Simple area calculations
You can calculate the size of the heating batteries for a certain room, focusing on its area. This is the easiest way - to use plumbing standards, which prescribe that a thermal power of 100 W per hour is needed to heat 1 sq. M. It must be remembered that this method is used for rooms with standard ceilings (2.5-2.7 meters), and the result is somewhat overestimated. In addition, it does not take into account such features as:
- the number of windows and the type of glass units on them;
- the number of external walls in the room;
- the thickness of the walls of the building and what material they are made of;
- the type and thickness of the insulation used;
- temperature range in a given climatic zone.
The heat that radiators must provide to heat the room: the area should be multiplied by the heat output (100 W). For example, for a room of 18 square meters, the following heating battery power is required:
18 m2 x 100 W = 1800 W
That is, 1.8 kW of power is needed per hour to heat 18 square meters. This result must be divided by the amount of heat that the heating radiator section emits per hour. If the data in his passport indicates that this is 170 W, then the next stage of calculations looks like this:
1800W / 170W = 10.59
This number must be rounded to the nearest whole (usually rounded up) - it will turn out to be 11. That is, in order for the room temperature to be optimal during the heating season, it is necessary to install a heating radiator with 11 sections.
This method is only suitable for calculating the size of the battery in rooms with central heating, where the temperature of the coolant is not higher than 70 degrees Celsius.
There is also a simpler method that can be used for the usual conditions of apartments in panel houses. This approximate calculation takes into account that one section is needed to heat 1.8 square meters of area. In other words, the area of the room should be divided by 1.8. For example, with an area of 25 square meters, 14 parts are needed:
25 m2 / 1.8 m2 = 13.89
But this method of calculation is unacceptable for a radiator with reduced or increased power (when the average output of one section varies from 120 to 200 W).
We are starting a short series of articles dedicated to calculating the power of heaters for apartments and private houses. Let's start with heating radiators. Why is it important? The answer is simple: the house should be warm and comfortable. Even in the most severe frosts, you do not wear boots and a hat indoors. And ideally - never buy electric heaters. On the other hand, heat is not an option either. The forced shutdown of radiators will not help save on utility bills, and regular airing of rooms is not always possible. Especially if there are children in the house.

Therefore, let's find out how many sections of radiators are needed for a comfortable life. And how to get this figure.
The simplest calculation
If you are building a house on your own, and do not understand too much about heating, then you will easily fall for the bait of consultants of building stores. Very often you can hear that the calculation of radiator sections is the most elementary:
100 watts of power per square meter
Or another option:
2 battery sections per 1 square meter
It would seem that everything is clear and understandable. But the point is in the nuances. Such a primitive formula does not take into account the characteristics of the room, the height of the ceilings, the number of doors and windows, the presence of thermal insulation and balconies. Everything that affects heat loss and without which the heating system will not work efficiently and - what is important - economically.


What information is needed
Before you start calculating the power of the heater, take a "history".
This is all information about a specific room where heating devices are planned to be installed.
- Local climate and air temperature during the heating season. The choice of heaters, the calculation of their number and power will be very different in the middle lane and the northern part of our country.
- The location of the room and specifically the windows (north, south, east, west)
- Purpose of the premises: living room, nursery, kitchen, utility room, attic.
- Wall material and thickness.
- The number of windows, doors, their configuration (conventional or French windows), the presence and type of balconies (loggia, attic).
- Ventilation - natural and forced.
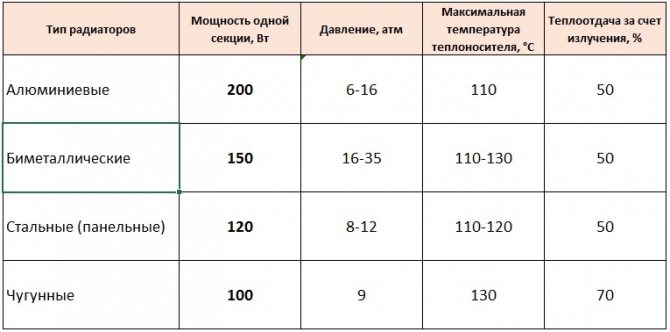
Then you need to decide on the material of future radiators. This usually happens at the stage of the design project, but if we are talking about an apartment with already installed devices, and you want to change them, the decision to replace is made at the first stages of repair. The number of radiator sections for a given room depends on their type:
- Steel have a power of 100-150 W per section
- Cast iron - 160 W
- Bimetallic - 170-180 W
- Aluminum - the most powerful, 180-200 watts.


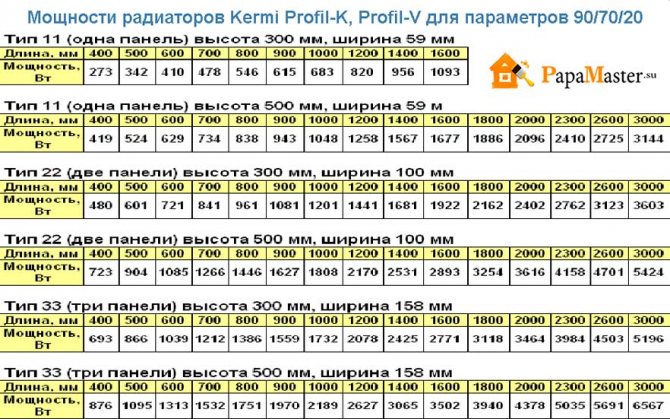
And one more parameter. The above power ratings for radiators of different materials are ideal. Their manufacturer indicates in the accompanying documentation, but they are slightly out of touch with reality. The power of the heating radiator section is affected by the temperature of the coolant. If you know him, the calculation will be more accurate. The so-called DT parameter takes into account the temperature of the heating medium at the inlet and outlet. The maximum power of the radiator section is reached with the parameter 90/70. But this temperature is rare for the Russian heating system. The standard figure is 67-75 / 53-55 ° C.
Area calculation
This is the same simple calculation that we talked about above, but with clarifications. Suitable for rooms with normal ceiling heights, no more than 3 meters.
Formula:
100W * S / N,
where S is the area of the room (m2) and N is the power of the radiator section
Example:
100*15/150=10
10 radiator sections are needed to heat a 15-meter living room.
To get a more real and accurate figure, add:
- + 20% for a balcony in the room or a bay window;
- + 30% for two windows, two outer walls and a corner arrangement of the apartment;
- + 10-15% for screens for radiators that completely hide them;
- + 15% is always added in case of abnormal cold weather.
The calculation formula is also specified by the climatic coefficient. It is relevant for the northern and southern regions, where the air temperature differs significantly from the middle zone of Russia. The coefficient for the north is 1.6. For the south - 0.9.
Calculation by the volume of the room
Conducted for rooms with high ceilings and non-standard configuration. It proceeds from the fact that heating 1 cubic meter of premises requires 40 W of thermal power.
Formula:
V * 40W / N,
Where V is the volume of the room m3, and N is the power of the radiator section
Calculation example:
104 (width 6.5 * length 5 * height 3.2) * 40/150 = 27.
Those. 27 sections will be needed for comfortable heating of a room with a volume of 104 m3.
Detailed calculation of the number of heating radiator sections
This formula has a lot of refinements. It can also be suitable for apartments, but for this you need to know all the subtleties of building a particular multi-storey building. Nevertheless, the owner of the cottage has the privilege to directly participate in the construction of the facility, to control the purchase of building materials and finishes, as well as to receive comprehensive information about each material used.


Formula
100W * S * K1 * K2 * K3 * K4 * K5 * K6 * K7,
where S is the area of the room (m2), and the set K are coefficients that will help to detail the calculation.
K1 - window glazing: coefficient for double glazing, 1.0 for double glazing, 0.85 for triple glazing.
K2 - coefficient of thermal insulation of walls: 1.27 low, 1.0 single-layer, 0.85 two-layer.
K3 - the ratio of the area of windows and floor: 0.8 (10%); 0.9; 1.0; 1.1; 1.2 (50%).
K4 - coefficient of the lowest temperature in winter: 0.7 (10 ° C); 0.9 (15 ° C); 1.1 (20 ° C); 1.3 (25 ° C); 1.5 (30 ° C).
K5 - coefficient of the number of external walls: one 1.1; two 1,2; three 1.3; four 1.4.
K6 - type of premises: attic coefficient 1; warm attic - 0.9; warm ground floor - 0.8
K7 - ceiling height: coefficient 1 for a height of 2.5 meters; 1.05 for 3 m; 1.1 for 3.5 m; 1.15 for 4 m; 1.2 for 4.5 m.
To save on the number of radiator sections without losing heat will help:
- High quality thermal insulation
- Insulation of doors and slopes
- Glazed and insulated loggias and balconies
- Heating appliances in the kitchen or in the dining area: stoves, ovens, grills, etc. That is why it is so important to consider the type of room for the installation and calculation of radiators.
Consider a calculation method for rooms with high ceilings
However, the calculation of heating by area does not allow you to correctly determine the number of sections for rooms with ceilings above 3 meters. In this case, you must apply a formula that takes into account the volume of the room. To heat each cubic meter of volume, according to the SNIP recommendations, 41 W of heat is required. So, for a room with a ceiling height of 3 m and an area of 24 square meters, the calculation will be as follows:
24 square meters x 3 m = 72 cubic meters (room volume).
72 cubic meters x 41 W = 2952 W (battery power for heating the room).
Now you should find out the number of sections. If the radiator documentation indicates that the heat transfer of one part of it per hour is 180 W, the found battery power must be divided by this number:
2952 W / 180 W = 16.4
This number is rounded to the nearest whole - it turns out, 17 sections to heat a room with a volume of 72 cubic meters.
Using simple calculations, you can easily determine the data you need.
Simplified calculation of heat loss compensation
Any calculations are based on certain principles. The basis for calculating the required thermal power of the batteries is the understanding that well-functioning heating devices must fully compensate for the heat losses that arise during their operation due to the characteristics of the heated premises.
For living rooms located in a well-insulated house, located, in turn, in a temperate climatic zone, in some cases, a simplified calculation of compensation for thermal leaks is suitable.
For such premises, calculations are based on a standard power of 41 W required for heating 1 cubic meter. living space.
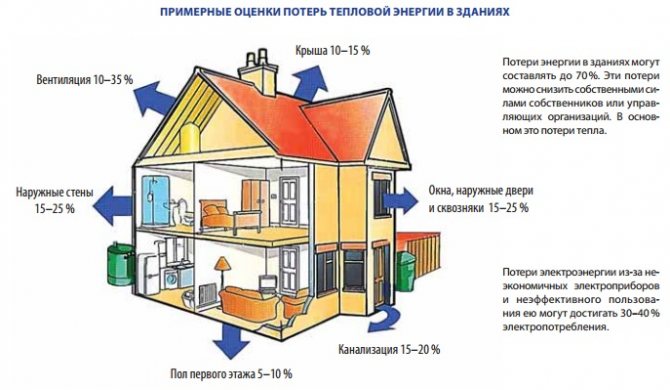

In order for the heat energy emitted by heating devices to be directed specifically to heating the premises, it is necessary to insulate walls, attics, windows and floors.
The formula for determining the thermal power of radiators required to maintain optimal living conditions in a room is as follows:
Q = 41 x V,
Where V - the volume of the heated room in cubic meters.
The resulting four-digit result can be expressed in kilowatts, reducing it from the calculation of 1 kW = 1000 W.
Additional parameters to consider
Having made an approximate calculation of the number of heating radiator sections for your apartment, do not forget to correct it, taking into account the characteristics of the room. They need to be considered as follows:
- for a corner room (two walls face the street) with one window, the radiator power must be increased by 20%, and with two windows - by 30%;
- if the radiator is mounted in a niche under the window, its heat transfer will decrease, this is compensated by an increase in power by 5%;
- should be increased by 10% if the windows face the north or north-east side;
- the screen, which covers the radiators for beauty, "steals" 15% of their heat transfer, which must also be taken into account when calculating.
At the very beginning, the total value of the required thermal power for the room should be calculated, taking into account all the available parameters and factors. And only then divide this value by the amount of heat that one section emits per hour. The result with a fractional value, as a rule, is rounded up to the nearest integer.
How to calculate radiator sections by room volume
With this calculation, not only the area is taken into account, but also the height of the ceilings, because all the air in the room needs to be heated. So this approach is justified. And in this case, the technique is similar. We determine the volume of the room, and then, according to the norms, we find out how much heat is needed to heat it:
- in a panel house, 41W is required to heat a cubic meter of air;
- in a brick house for m 3 - 34W.


You need to heat the entire volume of air in the room, therefore it is more correct to count the number of radiators by volume
Let's calculate everything for the same room with an area of 16m 2 and compare the results. Let the ceiling height be 2.7m. Volume: 16 * 2.7 = 43.2m 3.
Next, let's calculate for options in a panel and brick house:
- In a panel house. Heat required for heating 43.2m 3 * 41V = 1771.2W. If we take all the same sections with a power of 170W, we get: 1771W / 170W = 10.418 pieces (11 pieces).
- In a brick house. Heat is needed 43.2m 3 * 34W = 1468.8W. We count radiators: 1468.8W / 170W = 8.64pcs (9pcs).
As you can see, the difference turns out to be quite large: 11 pieces and 9 pieces. Moreover, when calculating by area, an average value was obtained (if rounded in the same direction) - 10 pcs.
Specificity and other features
It is also possible that there are other specificities for the premises for which the calculation is made, not all of them are similar and completely identical. These can be indicators such as:
- the temperature of the coolant is less than 70 degrees - the number of parts will have to be increased accordingly;
- the absence of a door in the opening between the two rooms. Then it is required to calculate the total area of both rooms in order to calculate the number of radiators for optimal heating;
- double-glazed windows installed on the windows prevent heat loss, therefore, fewer battery sections can be installed.
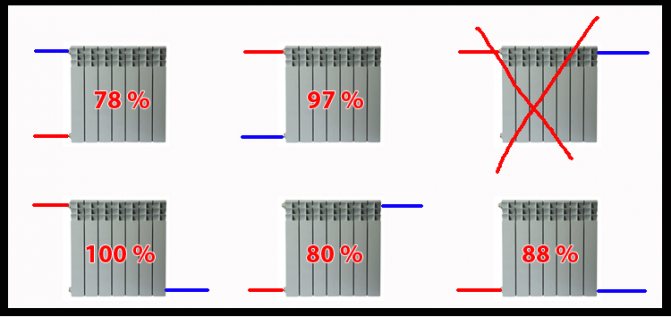
When replacing old cast iron batteries, which provided a normal temperature in the room, with new aluminum or bimetallic ones, the calculation is very simple. Multiply the heat dissipation of one cast iron section (150 W on average). Divide the result by the amount of heat of one new part.
How to calculate heat losses for a private house and apartment
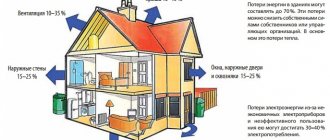
Heat escapes through windows, doors, ceilings, exterior walls, ventilation systems... For each heat loss, its own coefficient is calculated, which is used in calculating the required power of the heating system.
Coefficients (Q) are determined by the formulas:
Q = S * ΔT / R layer, R = v / λ
- S - the area of a window, door or other structure,
- ΔT - temperature difference inside and outside on cold days,
- v - layer thickness,
- λ - thermal conductivity of the material.
All received Qs are added, summed up with 10-40% of thermal losses through ventilation shafts... The amount is divided by the total area of the house or apartment and added to the estimated capacity of the heating system.
When calculating the area of the walls from them subtracts the dimensions of windows, doors, etc.since they are accounted for separately. The largest heat loss occurs in rooms on the upper floors with unheated attics and basement levels with an ordinary basement.
The orientation of the walls plays an important role in the normative calculations. The largest amount of heat is lost by rooms facing the north and north-east sides (Q = 0.1). The corresponding additives are also taken into account in the described formula.
Climatic zones are important too
It's no secret that in different climatic zones there is a different need for heating, therefore, when designing a project, these indicators must also be taken into account.
Climatic zones also have their own coefficients:
- the middle strip of Russia has a coefficient of 1.00, so it is not used;
- northern and eastern regions: 1.6;
- southern stripes: 0.7-0.9 (minimum and average annual temperatures in the region are taken into account).
This coefficient must be multiplied by the total thermal power, and the result obtained must be divided by the heat transfer of one part.
findings
Thus, the calculation of heating by area does not present any particular difficulties. It is enough to sit for a while, figure it out and calmly calculate.With its help, every owner of an apartment or house can easily determine the size of the radiator that should be installed in a room, kitchen, bathroom or anywhere else.
If you doubt your skills and knowledge, entrust the installation of the system to professionals. It is better to pay one time to the professionals than do it wrong, dismantle and re-start. Or do nothing at all.
Continuing the theme: high-quality interior doors www.dveri-tmk.ru will help keep warm in your house or apartment. And to simplify the calculations for the heating area.
How to calculate the number of radiator sections
There are several methods for calculating the number of radiators, but their essence is the same: find out the maximum heat loss in a room, and then calculate the number of heating devices required to compensate them.
There are different calculation methods. The simplest ones give approximate results. Nevertheless, they can be used if the premises are standard or apply coefficients that allow taking into account the existing "non-standard" conditions of each particular room (corner room, exit to the balcony, full-wall window, etc.). There is a more complex calculation using the formulas. But in fact, these are the same coefficients, only collected in one formula.
There is one more method. It determines the actual losses. A special device - a thermal imager - determines the real heat loss. And on the basis of these data, they calculate how many radiators are needed to compensate them. What's more good about this method is that the thermal imager clearly shows where the heat is most actively removed. This can be a defect in work or building materials, a crack, etc. So at the same time you can straighten things out.
The calculation of radiators depends on the heat loss in the room and the rated heat output of the sections.
Calculations of the number of sections by quadrature per room
The accuracy of the calculations depends on the number of factors taken into account. In general, they can be divided into three groups:
- Area calculation is based on the assumption that heating of each square meter requires at least 100 W... That is, a 1 kW radiator is needed for a room of 10 m2 (approximately 7 sections). The figures are relevant for rooms with ceilings up to 2.6 m.
- Accurate calculation involves taking into account the coefficients for all heat losses. The required number of sections for installing a heating radiator is calculated according to the following formula calculation - by multiplying 100 (watt / m2) for the area of the room in m2 and for each coefficient (q):
- Determination by volume gives about the same numbers as the formula for calculating by area... According to the SNIP recommendations, the heat consumption in the living room of a panel house with wooden windows is 41 W per cubic meter. If there are modern double-glazed windows, the standard is reduced to 34 W per 1 m3. Heat consumption is reduced for buildings with wide walls made of foam concrete, bricks, etc., as well as in the presence of high-quality thermal insulation.
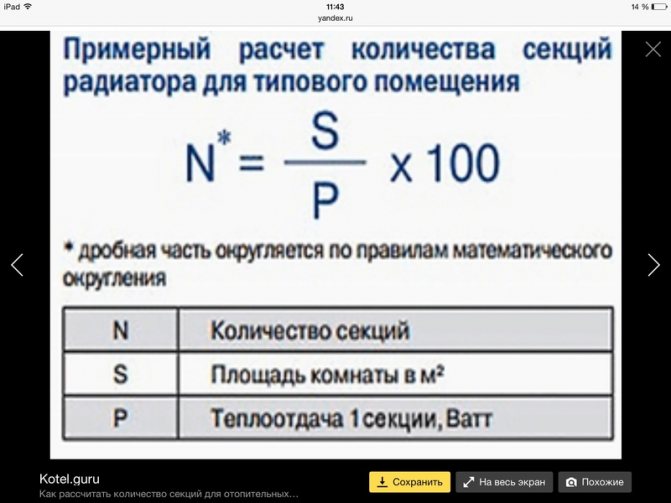
How to calculate the number of sections and the estimated power of heating radiators? The simplest formulas:
- N - the number of sections,
- P - the power of one section of the radiator,
- S - the area of the room,
- V - room volume 41W - heating capacity 1 m3,
- 1.2 Is the standard heat loss coefficient.
The heat transfer of the section for each specific model is indicated by the manufacturer on the edge of the product. On average, the indicators are as follows:
| Metal at the base of the section | Average heat transfer rate of a section |
| Aluminum | 170-200 Watt |
| Bimetal | 150 watts |
| Cast iron | 120 W |
To simplify all calculations, some specialized resources offer online calculators, where you just need to enter the initial data and get the finished result in a second. How to independently calculate the number of sections of bimetallic heating radiators read here.
Calculation example
If you calculate how many sections of an aluminum radiator are needed for a room with an area of 20 m2 at a rate of 100 W / m2, then you should also make correction coefficients for heat loss:
- each window adds 0.2 kW to the indicator;
- the door "costs" 0.1 kW.
If it is assumed that the radiator will be placed under the windowsill, then the correction factor will be 1.04, and the formula itself will look like this:
Q = (20 x 100 + 0.2 + 0.1) x 1.3 x 1.04 / 72 = 37.56
- first indicator Is the area of the room;
- second - standard number of watts per m2;
- third and fourth indicate that the room has one window and one door;
- next indicator Is the level of heat transfer from the aluminum radiator in kW;
- sixth Is the correction factor for the location of the battery.
Everything should be divided into the heat dissipation of one heater rib. It can be determined from the table from the manufacturer, which indicates the heating coefficients of the media in relation to the power of the device. The average for one rib is 180 W and the adjustment is 0.4. Thus, multiplying these numbers, it turns out that 72 W is given by one section when the water is heated to +60 degrees.
Since rounding is done upwards, the maximum number of sections in an aluminum radiator specifically for this room will be 38 fins. To improve the work of the structure, it should be divided into 2 parts with 19 ribs each.
Find out useful information about aluminum batteries on our website: