Home / Electric boilers
Back to
Published: 31.05.2019
Reading time: 4 minutes
0
917
The compact electrode electric boiler provides warmth in the room and makes it possible to remotely regulate the temperature. Its small size allows it to be installed in an existing heating system.
- 1 How the electrode boiler works
- 2 How it works
- 3 Is it possible to save with an electrode boiler
- 4 Review of the best models of electric electrode boilers
The principle of operation of electrode boilers
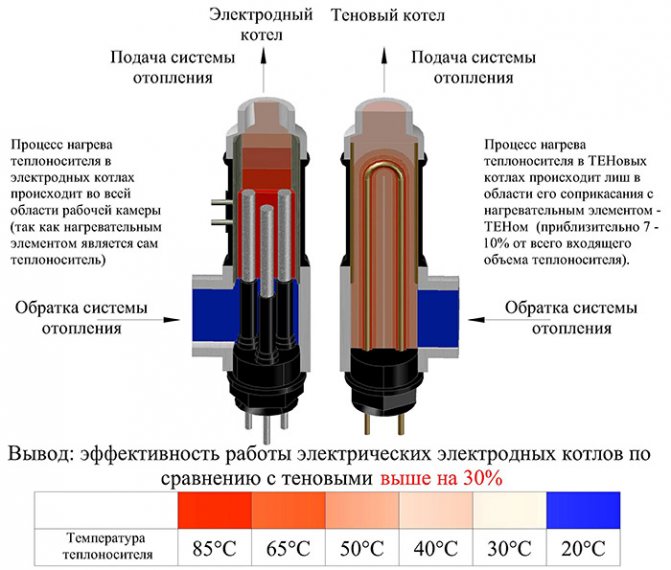
When describing the advantages of electrode boilers, the main emphasis is on the absence of intermediaries in the transfer of energy from the electrical network to the coolant. The main argument on which the marketing strategy for the promotion of electrode water heaters is bet is the direct heating of the liquid under the influence of an electric current, which occurs due to its high resistivity.
When using this type of equipment, the influence on the heat transfer of the scale crust formed on the surface of traditional tubular heating elements is eliminated. The low inertia of the system is also considered an obvious advantage: the coolant begins to heat up immediately after the voltage is applied to the electrodes, while when using resistive heaters, it takes some time to heat the coil itself and its dielectric insulation.
The device of the electrode boiler: 1 - terminals for connecting to the network; 2 - sealant and insulation of electrodes; 3 - supply of cooled heat carrier; 4 - block of electrodes; 5 - coolant; 6 - boiler drum; 7 - insulating layer; 8 - outlet of the heated coolant
However, not everything is so rosy. First of all, it is doubtful that the entire coolant is under the influence of a dangerously high potential difference. In particular, with a zero break, all metal parts of the heating system become fatal to humans, and breakdowns are also possible if the neutral is not properly grounded.
It is worth mentioning the fact that not all fluids have a resistivity high enough to convert all applied power to generate electricity. A certain part of the current load does not meet resistance and therefore flows freely into the ground. Against this background, statements that electrode boilers have an efficiency higher than 100% evoke a condescending smile from people who are well acquainted with the technical part of the issue.
Coolant requirements
In addition to natural losses when heating a liquid, electrode boilers have another nasty property. In the process of passing an electric current through water, the phenomenon of electrolysis is observed - the separation of the H2O molecule into gaseous components. This, among other things, further reduces the energy efficiency of the boiler, because in this case, electricity is consumed not for heating, but for electrolysis. However, the most obvious consequence of this effect is the formation of gas locks in pipes and radiators.
For these reasons, the heating medium for heating systems on electrode boilers must be selected with the greatest care. In order to reduce the conductivity of the coolant (increase the resistivity), the content of dissolved ions in the liquid used should be normalized. Distilled water is mainly used, to which electrolyte is mixed in the proportion recommended by the manufacturer, again, factory production.
The situation is more complicated if an antifreeze liquid must be used as a heat carrier.In this case, the system must be filled with a special antifreeze that cannot be diluted with water. With a significant displacement, refueling the system can cost a pretty penny, but this does not take into account the issue of the durability of the coolant. In the presence of metal parts in the system, the concentration of ions in the liquid increases over time, while effective methods for regenerating the coolant for electrode boilers have not yet been invented. But periodically at least part of the coolant will have to be drained, because each boiler requires cleaning the electrodes from plaque, and the system itself needs to be flushed.
Heat carrier
Electrode boilers are sensitive to the composition of the coolant. In accordance with the requirements of manufacturers, only distilled water should be used, to which table salt is added, approximately 80-100 grams for every 100 liters. The difficulty lies in the fact that the final density and conductivity of the solution must be in strict accordance with the manufacturer's requirements. It is impossible to verify the exact amount of salt, and it can give different results depending on its composition.
The final preparation of the solution is carried out on site, guided by the actual values of the current in the electronic boiler. The instructions for the device provide a table of required values depending on the boiler power, the volume of the coolant, etc. By adding distilled water or salt, the resistance of the heat carrier is brought to the ideal.
Only the compositions provided by the boiler manufacturer are used as antifreeze. When using them, the proportion of salt in the solution also changes.
There is a mandatory requirement before using an electronic boiler in an existing heating system in parallel with another boiler. The entire system is flushed, cleaned of scale and salt deposits, which can subsequently change the conductivity of the coolant.
Consequences of electrolysis and direct current action
The splitting of water into oxygen and hydrogen leads to the formation of air locks, which impede the normal circulation of the liquid. However, this is far from the main negative effect. In particular, during real operating experience, manifestations of electrochemical corrosion of aluminum radiators were found.
In the presence of cast-iron batteries in the heating system, the initial qualities of the coolant decrease, mainly due to the washing out of impurities from the open pores of the cast sections. Because of this, those wishing to use electrode boilers in such conditions have no choice but to replace the radiators or thoroughly flush the entire system.
The very fact that the coolant in the system is energized obliges every metal element of the system to be carefully grounded. If a clamp with a sufficiently low resistance can still be applied to a steel pipe, then high-quality grounding of a cast-iron radiator connected by a system of plastic pipes seems to be a very difficult task. So far, we can conclude that any heating system in which an electrode boiler is used requires a strictly individual approach.
Advantages and disadvantages
Despite the fact that such boilers have appeared relatively recently, there is enough information on their use. In addition to the simplicity of the design, ion boilers have other advantages:
- The efficiency reaches a record 99%, other systems have a lower coefficient due to the characteristics of their device;
- More economical than other heating devices by 15–20% with the same power output;
- Does not depend on voltage drops, it will warm up even with a strong drop, but with less efficiency;
- They are not afraid of liquid leakage; when switched on "dry", overheating will not occur due to the impossibility of the heating process without electrolyte;
- Silent operation;
- Compact dimensions of the device.
Unfortunately, ion boilers also have disadvantages:
- The heating system is prone to the accumulation of static electricity and electric shock, therefore, a high-quality grounding is required;
- The coolant must have certain resistance values, plain tap water is not suitable;
- The need to install an electronic control unit and temperature sensors to control a constant temperature;
- Electricity consumption and the cost of 1 kcal is higher than that of solid fuel or gas boilers;
- You will need to use special heating radiators.
Outstanding efficiency myths
When studying the advertising materials of electrode boilers, one gets the impression that consumers are considered deaf ignoramuses. Allegedly "ionic" boilers extract heat literally from nowhere, giving out thermal energy in the amount of 120-150% of the applied electrical power. At the same time, the laws of physics and, in particular, heat engineering are ignored in every possible way.
Statements that the electrode boiler is capable of mythically multiplying the energy put into it are absolutely groundless. Fortunately, today this trend in advertising campaigns has begun to decline, but its initial development can be attributed to the active spread of thermal equipment operating at the expense of heat pumps with a positive COP coefficient.
Even claims that 100% of electricity is converted into heat is an outright deception. Losses during formation still cannot be avoided, even when the coolant is heated due to its own electrical resistance, because at least 2-3% will be spent on heating the supply wiring, the same amount will drain into the grounding system due to a decrease in the energy of charge carriers due to insufficient chemical purity liquid in the system or due to the formation of plaque on the electrodes. Conclusion: electrode boilers are capable of demonstrating a conversion coefficient close to 100% only under conditions of a demonstration stand, which, as you know, are far from real.
Advantages of electrode heating equipment
Heating boilers "Galan" have undoubted advantages in comparison with other types of boiler equipment:
- high efficiency (up to 98%) is obtained due to the direct conversion of electricity into heat directly in the coolant;
- electricity savings of up to 40% are due to the use of automation and regulation of thermal conditions;
- simple installation provides small dimensions of devices and convenient connection of branch pipes;
- the ability to integrate into existing heating systems eliminates the need for re-laying pipes;
- the admissibility of parallel connection of boilers allows to increase the power of the heating system many times over;
- the reality of installing a reserve boiler excludes the sudden stop of heating the coolant.
Feasibility of use
For all their shortcomings, electrode boilers do not just have the right to life, they occupy their own niche, where they solve a certain range of problems. Basically, their use is reduced to heating small areas, where the cyclical mode of operation is especially important. Due to the low inertia, the heating systems on electrode boilers are instantly put into operation, which means that heating can be carried out in a strictly defined period of time.
In addition, one cannot fail to mention the small dimensions of the electrode boilers. They represent, in fact, a small flask that can be easily integrated into a compact technical niche. If you need to heat a small space and there is no way to equip a separate boiler room, this kind of boilers will come in handy.
However, it should be remembered that the class of equipment under consideration works best in closed-type systems with a small displacement.Electrode boilers can be used in combination with underfloor heating systems, and when heated with radiators. However, we repeat, it is necessary to properly prepare the coolant and use advanced electronic thermal control circuits.
Electrode boiler connection diagram: 1 - ball valve; 2 - filter; 3 - circulation pump; 4 - drain valve; 5 - electrode boiler; 6 - security group; 7 - expansion tank; 8 - heating radiators; 9 - three-way valve with a servo drive; 10 - circulation pump; 11 - underfloor heating contour; 12 - underfloor heating control unit; 13 - electrode boiler control unit; 14 - digital thermostat; 15 - contactor; 16 - automatic protection
Heating system maintenance on electrode boilers
During operation, electrode boilers do not cause any particular problems. They are compact, quiet, and require a minimum of protective devices in the electrical and hydraulic piping. Nevertheless, periodic revision and maintenance of such equipment will still have to be carried out.
The boiler electrodes generally require attention. The claims about the absence of scale formation are not groundless, but as a result of electrolysis, at least one of the electrodes forms a hard crust of insoluble plaque. It must be mechanically cleaned at least once a year. In addition, the density and chemical composition of the coolant should be monitored: for different systems, the methods for determining its suitability may differ.
Do not forget about electrical safety. The grounding of the heating system must be of high quality, at least once every two years it is necessary to check the operating parameters of the circuit of the main grounding conductors and the resistance of external connecting elements. Without proper attention in this matter, electrode boilers turn into potentially life-threatening devices.
rmnt.ru