Heat is the main parameter of a modern home that every owner of a living space wants. In order for this warmth to be year-round, heating systems work in houses and apartments during the cold period. These can be of various designs with many functional parts.
The part that gives heat to the room is called the heating radiator. Until recently, almost all radiators, or batteries, as they are more commonly called, had approximately the same structure. In modern times, there are a lot of such structures and they all differ in some way from each other.

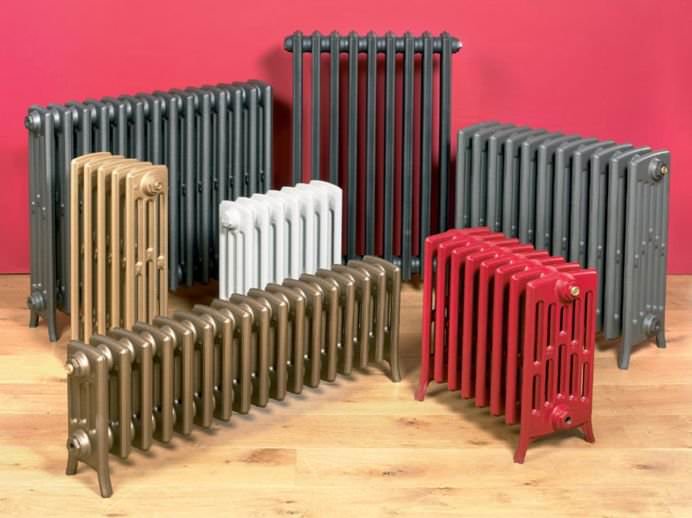
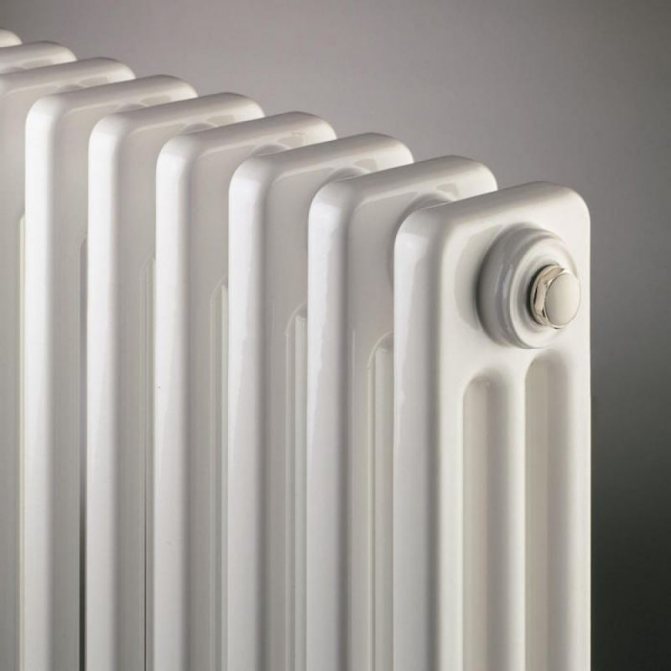
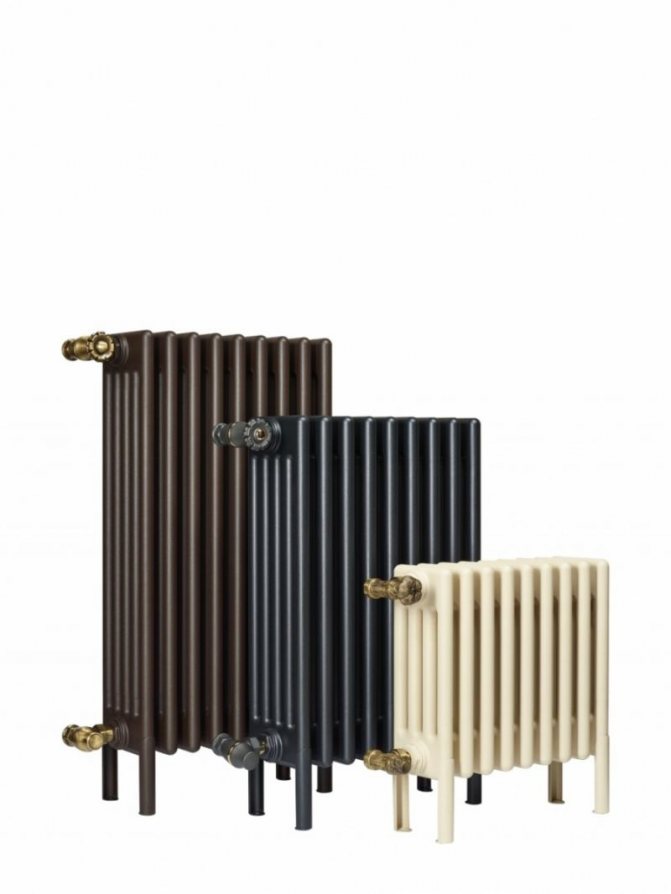
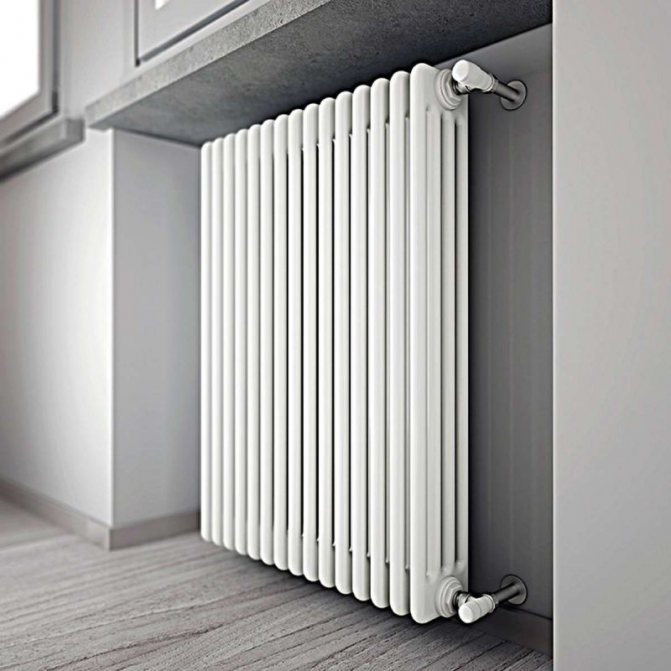
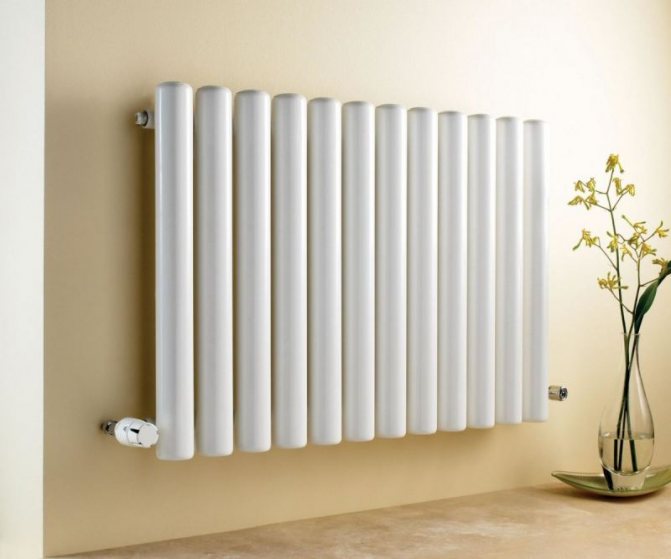
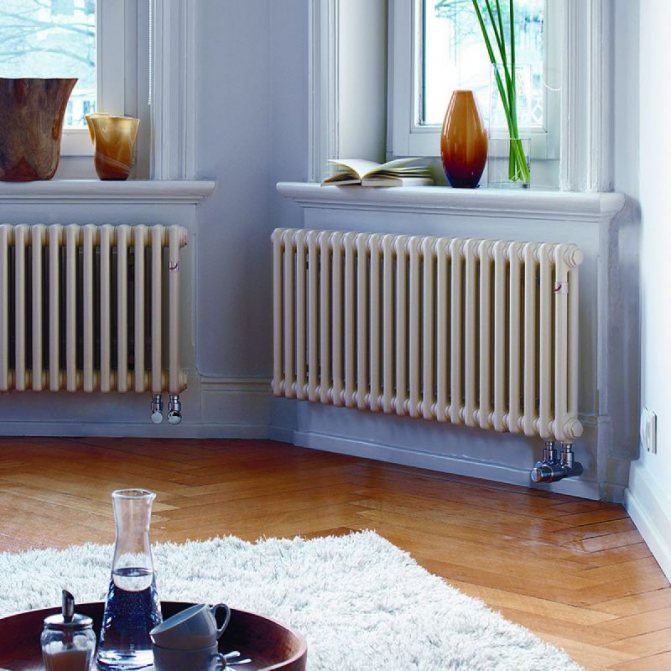
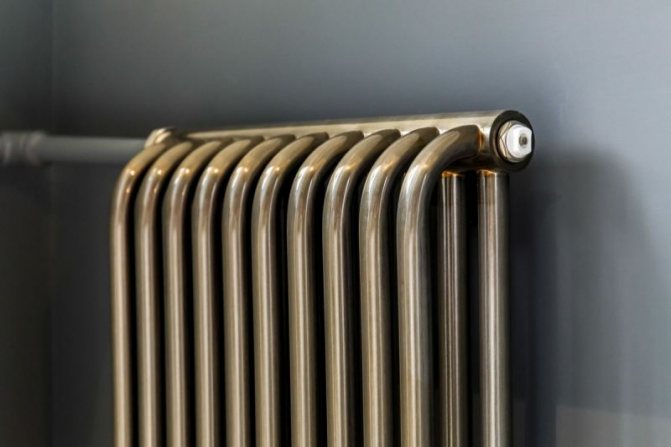
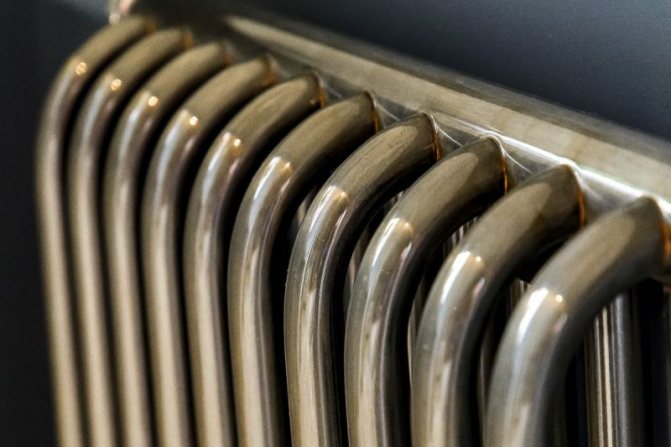
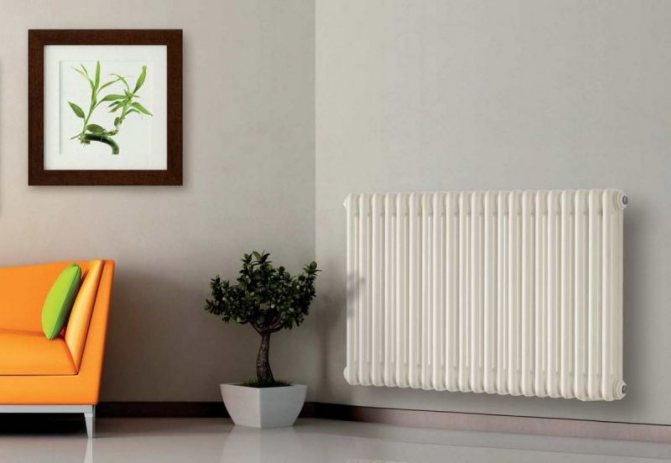
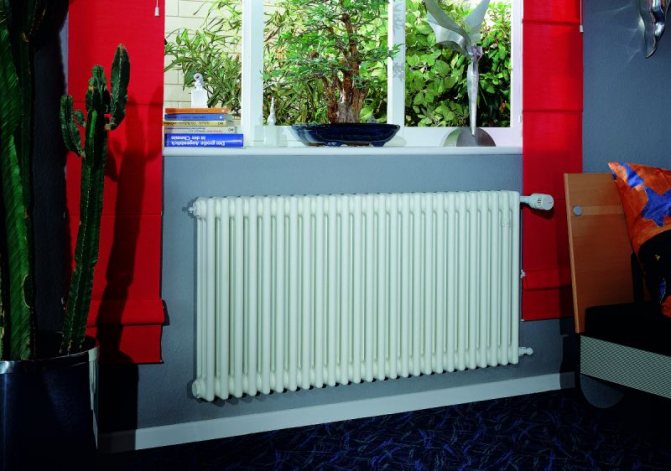
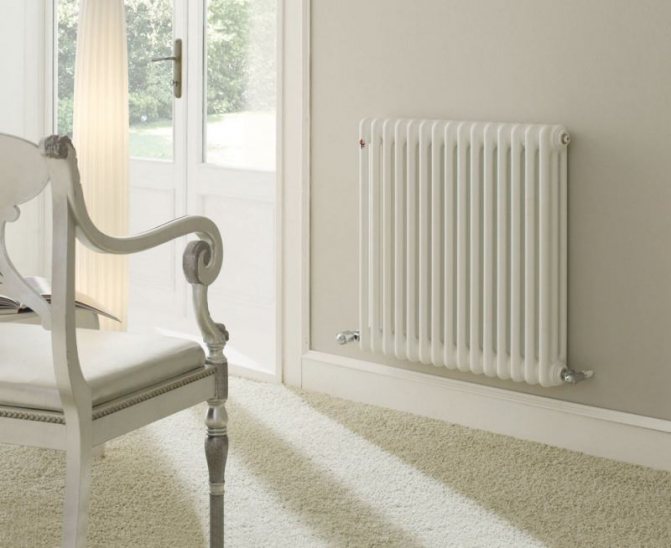
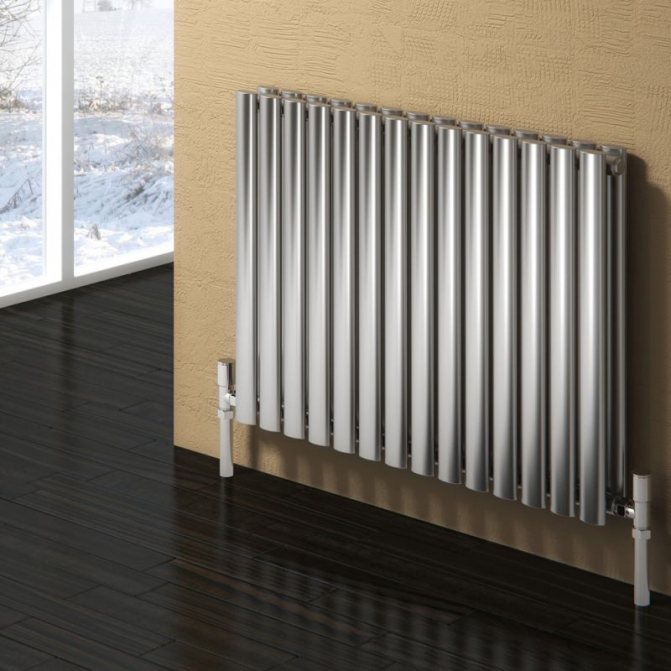
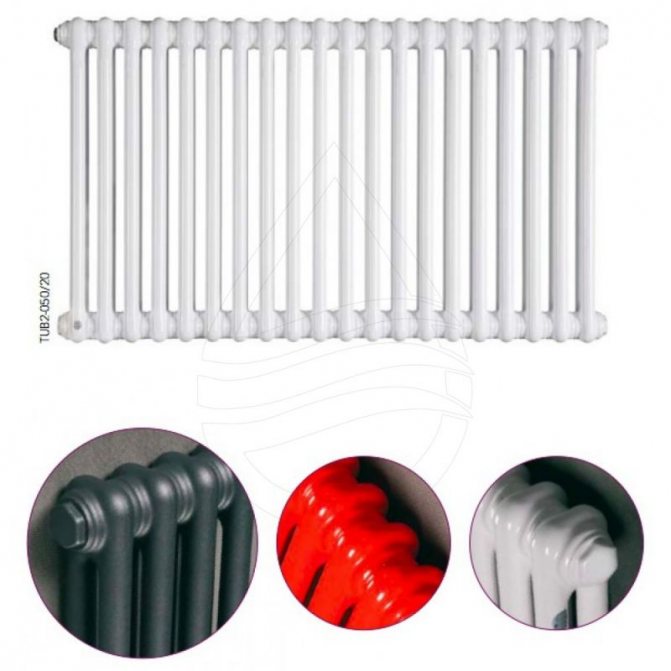
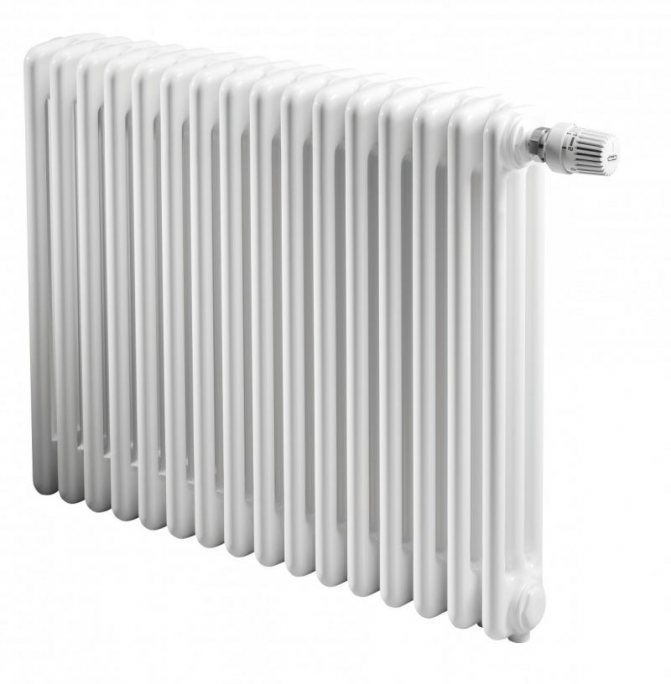
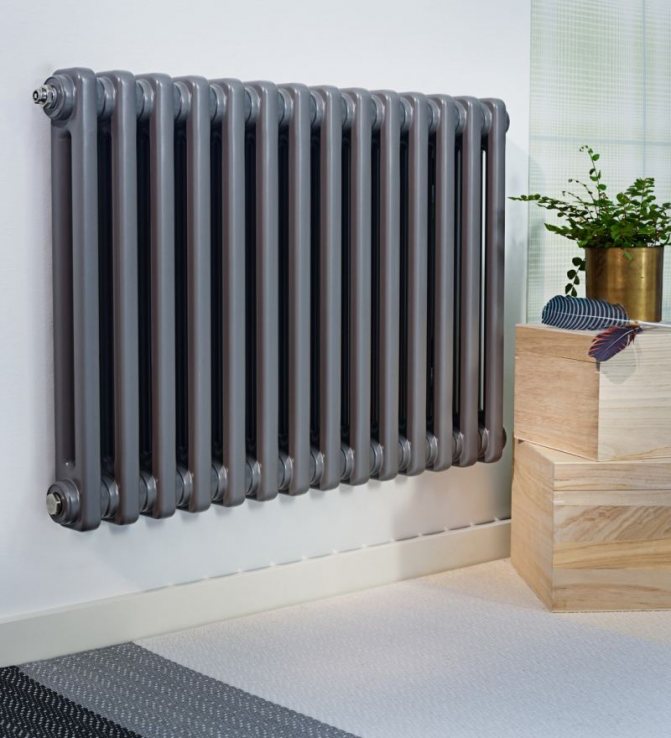
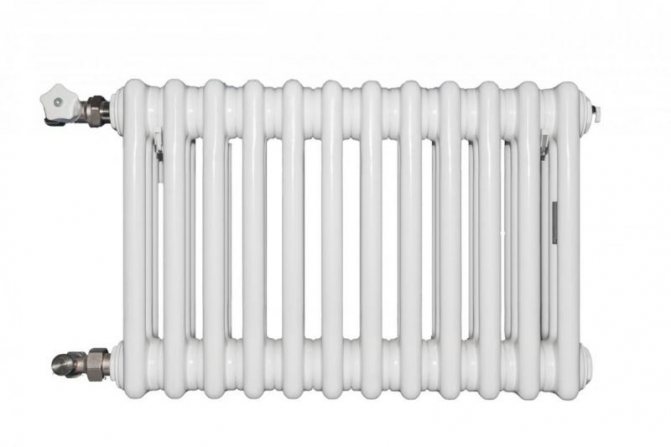
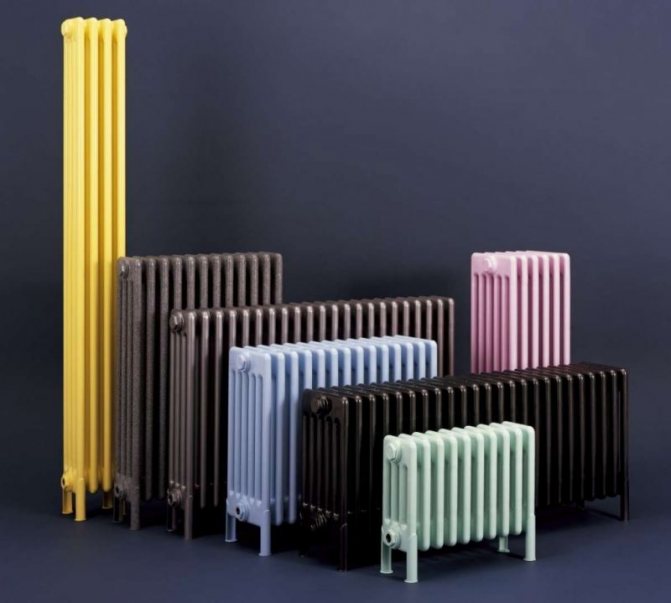
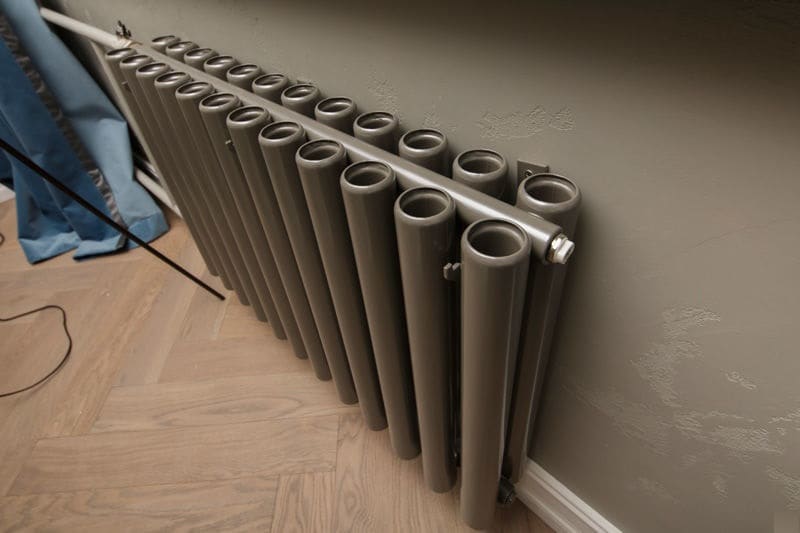
For example, the good old tubular heating radiators now have a large assortment depending on the size and shape, which is easy to see in the photo. And these units are not already suitable for every case of the heating system.


In this article, we will take a closer look at tubular radiators.
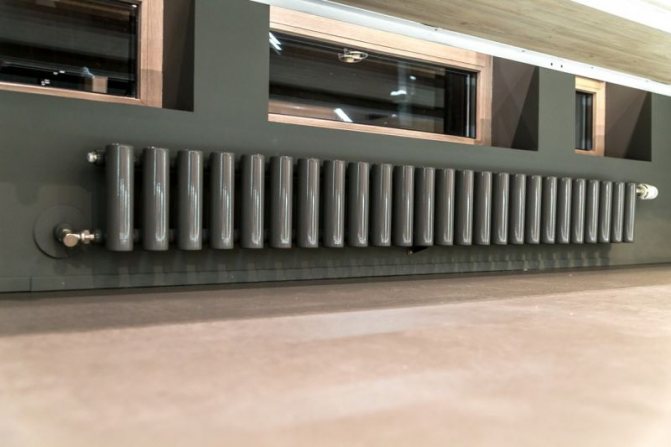


Tubular radiator design
Unlike the old cast iron versions of tubular batteries, modern designs are much prettier and better executed. They represent two functional compartments: upper and lower.


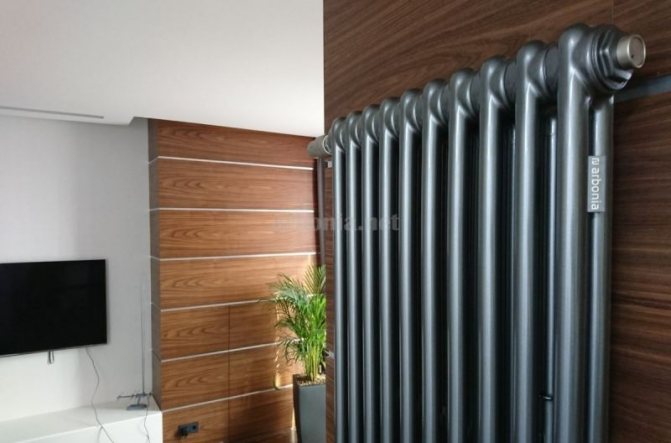
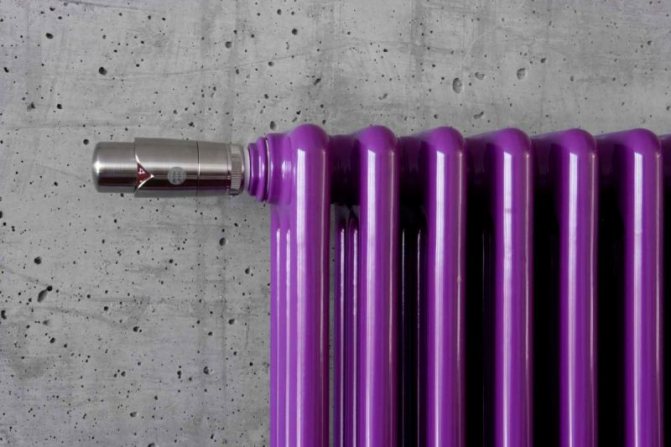
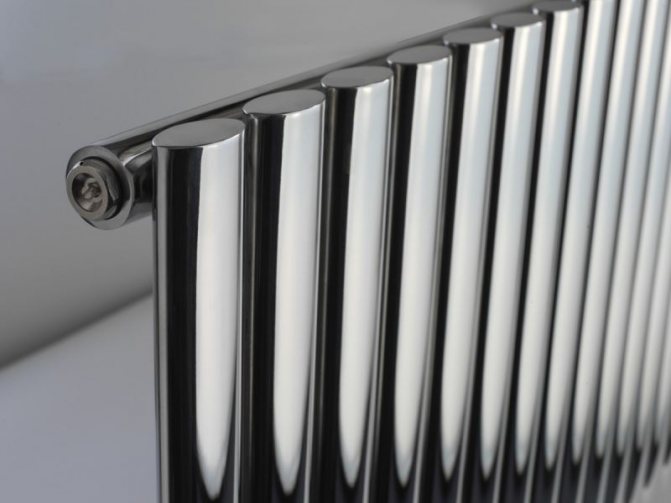
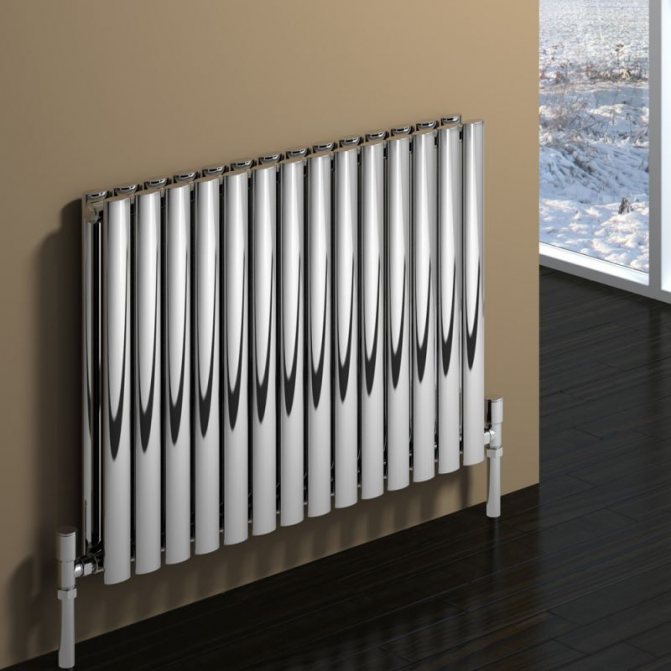
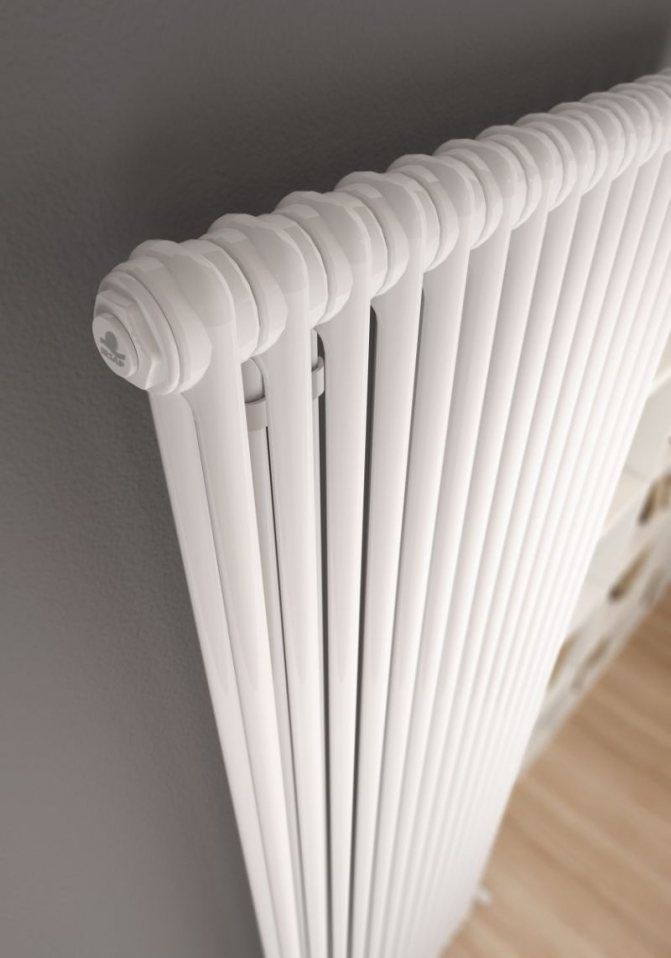
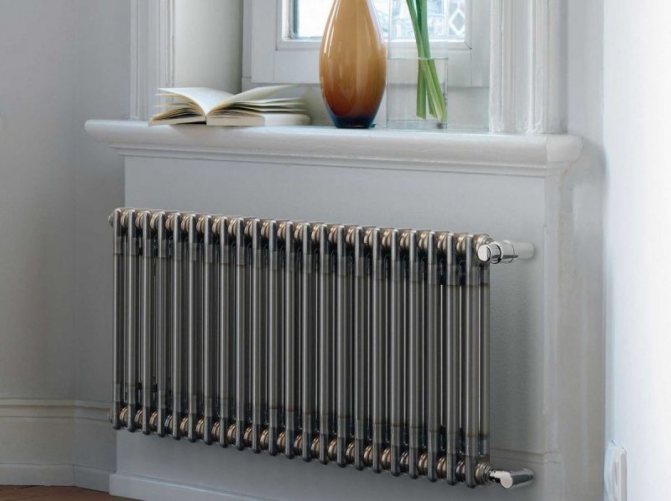
These compartments are interconnected by special steel pipes. Tubular steel radiators of modern models look very tiny and pretty.
In addition, all joints on them are extremely safe and are laser welded seams. Such a seam is very difficult to damage, which allows the batteries to be more durable.
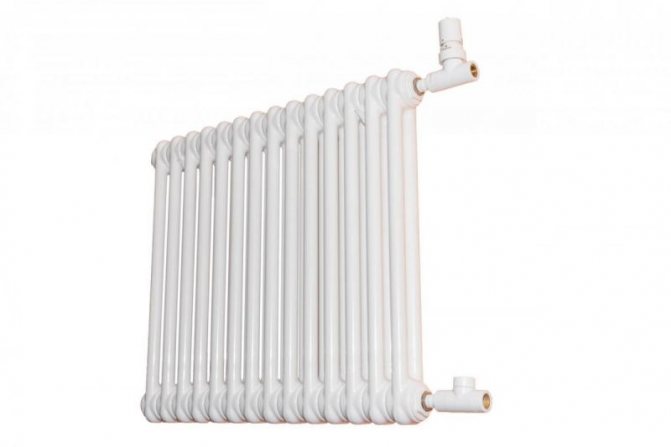


Despite their strength, steel tubular radiators are not able to withstand large pressure drops. For this reason, their installation is recommended only in private houses or apartments of five-story buildings.
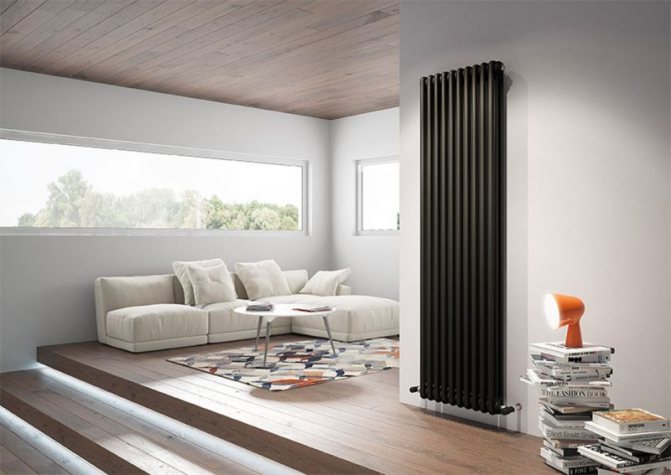


In high-rise buildings, there are often unforeseen power surges that exceed 10 atmospheres.
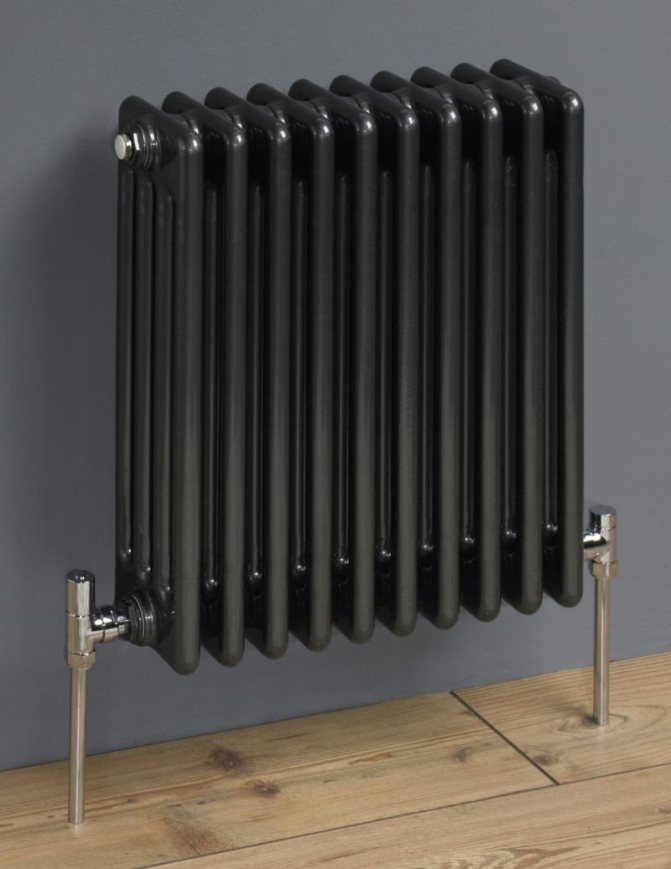


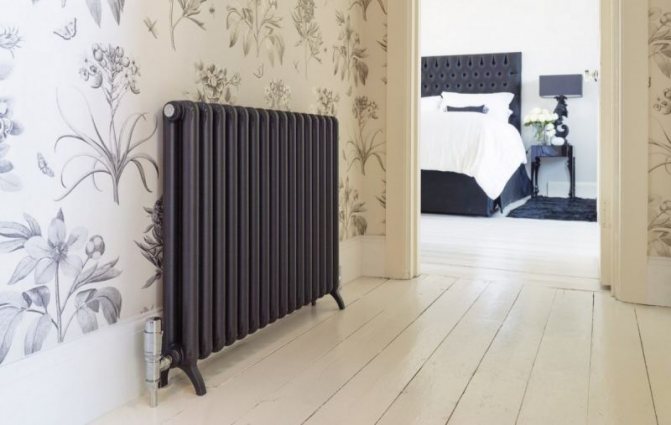
Tubular steel radiators are very popular in medical institutions. This is easy to explain, since tubular batteries do not contain any corners that could cause injury.


In addition, tubular radiators do not attract dust and do not require special cleaning. For hospital and outpatient institutions, these qualities are most important.


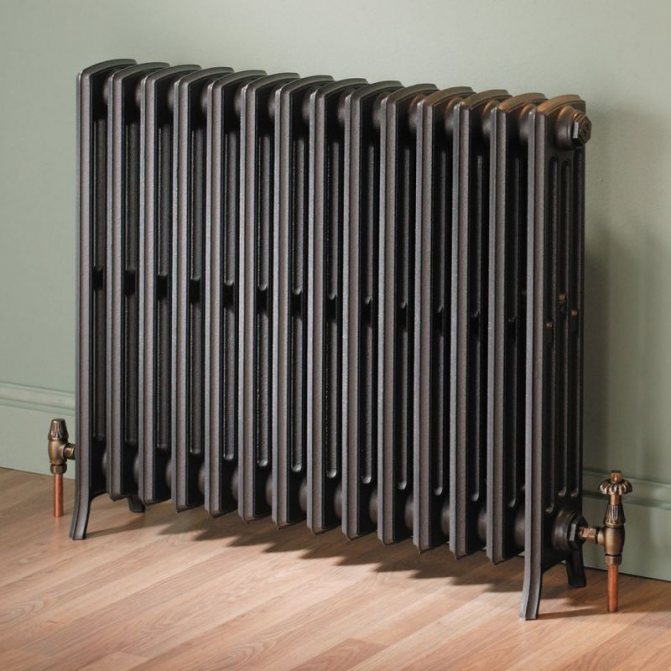
Cast iron radiators
The working pressure of cast iron radiators is 6-9 atm, the test pressure is 15-18 atm, the maximum temperature of the coolant is 130 ° С.
The main advantages of cast iron radiators are:
- high corrosion resistance. The fact is that during operation, dry rust forms inside the radiator from cast iron, which protects the battery from the effects of an aggressive environment. In addition, cast iron radiators have a low level of abrasive wear, which is why they are not afraid of debris that gets into heating equipment, a highly alkaline environment, etc.;
- cast iron is the least susceptible to aggressive action of the working fluid;
- relatively low cost, if we are not talking about artistically cast radiators;
- high heat transfer, cast iron radiators are quite inert: they heat up for a long time, but also cool down for a long time (compared to other radiators);
- the largest of the presented types of radiators with a service life (up to 35 years).
The disadvantages of cast iron batteries are:
- low thermal conductivity of metal and small heat transfer surface.In particular, a standard section of an M-140 cast-iron radiator (Russia) weighs 7.5 kg and holds 4.5 liters of water, but the heating area is only 0.23 m2, while, for example, a 2-kilogram aluminum radiator with a water volume of 0.5 liters heats about 0.4 m2.
- large thermal inertness, which does not allow cast iron radiators to cool down quickly, can be attributed to both the pluses and minuses of this heating equipment, since such batteries are completely unsuitable for regulated automatic water heating systems;
- vulnerability to water hammer;
- high weight of sections;
- due to the large roughness of the inner surface, such radiators are relatively quickly clogged with suspensions, "overgrown";
- the design of cast iron batteries, which are quite difficult to fit into modern interiors.
Differences between tubular systems
Radiators of any shape have a special subdivision into types depending on various factors. Tubular can also have several possible variations.
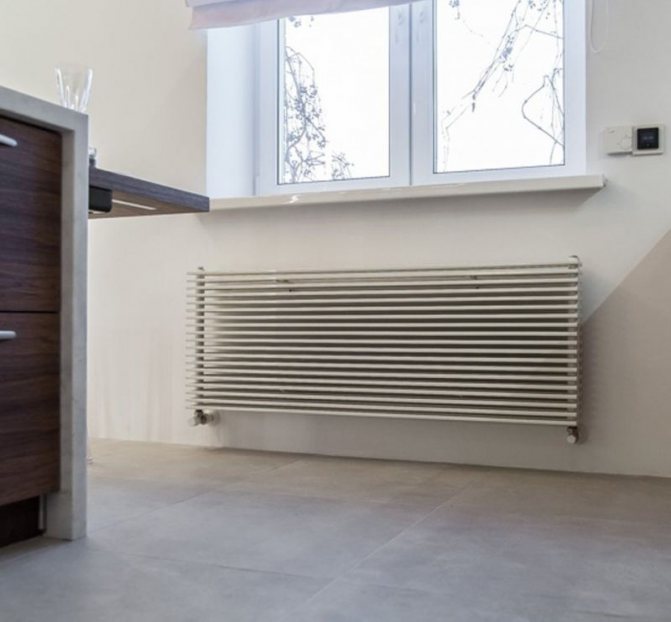


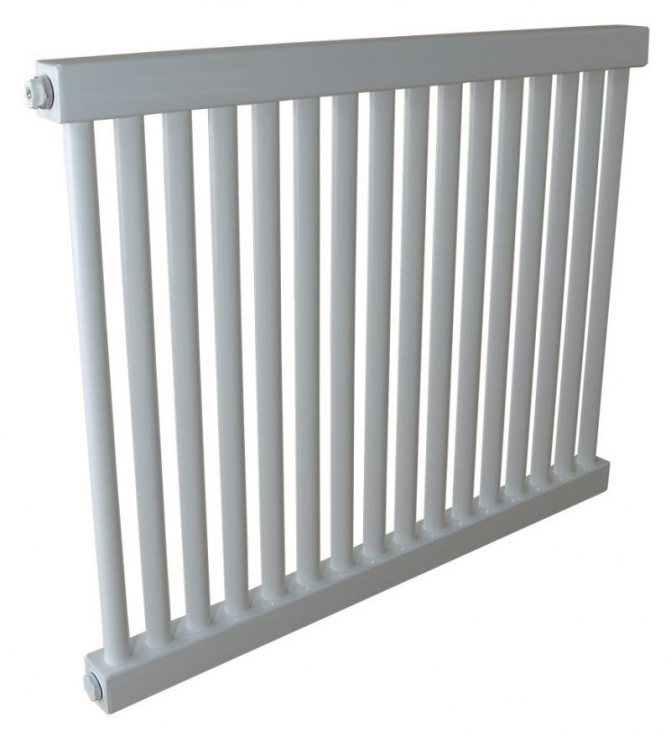
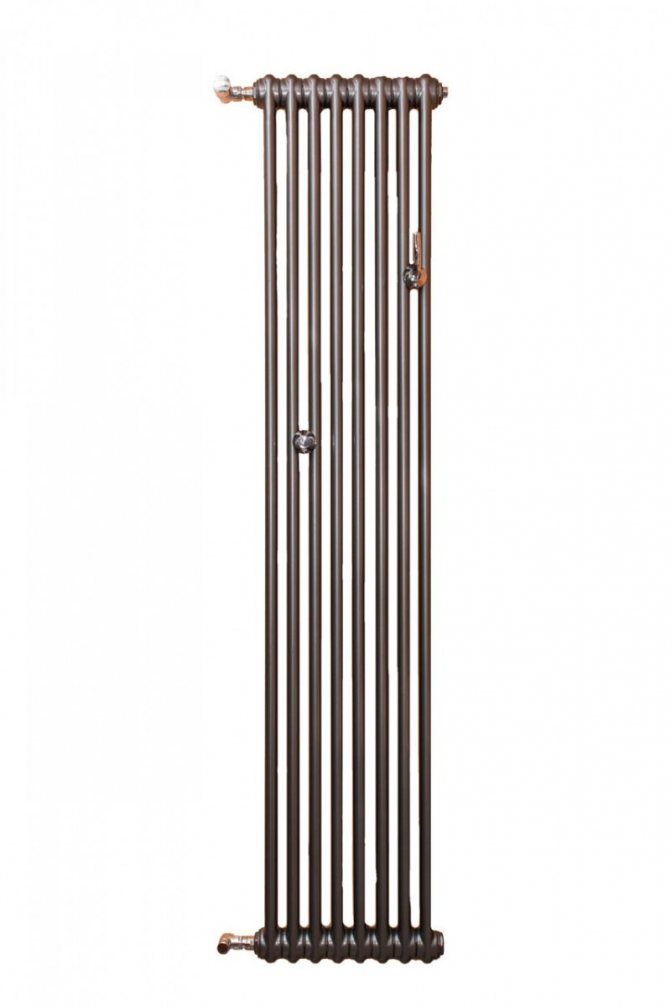
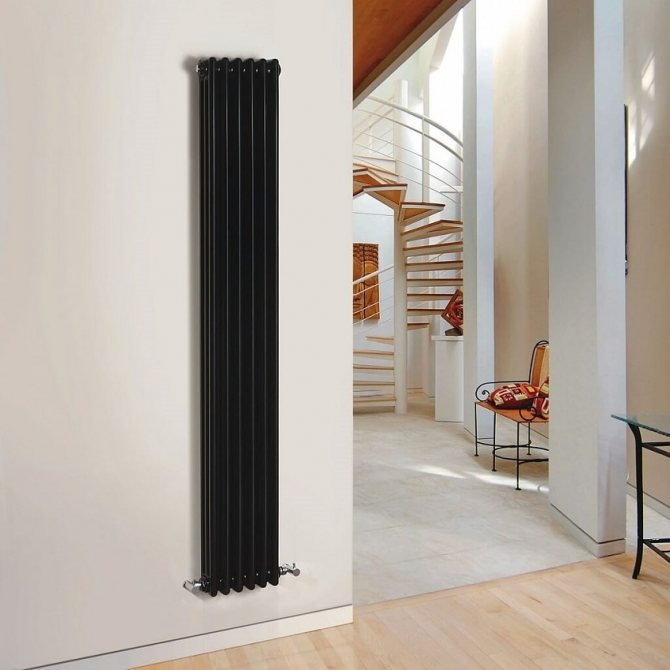
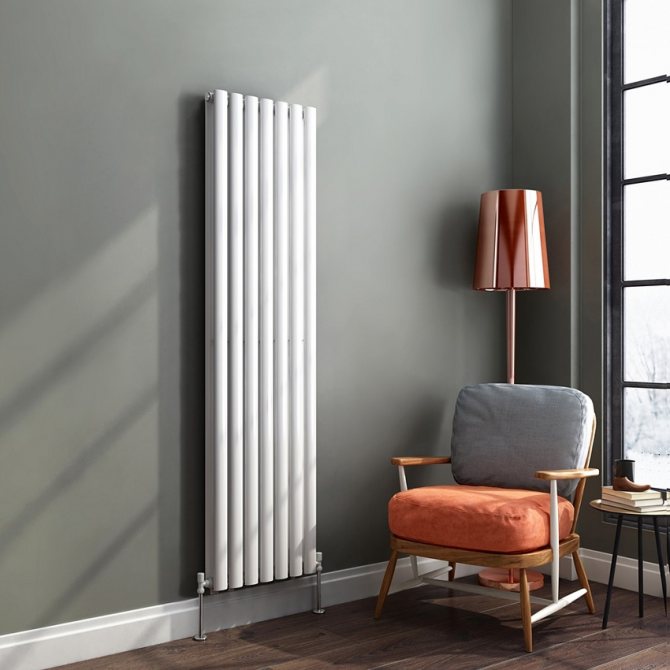
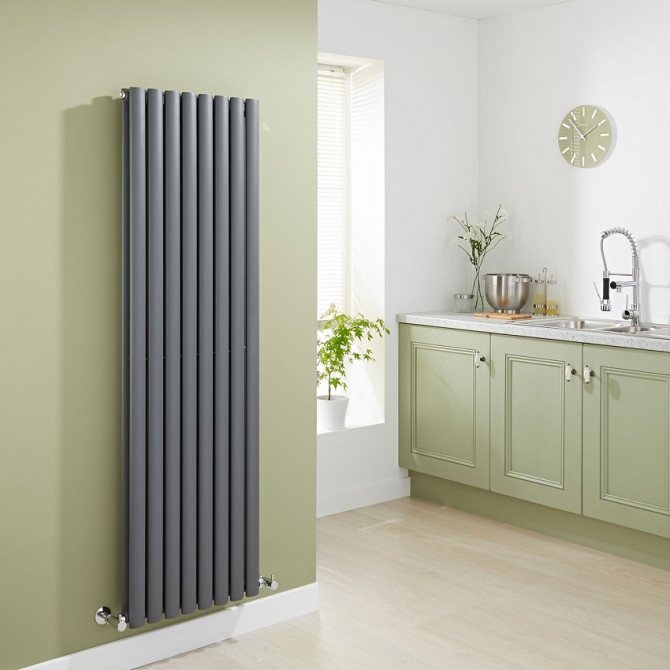
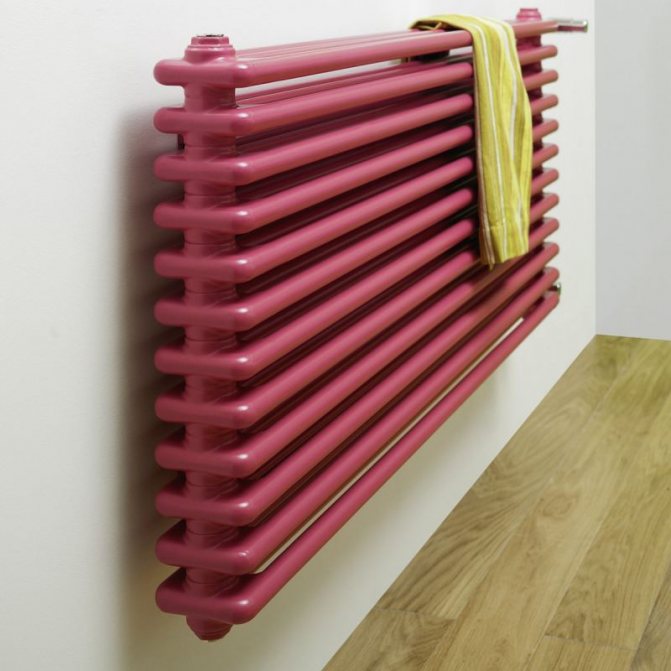
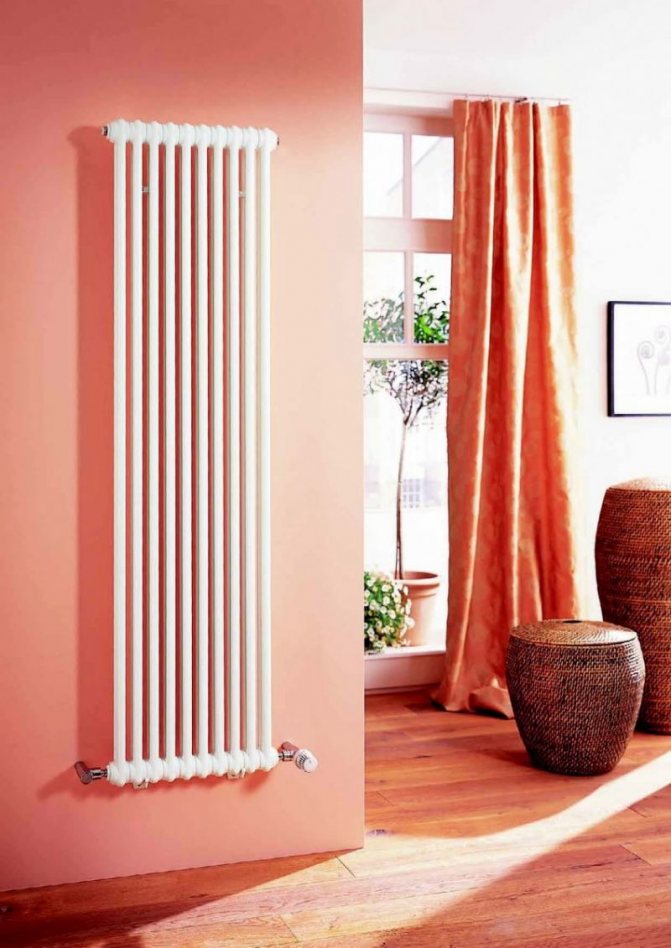
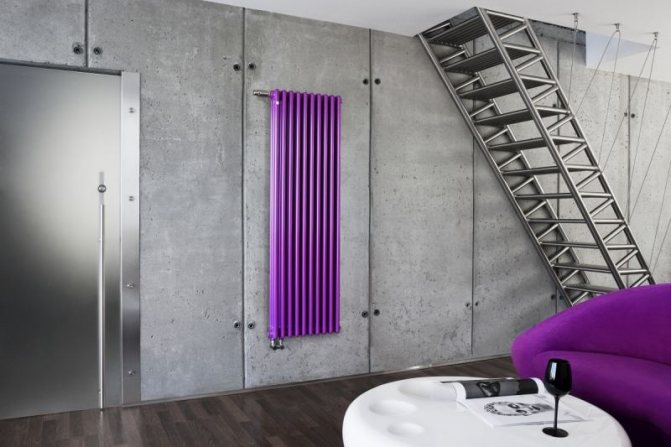
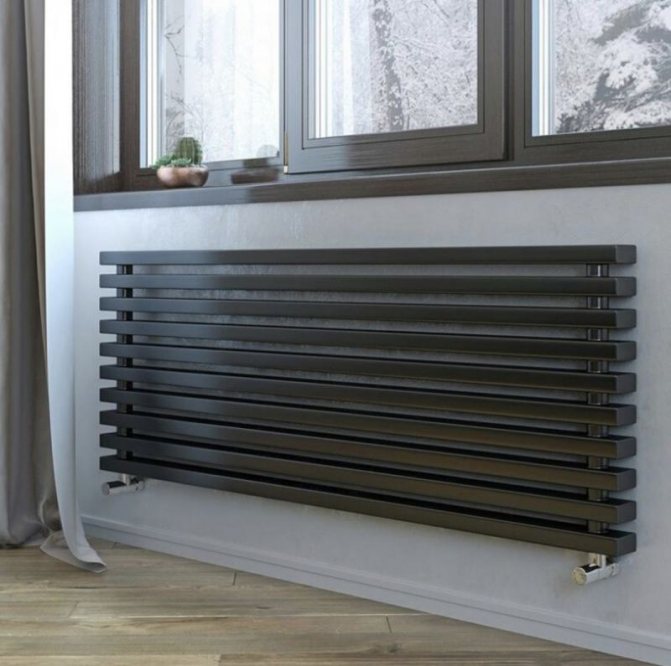
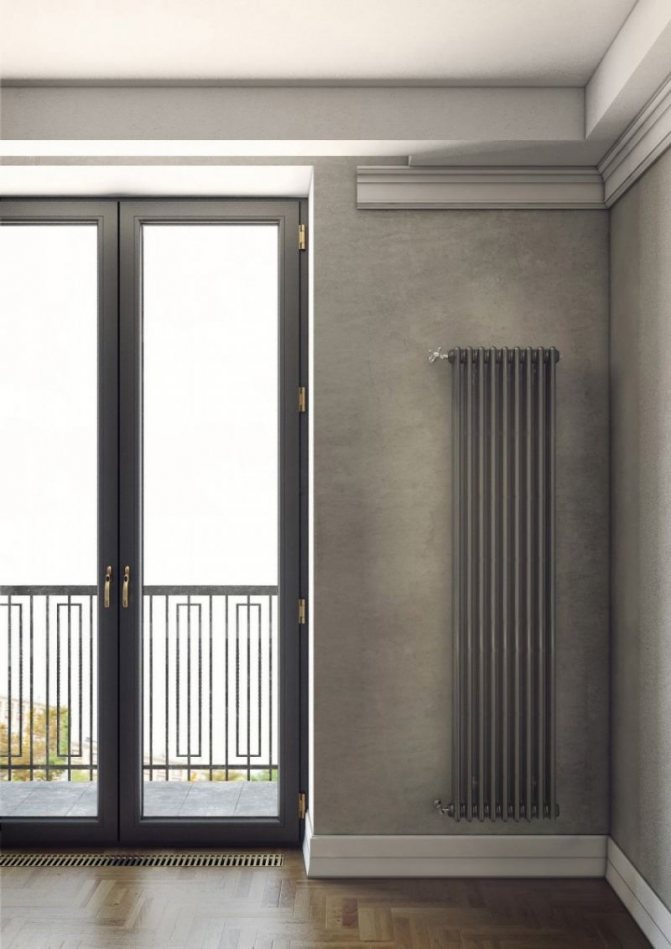
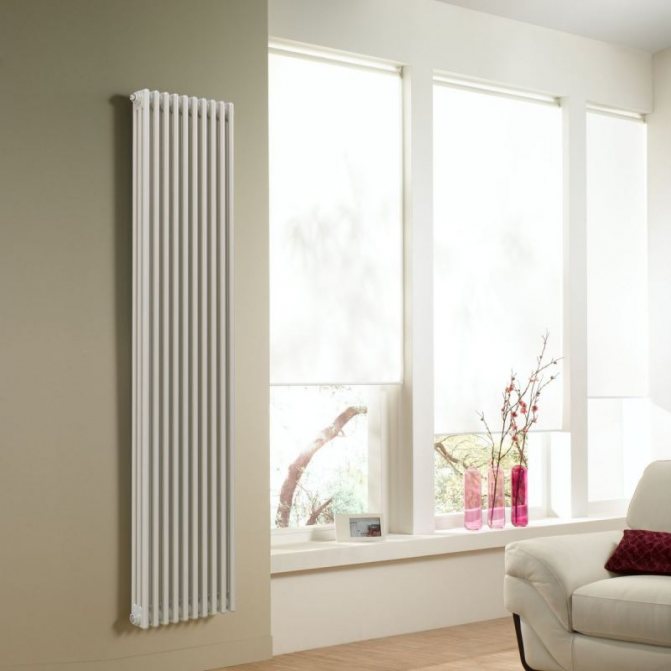
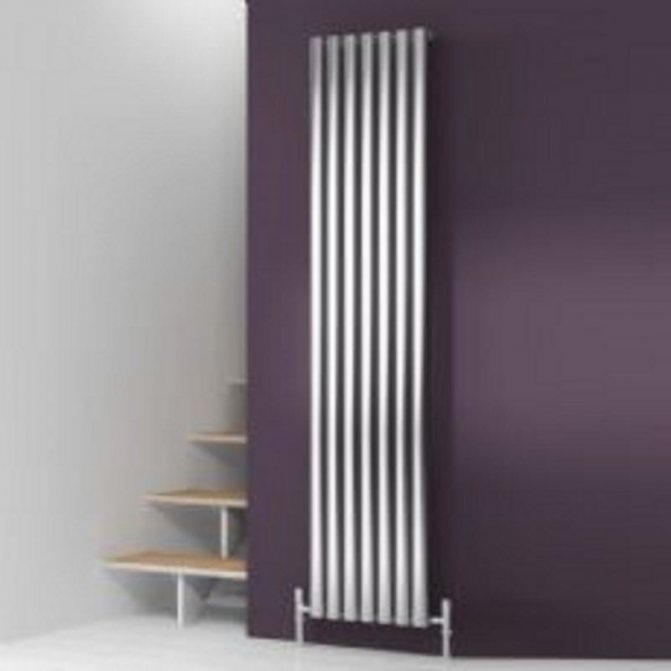
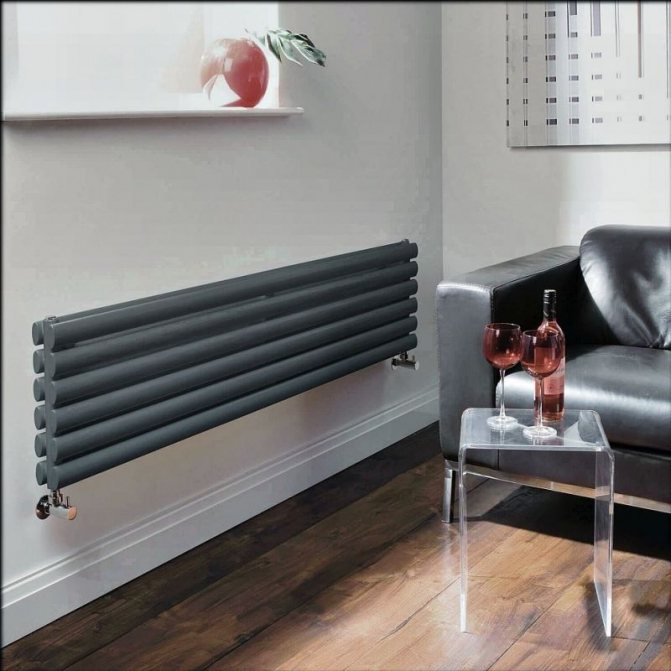
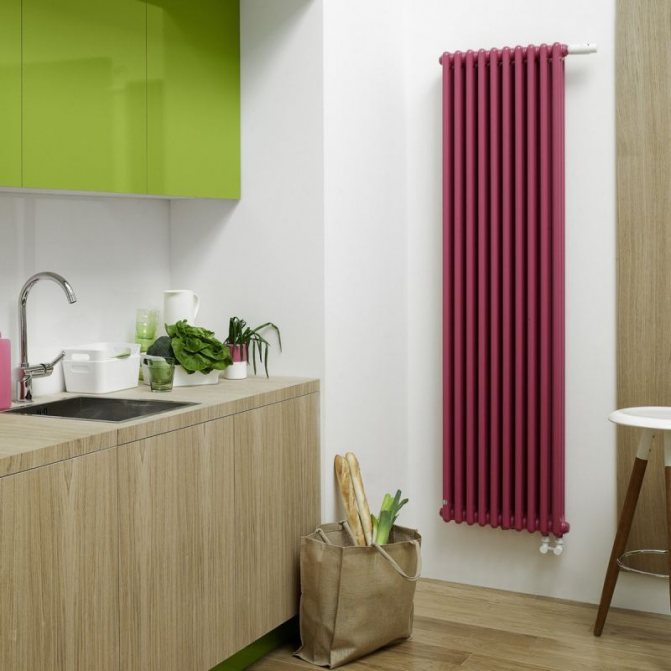
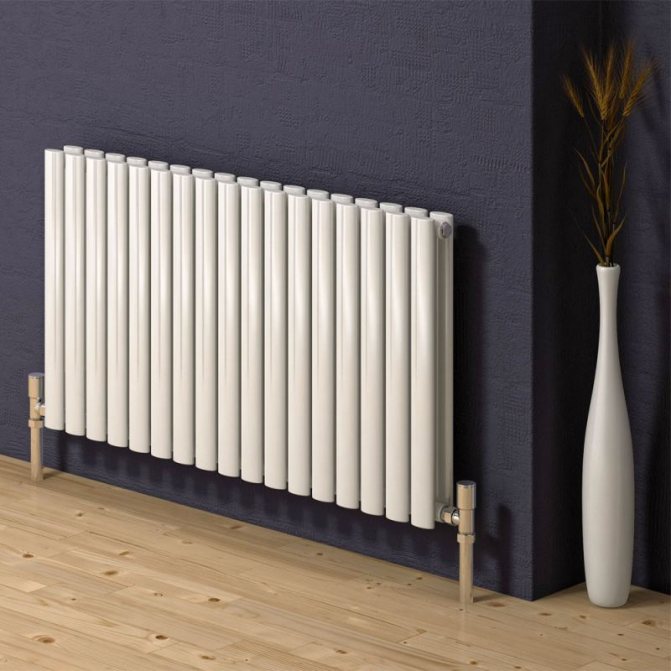
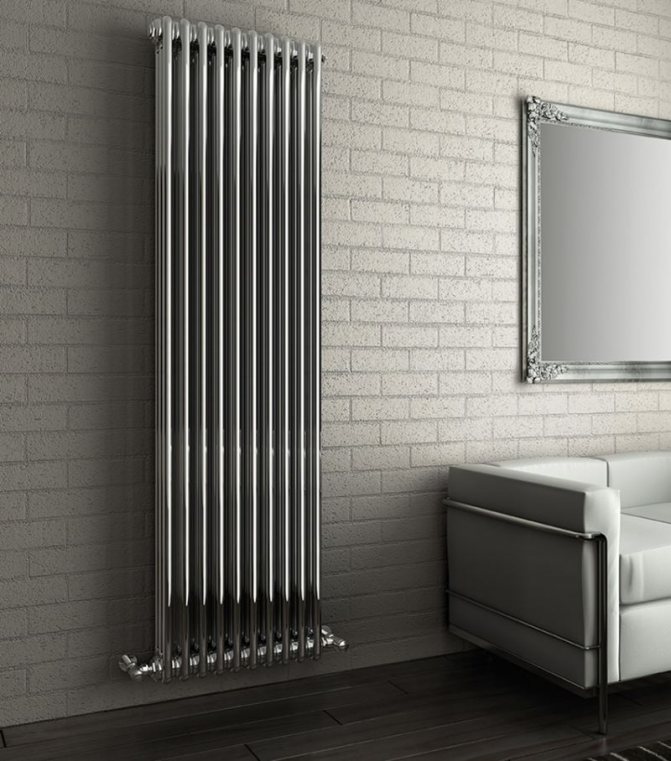
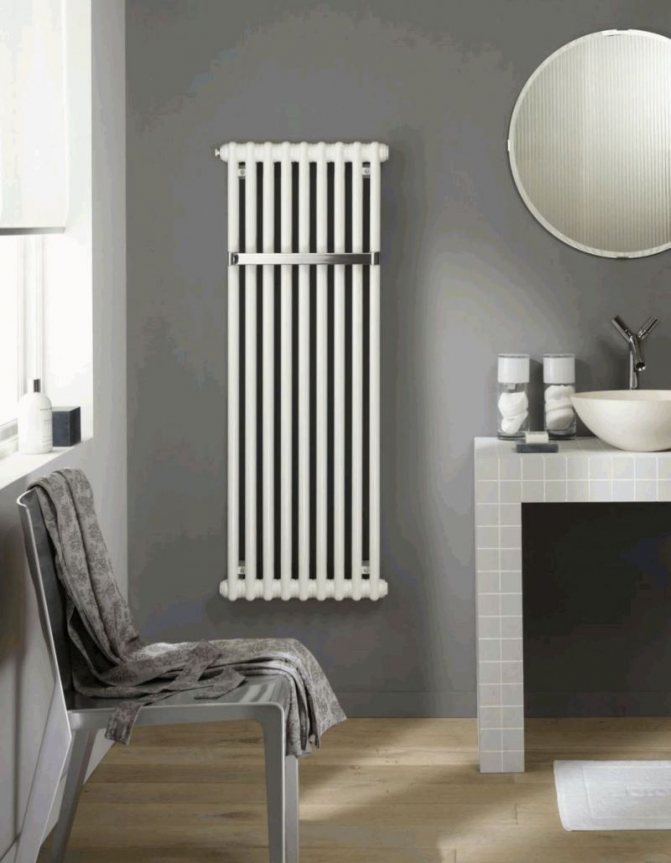
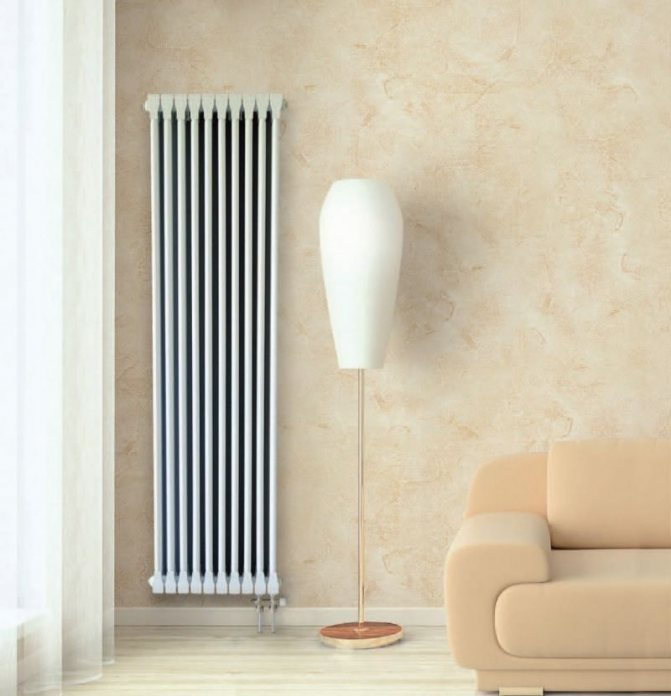
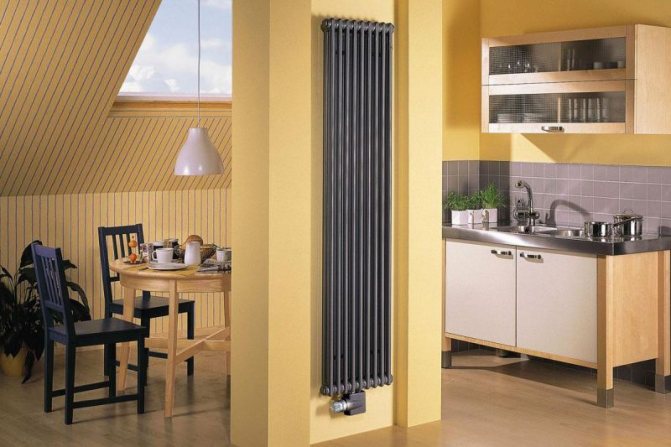
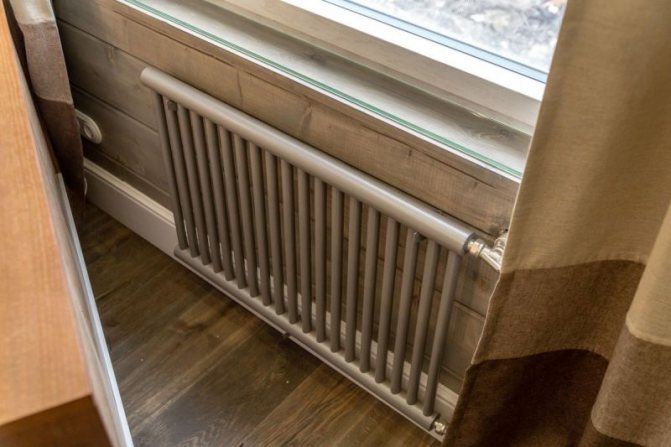
The largest separation is depending on the appearance of the device, namely, on the location of the pipes. These can be vertical and horizontal tubular heating radiators.
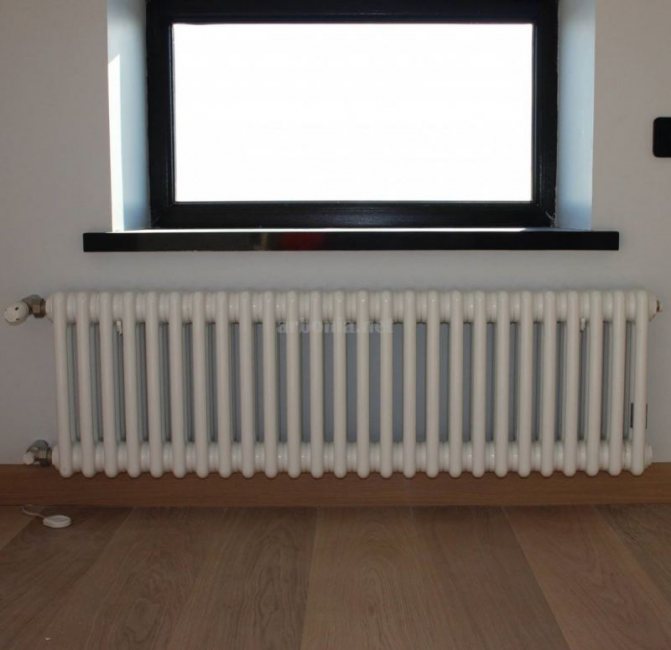


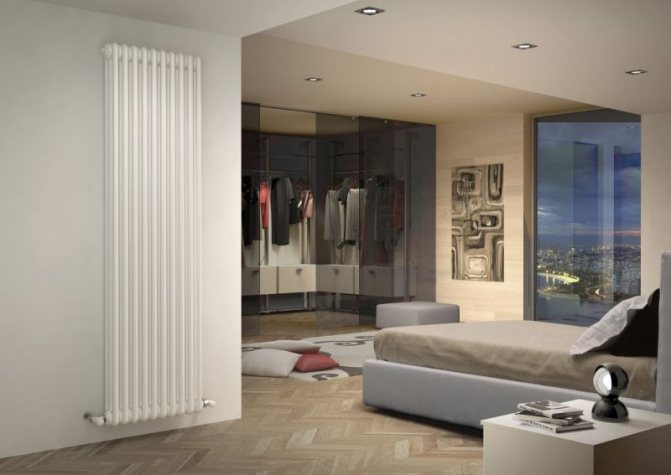
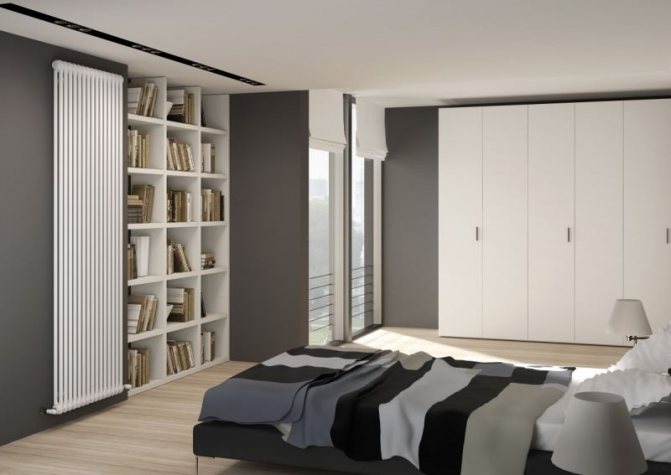
The first version of tubular radiators is the classic choice for private homes and medical institutions. They look beautiful, neat and do not accumulate dust on themselves.
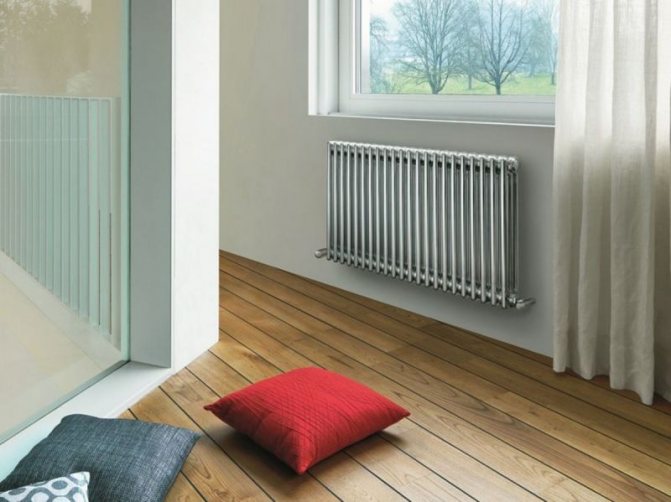
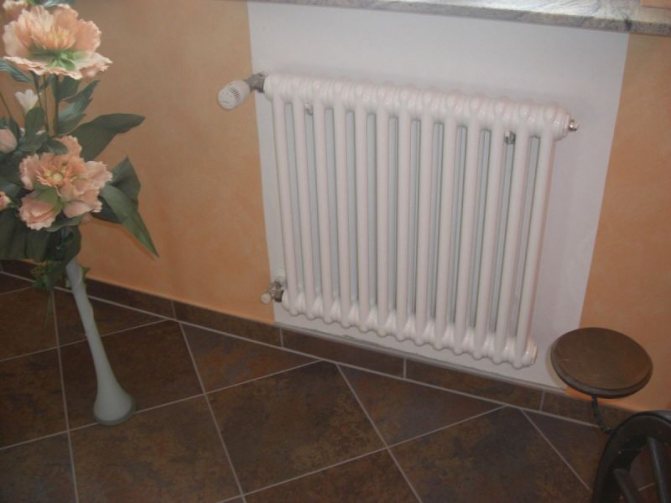
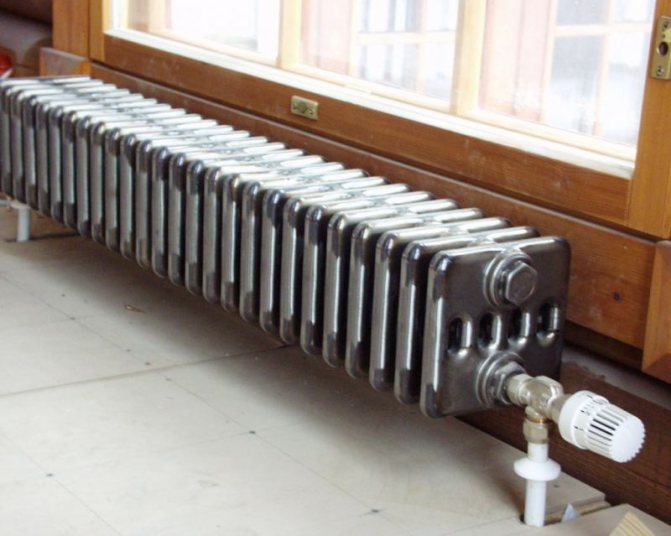
But the second type - horizontal - is the choice for large office premises where it is necessary to heat large areas.


Due to the peculiarities of the shape, there are no frames when choosing tubular radiators. These can be models for an angular arrangement, and simple flat ones, and any design ones.


- Cast iron heating radiators: description of the best models, installation and characteristics of radiators (120 photos)


Flushing heating radiators: purging, cleaning and maintaining the heating system (115 photos)
- Gas convectors - choice, features of use and owner reviews (video + 105 photos)
Most often, people choose just ordinary options, but in some cases they are made to order in the form that is closer to the homeowners.
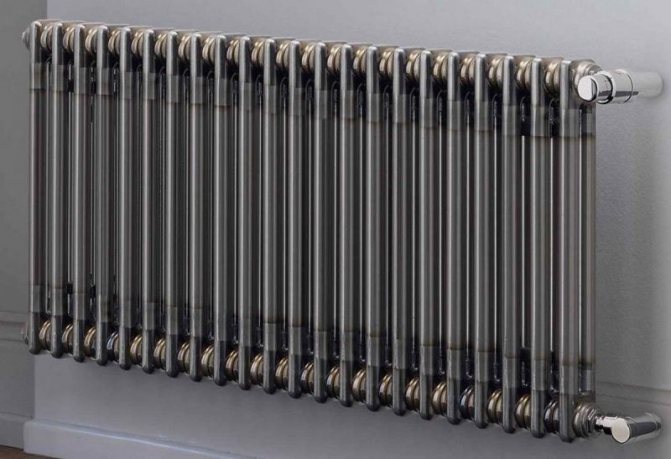


Radiator design


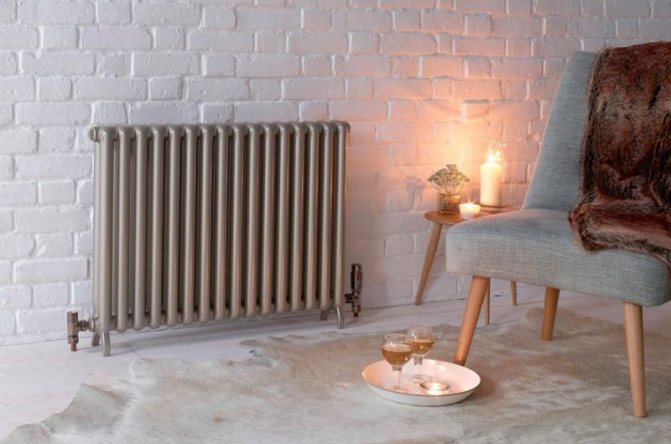
Steel tubular radiators can be made to order
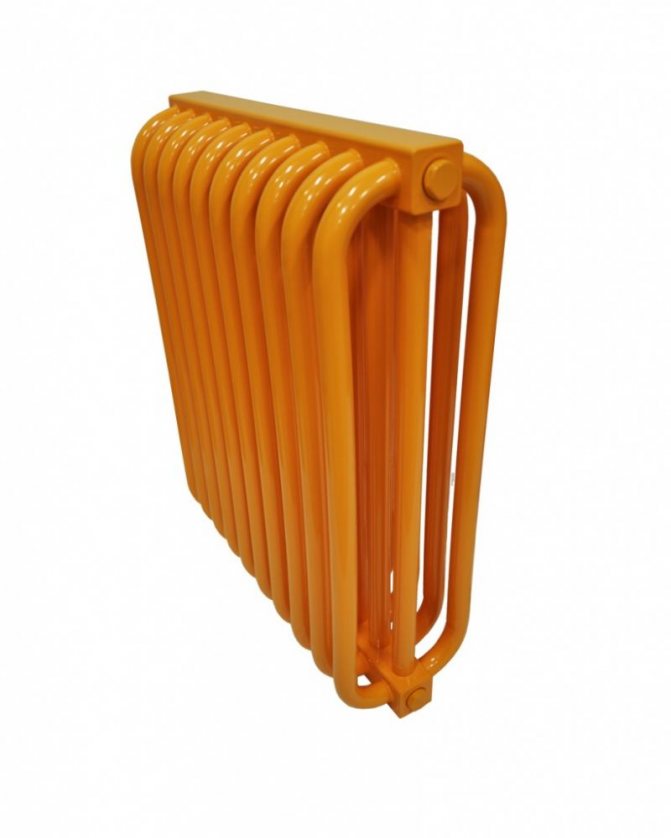
Steel tubular radiators can be made to order. The client can choose the dimensions of the device, its appearance, colors, technical characteristics and other important parameters.
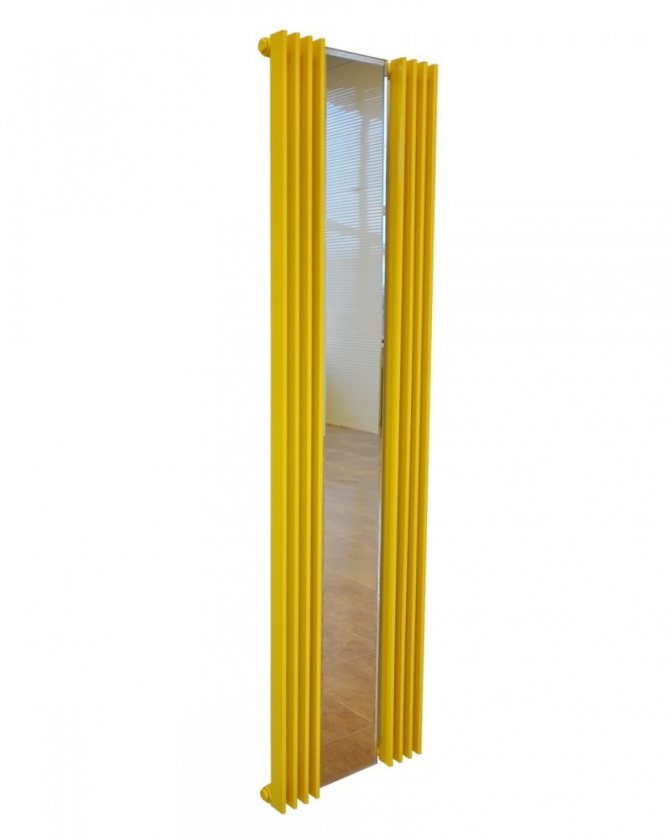
On sale you can find products of various designs. Such models are both a heating device and a stylish decorative item. They can be built into furniture, benches, bar counters.
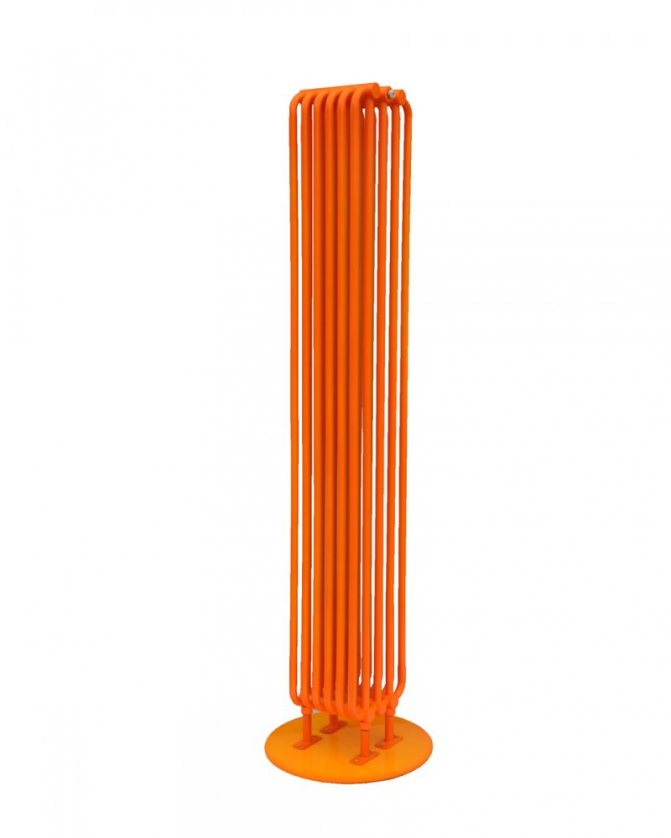
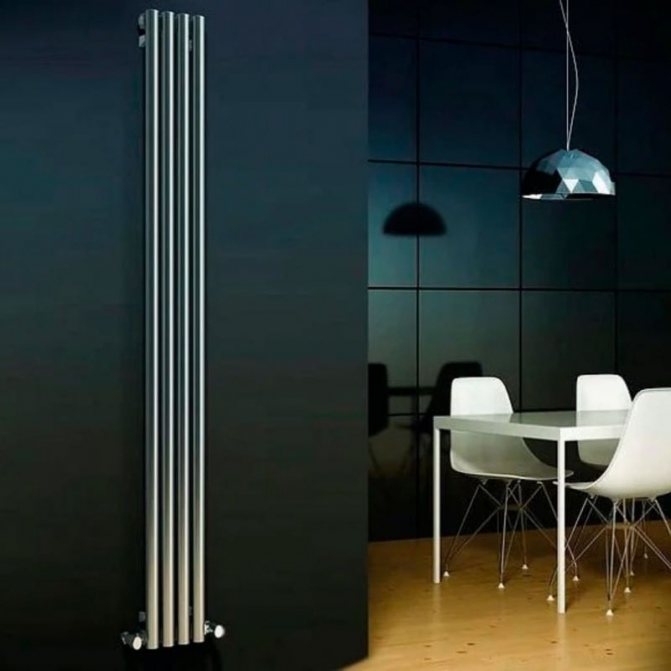
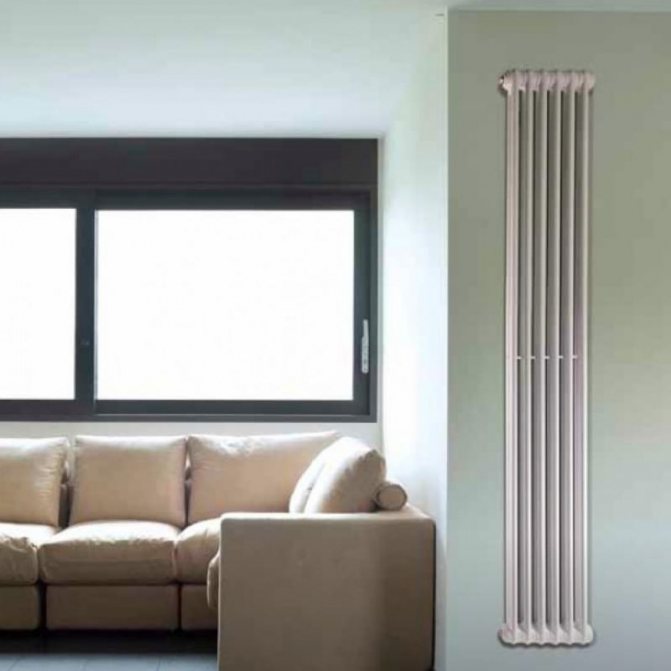
By the location of the tubes, vertical and horizontal radiators are distinguished. Vertical models are characterized by a height of up to 3 meters and a small width. Tubes are most often also stacked vertically in sections. Such tubular bimetallic radiators are actively used in places with limited space - flights of stairs, near balconies, in rooms with stained glass. Horizontal appliances are low in height and wide. The tubes can be placed horizontally and vertically. Connection to the heating system is made laterally.
Positive and negative qualities
The choice of a tubular heating radiator involves, first of all, the study of all its qualities. Both advantages and disadvantages should be taken into account, only then the choice will be competent.


Here is what is most often attributed to the advantages of tubular options:


This type of radiator is resistant to corrosion and does not deteriorate when exposed to hard water.


An extensive range of design solutions for the execution of Russian and foreign tubular heating radiators allows you to choose any model.


Thermostat for a heating radiator: purpose, types, device, installation in the system and tips for care and repair (video + 105 photos)

Vertical heating radiators - how to choose the ideal heating radiator and features of its application (90 photos + video)


Heating radiator power: calculation of thermal power and method for calculating heating radiators (85 photos and videos)


Caring for such radiators is simple, because they do not accumulate dust on themselves.


Any connection scheme will be relevant for such radiators. Tubular heating radiators can be either with bottom connection or with side connection.
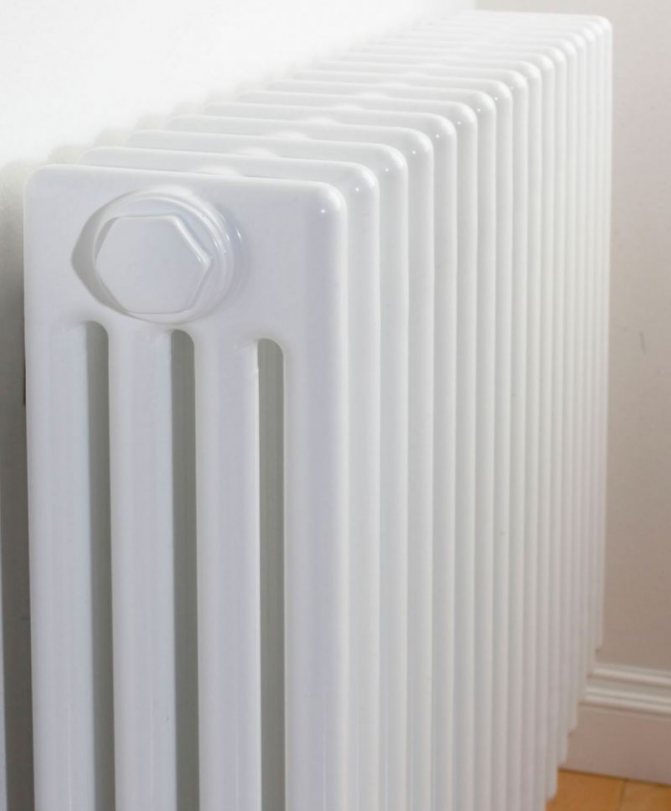


Although this variety has a lot of advantages, it cannot do without disadvantages. The most annoying thing on the list of shortcomings is the high price of tubular heating radiators.
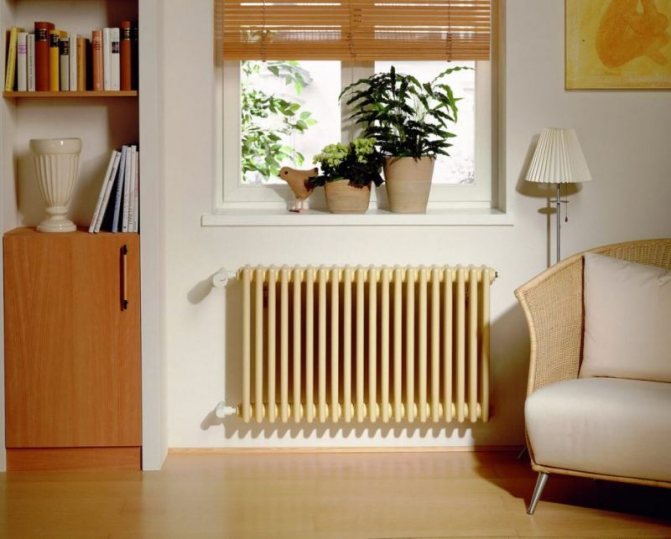


In addition, they have low power and poor heat dissipation. And also in some cases, smudges were noticed in the places where pipes were welded.


Aluminum radiators
Aluminum sectional radiators made of aluminum alloy with the addition of silicon are produced in 2 versions: cast and extrusion. In the first case, each section of the radiator is cast as a single piece, in the second, the section consists of several parts.
The advantages of aluminum radiators are explained by:
- attractive dimensions and weight of this heating equipment;
- high heat transfer and heating rate of the room, which allows us to talk about 30 percent savings in energy consumption;
- their service life is 15–25 years (less than that of radiators of other classes, but still quite long);
- high working pressure (up to 25 atm, some 60 atm), and the cost of the radiator depends on the parameters of the working pressure: the higher it is, the more expensive the radiator;
- modern elegant design;
- thermoregulation;
- the ability to select equipment with the required number of sections and replace, if necessary, a damaged section.
However, light and beautiful aluminum radiators have their drawbacks:
- insignificant range of standard sizes in comparison with steel panel;
- susceptible to electrochemical corrosion: if the equipment is improperly installed, aluminum enters into a chemical reaction with steel pipes (this also applies to copper pipelines) and requires careful attention to the materials from which the heating system is made;
- the service life of aluminum radiators is also affected by the chemical composition of the coolant, the optimal PH level of which should be 7-8;
- to improve the heat transfer properties, manufacturers make the walls of aluminum radiators thin, so the section can burst from a medium-power impact.
Aluminum, like any metal, is susceptible to the corrosive effects of the coolant, in addition, in the copper-aluminum pair, due to the peculiarities of the chemical reactions occurring, increased gas formation is observed. To protect them from the negative effects of acids and alkalis, some companies use a special inner coating - Teflon, zirconium, etc. Gas can create excess pressure from the inside of the radiator and break its walls. To avoid this, copper fittings are not attached to such radiators - it is better to use brass here. In addition, in such systems it is customary to use air vent valves, manual - the so-called "Mayevsky crane" or automatic. The latter differ not only in the principle of operation, but also in price (they cost several times more).
Photo of tubular heating radiators




Heating radiator piping - connection diagrams and options for choosing a connection method (drawings + 90 photos)

Water heating convectors: pros, cons and types of convectors. Expert advice on the selection and use of water convectors (135 photos and videos)


Which heating radiators are better: an overview of the best models for an apartment and a private house (115 photos)
Did you like the article? Share


0
1
Bimetallic radiators
In the manufacture of bimetallic heating radiators, two metals are used: steel and aluminum, hence not only the name follows, but also the absence of the disadvantages inherent in steel and aluminum radiators. Bimetallic radiators are a system of steel pipes enclosed in an aluminum shell. The production of such devices was started in Europe about 60 years ago. But then, when the technology of reliable welding of aluminum and its alloys was mastered, the production of such radiators for European countries gradually ceased - they were ousted from the market by cheaper aluminum radiators. On the Russian market, bimetallic radiators remained represented, primarily due to their reliability (in comparison with their aluminum counterparts). The service life of a bimetallic radiator is 20-25 years, and the operating pressure that it can withstand is up to 25 atm, which is more than that of an aluminum one. But the price of bimetal is also higher. Bimetallic radiators are designed to solve the problem of corrosion, this is due to the fact that the pipes of the bimetallic radiator are made of steel and the coolant does not come into contact with aluminum. They have the high aesthetics of aluminum and the ability to withstand the water hammer inherent in steel. The wall thickness of the steel pipe in bimetallic radiators is about 3 mm. This is usually more than in tubular steel products. And the use of stainless steel in tubular radiators removes most of the listed problems, such devices are elite and are not cheap.
The main advantage of bimetallic radiators is the high degree of heat transfer provided by aluminum. Bimetallic radiators are often used in systems with increased pressure, because the working pressure of the radiator can withstand 25 atm.
Disadvantages of bimetallic radiators: high cost, small diameter of internal channels, as well as presence on the market of the so-called. "Semi-bimetallic" radiators, which sellers pass off as bimetallic radiators, but the difference between them is significant. Bimetallic radiators are made of a one-piece welded steel frame, which is filled with aluminum alloy, horizontal collectors and vertical channels in them are a steel welded structure. In "semi-metallic" devices, steel pipes only reinforce the vertical channels, which weakens the strength and corrosion resistance of the radiator.
Varieties
According to the location of pipes and collectors, only 2 types of heating batteries are produced:
1. collectors horizontally, tubes vertically ("accordion");
2. tubes horizontally, collectors vertically.
Also differ in shape:
- flat - all tubes are in an even row;
- corner - for installation on the corner of walls;
- radius (arcuate) - for rooms without corners;
- wavy.
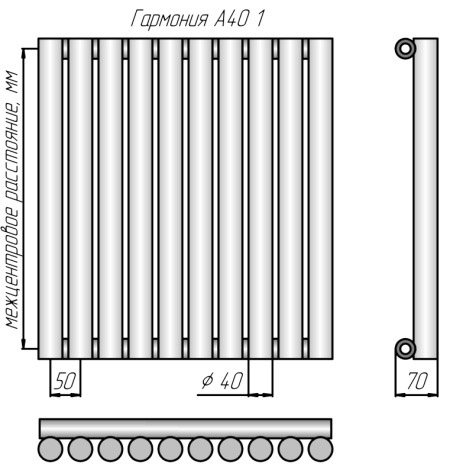
Height starts from 19 cm and can reach 3 m, length - from 18 cm to 3 m, depth - from 7 cm and more. Tubes in vertical heating radiators are produced with round, oval, square and triangular sections, while, judging by the reviews of experts, the shape does not affect their heat transfer in any way. Permissible pressure - 12 atm, pressure testing - 15 atm or 22.5 (Russia), wall thickness from 1.5 mm (Arbonia, Zehnder, Purmo) and up to 2 mm (from Russian manufacturers). The number of sections is from 6 to 30, while each of them provides heat transfer in the amount of 80-120 W, located at a distance of 45 or 65 mm from each other.
Many models (Purmo, Arbonia), including Russian-made radiators, have the inner side of the tubes trimmed with a special film to protect them from corrosion, which significantly increases their service life. Their diameter from the options from Russia is 25 mm, while for imported ones it can be different. 1 section can contain from 1 to 6 tubes.


Advantages and disadvantages
The room is heated by vertical tubular radiators due to heat radiation and convection. The latter exists due to the oval space between 2 tubes in each section. The greatest heat transfer, judging by the recommendations of experts and customer reviews, is obtained from heating batteries painted in dark shades.
The main advantages of a steel radiator:
1.thanks to the pipes, the heater is able to withstand pressure surges;
2. in the event of a heat supply cutoff, the possibility of air ingress is excluded;
3. little inertness - heats up quickly and cools down in the same way;
4. It has a smooth surface due to high-quality painting and laser welding, which makes it easy to clean dust and gives it an attractive appearance;
5. there is no risk of leakage between sections;

6. long service life;
7. a large number of different shapes and colors, suitable for rooms with almost any style of interior;
8. it is possible to add additional sections (on order before installation);
9.Easy installation (most often all fastening elements are included), there are options with side or bottom connection.
In addition to all this, due to the shape of the tubes and the absence of sharp corners, it can be installed in children's rooms or other institutions where increased safety is required (hospitals, kindergartens), moreover, it does not dry the air. Unlike cast iron batteries, steel radiators have a higher thermal conductivity with a smaller amount of coolant, therefore temperature regulators are often installed on them, since it will quickly change it.
Among the shortcomings, the following stand out - this is a weaker heating relative to other heating methods, such as a bimetallic radiator, it gives more heat, as a result of which they are used in rooms with a small area. Due to the fact that they are made of steel, there is a chance of corrosion, especially if the water contains an increased amount of various salts, therefore it is recommended to purchase options with a film and thicker tube walls. If the tubular battery is in a private house, then it is better to use antifreeze instead of water as a coolant, which will completely eliminate the possibility of metal damage.

Narrow radiators
Varieties
The definition of "narrow" appears to be rather streamlined and vague, so some clarity is needed.
Let's start with the fact that not only the horizontal, but also the vertical projection of the product can be called narrow, so we get two groups:
- Narrow horizontal devices, in which the height is much less than the width, that is, the horizontal projection of the case is considered;
- Vertical instruments, in which the width is much less than the height, and the object of consideration is the vertical projection of the body.
Important! Vertical and horizontal batteries are used in different ways and solve different technical and design problems.
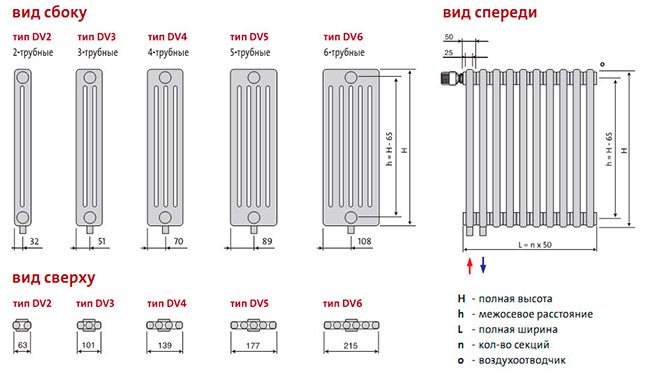
This group of convectors can be subdivided on the basis of a generally accepted classification, so we can safely distinguish the following varieties:
- Tubular registersmade of steel, copper or cast iron. The design is a system of vertical or horizontal pipes connected by manifolds, it is very popular in a narrow-profile design;
- Sectional cast iron batteries... This is a familiar model for residents of post-Soviet cities, which is also very popular in the production of non-standard products;
- Finned sectional convectors... These are modern aluminum or bimetallic devices with characteristic vertical plates;
- Steel panels... They are welded profiled steel plates that form internal channels due to profiling.The coolant circulates through the channels and heats the panel.
Important! Each type of construction has its pros and cons, therefore, when designing a heating system with your own hands, it is better to read individual articles on our website dedicated to the types of radiators.
Among other things, narrow convectors can be made of various materials. The material used also greatly affects the efficiency of the device, so this factor should be taken into account.
Today, batteries are produced from the following metals:
- Cast iron;
- Steel;
- Aluminum;
- Copper;
- Steel + aluminum;
- Copper + aluminum.
The highest heat transfer is observed in copper and aluminum products, however, the former are too expensive, and the latter are demanding on the coolant and pressure in the system. Steel devices are afraid of water hammer and corrosion, cast iron ones are too heavy and inert.
A bimetallic steel-aluminum radiator is considered a compromise solution.
Important! The classification and differences in the types of devices do not depend on their size and are made according to general rules.
Appointment
Let's talk about the purpose of narrow heating devices. Why are they needed?
The fact is that it is far from always possible to successfully fit standard products into the interior, especially in modern apartments and houses. As you know, it is customary to install radiators under windows, but modern trends tend to increase window openings, and the usual batteries simply do not fit on the window sill.
Often the window takes up the entire height of the wall. In this case, underground convectors are mounted, or a high and narrow radiator is placed next to the window, which solves the problem of heating this area of the house.
Often there are houses with non-standard design layouts that do not involve the usual placement of batteries. In this case, heaters can be installed in special niches, on walls or in corners.
Rooms in bathrooms and toilets, as well as kitchens and hallways, often have unusual shapes and sizes. Here it also turns out to be appropriate to use convectors with narrowed dimensions.
Finally, it often happens that the device itself of an unusual shape becomes an accessory and decorates a room, shapes its style and creates a certain atmosphere. In this case, its application is purely artistic.
Important! The use of narrowed radiators is due to the fact that standard devices do not fit or do not fit well into the interior, as well as due to the design delights of the architect. Typically, both reasons play a role.
disadvantages
- Low power. Therefore, they are recommended for small houses and buildings.
- Low heat dissipation.
- High cost. Since tubular heating batteries have recently come into use and various new technologies and materials are used in their creation, the price, respectively, is still high.
- In places of pipe welding, a leak forms over time. Therefore, it is not recommended for use in apartment buildings. With proper care and installation, leaks can be prevented in time.
- Poorly withstand pressure drops inside the heating system.


Vertical radiators are characterized by high cost
Based on the above, steel tubular heating batteries are advised to be installed only in the private residential sector, in small houses and buildings, here they will perfectly cope with heating the room and will serve for a long time and reliably for many years, as the reviews say. The main thing is to correctly install, install high-quality radiators and follow all instructions for their maintenance.
Steel heating radiators
Design
Flat radiators are made of steel, equipped with special fins inside that keep high temperature power. The joints and joints with pipes are practically invisible due to the use of special fittings.
Flat batteries are not standard, available in various shapes, heights and depths.The release of heat occurs through radiation.
Forms of battery and radiator designs:
- single-row or multi-row,
- flat compact,
- the front side is smooth,
- the surface is profiled on all sides or only on one side,
- with or without rib element,
- with valve - thermostat.
Flat radiators for heating are represented by two plates, fastened by welding. They are made by stamping. The heat carrier is placed between them; there is a special channel for it inside. Radiators are connected to the heating system with special pipes.
If you use a special connection, then flat heating radiators can be formed from several plates. The presence of convector fins on each of them increases the heat transfer. The power parameters of a flat radiator equipped with a ribbed surface inside will be half that. There will be much more dust on these devices, therefore they are installed in buildings with high sanitary standards. As you can see, the flat battery design is not complicated.