions require greater air exchange than specified in this standard.
1.4. This standard applies to all premises in which the microclimate parameters are ensured in accordance with the requirements of GOST 30494-96 “Residential and public buildings. Indoor microclimate parameters ", SNiP 31-01-2003" Residential apartment buildings ", SNiP 2.08.02-89 *" Public buildings and structures ", SNiP 31-05-2003" Public administrative buildings ", MGSN 3.01-01" Residential buildings ".
1.5. This standard deals with chemical, physical and biological pollutants entering, emitted or generated in a room that can affect air quality.
1.6. This standard does not address factors that influence human perception of air quality, such as:
- unidentified and unexplored pollutants;
- the difference in susceptibility among different people, psychological stress, etc.
1.7. This International Standard proposes two methods for calculating the minimum air exchange rates sufficient to provide an acceptable indoor air quality.
1.7.1. Methodology based on specific air exchange rates: the required air quality is ensured by supplying a certain amount of outdoor air to the room, depending on the purpose of the room and its mode of operation. This technique is recommended to be used to calculate the amount of air exchange in rooms, in which, as a rule, changes in their purpose, the amount and nature of pollutants entering the room during the operation period are not expected.
1.7.2. Methodology based on the calculation of permissible concentrations of pollutants: the required air quality is ensured by supplying a certain amount of outdoor air to the room, depending on the size and nature of the pollutants in the room. This technique is recommended to be used to calculate the amount of air exchange in rooms that can change their purpose and / or mode of operation during operation, in which intense sources of pollutants can be present or appear, etc.
1.8. The design documentation should indicate which of the methods was used when calculating air exchange.
Frequency rate of air exchange in the premises of sports and recreation institutions
| № | Names of premises | Design air temperature, ° С | Air exchange rate per hour | |
| inflow | hood | |||
| 1 | Sports halls without seats for spectators (except for rhythmic gymnastics halls) | 15 | By calculation, but not less than 80 m3 / h per one practitioner | |
| 2 | Rhythmic gymnastics halls and choreographic classes | 18 | According to the calculation, but not less than 80 m3 / h per one practitioner | |
| 3 | Rooms for individual strength and acrobatic training, individual warm-up before the competition | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 4 | Workshops | 16 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | Classrooms, methodological rooms, rooms for instructors and coaches, judges, press, administrative and engineering staff | 18 | 3 | 2 |
| 6 | Household premises of workers, employees of the protection of public order | 18 | 2 | 3 |
| 7 | Fire post premises | 18 | — | 2 |
| 8 | Outerwear dressing room for practitioners | 16 | — | 2 |
| 9 | Locker room (including massage rooms) | 25 | Balance taking into account showers | 2 (via showers) |
| 10 | Showers | 25 | 5 | 10 |
| 11 | Massage | 22 | 4 | 4 |
| 12 | Sanitary facilities: | |||
| common use | 16 | — | 100 m3 / h per toilet or urinal | |
| for practicing (with dressing rooms) | 20 | — | 50 m3 / h per toilet or urinal | |
| individual use | 16 | — | 25 m3 / h per toilet or urinal | |
| 13 | Washrooms at public sanitary facilities | 16 | — | At the expense of sanitary facilities |
| 14 | Inventory at the halls | 15 | — | 1 |
| 15 | Storerooms and warehouses: | — | ||
| with the constant presence of service personnel; | 16 | — | 2 | |
| with a short stay of service personnel | 10 | — | 1 | |
| 16 | Warehouses for reagents, household chemicals and paints | 10 | — | 2 |
| 17 | Drying rooms for sportswear | 22 | 2 | 2 |
Air exchange rates
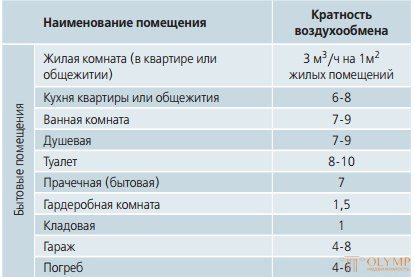
This table shows the values of the air exchange rate for domestic premises: Air exchange rates for industrial premises and premises with a significant volume:
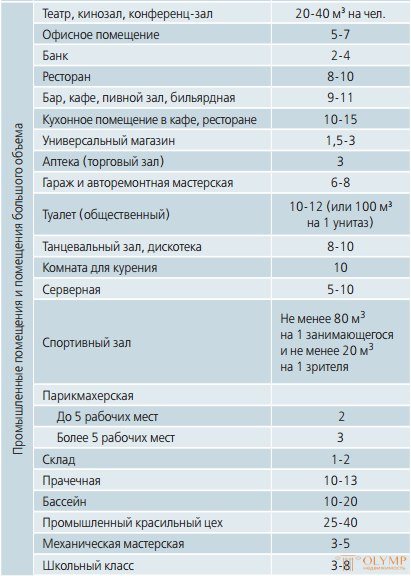

The above data are taken from the reference books of the well-known Ukrainian company Vents.
Air exchange rate in the premises of a credit and financial institution
| № | Names of premises | Design air temperature, ° С | Air exchange rate per hour | |
| inflow | hood | |||
| 1. | Operating and checkout rooms | 18 | Based on the assimilation of heat and moisture surpluses, but not less than twice the air exchange | |
| 2. | Shared work rooms, coin counters | 18 | 2 | 2 |
| 3. | Room for meetings and negotiations | 18 | 3 | 3 |
| 4. | Cashier for counting banknotes | 18 | 3 | 3 |
| 5. | Computing facilities, computing center | 18 | Calculated for assimilation of heat and moisture surplus | |
| 6. | Communication room (teletype) and photocopying | 18 | 2,5 | 2,5 |
| 7. | Offices and receptions | 18 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| 8. | Archive, pantry of forms, pantry of equipment and inventory, pantry of bank materials, room for storing personal belongings of cashiers | 18 | — | 1,5 |
| 9. | Repair shops | 18 | 2 | 2 |
| 10. | Meal room, buffet | 16 | 3 | 4 |
| 11. | Room for storing weapons, loading and cleaning weapons | 16 | — | 1 |
| 12. | Boxes for collector cars | 18 | According to the design standards for parking garages | |
| 13. | Security premises with a fire station | 18 | 1 | 1,5 |
| 14. | Women's personal hygiene facilities | 23 | — | 5 |
| 15. | Sanitary facilities | 16 | — | 50 m3 / h per toilet or urinal |
| 16. | Lobby | 16 | 2 | — |
| 17. | Wardrobes | 16 | — | 2 |
| 18. | Premises for placement of uninterruptible power supply sources | 16 | Calculated for assimilation of heat and moisture surplus | |
General information
Before determining the optimal rate of air exchange rate according to SNiP in premises (residential or industrial), it is necessary to study in detail not only the parameter itself, but also the methods of its calculation. This information will help you choose the value as accurately as possible, which is suitable for each specific room.
Air exchange is one of the quantitative parameters characterizing the operation of the ventilation system in closed rooms. In addition, it is considered the process of replacing air in the interior of a building. This indicator is considered one of the most important in the design and creation of ventilation systems.
There are two types of air exchange
:
- 1. Natural. It occurs due to the difference in air pressure inside and outside the room.
- 2. Artificial. It is carried out with the help of ventilation (opening windows, transoms, vents). In addition, it includes the ingress of air masses from the street through cracks in walls and doors, as well as through the use of various air conditioning and ventilation systems.
Its value is determined not only by SNiP, but also by GOST (state standard). A set of measures that need to be taken to maintain optimal conditions in residential apartments and office premises depends on this indicator.
Ventilation in the apartment. What is natural ventilation in an apartment?
Calculation rules
Most of the newly erected buildings are equipped with sealed windows and insulated walls. This helps to reduce heating costs during the cold season, but leads to a complete cessation of natural ventilation. Because of this, the air in the room stagnates, which causes the rapid multiplication of harmful microorganisms and a violation of sanitary and hygienic standards.
Therefore, in new buildings, it is important to provide for the possibility of artificial air ventilation, taking into account the multiplicity indicator
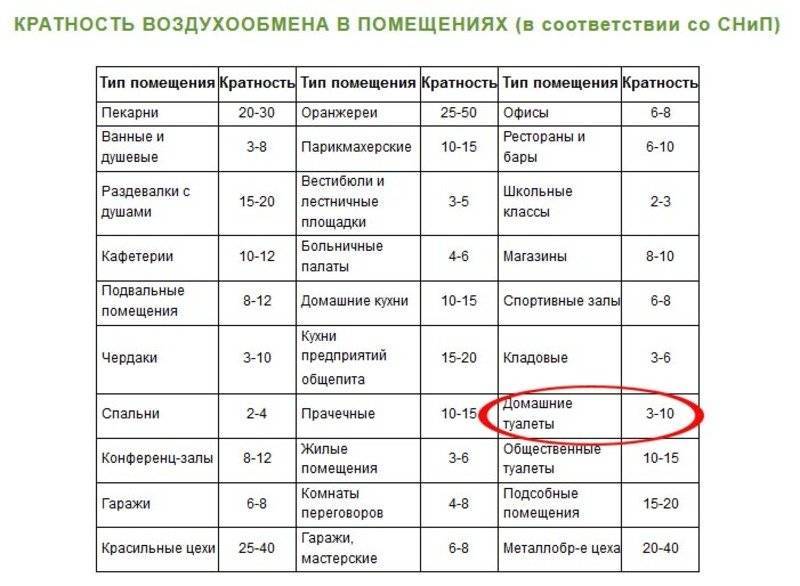

Air exchange rates in premises (residential or industrial) depend on several factors
:
- the purpose of the building;
- the number of electrical appliances installed;
- heat output of all operating devices;
- the number of people who are constantly in the room;
- level and intensity of natural ventilation;
- humidity and.
The air exchange rate can be determined using the standard formula.It provides for dividing the required amount of clean air entering the building in 1 hour by the volume of the room.
Air exchange rate in administrative and residential buildings
SNiP 2.09.04-87 *
| № | Premises | Temperature during the cold season | Frequency rate or volume of air exchange, m3 / h | |
| Inflow | Hood | |||
| 1. | Lobby | +16° | 2 | — |
| 2. | Heated passages | Not lower than by 6 ° C the design temperature of the rooms connected by the transitions | — | — |
| 3. | Streetwear wardrobes | +16° | — | 1 |
| 4. | Wardrobes for joint storage of all types of clothing with part-time dressing of workers | +18° | Based on the compensation of the hoods from the shower rooms (but not less than one air change in 1 hour) | According to clause 4.8 |
| 5. | Dressing rooms at showers (pre-showers), as well as with full dressing of workers a) dressing clothes | +23° | 5 | 5 |
| b) dressing rooms of home (street and home) clothes | +23° | Based on the compensation of the hoods from the shower rooms (but not less than one air change in 1 hour) | According to clause 4.8 | |
| 6. | Showers | +25° | — | 75 m3 / h for 1 shower net |
| 7. | Lavatories | +16° | — | 50 m3 / h for 1 toilet and 25 m3 / h for 1 urinal |
| 8. | Washrooms at latrines | +16° | — | 1 |
| 9. | Smokers | +16° | — | 10 |
| 10. | Rest, heating or cooling rooms | +22° | 2 (but not less than 30 m3 / h for 1 person. | 3 |
| 11. | Premises for personal hygiene of women | +23° | 2 | 2 |
| 12. | Premises for the repair of workwear | +16° | 2 | 3 |
| 13. | Premises for shoe repair | +16° | 2 | 3 |
| 14. | Premises for administrations, design bureaus, public organizations, with an area: a) no more than 36 m2 | +18° | 1,5 | — |
| b) more than 36 m2 | +18° | By calculation | ||
| 15. | Drying rooms for workwear | According to technological requirements within the range of 16-33 ° С | Also | |
| 16. | Dust collection rooms for workwear | +16° | « | |
Source: Administrative and domestic buildings SNiP 2.09.04-87 *
5.1. Methodology based on specific air exchange rates
This technique establishes:
- permissible quality of the outside air, determined by the value of the MPC of pollutants in the outside air;
- methods of processing outdoor air, if necessary;
- rates of specific air exchange in residential and public buildings;
- operating modes of ventilation (air conditioning) systems under variable loads and / or with periodic use of premises.
5.1.1. The concentration of harmful substances in the outside (atmospheric) air used for ventilation (air conditioning) should not exceed the MPC in the air of populated areas.
The MPC values should be taken in accordance with GN 2.1.6.1338-03 and GN 2.1.6.1339-03.
The MPC values for pollutants most often present in the air are presented in Table 1.
With the joint presence in the atmospheric air of several harmful substances with the summation of the action, the sum of their relative concentrations, calculated according to the following formula, should not exceed 1:
Here Сi is the concentration i
-th pollutant in the outside air, mg / m3.
5.1.2. If the level of outdoor air pollution exceeds the values given in table 1, it must be cleaned.
In cases where existing cleaning technologies do not allow to ensure the required cleanliness of the outside air, a short-term (for example, during rush hours on highways) reduction in the amount of outside air is allowed.
5.1.3. The room will ensure the permissible air quality if the established norms of specific air exchange are observed (tables 2 and 3).
Notes (edit)
1. If it is known or suspected that unusual pollutants or their sources are present in the room, the amount of air exchange should be established using a methodology based on the calculation of permissible concentrations of pollutants.
2. Tables 2 and show the rates of specific air exchange in m3 / h per person or m3 / h · m2 premises.
In most cases, the amount of pollutants is taken in proportion to the number of people in the room.
In cases where the rates of specific air exchange are presented in m3 / h · m2 and it is known that the number of people in the room differs from the "standard" value, the rates of air exchange per person should be used for the expected number of people in the room.
3. The norms of specific air exchange in tables 2 and for the premises presented in them are established in such a way that when external air of the required quality is supplied, human bio-fluids (solid particles, odors and other pollutants common for the premises presented in them) are diluted and the permissible level is reached indoor air quality.
Comfort criteria (including odor) taking into account bio-efluents are likely to be met if air exchange is sufficient to maintain indoor carbon dioxide concentrations no more than 1250 mg / m3 higher than outdoor carbon dioxide concentrations.
4. The rates of specific air exchange cannot be reduced when using recirculated air.
5. The norms of specific air exchange (table 2 and) determine the need for outdoor air in occupied rooms with air exchange organization schemes that ensure good mixing of air in the room (coefficient of air exchange efficiency Kq = 1).
For circuits with Kq> 1, as a rule, this is possible when air is supplied to the served area of public buildings through floor perforated air diffusers, a methodology based on the calculation of permissible concentrations of pollutants should be applied (see 5.2).
6. A possible scheme for organizing air exchange in an apartment and options for its calculation are presented in Appendix A.
5.1.4. Rooms equipped with exhaust systems (kitchens, bathrooms, toilets, smoking rooms, etc.) can use the air supplied through adjacent rooms to compensate for the exhaust air. The quality of the supply air must meet the requirements of Table 1.
Table 2 - Norms of minimum air exchange in premises of residential buildings1)
| Premises | Air exchange rate2) | Notes (edit) |
| Living sector | The air exchange rate is 0.35 h-1, but not less than 30 m3 / h | To calculate the air flow rate (m3 / h) by multiplicity, the volume of the premises should be determined by the total area of the apartment |
| 3 m3 / m2 of residential premises, if the total area of the apartment is less than 20 m2 / person. | Apartments with air-tight enclosing structures require additional air flow for fireplaces (by calculation) and mechanical hoods | |
| Kitchens | 60 m3 / h with electric cooker | Supply air can come from living quarters3) |
| 90 m3 / h with 4-burner gas hob | ||
| Bathrooms, toilets | 25 m3 / h from each room | Also |
| 50 m3 / h with a combined bathroom | ||
| Laundry room | Air exchange rate 5 h-1 | » |
| Dressing room, pantry | Air exchange rate 1 h-1 | » |
| Heat generator room (outside the kitchen) | Air exchange rate 1 h-1 | » |
| 1) The concentration of harmful substances in the outside (atmospheric) air should not exceed the MPC in the air of populated areas. 2) During the time when the room is not used, the air exchange rate should be reduced to the following values: in the residential area - up to 0.2 h-1; in the kitchen, bathroom, toilet, laundry room, dressing room, pantry - up to 0.5 h-1. 3) If the supply air enters directly into the kitchen, bathroom or toilet, it should not be allowed to flow into the living area. | ||
Table 3 - Norms of minimum air exchange in public buildings
| Premises | Air exchange rate | Notes (edit) |
| Catering establishments | ||
| A restaurant: | ||
| Lobby | 20 m3 / h | — |
| The entrance hall | 20 m3 / h | — |
| No smoking dining room | 40 m3 / h | — |
| Dining room with smoking | 100 m3 / h | — |
| Cafe: | ||
| No smoking dining room | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Children's cafe: | ||
| Dining room | 20 m3 / h | — |
| Play room | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Canteens: | ||
| Dining room | 20 m3 / h | — |
| Bars: | ||
| Smoking rooms | 40 m3 / h | — |
| Smoking rooms | 100 m3 / h | — |
| Hotels | ||
| No smoking hotel room living room | 60 m3 / h room | Number used |
| 10 m3 / h room | Number is not used | |
| Living room of a hotel room with smoking | 100 m3 / h room | Number used |
| 20 m3 / h room | Number is not used | |
| Combined bathroom in a hotel room | 120 m3 / h room | The bathroom is used |
| 20 m3 / h room | The bathroom is not used | |
| Conference halls | 30 m3 / h room | — |
| Halls for concerts and balls | 30 m3 / h room | — |
| No smoking casino | 40 m3 / h room | — |
| Smoking casino | 100 m3 / h room | — |
| Offices | ||
| Work room | 60 m3 / h | — |
| Cabinet | 60 m3 / h | — |
| Reception | 40 m3 / h | — |
| Meeting room | 40 m3 / h | — |
| Meeting rooms | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Corridors and halls | 1 h -1 | — |
| Toilets | 75 m3 / h | — |
| Smokers | 100 m3 / h | — |
| The shops | ||
| Basements | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Overground premises | 20 m3 / h | — |
| Warehouses | 20 m3 / h person, but not less than 0.5 h-1 | — |
| Fitting rooms | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Passages | 20 m3 / h | — |
| Loading and unloading premises | 20 m3 / h, but not less than 0.5 h -1 | — |
| Flowers | 30 m3 / h | Requirements for air exchange can be dictated by the need to create conditions that are optimal for the growth and development of plants. |
| Pet shops | 30 m3 / h | Requirements for air exchange can be dictated by the need to create conditions for zoological requirements |
| Clothes, fabrics, shoes | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Household goods, furniture, carpets | 30 m3 / h | Air exchange requirements may be dictated by the need to remove technological hazards |
| Hairdressers | 40 m3 / h | — |
| Beauty salons | 60 m3 / h | — |
| Theaters | ||
| Lobby | 20 m3 / h | — |
| Checkout | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Auditoriums | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Scenes and dressing rooms | 30 m3 / h | To eliminate the consequences of some stage effects (for example, dry steam, fog, etc.), special ventilation will be required. |
| Educational institutions | ||
| Classes for students in grades 1-4 | 20 m3 / h | — |
| Classes for students in grades 5-11 | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Laboratories | 40 m3 / h | — |
| Libraries | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Audience | 40 m3 / h | — |
| Health care institutions | ||
| Lookout | 50 m3 / h | — |
| Procedural | 60 m3 / h | Air Pollution Procedures May Require Higher Standards |
| Operating | 80 m3 / h | — |
| Chambers | 80 m3 / h | — |
| Physiotherapy | 60 m3 / h | — |
| Correctional facilities | ||
| Cameras | 30 m3 / h | — |
| Canteens | 20 m3 / h | — |
| Security premises | 30 m3 / h | — |
The supply of outdoor air to the premises is not necessary if the premises are not used and there are no sources of pollution that are not related to the presence of people and their activities (for example, pollution from building materials, furnishings, etc.).
If the pollution of the premises is associated only with the presence of people and their activities, which do not pose a health hazard in a short time, then the supply of outdoor air may lag behind in time from the beginning of the use of the premises.
The lag time, the time lag can be determined from the graph in Figure 1.
Figure 1 - Maximum allowable ventilation lag time Example - Air consumption - 60 m3 / h · person; room volume - 30 m3 / person; permissible ventilation lag time - 0.6 h
5.1.7. If the pollution of the premises is associated with the presence of pollution sources in it that are not related to the presence of people and their activities, the supply of outdoor air must precede the start of use of the premises.
The start time of the outdoor air supply can be determined from the graph in Figure 2.
Figure 2 - Minimum required ventilation time before filling the room Example - Air consumption - 30 m3 / h · person; room volume - 3.5 m3 / person; admissible ventilation lag time - 0.5 h
5.1.8. If the maximum pollution of the room lasts less than 3 hours during the working day, the outdoor air consumption can be determined by the average amount of pollution, but not less than half of the maximum value.
Air exchange rate in healthcare institutions
| № | Name of premises | T, ° C | Air exchange rate | Room frequency category | Exhaust rate with natural air exchange | ||
| inflow | hood | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| I. | Hospitals, clinics, emergency and ambulance stations | ||||||
| 1. | Manipulation toilet for newborns | 25 | 2 | H | 2 | ||
| 2. | Manipulation with the use of chlorpromazine | 22 | 8 | 10 | D | not allowed | |
| 3. | Doctor's offices, staff rooms, rest rooms for patients using hydrotherapy and mud therapy, acupuncture rooms, discharge rooms, audiometry and anthropometry rooms, dispatch rooms for receiving calls and sending teams, a room for filling out documents, a rest room for dispatchers, doctors, paramedics, orderlies, drivers , mobile teams, medical statistics | 20 | influx from the corridor | 11 | H | 1 | |
| 4. | Angiography rooms, procedural X-ray diagnostic rooms, procedural and dressing rooms of fluorographic rooms, electro-light therapy rooms, massage rooms | 20 | 3 | 4 | D | not allowed | |
| 5. | Undressing rooms at X-ray diagnostic rooms | 20 | 3 | — | H | » | |
| 6. | Procedural for X-ray. dental pictures, washing laboratory glassware, pathological departments, control rooms of X-ray rooms and radiological departments, darkroom | 18 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 7. | Sterilization in operating rooms | 18 | — | 3 septic compartments | D | 2 | |
| 3 | aseptic departments | H | 2 | ||||
| 8. | Laboratories and rooms for the production of analyzes, rooms (rooms) for radiotelemetric, endocrinological and other research, rooms for receiving, sorting and taking samples for laboratory analyzes, assembly and washing rooms for an artificial kidney and rooms for a heart-lung machine, solution-demineralization, preparative laboratories, rooms for painting smears, weighing, colorimetric, medium cookers, material and apparatus laboratories, fixation, prescription, rooms for the preparation of dressing and operating materials and linen, control, collection and packaging of instruments, reception, disassembly, washing and drying of surgical instruments, syringes, needles , catheter, procedural rooms for treatment with neuroleptics, radio post, dictaphone center, current sterilization rooms, equipment room | 18 | — | 3 | see table. 3 | 2 | |
| 9. | Halls of medical physical culture | 18 | 50 m3 / h for one person engaged in the gym 80% | 100 % | D | ||
| 10. | Functional diagnostics rooms, rooms for sigmoidoscopy | 22 | — | 3 | D | 2 | |
| 11. | Physical therapy, mechanotherapy rooms, dental rooms, sounding rooms, rooms for deworming | 20 | 2 | 3 | D | 2 | |
| 12. | Premises (rooms) for the sanitization of patients, showers, personal hygiene booths, premises for subaquatic, hydrogen sulfide and other baths (except for radon), rooms for heating paraffin and ozokerite, therapeutic swimming pools | 25 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | |
| 13. | Premises for storing plaster bandages, plaster, museums and preparatory rooms with them in pathological departments, compressor inhalers, central linens, pantries of infected linen and bedding, pantries of household equipment, pantries of patients' belongings and ironing, instrumental-material, pantries of reagents and equipment in pathological anatomical departments, premises for the current repair of physiotherapy equipment, storage of boxes for mobile teams, the current stock of medicines, a pharmacy room, a pantry for a month's supply of medicines, a pantry of non-sterile materials and linen | 18 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 14. | Sterilization rooms - autoclave central sterilization rooms: | 18 | by calculation | is allowed | |||
| a) clean compartment | 100 % | — | H | ||||
| b) dirty compartment | — | 100 % | D | ||||
| 15. | Premises for washing, sterilizing and storing ships, pots, washing and drying oilcloths, sorting and temporary storage of dirty linen, for storing cleaning items, premises for temporary storage of linen and solid waste contaminated with radioactive substances, pantries of acids and disinfectants, stretcher washing rooms and oilcloths, a room for drying clothes and shoes of mobile teams | 18 | — | 5 | D | 3 | |
| 16. | Receptions, information lobbies, dressing rooms, rooms for receiving parcels for patients, waiting room, storage rooms for warm clothes at verandas, pantries, canteens for patients, dispensers with a utility room in milk dispensing points, pantries for patients' clothes and clothes, medical archives | 18 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 17. | Premises for processing rubber gloves, for washing and sterilizing table and kitchen utensils in pantry and canteen departments, hairdressing salons for serving patients, dummy | 18 | 2 | 3 | D | 2 | |
| 18. | Storage of radioactive substances, filling and washing in radiological departments, washing in laboratories | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | not allowed | |
| 19. | Procedural rooms for static and mobile tele-gamma therapy, rooms for centralization in rooms for mobile tele-gamma therapy, procedural X-ray therapy rooms, microwave therapy rooms, ultra-high-frequency therapy rooms, thermotherapy rooms, wrap-up rooms for the preparation of solutions for radon sculpts, ultrasound treatment rooms | 20 | 4 | 5 | D | » | |
| 20. | Dressing rooms and undressing rooms in hydrotherapy departments | 23 | inflow according to the balance of the exhaust from the halls with bathrooms, mud procedures | H | 2 | ||
| 21. | Corpse storage rooms | 2 | — | 3 | D | 3 | |
| 22. | Premises for radon baths, mud treatment halls. shower room with a chair, mud treatment rooms for gynecological procedures | 25 | 4 | 5 | D | does not go down | |
| 23. | Premises for storing and reclaiming dirt | 12 | 2 | 10 | D | » | |
| 24. | Premises for dressing corpses, issuing corpses, storage rooms for funeral accessories, for processing and preparing for burial of infected corpses, premises for storing bleach | 14 | — | 3 | D | » | |
| 25. | Premises for disinfection chambers: | ||||||
| a) reception rooms; | 16 | from the clean compartment | 3 | D | » | ||
| b) dirty compartments: | from the clean compartment | 5 | D | » | |||
| c) unloading (clean) compartments | 5 | Through dirty compartments | |||||
| 26. | Hydrogen sulfide bath locks | 25 | 3 | 4 | H | not allowed | |
| 27. | Undressing rooms for hydrogen sulphide baths | 25 | 3 | 3 | H | » | |
| 28. | Room for the preparation of a solution of hydrogen sulfide baths and storage of reagents | 20 | 5 | 6 | D | » | |
| 29. | Room for washing and drying sheets, canvases, tarpaulins, mud kitchens | 16 | 6 | 10 | D | » | |
| 30. | Inhalation (procedural) | 20 | 8 | 10 | D | ||
| 31. | Sectional | 16 | — | 4 | D | 4 | |
| 32. | Gateways in front of the newborn wards | 22 | by calculation, but not less than 5 times the exchange | H | not allowed | ||
| 33. | Premises for discharge of puerperas and irradiation of children with a quartz lamp | 22 | — | 1 | H | 1 | |
| 34. | Bathrooms | 20 | — | 50 m3 for 1 toilet and 20 m3 for 1 urinal | D | 3 | |
| 35. | Washrooms | 20 | — | 3 | D | 3 | |
| 36. | Enema | 20 | — | 5 | D | 2 | |
| 37. | Gateways in boxes and semi-boxes of infectious wards | 22 | by calculation, but not less than 5 times the exchange | H | not allowed | ||
| 38. | Small operating rooms | 22 | 10 | 5 | H | 1 | |
| 39. | Premises of hospital pharmacies (see section General self-supporting pharmacies) | ||||||
| Vivariums5) | |||||||
| 40. | Quarantine room for the entry of cars with animals. Reception with a warm vestibule | 16 | 1 | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 41. | Washing for dogs, cats, miniature pigs with bathtub and circular shower | 22 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | |
| 42. | Hot air dryer for dogs and miniature pigs | 25 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | |
| 43. | Premises for keeping laboratory animals: 6) | ||||||
| a) mice | 20:22 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| b) hamsters | 20 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| c) guinea pigs | 14:16 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | ||
| d) rabbits7) | 5 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | ||
| e) dogs (with walking) | 14 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | ||
| f) cats | 18 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| g) sheep (with access to the walk) | 5 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| h) dwarf pigs | 18 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| i) roosters | 18 | 10 | 12 | D | 2 | ||
| 44. | Staff room | 18 | 1 | 1 | H | 1 | |
| 45. | Cell and inventory warehouse | 10 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 46. | Examination of sick animals and disinfection | 20 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | |
| 47. | Large animal isolator | 15 | 8 | 10 | D | 2 | |
| 48. | Premises for storage and preparation of disinfectants (with a fume hood) | 18 | according to technologists | D | 3 | ||
| 49. | Storing feed and bedding | 10 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| Disinfection and washing department | |||||||
| 50. | Cleaning and washing inventory: | ||||||
| a) for manual washing; | 16 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | ||
| b) with a machine wash: | |||||||
| rough cleaning room | 16 | 3 | 5 | D | 2 | ||
| washing | 16 | 5 | 6 | D | 2 | ||
| 51. | Sterilization and drying of equipment | 18 | by calculation | H | not allowed | ||
| 52. | Storing clean cages, racks, containers, feeders, stretchers, bedding | 10 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 53. | Loading into cages of feed, water, bedding | 18 | — | 3 | D | 1 | |
| 54. | Temporary storage of animal corpses | 2:4 | — | 3 | D | 3 | |
| Department of keeping experimental animals | |||||||
| Block for keeping small laboratory rodents (mice, rats, guinea pigs) in conditions excluding the penetration of pathogenic flora8) Rooms of the barrier zone. | |||||||
| 55. | Compulsory sanitary inspection | 25 | 3 | 5 | D | not allowed | |
| 56. | Putting on sterile clothing: | 1 | |||||
| - clean area | 25 | by calculation | H | » | |||
| - dirty area | 25 | » | D | » | |||
| 57. | Sterilization with steam autoclave | 18 | » | D | » | ||
| 58. | Bactericidal hydraulic sluice: | 18 | 3 | H | » | ||
| - clean area | 18 | 3 | H | » | |||
| - dirty area | 18 | 3 | D | » | |||
| 59. | Germicidal air lock | 18 | by calculation | H | » | ||
| Barrier area premises3) | |||||||
| 60. | Premises for keeping animals SViB and conducting experiments: | ||||||
| a) for mice | 20:22 | 15 | 10 | OCH | » | ||
| b) for rats | 18 | 15 | 10 | OCH | not allowed | ||
| c) for guinea pigs | 14:16 | 15 | 10 | OCH | » | ||
| 61. | Room for experiments | 20 | OCH | » | |||
| 62. | Staff | 18 | 1 | 1 | OCH | » | |
| 63. | Warehouse for sterile equipment, feed, bedding | 18 | 1 | 1 | OCH | » | |
| 64. | Distribution and distribution of feed | 18 | 1 | 1 | OCH | » | |
| 65. | Sterilizing water | 18 | 1 | 1 | OCH | » | |
| Unit for keeping laboratory animals under normal conditions | |||||||
| 66. | Premises for keeping laboratory animals (except for rams) | on items 50a: 50i | |||||
| 67. | Rooms for experiments | 18 | 1 | 3 | D | 2 | |
| 68. | Surgical section premises: | ||||||
| a) preoperative with sterilization | 18 | 1 | 2,5 | H | not allowed | ||
| b) operating room, postoperative room, intensive care room for recovering animals | 20:22 | by calculation | OCH | — | |||
| 69. | Premises for infecting animals and working with them: | ||||||
| a) premises for toxicological studies | 18 | ||||||
| b) premises for infecting animals (manipulation, boxes for control animals) | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | not allowed | ||
| c) personnel and specialists | 18 | — | 1,.5 | H | » | ||
| d) storage of clean: inventory, feed, bedding | 18 | — | 1 | D | » | ||
| e) waste collection | 10 | — | 10 | D | » | ||
| Department of Veterinary Services | |||||||
| 70. | Doctor's office | 18 | 1 | 1 | H | » | |
| 71. | Sectional | 16 | 3 | 3 | D | » | |
| 72. | Laboratory diagnostics with an autopsy box | 18 | 1 | 3 | D | » | |
| 78. | Storage of medicines | 18 | 1 | 3 | D | not allowed | |
| 74. | Sick animal isolation unit: | ||||||
| a) room for patients with a gateway | on paragraphs 50a-50i | ||||||
| b) storage of feeders, cages, inventory, storage of bedding and feed | 10 | — | 1 | D | » | ||
| c) staff | 18 | 1 | 1 | H | » | ||
| d) cleaning items with a tap, ladder and drying | 10 | — | 10 | D | » | ||
| Feed preparation department | |||||||
| 75. | Preparation of vegetables from the washing machine, preparation of grain mixtures | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 76. | Digestive hall | 16 | by calculation | » | |||
| 77. | Washing-kitchen utensils | 18 | 4 | 6 | D | » | |
| 78. | Sterilization of feed | 18 | 1 | 3 | D | » | |
| 79. | Refrigerated food chamber | 2-4 | — | — | D | » | |
| II. General self-supporting pharmacies | |||||||
| 80. | Public service halls | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | 3 | |
| 81. | Work rooms or isolated work areas in the service hall, forwarding rooms for receiving and placing orders from the attached institution, prescription | 18 | 2 | 1 | H | 1 | |
| 82. | Assistant, aseptic, defective, gateway; billet and filling with a sluice, seaming and control-marking sterilization-autoclave, sterilization distillation | 18 | 4 | 2 | H | 1 | |
| 83. | Packaging, control and analytical room, washing, sterilization solutions, distillation and sterilization room, cocktail, unpacking | 18 | 2 | 3 | D | 1 | |
| 84. | Premises for the preparation of dosage forms under aseptic conditions | 18 | 4 | 2 | OCH | not allowed | |
| 85. | General stock storage rooms: | ||||||
| a) medicinal substances, finished medicinal products, including thermolabile and medical supplies; dressings | 18 | 2 | 3 | D | 1 | ||
| b) medicinal plant materials | 18 | 3 | 4 | D | 3 | ||
| c) mineral waters, medical glass and recyclable shipping containers, glasses and other optical items, auxiliary materials, clean dishes | 18 | — | 1 | D | 1 | ||
| d) poisonous drugs and drugs | 18 | — | 3 | D | 3 | ||
| 86. | Flammable and flammable liquids | 18 | — | 10 | D | 5 | |
| 87. | Disinfectants and acids, disinfection with sluice | 18 | — | 5 | D | 3 | |
| 88. | Administrative premises | on PP. 13, 19, 20, 25, 26, 44 of this table | |||||
| 89. | Refrigeration machine room | 4 | — | 3 | D | 3 | |
| 90. | Electrical control room | 15 | — | 1 | |||
| SANITARY-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STATIONS (SES) | |||||||
| Radiological group | |||||||
| 91. | Laboratory room | 18 | 3 | 5 | D | not allowed | |
| 92. | Bacteriological group Premises for doctors and laboratory assistants study rooms | 18 | — | 1,5 | H | » | |
| 93. | Room for serological research, sowing, rooms for express diagnostics | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | |
| 94. | Boxes | 18 | 6 | 5 | H | » | |
| 95. | Preboxes | 18 | — | 10 | D | » | |
| 96. | Entomology premises for helminthological research, environment | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | |
| 97. | Washing rooms | ||||||
| a) without washing machine | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | ||
| b) with a washing machine | 18 | 3 | 5 | D | » | ||
| 98. | Sterilizing autoclave | 18 | — | 3 | D | not allowed | |
| 99. | Thermal rooms | At the request of the technology The internal air temperature is provided by the technological equipment | |||||
| 100. | Rooms for receiving registration, sorting and issuing test results | 18 | — | 3 | D | » | |
| Virology Department and Laboratory of the Department of Highly Dangerous Infections | |||||||
| 101. | Rooms for the identification of respiratory, enteric viruses, for the preparation of tissue culture | ||||||
| a) working rooms of doctors and laboratory assistants | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | ||
| b) boxes | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | ||
| c) preboxes | 18 | 6 | 5 | H | » | ||
| d) boxes | 18 | 6 | 5 | H | » | ||
| e) pre-boxes for preparing tissue culture | 18 | — | 10 | D | » | ||
| 102. | Room for the identification of arboviruses: | ||||||
| a) working rooms of doctors and laboratory assistants | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | not allowed | ||
| b) boxes | 18 | 5 | 6 | D | » | ||
| c) preboxes | 18 | — | 10 | D | » | ||
| 103. | Rooms for bacteriological research, rooms for processing traps and preparing baits, | 18 | 3 | 6 | D | » | |
| 104. | Rodent infestation rooms (bioassay) | 18 | 8 | 10 | D | » | |
| 105. | Corridors | 18 | By the balance of the branch | H | » | ||
| Dairy kitchens | |||||||
| 106. | Brewhouse | 5 | By calculation | D | » | ||
| 107. | Mashed potatoes workshop | 16 | 3 | H | » | ||
| 108. | Packing milk and juices | 16 | 2 | 3 | D | » | |
| 109. | Sterilization of finished products | ||||||
| a) "clean zone" | 16 | 6 | — | H | not allowed | ||
| b) "dirty zone" | 16 | — | 4 | D | » | ||
| 110. | Washing flasks | 20 | 4 | 6 | D | » | |
| 111. | Milk intake | 16 | — | 1 | D | » | |
| 112. | Preparation of biolact | 16 | 12 | 12 | H | » | |
| 113. | Filtration and milk filling room | 16 | 19 | 19 | H | » | |
| 114. | Premises for heat treatment of milk and preparation of milk mixtures | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 115. | Cooling room | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 116. | Room for the preparation of lactic acid products and lactic acid mixtures: | ||||||
| a) room for the preparation of starter cultures | 16 | 3 | 4 | H | » | ||
| b) kefir shop | 16 | 20 | 20 | H | » | ||
| c) shop for acidophilic milk | 16 | 20 | 20 | H | » | ||
| d) thermostatic | 16 | 12 | 12 | H | » | ||
| 117. | Premises for the preparation and packaging of cottage cheese | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 118. | Premises for the preparation of fruits, fruits, vegetables | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 119. | Premises for the preparation of fruit and vegetable mixtures | 16 | 12 | 12 | H | » | |
| 120. | Premises for preparation of fish, meat, preparation of fish and meat dishes | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 121. | Laboratory | 18 | 2 | 3 | D | » | |
| 122. | Premises for receiving containers for finished products | 16 | 4 | 6 | D | » | |
| 123. | Premises for receiving raw materials | 16 | 3 | — | D | » | |
| 124. | Washing and sterilization room | 20 | 4 into the "clean" zone inflow | 6 exhaust - through the "dirty" area | D | » | |
| 125. | Washing kitchen utensils | 20 | 4 | 6 | D | » | |
| 126. | Washing room: | ||||||
| a) milk pipelines | 20 | 4 | 6 | D | » | ||
| b) inventory | 20 | 4 | 6 | ||||
| 127. | Expedition loading | 16 | 3 | — | H | » | |
| 128. | Refrigeration machinery room | 16 | — | 3 | D | » | |
| 129. | Temporary storage room | 12 | — | 1 | D | » | |
| milk | periodic ventilation | ||||||
| 130. | Dry food pantry | 12 | — | 2 | H | » | |
| 131. | Pantry of vegetables and fruits | 4 | 4 (per day) | 4 (per day) | D | » | |
| 132. | Premises for storing and receiving containers | 12 | 4 | 6 | D | 1 | |
| 133. | Pantry of household equipment | 12 | 2 | 2 | D | » | |
| 134. | Linen | 16 | 2 | 1 | D | » | |
| 135. | Material pantry | 12 | — | 1 | D | » | |
| 136. | Chilled food waste chamber with a vestibule | 2 | — | 10 | D | not allowed | |
| 137. | Service and utility rooms | under section I of this table | |||||
| Donor point | |||||||
| 138. | Breast milk pumping room | 22 | — | 2 | H | » | |
| 139. | Sterilization room | 18 | — | 3 | H | » | |
| 140. | Filtration and milk filling | 16 | 19 | 19 | H | » | |
| 141. | Heat treatment | 16 | 3 | 4 | D | » | |
| 142. | Cooling room | 16 | 3 | 4 | H | » | |
| Milk distribution points | |||||||
| 143. | Handout | 16 | 2 | 2 | H | 1 | |
| 144. | Refrigerating chamber (for finished products) | 2 | Periodic ventilation | ||||
| 145. | Premises for receiving and storing dishes from the population | 12 | — | 1 | D | 1 | |
| 146. | Cashier | 18 | — | 1 | H | » | |
| 147. | Pantry of disinfectant solutions and cleaning equipment | 16 | — | 5 | D | 3 | |
| Sauna | |||||||
| 148. | Expected | 18 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 149. | The corridor | 18 | — | 2 | H | ||
| 150. | Dressing room | 22 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 151. | Shower room | 22 | — | 8 | D | ||
| 152. | Steam room10) | 100/80 (85/80) | — | 5 | D | ||
| 153. | Cooling room inside the sauna | 1 | — | 4 | D | ||
| 154. | Restroom | 26 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 155. | Massage room | 25 | — | 4 | D | ||
| 156. | Solarium | 23 | — | 3 | H | ||
| 157. | Restroom | 22 | — | 50 m3 for 1 toilet | D | ||
Source: Manual for the design of healthcare institutions (to SNiP 2.08.02-89)
Normative references
This standard uses references to the following normative documents:
GOST 30494-96 Residential and public buildings. Indoor microclimate parameters
SNiP 2.08.02-89 * Public buildings and structures
SNiP 31-01-2003 Residential apartment buildings
SNiP 31-05-2003 Public buildings for administrative purposes
SNiP 41-01-2003 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning
MGSN 3.01-01 Residential buildings
SanPiN 2.1.6.1032-01 Hygienic requirements for ensuring the quality of atmospheric air in populated areas
GN 2.1.6.014-94 Maximum permissible concentration (MPC) of polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans in the air of populated areas
GN 2.1.6.1338-03 Maximum permissible concentration (MPC) of pollutants in the air of populated areas
GN 2.1.6.1339-03 Approximate safe exposure levels (TSEL) of pollutants in the air of populated areas
GN 2.1.6.2177-07 Maximum permissible concentrations (MPC) of microorganisms-producers, bacterial preparations and their components in the air of populated areas
NM 113-91 Recommendations for the application of regulatory requirements in the design of heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems for buildings for various purposes
NRB-99 Radiation Safety Standards
TR AVOK-4-2004 Technical recommendations for organizing air exchange in apartments of a multi-storey residential building
ASHRAE 62-1999 Ventilation for acceptable indoor air quality
DIN EN 13779: 2007 Ventilation for non-residential buildings - Performance requirements for ventilation and room-conditioning systems
DIN EN 15251: 2007 Indoor environmental input parameters for design and assessment of energy performance of buildings addressing indoor air quality, thermal environment, lighting and acoustics , lighting and acoustics)
CIBSE Guide A: 2006 Environmental design. Ch. 1. Environmental criteria for design
Air exchange rate in the premises of preschool organizations
| Premises | t ° (С) -not lower | Air exchange rate per hour | |||
| In IA, B, D climatic regions | In other climatic regions | ||||
| inflow | hood | inflow | hood | ||
| Reception, playroom nursery group cells | 22-24 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Reception, playroom junior, middle, senior group cells | 21-23 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Bedrooms of all group units | 19-20 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Dressing nursery groups | 22-24 | — | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Dressing preschool groups | 19-20 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Medical premises | 22-24 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Halls for muses. and gymnastics | 19-20 | 2,5 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 |
| Walking verandas | not less than 12 | by calculation, but not less than 20 m3 per child | |||
| Hall with pool bathroom | not less than 29 | ||||
| Locker room with shower pool | 25-26 | ||||
| Heated passages | not less than 15 | ||||
Source: Sanitary and Epidemiological Rules and Norms SanPiN 2.4.1.3049-13. Appendix 3
Terms and Definitions
The following terms and definitions are used in this standard:
3.1. bioefluents
: Contaminants from people, pets, birds, etc., such as odor, carbon dioxide, skin debris, hair, etc.
3.2. ventilation
: Organized air exchange in the premises to ensure the microclimate parameters and air purity in the serviced area of the premises within the permissible limits.
3.3. natural ventilation
: Organized exchange of air in rooms under the influence of thermal (gravitational) and / or wind pressure.
3.4. mechanical ventilation (artificial)
: Organized exchange of air in rooms under the influence of pressure generated by fans.
3.5. outdoor air
: Atmospheric air taken in by the ventilation or air conditioning system for supply to the manned room and / or entering the manned room by infiltration.
3.6. supply air
: Air supplied to the room by the ventilation or air conditioning system and entering the manned room due to infiltration.
3.6. evacuated air
(outgoing): Air taken from a room and no longer used in it.
3.7. harmful (polluting) substances
: Substances for which the maximum permissible concentration (MPC) has been established by the sanitary and epidemiological authorities.
3.8. harmful discharge
: Streams of heat, moisture, pollutants entering the room and negatively affecting the parameters of the microclimate and air purity.
3.10. permissible indoor air quality (air purity)
: Composition of air in which, as determined by the competent authorities, the concentration of known pollutants does not exceed the MPC and to which more than 80% of exposed people have no claims.
3.11. permissible microclimate parameters
: Combinations of values of microclimate indicators, which, with prolonged and systematic exposure to a person, can cause a general and local feeling of discomfort, moderate tension of thermoregulatory mechanisms that do not cause damage or health disorders.
3.12. smell
: A sensation that occurs when gases, liquids or particles in the air affect the receptors of the nasal mucosa.
3.13. infiltration
: Unorganized flow of air into the room through leaks in the building envelopes under the influence of thermal and / or wind pressure and / or due to the operation of mechanical ventilation.
3.14. concentration
: The ratio of the amount (weight, volume, etc.) of one component to the amount (weight, volume, etc.) of the mixture of components.
3.15. place of permanent residence of people in the room
: A place where people stay for more than 2 hours continuously.
3.16. microorganisms
: Bacteria, fungi and unicellular organisms.
3.17. room microclimate
: The state of the indoor environment of a room, characterized by the following indicators: air temperature, radiation temperature, movement speed and relative humidity in the room.
3.18. served area (habitat)
: The space in the room, limited by planes parallel to the fences, at a height of 0.1 and 2.0 m above the floor level, but not closer than 1.0 m from the ceiling with ceiling heating; at a distance of 0.5 m from the inner surfaces of external walls, windows and heating appliances; at a distance of 1.0 m from the distributing surface of the air distributors.
3.19. local suction
: A device for capturing harmful and explosive gases, dust, aerosols and vapors at the places of their formation, connected to the air ducts of local ventilation systems and, as a rule, is a part of technological equipment.
3.20. air cleaning
: Removal of pollutants from the air.
3.21. room free of emissions of harmful substances
: A room in which harmful substances are released into the air in quantities that do not create concentrations exceeding the MPC in the air of the served area.
3.22. room with permanent residence of people
: A room in which people are at least 2 hours continuously or 6 hours in total during the day.
3.23. premises with a mass stay of people
: Premises (halls and foyers of theaters, cinemas, meeting rooms, conferences, lecture halls, restaurants, lobbies, checkout rooms, production halls, etc.) with a permanent or temporary stay of people (except for emergencies) numbering more than 1 person. per 1 m2 of premises with an area of 50 m2 or more.
3.24. air recirculation
: Mixing room air with outdoor air and supplying this mixture to this or other rooms.