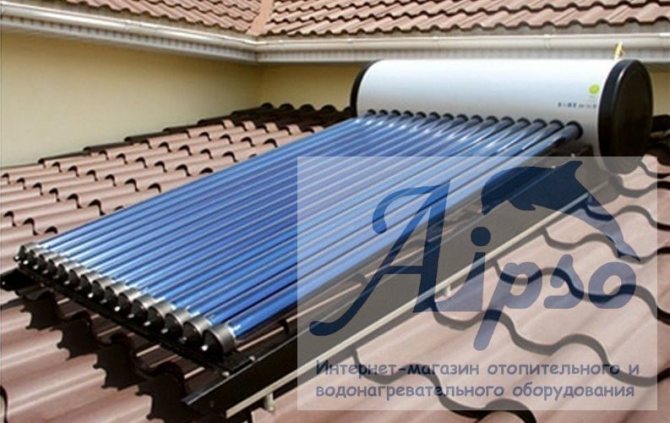
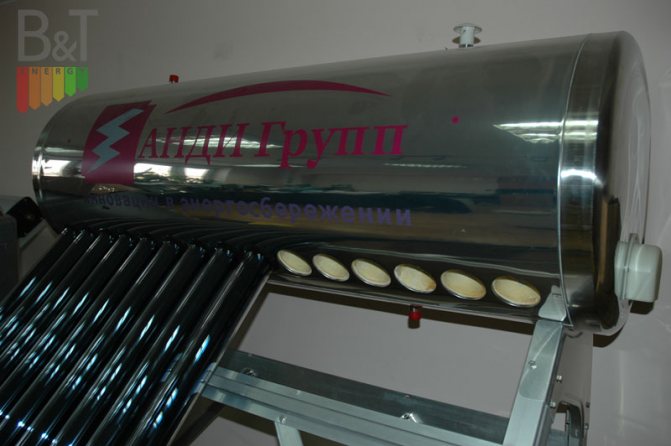
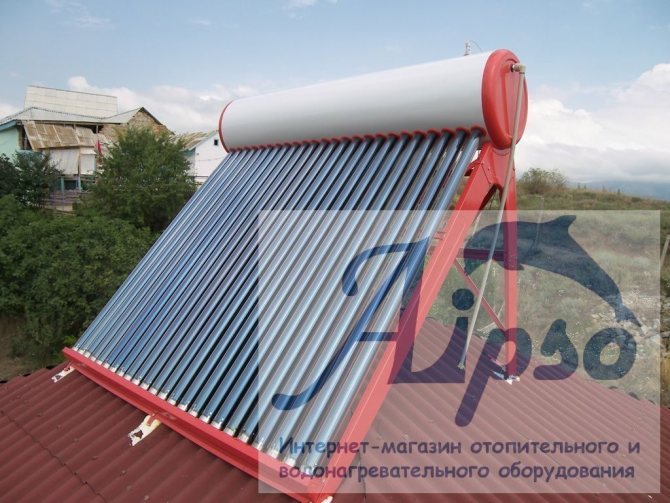
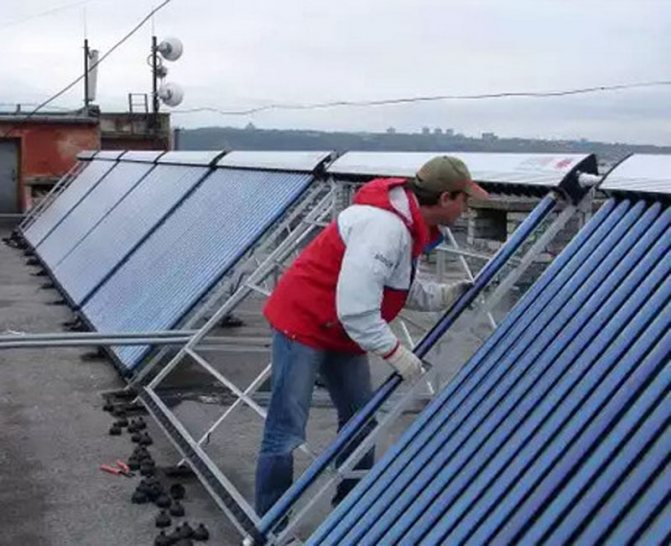
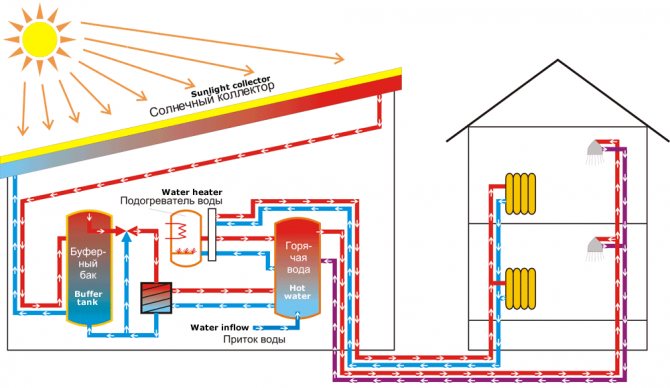
Devices that collect solar thermal energy are called solar collectors. Solar collectors are capable of heating the heat-carrying material. This is how they differ from solar panels, which are capable of producing only electrical energy. Due to this advantage, vacuum collectors are widely used for space heating and hot water supply systems. There are two types of solar collectors: flat and vacuum. The purpose of this article is to talk about vacuum solar collectors.
Types of vacuum tubes
There are five types of vacuum tubes for solar collectors. They differ in internal structure and design. In addition, each of them can be supplemented with a metal (usually aluminum) absorber, which is placed inside a glass bulb in the form of a tube.
Important! Most manufacturers fill the bottom gap between the glass walls with barium - it absorbs gas impurities and improves thermal insulation properties. Its absence can reduce the efficiency of the collector by up to 15%.
Thermosiphon (open) vacuum tubes
This type of solar collector tube is used in collectors with an external storage tank. they are filled with water and form one volume with the reservoir. The heated water from the flask rises into the tank, and the cooled water goes down.
Thermosiphon vacuum collectors are used in the following cases:
- For connection to a hot water supply system;
- In regions with a high level of insolation during the cold season;
- For seasonal use (spring, summer, autumn).
Coaxial pipe (Heat Pipe)
This is the most common type of vacuum tube. It contains a copper tube inside a glass bulb filled with a liquid with a low boiling point or low pressure water.
When heated, the liquid or water begins to boil, the steam rises, simultaneously heating up from the copper walls. At the top, it enters the heat exchanger - an expansion at the end, in which it gives off heat through the walls to the water that circulates around it.
After cooling, the steam condenses on the walls of the heat exchanger and flows down. The cycle is repeated anew.
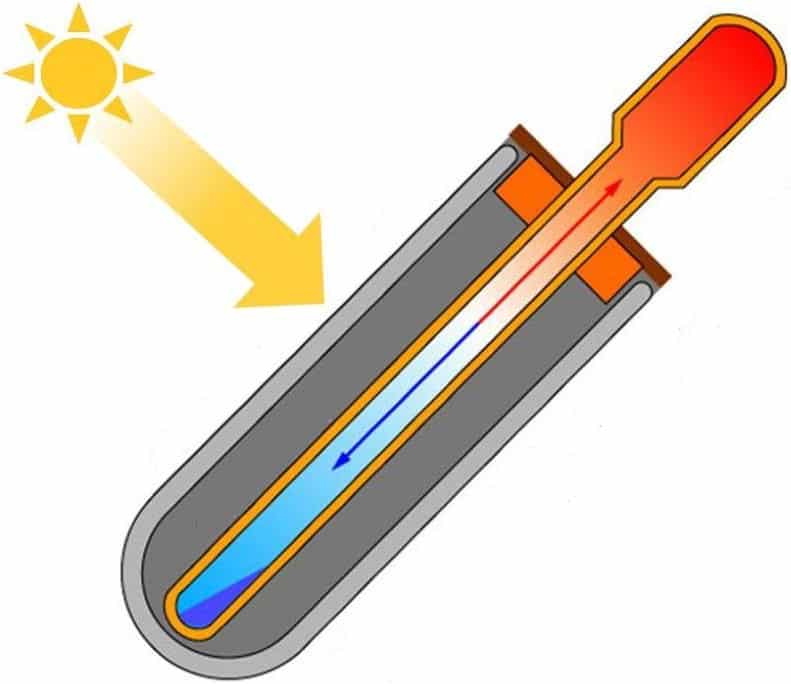
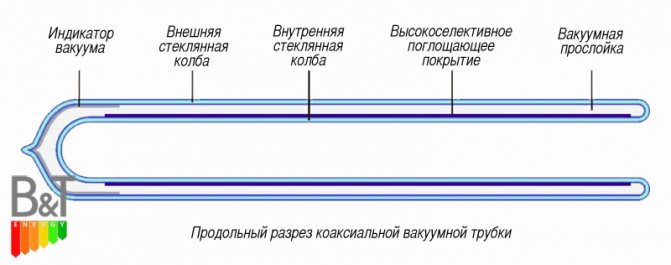
Schematic internal structure of a coaxial tube and heat exchanger.
Twin coaxial tubes
The principle of operation of such a heat sink is the same as that of the previous one, with one exception - two copper pipes with liquid are connected to one heat exchanger. The tandem system allows for more efficient heat extraction, and the large capacity and wall area of the heat exchanger allows you to quickly heat the water.
A twin coaxial vacuum manifold is installed where necessary:
- Provide small heating of large volumes of water;
- There is a need for thermal energy during a sunny day;
- High average level of insolation;
- There is a rapid pumping of water through the system.
Feather vacuum tubes
They have an additional heat exchanger in their design, which allows more efficient heat removal from the inside of the glass bulb. It is usually made in the form of two longitudinal plates located on the sides of the copper heat sink.
Otherwise, the principle of operation is exactly the same as that of a coaxial tube.
U-shaped vacuum tubes (U-type)
This system is fundamentally different from the previous ones. It uses two lines - for cold and heated water.
A heat exchanger in the form of an English letter U is installed in a glass flask, through which water flows.From the line with cold water, it enters it, heats up and returns to the pipe with heated water.
The U-type vacuum tube manifold is the most efficient, but installation is difficult. During assembly, the flow lines are welded to the copper tubes inside the glass bulb. The result is a single integral system with high energy efficiency, but low maintainability.
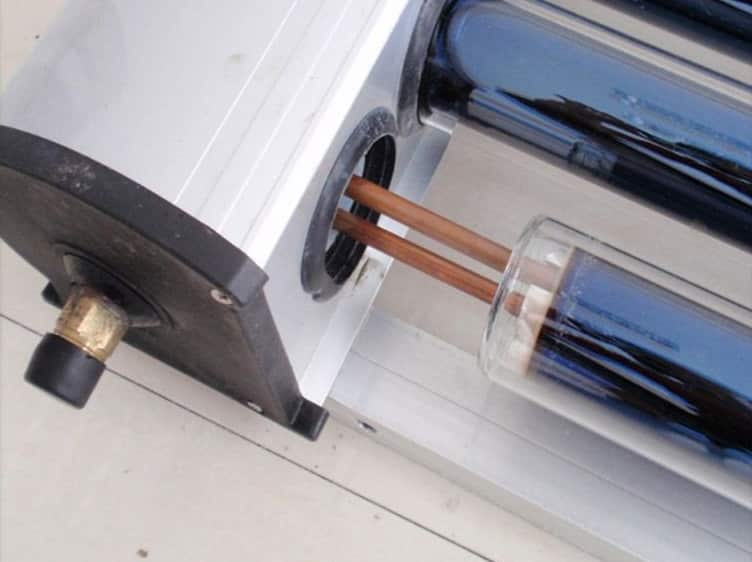


Installing the flask on a U-shaped copper tube.
Plug
If it is not possible to buy ready-made plugs, you will have to make it yourself. Any polymer with a melting point above 150 degrees is suitable for this. For example, polyurethane.
You need to cut a circle of such a diameter that it enters the flask with effort. In the center of it, cut a hole for the copper tube. It should also enter with little effort. The thickness of the plug should be 5-10 mm, this will be sufficient.
The top of the plug should be larger in diameter. Such that it completely blocks the inlet of the block in which the coolant circulates.
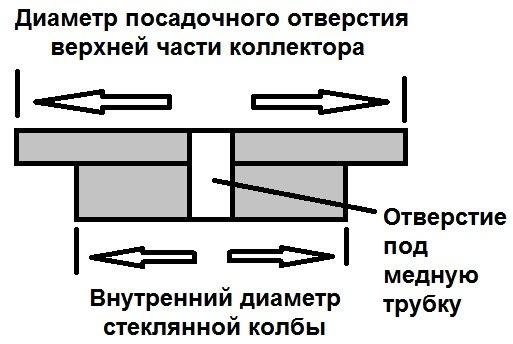

Vacuum manifold tube plug, side view.
Pros and cons of vacuum collectors
The main advantage of the units is called the almost complete absence of heat loss during operation. This is ensured by a vacuum environment, which is one of the highest quality natural insulators. But the list of benefits doesn't end there. The devices have other pronounced advantages, for example:
- efficiency of work at low temperature indicators (up to -30 ° С);
- ability to accumulate temperature up to 300 ° С;
- maximum possible absorption of thermal energy, including the invisible spectrum;
- operational stability;
- low susceptibility to aggressive atmospheric manifestations;
- low windage, due to the design features of tubular systems capable of passing air masses of different densities through themselves;
- high level of efficiency in regions with temperate and cool climates with few clear and sunny days;
- durability subject to the basic rules of operation;
- availability for repair and the ability to change not the entire system, but only one failed fragment.


The disadvantages include the inability of the collectors to self-cleaning from frost, ice, snow and the high price of component parts needed to assemble the unit at home.
How to place the appliance correctly
In order for the vacuum collector to work fully and effectively provide the living space with the necessary energy, it is necessary to find the most favorable place for it and correctly orient the device relative to the parts of the world.


For settlements in the northern hemisphere, it is important to place the collector in the southern part of the roof of the house or on the sunny side of the site. It is desirable to provide a minimum deviation for the plane of the device.
If there is no way to direct the surface to the south, it is worth choosing among the west and east the brightest perspective in an open space.


The solar energy complex should not be obstructed by chimneys, decorative fragments of roofing, spreading tree branches and tall residential or technical buildings. This will reduce the efficiency of the work and reduce the level of heating of the active elements.
If the unit is positioned correctly, it will provide almost the same heat output throughout the year, regardless of the season.
If you do not have a lot of experience in performing complex repair, installation and plumbing work, it is irrational to vacuum the tubes at home. This process is very laborious and requires special knowledge and specialized equipment.
In addition, self-made vacuum-type elements have a much lower level of efficiency than factory-made parts. Therefore, it is most reasonable to purchase products from a specialized manufacturer, and then try to assemble several sections at home.
Varieties of solar panels
The solar systems are classified according to the design features of the tubes and the type of heat channel used as a receiver:
1. The coaxial model of a vacuum solar collector for heating a house is a double flask made of glass, in the cavity of which air is evacuated. The surface is coated with an absorbent coating, so the energy is transferred from the tube itself.
2. The feather structure is single-walled, the void is located here in the space of the heat channel, part of which, together with the storage, is integrated into the flask.

4. In systems with forced circulation, a low-power pump is installed to facilitate the movement of the carrier. At the same time, the power consumption is much less than the energy received for heating a private house.
5. There is also a difference in the number of circuits. In the simplest collectors, heating water is heated and consumed from the storage tank.
6. More complex ones consist of a vacuum tube and fluid sampling elements. The device contains an anti-freeze and non-toxic media with anti-corrosion and antifoam additives. This method reliably protects the equipment from salts and scale and contributes to a longer operation during heating.


Overview of models and their characteristics
At the moment, China is the leader in the production of solar collectors. According to the reviews of the owners of private houses, domestic manufacturers also supply equipment with good characteristics for sale. European devices are quite expensive, but over time, the costs of purchasing and installing devices are fully justified. The most famous companies produce the following collectors:
Plumbers: You will pay up to 50% LESS for water with this faucet attachment
Collectors Dacha and Universal are the most famous devices of a domestic manufacturer. The SCH-18 is highly efficient with condensate temperatures up to 250 ° C. The flasks are made of red copper, the heat carrier is liquid. The absence of water in a vacuum ensures resistance to freezing. Robust case with good wind resistance. The pipeline is protected by a polyurethane manifold. Rubber anti-dust seals keep dust and precipitation out.
They work effectively at temperatures down to -35 ° C, the type of functionality is a pressure system for heating. There is a controller for controlling the heater, the size of the tubes is 1800 mm, the volume of the tank is 135-300 liters, the power of the heating element is 1.5-2 kW. The manifolds are manufactured in accordance with international certifications, which ensures their safety and reliability.
How is the collector of a vacuum type
Modern vacuum devices that provide rooms with heat and hot water due to solar energy are technologically somewhat different and are subdivided into such types as:
- tubular without glass protective coating;
- module with reduced conversion;
- standard flat version;
- device with transparent thermal insulation;
- air unit;
- flat vacuum manifold.


They all have a common constructive similarity, so they consist of:
- an outer transparent pipe, from where air is completely pumped out;
- a heated pipe located in a large pipe where a liquid or gaseous heat carrier moves;
- one or two prefabricated distributors, to which pipes of a larger caliber are connected and the circulation circuit of thin pipes placed inside enters.
The whole structure is somewhat reminiscent of a thermos with transparent walls, in which an unprecedented high level of thermal insulation is maintained. Thanks to this feature, the body of the inner tube acquires the ability to warm up qualitatively and fully give the energy resource to the coolant circulating inside.
What is a collector and the purpose of solar collectors
A solar collector is understood as a device that collects radiation energy and then transfers the accumulated heat to consumers. In practice, another term is used - a solar collector.
According to the purpose, solar installations (solar installations) use are subdivided:
- solar concentrators are devices that collect solar energy into a narrow stream. They are used to melt metal. At the Institute NPO "Physics-Sun" (Tashkent), melting furnaces were developed and manufactured, in which temperatures of more than 5000 ... 5500 ° C were achieved;
- solar panels - devices for converting radiation from the Sun into electrical energy;
- solar desalination plants - machines designed to obtain fresh water from water with a high content of mineral salts;
- solar drying installations - thermal devices in which moisture is removed from vegetables and fruits using the energy of the sun;
- solar heaters (solar air collector) are installations for transferring heat flux from infrared radiation to heat carriers.
Varieties of vacuum collectors
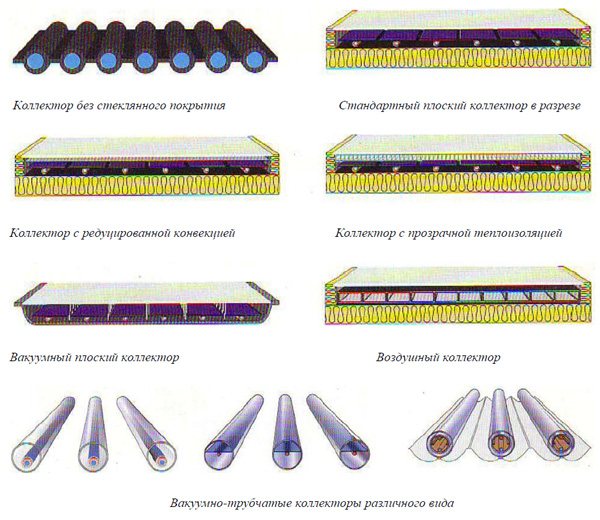

Varieties of vacuum collectors
There are two types of glass tubes used in the design of the collectors:
- coaxial;
- feather.
Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Coaxial tube
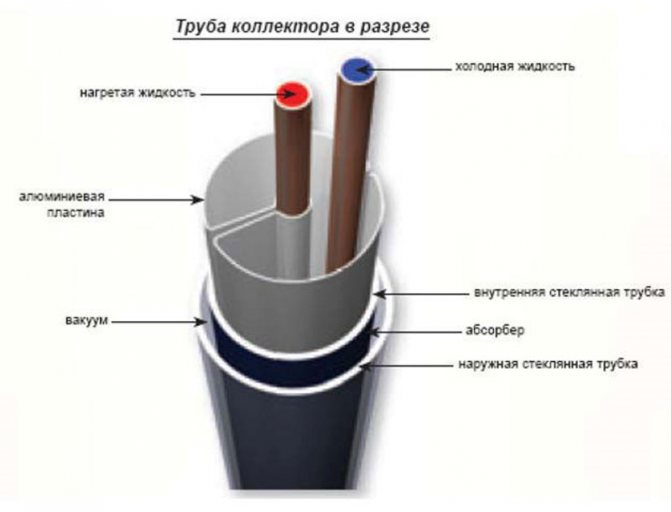
It is a kind of thermos that consists of a double flask. The outer bulb is coated with a special heat-absorbing substance. A vacuum is created between the two tubes. This made it possible to ensure that the heat during operation is transferred directly from the glass bulbs.
Inside each tube there is one more - copper (it is filled with an ethereal liquid). When the temperature rises, this liquid evaporates, transfers the stored heat and flows back as condensation. Then the cycle repeats over and over.
Feather tube
This type of tube consists of a single wall bulb. By the way, they significantly exceed their coaxial counterparts in wall thickness. The copper tube is reinforced with a special corrugated plate treated with a moisture-absorbing substance. It turns out that air in this case is pumped out from the entire heat channel.
Such channels, by the way, are also different:
- direct-flow;
- Hit Pipe.
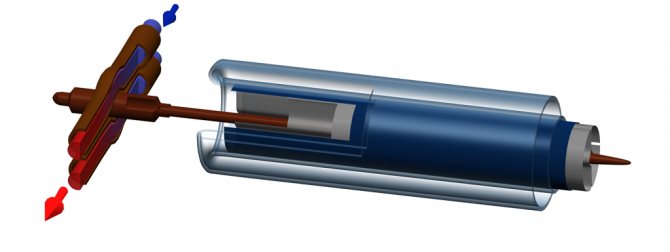
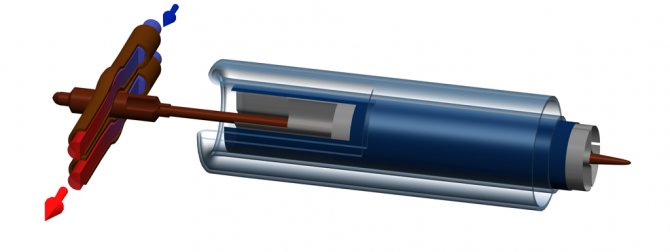
"Hit Pipe" type channels
Heat transfer in a vacuum solar collector type "Heat Pipe"
Their other name is heat pipes. They work as follows: when the temperature rises, the ethereal liquid in closed pipes rises up the channel, after which it condenses there in a specially equipped heat collector. In the latter, the liquid transfers heat energy and descends down the tube. From the heat collector, heat is transferred further into the system using a circulating heat carrier.
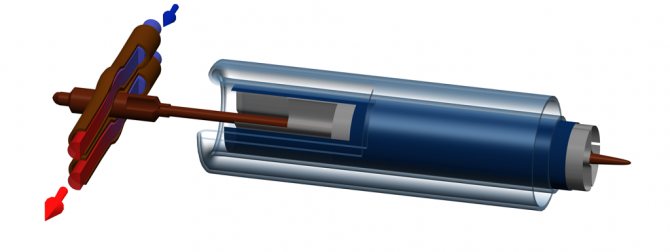

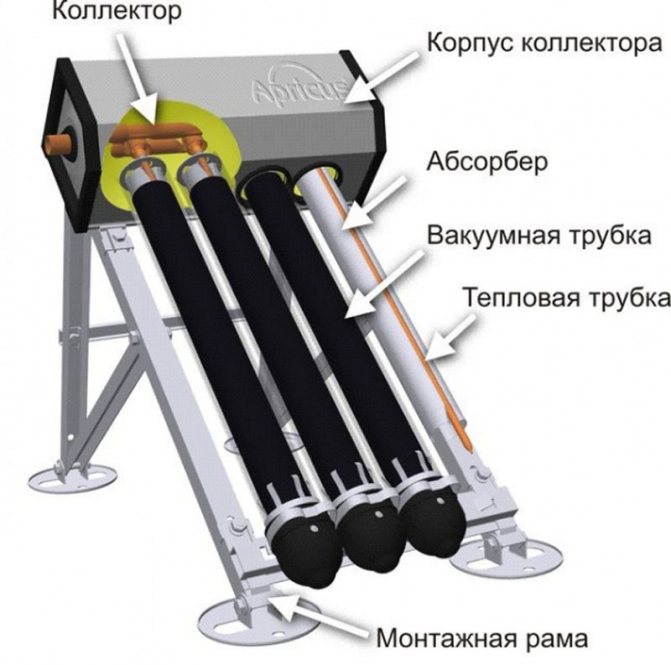
Coaxial vacuum pipe heat-pipe with 2-pipe manifold
It is characteristic that metal tubes here can be not only copper, but also aluminum.
Direct-flow channels
In each of these channels in the glass tube there are two metal pipes at once. On one of them, the liquid enters the flask, heats up there and exits through the second.
Making a vacuum manifold with your own hands
Important! It is extremely difficult to make a solar collector with your own hands of a vacuum type. The costs can be very high.
You can make a vacuum solar collector with your own hands. You will need to purchase glass tubes for the dairy industry or milking machines.They are realized together with special rubber sleeves, with the help of which they can be mounted in various wiring diagrams.
Inside the glass pipes, you will need to place black painted steel or copper pipes. Welding or soldering will have to be additionally protected with heat-insulating tapes, for example, cut from polyethylene foam.
When making a solar collector of a vacuum type, it will be necessary to pump out air from glass pipes. The air is evacuated using a vacuum pump. Here you need to use a special fitting, which will close tightly immediately after disconnecting the suction pipe from the vacuum pump. Modern plate devices make it possible to obtain a vacuum of up to 25 ... 30% of the initial atmospheric value.
Before starting work, you should evaluate your strengths. Such devices are quite expensive to manufacture. Not only expensive tools and devices are needed here. You also need the skill of performing work with vacuum installations.
You can assemble the installation from ready-made elements:


- A frame is made for installation.
- Orient it relative to the cardinal points.
- Purchase coaxial tubes complete with heat exchangers.
- Installation of supply and discharge pipelines is carried out.
- Vacuum tubes are installed and connected to the main pipelines.
- Perform work on thermal insulation of all points of connection of flasks and pipelines.
Advantages and disadvantages
Solar vacuum collectors have less heat loss compared to flat ones. The use of vacuum nanotechnology in the production of collectors has made it possible to achieve high efficiency and reliability of solar systems.
Let's consider the main advantages of using vacuum collectors:
- Performance. There is a vacuum in the collector pipes - an ideal heat insulator, which allows you to maintain an optimal level of heat even in the autumn-winter period. By keeping the efficiency at a high level, the productivity of the vacuum collector is 40% higher than that of the flat collector.
- Reliability. The service life of vacuum collectors is about 30 years. Their durability and trouble-free operation are due to modern durable materials. The vacuum tubes contain high quality copper. The outer casing of the tubes is cast from borosilicate glass, which is able to withstand high loads. The use of vacuum collectors is especially important for climatic zones where squalls, hurricanes, hail are not uncommon.
- Solar energy efficiency. The cylindrical shape of the vacuum collector absorber captures and retains even the scattered solar energy, which the flat corrector cannot convert. 40% more solar energy can be retained from one square meter of the absorber of a vacuum solar system than from a similar area of a flat-type solar installation. The roundness of the tubes allows you to receive up to 97% of solar energy from early morning until late evening.
- Ease of use. In case of damage to the vacuum tube, it is replaced without stopping the operation of the system (no need to drain the circulating fluid). If there is a lack of heat, you can add several pipes, and if there is an excess of it, you can temporarily remove it. After cleaning the vacuum manifold from snow or ice, it quickly becomes operational. The collector surface has low thermal inertia due to the thin glass coating.
- Disinfection of water. The temperature of water heating during the operation of the solar system reaches high levels, which ensures its disinfection and prevents the multiplication of pathogenic organisms.
- Ease of installation. When installing vacuum collectors, there are no special difficulties, the main thing that must be adhered to is to position the collector at an angle to allow the liquid inside the tubes to drain down.
The disadvantages of solar heating are reduced to extremely low efficiency at low temperatures and at night, thus the question arises that this heating system cannot be the only one in the house. Also, vacuum solar collectors are more expensive than flat ones.
Vacuum solar installations are becoming increasingly popular among the population and large companies. If before many were frightened off by the price of the issue, today the cost of equipment has slightly decreased, and the functionality has improved and modified.
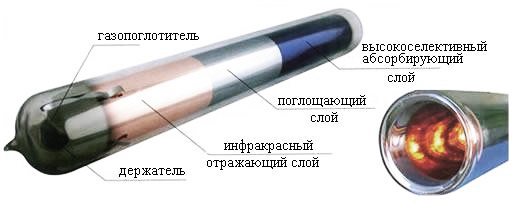
The principle of operation of the SKE vacuum tube.
The key to the solar system is the glass vacuum tube. Each vacuum tube consists of two glass bulbs.
The outer flask is made of extremely tough borosilicate glass that can withstand the impact of hailstones falling at a speed of 18 m / s and is up to 35 mm in diameter.
The inner bulb is also made of borosilicate glass and covered with a special three-layer coating with a gradual change of the ALN / AIN-SS / CU absorbing layers. Due to the use of new technologies, a high absorption coefficient and a low beating ability are achieved, which allows reaching + 380 ° С in the middle of the tube in direct sunlight, without harming the product itself.


Air is pumped out between the two glass bulbs to create a vacuum that prevents reverse heat conduction and convective heat loss. In the middle of the glass bulb there is a sealed heat pipe (HEAT PIPE), made of pure red copper, in the middle of which there is a low-boiling and evaporating liquid, which performs the function of transferring heat to the coolant. The figure below shows the working principle of the vacuum tube.
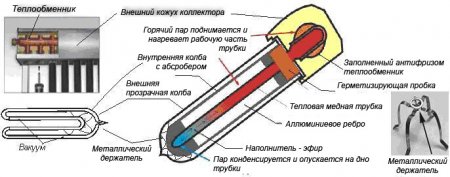

The main intensity of solar radiation in terrestrial conditions is in the spectral range 0.28 µm - 3 µm. Borosilicate glass transmits solar radiation waves in the range of 0.4 microns - 2.7 microns. Penetrating through the outer transparent flask, energy is retained on the second flask, on which a highly selective opaque absorber layer is applied.
As a result of the absorption of light by the absorber and its subsequent emission, the wavelength increases to 11 μm. Glass is an impenetrable barrier to electromagnetic waves of this length. Solar energy entering the absorber is trapped. Absorbing solar radiation, the absorber, even without an external bulb, can heat up to a temperature of + 80 ° C. The absorber heated to such a temperature emits heat energy, which, penetrating through the body of the second bulb, is transferred to the HEAT PIPE. Due to the appearance of the greenhouse effect, which is based on the accumulated energy under the glass, in the middle of the second flask the temperature rises to + 180 ° C. This heat heats up a low-boiling and evaporating liquid, which at + 25 ° C - + 30 ° C, turning into steam, rising, transfers heat to the working part of the HEAT PIPE, where heat exchange with the coolant takes place. The release of heat forces the steam to condense and flow to the bottom of the HEAT PIPE, and the cycle repeats again.
The high heat transfer coefficient of an easily boiling and evaporating liquid, its insignificant amount and the relatively small dimensions of HEAT PIPE provide effective thermal conductivity. HEAT PIPE works like a thermal diode. Thermal conductivity is very high in one direction (up) and low in the opposite direction (down).
In order to maintain a vacuum between the two glass flasks, a layer of barium is applied to the lower interior of the flask. It actively absorbs CO, CO, N, O, HO and H during tube storage and operation. The barium layer also provides a clear visual indication of the vacuum status. White color means that vacuum conditions are violated.
The ideal combination of vacuum and heat copper pipes gives us the following advantages over flat collectors:
High thermal efficiency.thanks to modern methods of heat transfer, high quality absorbing coating.
A wide range of work: due to its low thermal capacity, it is able to work in high clouds (in the infrared range of rays that pass through the clouds).
Each tube works independently of one another. Since the antifreeze does not flow into the middle of the tube, and its access is limited by the heat exchanger, in the event of physical damage, the collector continues to work.
Less collector weight with better collector efficiency.
Better work efficiency in winter thanks to the vacuum. The tube can withstand frosts at -50 ° C.
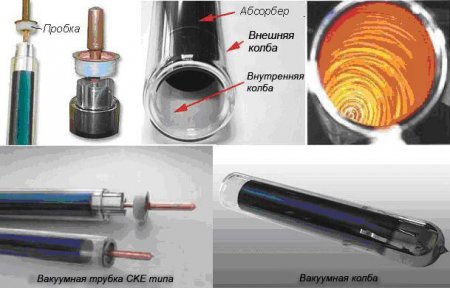

How vacuum tubes work
The function of the evacuated solar collector tubes is to absorb solar radiation and prevent it from escaping into the environment. Thermal energy can leave the working part of the vacuum solar collector in two ways - due to direct heat transfer and in the form of infrared radiation.
The cavity between the glass walls practically completely excludes the possible direct transfer of heat in a vacuum, there are no molecules of substances that could carry it out.
The selective coating (absorbent) absorbs solar energy and prevents it from escaping. There are different types of such coatings, differing in absorption and emissivity.
Some part of the solar radiation is reflected by glass, but it is insignificant - visible light makes up only a part of the absorbed spectrum. High-quality collectors are made of high strength borosilicate glass, which is resistant to mechanical damage.
Borosilicate glass is difficult to scratch or mat and will last for decades without changing the throughput.
How to choose / finance
As mentioned at the beginning of the article, the more tubes there are in the vacuum manifold and the thicker they are, the better. The collector should be chosen according to the size of the heated area.
Models with 10 pipes and a collector diameter of 850 mm are capable of fully heating 2-3 rooms. The average price of such a model is from 12,000 rubles.
For medium-sized private houses, it is worth choosing a model with 20-25 pipes and a collector width of up to 2000 mm. Average price - from 20,000 rubles.


For large houses, a 30-pipe model with a diameter of 2,500 mm can be purchased. The price of such devices starts from 22,000 rubles.
It should be borne in mind that additional components also have a wide range of prices and may significantly differ in price. For example, the price of the most expensive storage tank with two heat exchangers reaches 125,000 rubles.
On average, vacuum solar collectors pay for themselves within 2-5 years.
Flat collectors
A flat solar collector heats the heat carrier using a plate absorber. It is arranged quite simply. In fact, this is a plate of heat-absorbing metal, painted black on top with a special paint. A serpentine tube is tightly attached (welded) to the lower surface of the plate, through which the liquid circulates.
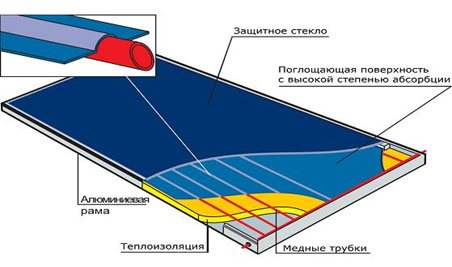

Selective black ink ensures maximum absorption of sunlight with virtually zero reflection. The absorbed rays heat the coolant under the absorber, which, in turn, is fed further into the system. To minimize heat loss, the absorber is insulated from the collector body and tempered glass, which is almost free of iron oxides. It is installed above the absorber and acts as the top cover of the housing. In addition, the use of such glass allows you to create a kind of "greenhouse effect", which further increases the heating of the absorber, and hence the temperature of the coolant.
How a solar collector works
In addition to visible light, solar radiation also has an invisible infrared spectrum. It is he who transfers thermal energy.On the basis of research, it was found that in a temperate climate zone, the intensity of thermal radiation at noon reaches more than 5 kW / m2. In fig. 1 shows the dependence of the total insolation for 48 ° north latitude.
Fig. 1 Total insolation of solar radiation for different periods of the temperate zone of Europe
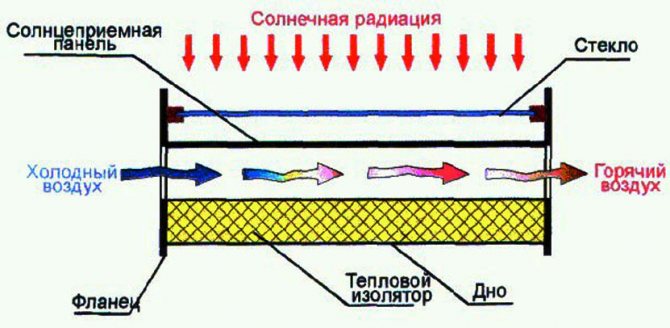

Food for thought! Thermal radiation is divided into: direct and diffuse. Therefore, even on a cloudy day, the influx of solar heat flow is felt. It can be seen from the presented illustration that the amount of incoming heat in the summer and winter periods has significant differences. Therefore, when designing devices, possible efficiency is taken into account in relation to costs.
The schematic diagram of the solar collector is shown in Fig. 2. Solar radiation enters the collector through a translucent fence. Heat is absorbed on the receiving panel, which is painted black. As a result, the black body heats up. The subsequent heat transfer process takes place by convection. Heat is transferred from the heated wall to the flow of liquid (gas) moving through the pipelines. The moving medium heats up.
Attention! To prevent heat loss, the collector fence is thermally insulated. Since the heat received inside is used to heat the flow, the intensity of the reflected radiation from the panel that receives the radiation is low.