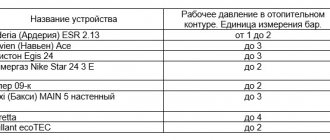
Central heating system pressure
High pressure in the central heating system of an apartment building is necessary in order to raise the heating medium to the upper floors. In high-rise buildings, circulation occurs from top to bottom. The supply is carried out by boilers using blowers. These are electric pumps that propel hot water. The reading of the pressure gauge on the return flow depends on the height of the building. Knowing what pressure is assumed in the heating system of a multi-storey building, the appropriate equipment is selected. For a nine-story building, this figure will be approximately three atmospheres. The calculation is based on the assumption that one atmosphere raises the flow by ten meters. The height of the ceilings is approximately 2.75 m. We also take into account a five-meter gap to the basement and technical floor. Based on this calculation, you can find out what the pressure should be in the heating system of a multi-storey building of any height.
Distribution of temperatures and pressure in the elevator unit of an apartment building
The central city and housing and communal networks are separated by elevators. An elevator is a unit through which the coolant is supplied to the heating system of a high-rise building. It mixes the supply and return flow, depending on what pressure is required to heat an apartment building. The elevator has a mixing chamber with an adjustable opening. It's called a nozzle. Adjusting the nozzle allows you to change the temperature and pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building. The hot water in the mixing chamber mixes with the water from the return flow and draws it into a new cycle. By changing the size of the nozzle orifice, you can decrease or increase the amount of hot water. This will lead to a change in temperature in the radiators of the apartments and a change in pressure. The temperature in the heating system of the house at the entrance is 90 degrees.
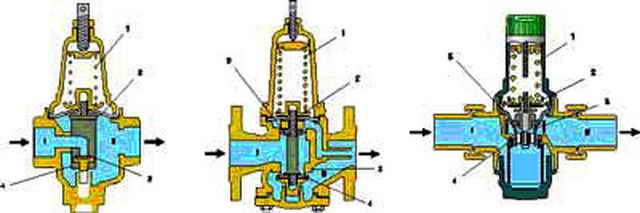
Pressure regulator
To comply with all measures for the safe functioning of the heating system, it is necessary to constantly monitor the temperature and pressure of the coolant.
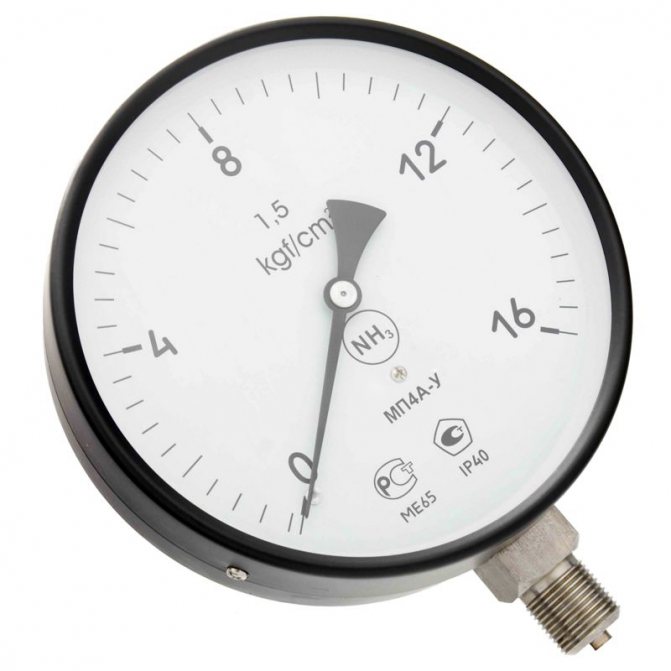
The pressure is controlled using a Bourdon tube pressure gauge... This device has an elastic measuring component, which, under the influence of a compressive load, is deformed in a certain way.
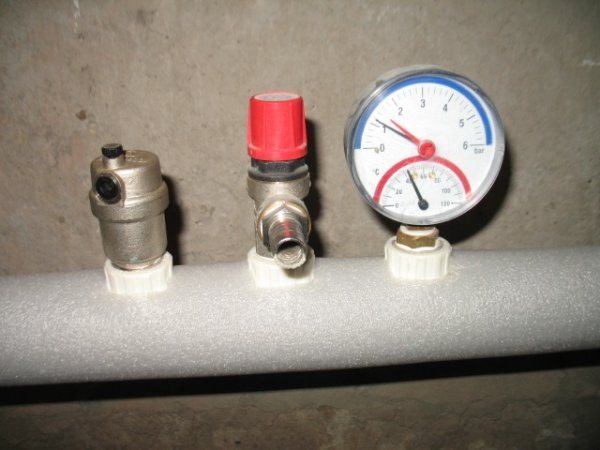

Photo 1. Pressure gauge installed in the heating system. The device allows you to measure pressure indicators.
Converting changes displayed on the rotational movement of the arrow, showing on the dial the exact value in the usual terms.
Important! After water hammer, the pressure gauges must be checked, since subsequent readings may be overstated.
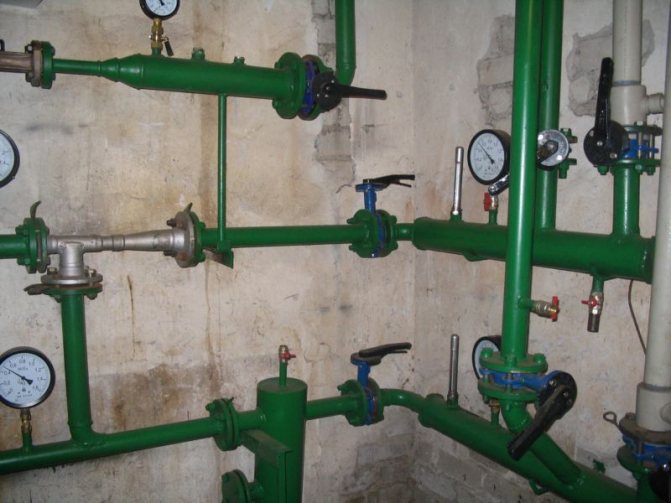
Pressure gauges are installed in the most critical areas of the system:
- at the inlet and outlet of the line with the coolant (centralized heating);
- before and after the heating boiler (individual heating);
- before and after the circulation pump (forced circulation);
- near filters, appropriate regulators and valves.
How to adjust metrics
There are several proven methods for this procedure:
- Correct design, including hydraulic calculations and installation of pipelines:
- the supply line should be on top, and the return line should be on the bottom;
- pipes are needed for risers 20-25 mm, and for bottling - 50-80 mm;
- pipes for risers are also used for supplying heating devices.
- Change in water temperature. When heated, the coolant expands, thereby increasing the pressure in the heating system. For instance, at 20 ° C it can jump on 0.13 MPa, but at 70 ° C - on the 0.19 MPa. Therefore, a decrease in temperature will lead to its corresponding adjustment.
- Circulation pump applications to provide warmth to apartments upper floors in high-rise buildings.


Photo 2. Circulation pumps installed in a multi-storey building. With the help of devices, the coolant is circulated through the heating system.
- The introduction of expansion tanks. With individual heating, the "extra" volume of the heated coolant will go into the tank, and the cooled one will return to the system, while maintaining the stability of the pressure.
- Using special controls... Such devices are able to prevent airing of the system during sudden pressure surges in the lines. Installation is carried out on the bypass line of the pump or on a jumper located between two pipelines - supply and return.
Causes of pressure drops in heating an apartment building
The return pressure in the heating of apartment buildings is lower than the flow. The normal deviation is two bars. In normal operation, the boiler houses supply the coolant to the system with a pressure of more than seven bar. The heating system of a high-rise building reaches about six bar. The flow is affected by hydraulic resistance, as well as branches in housing and communal networks. On the return line, the pressure gauge will show four bars. The pressure drop in the heating of an apartment building can be caused by:
- airlock;
- leakage;
- failure of system elements.
In practice, swings often occur. The water pressure in the heating system of an apartment building largely depends on the inner diameter of the pipes and the temperature of the coolant. Nominal technical marking - DU. For spills, pipes with a nominal bore of 60 - 88.5 mm are used, for risers - 26.8 - 33.5 mm.
Important! The pipes connecting the heating radiators and the riser must be of the same cross section. Also, the supply and return must be connected to each other before the battery.
The most important thing is that the apartment is warm. The hotter the water in the radiators, the higher the pressure in the central heating system of an apartment building. The return temperature is also higher. For stable operation of the heating system, the water from the return cycle pipe must be at a fixed temperature.
Differential pressure and its importance for the functioning of the heating system
For optimal functioning of any heating circuit, a stable and definite pressure drop is required, i.e. the difference between its values at the coolant supply and return. As a rule, it should be 0.1-0.2 MPa.
If this indicator is less, this indicates a violation of the movement of the coolant through the pipelines, as a result of which the water passes through the radiators without heating them to the required degree.
If the value of the drop above the value is exceeded, we can talk about "stagnation" of the system, one of the reasons for which is airing.
It should be noted that sudden changes in pressure negatively affect the performance of individual elements of the heating circuit, often disabling them.
Methods for regulating the working pressure and ensuring the stability of its differential on the supply and return
- First of all, it must be remembered that the optimal operation of the heat supply system, incl. the creation of the required pressure in it depends on the correctness of the design, in particular, hydraulic calculations, and the installation of highways and pipelines, namely: - the supply line in most schemes should be located at the top, the opposite, respectively, at the bottom; - for the manufacture of bottling, pipes with a diameter of 50-80 mm should be used, for risers - 20-25 mm; - the supply to heating devices can be made from the same pipes from which the risers are made, or one step less.
It is allowed to underestimate the cross-section of the radiator piping only if there is a jumper in front of them.


Figure 3 - Jumper in front of the heating radiator
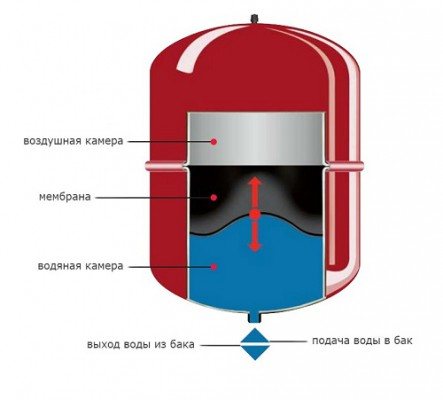

Figure 4 - Diaphragm expansion tank
The expansion tank, the volume of which is usually assumed to be about 10% of the total system volume, can be installed in any part of the circuit. However, experts recommend installing it in a straight section of the return pipeline in front of the circular pump (if any).
To prevent a situation when the capacity of the device is not enough with a continuing increase in pressure, the schemes provide for the use of a safety valve that removes excess coolant from the system.


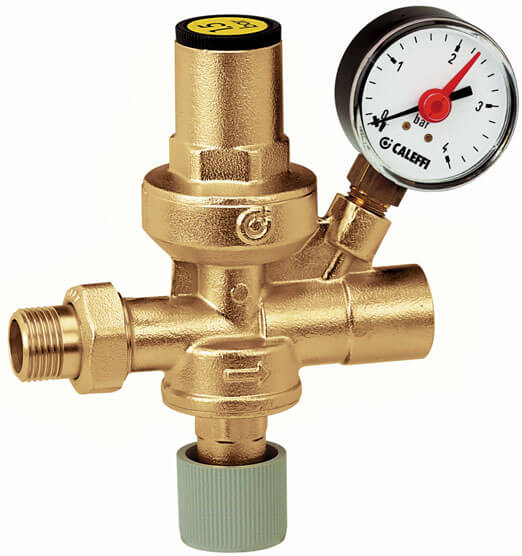
Figure 5 - Pressure regulator
Finding the causes of the drop and increase in pressure drop
The deviation of pressure up or down from the normative requires the establishment of the cause of this phenomenon and its elimination.
Pressure drop in the heating circuit
If the pressure in the heating system drops, then with a greater degree of probability we can talk about a coolant leak. The most vulnerable are existing seams, joints and joints.
To check this, the pump is turned off and the static pressure is monitored. With a continuing decrease in pressure, it is necessary to find the damaged area. To do this, it is recommended to sequentially disconnect various sections of the circuit, and after determining the exact location, repair or replace worn out elements.
If the static pressure remains stable, the reason for the decrease in head is associated with a malfunction of either the pump or the heating equipment.
It should be borne in mind that a short-term pressure drop may be due to the peculiarity of the regulator, which, with a certain frequency, bypasses part of the water from the supply to the return. In the case when the heating radiators warm up evenly and up to the required temperature, we can say that the difference was associated with the above cycle.
Other possible reasons include:
- removal of air through the air vents, as a result of which the volume of the coolant in the system decreases;
- decrease in water temperature.
Increasing pressure in the system
A similar situation is observed when slowing down or stopping the movement of the coolant in the heating circuit. The most likely reasons for this are:
- the occurrence of an airlock;
- contamination of filters and mud collectors;
- features of the functioning of the pressure regulator or incorrect setting of its operation;
- constant replenishment of the coolant due to a failure of automation or incorrectly adjusted valves on the supply and return.
It should be noted that pressure instability is most often observed in newly launched systems and is associated with the gradual removal of air. This can be considered normal if, after bringing the volume of the coolant and pressure to operating values, which lasts from several days to several weeks, no deviations are recorded. Otherwise, we should talk about an incorrectly performed hydraulic calculation, in particular, the accepted volume of the expansion tank.
Elimination of drops
Elevator nozzle device
When the return flow temperature drops and the pressure in the heating pipes in an apartment building changes, the diameter of the elevator nozzle is adjusted. It is reamed out if necessary. This procedure must be agreed with the service provider (CHP or boiler house). Amateur performance should not be allowed. In extreme situations, when defrosting of the system is threatened, the adjustment mechanism can be completely removed from the elevator. In this case, the coolant enters the communications of the house without hindrance. Such manipulations lead to a decrease in pressure in the central heating system and a significant increase in temperature, up to 20 degrees. Such an increase can be dangerous for the heating system of the house and city networks in general.
An increase in the temperature of the working medium from the return flow is associated with an increase in the diameter of the nozzle, which leads to a decrease in pressure in the heating of apartment buildings. In order to lower the temperature, it should be decreased. Here you cannot do without welding. Then a new hole is drilled with a smaller drill. This will reduce the amount of hot water in the mixing chamber of the elevator. This manipulation is carried out after stopping the circulation of the coolant. If there is an urgent need, without stopping the system, to reduce the return temperature, the valves are partially closed. But this can be fraught with consequences. Metal shut-off valves create a barrier in the path of the coolant. The result is increased pressure and frictional force. This increases the wear on the dampers. If it reaches a critical level, the damper can come off the regulator and completely shut off the flow.
Adjustment
Heating regulator
Automatic control is provided by the heating controller.
It includes the following details:
- Computing and matching panel.
- Executive device
on the water supply section. - Executive device
, performing the function of mixing liquid from the returned liquid (return). - Boost pump
and a sensor on the water supply line. - Three sensors (on the return line, on the street, inside the building).
There may be several of them in the room.
The regulator covers the liquid supply, thereby increasing the value between the return and supply to the value provided by the sensors.
To increase the flow, there is a step-up pump, and a corresponding command from the regulator.
The inlet flow is controlled by a "cold bypass". That is, the temperature drops. Some part of the liquid, circulated along the circuit, is sent to the supply.
The sensors remove information and transmit it to the control units, as a result of which there is a redistribution of flows, which provide a rigid temperature scheme of the heating system.
Sometimes, a computing device is used, where DHW and heating regulators are combined.
The hot water regulator has a simpler control circuit. The hot water sensor regulates the water flow to a stable value of 50 ° C.
Regulator advantages:
- The temperature scheme is strictly adhered to.
- Elimination of liquid overheating.
- Fuel economy
and energy. - The consumer, regardless of distance, receives heat equally.
Features of autonomous heating
The normal value for a closed circuit is 1.5-2.0 bar, which is much different from the pressure in the central heating pipes. The reason for the downgrade may be:
- depressurization - when a leak or microcracks appears, through which water can escape. Visually, this may not be noticeable, since a small amount of water has time to evaporate;
- decrease in the temperature of the coolant. The lower the water temperature, the less its expansion;
- the presence of autonomous pressure regulators that bleed air. They are installed to remove air pockets. Leak frequently;
- changing the radius of the nominal pipe bore. When heated, plastic pipes can change their geometry - they become wider.
Not only the circulation of the coolant depends on the pressure indicator in the heating system, but also the serviceability of the equipment. To prevent a decrease and increase in pressure in any part of the system, an expansion tank is installed. It is a metal container with a rubber membrane inside. The membrane divides the tank into two chambers: with water and air. At the top there is a valve through which air exits at extreme pressure rise. It can occur due to excessive heating of the fluid. After the water cools down and decreases in volume, the pressure in the system will not be enough, because the air has escaped.The volume of the expansion tank is calculated based on the total volume of the coolant in the system.
Radiator selection
It is important to choose the optimal radiator for the heating system
The temperature in the house also depends on the efficiency of the radiators. Manufacturers offer batteries in the following materials:
Each of the materials determines the working pressure of the radiator, its thermal power and the heat transfer coefficient. Before purchasing batteries, you should ask the housing office what the pressure is in the central heating. In a private house and in a high-rise building, the pressure is different:
- private up to 3 bar;
- the operating pressure in the heating system of an apartment building is 10 bar.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account periodic checks of the reliability of the heating system, the so-called water hammer.
And it is carried out in order to find out what is the pressure in heating in the apartment, to identify clogging, weak points and leaks. To remove dirt from the pipes, you need to turn off the valve and drain the water. Then dial the complete system and repeat the procedure. The use of special products with high acidity is allowed. This will require equipment. To find a leak or a weak spot in the heating system of a multi-storey building, it is necessary to increase the pressure to 10 bar. If any connection cannot withstand this load, it should be reinforced or replaced. It is best to spot weak spots as a result of water hammer in summer. Since it is much more difficult to carry out work of this kind in winter. This is due to the short period of time during which the system can unfreeze.
When organizing heating systems, undeservedly little attention is paid to the pressure in the system. For example, in the absence of a sufficient pressure drop between pipes and radiators, the coolant will "slip through" the radiator without heating it. The pressure drop in the heating system is a fairly common problem that can be dealt with quite simply.
Effect of water pressure on system performance
When purchasing the appropriate plumbing equipment or household appliances connected to the water supply system, you need to familiarize yourself with their technical characteristics in advance. One of the parameters is the optimal pressure level at which the devices will operate normally and no drop will be observed.
If there is a difference in heating, then problems with heating the room begin. Such an indicator for washing machines and dishwashers is considered to be a pressure of 2 atmospheres. However, for baths with automation and watering equipment for a vegetable garden or garden, this value is already 4 atmospheres.
The minimum indicator of water pressure for autonomous water supply networks in private houses must be at least 1.5 - 2 atmospheres. It should be taken into account that several objects of water consumption can be connected to the water supply source at the same time.
Also, creating the necessary water pressure is especially important for private homeowners in case of a fire hazard.

Types of pressure in the heating system
The pressure in the heating system is the force with which liquids and gases act on the walls of the heating system elements, it is determined by the ratio to atmospheric pressure. Working pressure is the pressure that is present in a working system with normal operating characteristics. Working pressure is the sum of two values - static and dynamic pressure. (See also: )
Static pressure is a quantity measured when the water is stationary, taking into account its height.
Dynamic pressure is the effect of moving liquids or gases on the walls of the equipment.
The pressure drop is the pressure difference in the zones of supply and return of the coolant on the pumps.
The working pressure changes depending on the temperature of the heating medium.For example, at a temperature of +20 0 С this pressure is 1.3 bar, and at +70 0 С - 1.9 bar.
If the pressure in a single-circuit system is lower than the prescribed one, then the coolant will stagnate and will not give effective heat transfer from heating devices.
Installation of differential pressure regulators
In heating circuits with a variable flow rate of the coolant - on risers and horizontal sections of branches, the installation of pressure drop regulators makes it possible to exclude the influence on the branches of changes in the hydraulic regime of the system. They also help to prevent noise generation on the control valves at high head. (See also: )
The installation of regulators allows for optimized regulation by increasing the role of control valves. Connecting impulse pipes before and after the control valve allows you to set the exact value of the flow rate of the coolant and prevent it from being exceeded.
Differential pressure regulators can be installed in the pump bypass line. They are used in systems with variable flow rate of the heating agent. Reducing the flow rate of the heating medium will increase the pressure drop between the suction and discharge nozzles. The regulator reacts to the increased differential by opening and bypassing the coolant from the pressure head to the suction nozzle, as a result of which the coolant flow through the pump remains constant.
The installation of pressure regulators creates stable barometric conditions for the functioning of the boiler and the heating system as a whole.
The use of materials is permitted only with an indexed link to the page with the material.
It is almost impossible to find old-style ovens used for heating and cooking. Long ago they were replaced by closed heating circuits involving the use of gas equipment. Even with correct installation, malfunctions of the heating system are possible. Why is this happening?
Automatic differential pressure regulator, good solution to the problem of differential pressure
Normal pressure in the system, affecting the quality of heating: if this parameter is outside the normal range - with the failure of expensive equipment.
With an increase in the indicator above the critical levels, the elements are destroyed, leading to a complete stop of the system. And by reducing it brings the liquid to a boil. They urgently take action if the pressure in the heating system drops to the limit value of 0.02 MPa.
Heating is presented not in absolute, but in excess value. This parameter regulates the operation of heating systems and household boilers, and it is also fixed by a pressure gauge to measure water pressure.
Differential pressure and its importance for the functioning of the heating system
For optimal functioning of any heating circuit, a stable and definite pressure drop is required, i.e. the difference between its values at the coolant supply and return. As a rule, it should be 0.1-0.2 MPa.
If this indicator is less, this indicates a violation of the movement of the coolant through the pipelines, as a result of which the water passes through the radiators without heating them to the required degree.
If the value of the drop above the value is exceeded, we can talk about "stagnation" of the system, one of the reasons for which is airing.
It should be noted that sudden changes in pressure negatively affect the performance of individual elements of the heating circuit, often disabling them.
Methods for regulating the working pressure and ensuring the stability of its differential on the supply and return
- First of all, it must be remembered that the optimal operation of the heat supply system, incl. the creation of the required pressure in it depends on the correctness of the design, in particular, hydraulic calculations, and the installation of highways and pipelines, namely: - the supply line in most schemes should be located at the top, the opposite, respectively, at the bottom; - for the manufacture of bottling, pipes with a diameter of 50-80 mm should be used, for risers - 20-25 mm; - the supply to heating devices can be made from the same pipes from which the risers are made, or one step less.
It is allowed to underestimate the cross-section of the radiator piping only if there is a jumper in front of them.
Figure 3 - Jumper in front of the heating radiator
Figure 4 - Diaphragm expansion tank
The expansion tank, the volume of which is usually assumed to be about 10% of the total system volume, can be installed in any part of the circuit. However, experts recommend installing it in a straight section of the return pipeline in front of the circular pump (if any).
To prevent a situation when the capacity of the device is not enough with a continuing increase in pressure, the schemes provide for the use of a safety valve that removes excess coolant from the system.
Figure 5 - Pressure regulator
Finding the causes of the drop and increase in pressure drop
The deviation of pressure up or down from the normative requires the establishment of the cause of this phenomenon and its elimination.
Pressure drop in the heating circuit
If the pressure in the heating system drops, then with a greater degree of probability we can talk about a coolant leak. The most vulnerable are existing seams, joints and joints.
To check this, the pump is turned off and the static pressure is monitored. With a continuing decrease in pressure, it is necessary to find the damaged area. To do this, it is recommended to sequentially disconnect various sections of the circuit, and after determining the exact location, repair or replace worn out elements.
What the indicator is composed of
The working pressure is characterized by two parameters:
- Dynamic, which is created by circulation pumps.
- Static pressure determines the height of the water column inside the pipeline (an indicator of 1 atmosphere is created by 10 meters). That is, static pressure is a parameter indicating the force with which the fluid acts on radiators and pipes.
Working pressure (optimal) is characterized by an indicator that ensures the correct operation of the components of the heating system when all elements of the circuit are turned on.
Only specific types of batteries can withstand high system pressures. Bimetallic products do the best with this, while radiators made of one metal are poorly tolerated, manifesting themselves as drops in the heating network.
How to control pressure
The nominal pressure is adjusted using the readings recorded on the measuring instruments. For this purpose, manometers are cut in. If the results deviate from the standard, urgently fix the problems, otherwise it will lead to a decrease in the efficiency of the equipment.
The pressure gauges are mounted on the pipeline at the following points:
- highest and lowest;
- after the boiler, filters and before it;
- at the entrance of heating networks into the house;
- when leaving the boiler room.
The optimum pressure inside the heating system is 1.5 to 2 atmospheres. The indicator is calculated when designing a house, taking into account the nuances of the equipment. In addition, the parameter depends on the number of floors. The pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building reaches 12-16 atm.
Such a device is suitable for any heating system.
To optimize the performance, safety valves and air vents are used, which do not allow air locks to appear.
Sometimes, in order to minimize the uneven distribution of the coolant through the pipes, a balancing valve is used in the heating system. It is advisable to use it inside multi-storey buildings.
Regulators work as pressure limiters. Thanks to the device, the likelihood of accidents after water hammer is reduced and taps, pipes and mixers are better preserved.
Pressure and temperature are indicators on the level of which the heat inside the room depends.
The coolant is pumped in after assembling the heating units. Then create a head with a value of 1.5 atmospheres. When the liquid inside the pipes is heated, the pressure constantly increases.The correction of the indicator inside the heating network is carried out by changing the temperature of the liquid.
The norms are regulated by SNiP 41-01-2003 and differ at a specific point in the system. For a one-pipe scheme, it should not be more than 105 degrees, and for a two-pipe scheme, the maximum is +95 degrees.
In order to prevent too strong a pressure, expansion tanks are used. As soon as the indicator in the system becomes more than 2 atmospheres, the unit is triggered. Excess hot coolant is taken away by means of, while the pressure is normalized and kept at an optimal level.
When the capacity of the tank is not enough to collect excess water, the head in the heating system can reach 3 atmospheres, which is considered a critical indicator. The safety one helps to get out of the situation. The element frees the heating system from excess fluid as follows: the spring lifts the flap, after which excess water is removed from the line. The process continues until the parameter level stabilizes. Thus, the boiler safety valve preserves the equipment.
Before the heating season, the system is tested to see if it will withstand possible water hammer. For this, pressure testing is carried out and overpressure is created, after which weak sections of the pipeline are identified and measures are taken.
The functionality of the circuit is checked in 2 ways:
- By simultaneously checking the system.
- Checking specific sites.
The first option is beneficial only from the point of view of reducing time costs, but the second, despite the duration, deals with the integrity of the system in part, in specific areas. At the same time, it is easier to fix the found defect inside the covered area than to search for components.
Pressure meter
Allocate the established testing scheme:
- first, air is released from part of the circuit or the entire pipeline;
- then a pressure is supplied to the inside of the pipes, which exceeds the operating pressure by one and a half times.
- tightness test: first, chilled liquid is introduced into the pipes, then, after connecting the heating device, they are filled with hot coolant.
If there is no leakage and the pipe has not burst, there is no cause for concern.
Fluid leaking from the pipes minimizes the pressure. Often this problem occurs at the joints of the elements, sometimes a breakthrough occurs when using defective or worn pipes.
A leak occurs if the pressure in the boiler drops, measured when the pumps are not running. If it is normal, then the problem is not inside the pipes, but in the pump. To detect a problem area, the sections of the circuit are turned off in turn, observing the change in indicators. When a defective area is found, it is cut off, repaired, joints are sealed or damaged components are replaced.
Additional reasons for the reduced rate:
- bithermal heat exchanger damaged during a water hammer;
- defective expansion tank chambers;
- the presence of scale inside the heat exchanger;
- pressure drops when using a heat exchanger with cracks (the reason is considered to be a factory defect, physical wear of the unit).
Specific approaches have been developed to a specific problem: the tanks are muffled, the heat exchanger is changed, and hard water is softened with additives.
First, they check the boiler and the heating regulator, due to a failure of which the movement of the coolant sometimes stops.
The indicator rises if the heating network is incorrectly fed; if the tap is closed in the direction of the circulating fluid; if dirt collectors or filters are clogged or boiler malfunctions are noticed.
After the heating system is put into operation, air comes out through the automatic taps on the radiators or vents, so a quick pressure optimization is not possible. To establish the operation of the circuit, liquid is additionally pumped there.If time passes, an increase in the indicator still makes itself felt, then the malfunctions are associated with an error in calculating the volume of the tank (expansion).
To avoid such problems, the nuances are considered even at the design stage of the house, and the installation is carried out strictly according to the established rules.
What should be the pressure in a high-rise building?
From this article you will find out what pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building is considered normal, the reasons for its differences and how to troubleshoot. We will also talk about methods of checking the circuit for strength and choosing the optimal radiators for the system.
Central heating system pressure
High pressure in the central heating system of an apartment building is necessary in order to raise the heating medium to the upper floors. In high-rise buildings, circulation occurs from top to bottom. The supply is carried out by boilers using blowers. These are electric pumps that propel hot water. The reading of the pressure gauge on the return flow depends on the height of the building. Knowing what pressure is assumed in the heating system of a multi-storey building, the appropriate equipment is selected. For a nine-story building, this figure will be approximately three atmospheres. The calculation is based on the assumption that one atmosphere raises the flow by ten meters. The height of the ceilings is approximately 2.75 m. We also take into account a five-meter gap to the basement and technical floor. Based on this calculation, you can find out what the pressure should be in the heating system of a multi-storey building of any height.
Distribution of temperatures and pressure in the elevator unit of an apartment building
The central city and housing and communal networks are separated by elevators. An elevator is a unit through which the coolant is supplied to the heating system of a high-rise building. It mixes the supply and return flow, depending on what pressure is required to heat an apartment building. The elevator has a mixing chamber with an adjustable opening. It's called a nozzle. Adjusting the nozzle allows you to change the temperature and pressure in the heating system of a multi-storey building. The hot water in the mixing chamber mixes with the water from the return flow and draws it into a new cycle. By changing the size of the nozzle orifice, you can decrease or increase the amount of hot water. This will lead to a change in temperature in the radiators of the apartments and a change in pressure. The temperature in the heating system of the house at the entrance is 90 degrees.
Causes of pressure drops in heating an apartment building
The return pressure in the heating of apartment buildings is lower than the flow. The normal deviation is two bars. In normal operation, the boiler houses supply the coolant to the system with a pressure of more than seven bar. The heating system of a high-rise building reaches about six bar. The flow is affected by hydraulic resistance, as well as branches in housing and communal networks. On the return line, the pressure gauge will show four bars. The pressure drop in the heating of an apartment building can be caused by:
- airlock;
- leakage;
- failure of system elements.
In practice, swings often occur. The water pressure in the heating system of an apartment building largely depends on the inner diameter of the pipes and the temperature of the coolant. Nominal technical marking - DU. For spills, pipes with a nominal bore of 60 - 88.5 mm are used, for risers - 26.8-33.5 mm.
Important! The pipes connecting the heating radiators and the riser must be of the same cross section. Also, the supply and return must be connected to each other before the battery.
The most important thing is that the apartment is warm. The hotter the water in the radiators, the higher the pressure in the central heating system of an apartment building. The return temperature is also higher.For stable operation of the heating system, the water from the return cycle pipe must be at a fixed temperature.
Pressure rise
If the maximum pressure in the heating system is exceeded, then the reason for this is a slowdown or stoppage of the flow of water in the heating circuit.
This can lead to:
- contamination of mud collectors and filters;
- the occurrence of an airlock;
- replenishment of the coolant due to a failure of automation or incorrectly adjusted valves located on the supply and return (read: "Automatic recharge of the heating system - diagram of the unit and recharge valve");
- feature of the regulator or its incorrect setting.


Unstable pressure is especially common in newly started heating systems due to the removal of air. It is considered normal if no deviations are observed for several weeks after adjusting the water volume and pressure to operating values.
Otherwise, most likely, the pressure instability is associated with incorrect hydraulic calculations, including the insufficient volume of the expansion tank. That is why, when installing a heating system, it is important to correctly perform all calculations - in the future this will save you from various problems with its functioning.
Any heating circuit operates at certain values of the head and temperature of the coolant, which are calculated at the stage of its design. However, during operation, situations are possible when the pressure drop in the heating system deviates from the standard level to a greater or lesser extent and, as a rule, requires adjustment to ensure efficiency, and in some cases, safety.
Elimination of drops
Elevator nozzle device
When the return flow temperature drops and the pressure in the heating pipes in an apartment building changes, the diameter of the elevator nozzle is adjusted. It is reamed out if necessary. This procedure must be agreed with the service provider (CHP or boiler house). Amateur performance should not be allowed. In extreme situations, when defrosting of the system is threatened, the adjustment mechanism can be completely removed from the elevator. In this case, the coolant enters the communications of the house without hindrance. Such manipulations lead to a decrease in pressure in the central heating system and a significant increase in temperature, up to 20 degrees. Such an increase can be dangerous for the heating system of the house and city networks in general.
An increase in the temperature of the working medium from the return flow is associated with an increase in the diameter of the nozzle, which leads to a decrease in pressure in the heating of apartment buildings. In order to lower the temperature, it should be decreased. Here you cannot do without welding. Then a new hole is drilled with a smaller drill. This will reduce the amount of hot water in the mixing chamber of the elevator. This manipulation is carried out after stopping the circulation of the coolant. If there is an urgent need, without stopping the system, to reduce the return temperature, the valves are partially closed. But this can be fraught with consequences. Metal shut-off valves create a barrier in the path of the coolant. The result is increased pressure and frictional force. This increases the wear on the dampers. If it reaches a critical level, the damper can come off the regulator and completely shut off the flow.
Features of autonomous heating
The normal value for a closed circuit is 1.5-2.0 bar, which is much different from the pressure in the central heating pipes. The reason for the downgrade may be:
- depressurization - when a leak or microcracks appears, through which water can escape. Visually, this may not be noticeable, since a small amount of water has time to evaporate;
- decrease in the temperature of the coolant.The lower the water temperature, the less its expansion;
- the presence of autonomous pressure regulators that bleed air. They are installed to remove air pockets. Leak frequently;
- changing the radius of the nominal pipe bore. When heated, plastic pipes can change their geometry - they become wider.
Not only the circulation of the coolant depends on the pressure indicator in the heating system, but also the serviceability of the equipment. To prevent a decrease and increase in pressure in any part of the system, an expansion tank is installed. It is a metal container with a rubber membrane inside. The membrane divides the tank into two chambers: with water and air. At the top there is a valve through which air exits at extreme pressure rise. It can occur due to excessive heating of the fluid. After the water cools down and decreases in volume, the pressure in the system will not be enough, because the air has escaped. The volume of the expansion tank is calculated based on the total volume of the coolant in the system.
Radiator selection
It is important to choose the optimal radiator for the heating system
- private up to 3 bar;
- the operating pressure in the heating system of an apartment building is 10 bar.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account periodic checks of the reliability of the heating system, the so-called water hammer.
What is the pressure in the heating system for?
In this article, you will learn about the importance of pressure, methods of increasing or decreasing it, and the causes of pressure drops in the heating system. Also familiarize yourself with the equipment that is used to regulate and control pressure in heating.
Pressure function in the heating system
The operating pressure in the heating system is used to maintain a high efficiency of the artificial heating circuit. The condition ensures the delivery of hot water from the boiler room to the structure of the residential building until the radiators take on a certain amount of heat energy.
The pressure of heating networks has several types:
- static - determining the pressure on the inner walls of pipelines, depending on the number of storeys of the structure, and the liquid remains stationary;
- dynamic - formed as a result of the launch of a centrifugal pump and the supplied medium;
- worker, is represented by the sum of the first two pressures, ensuring the continuous operation of all elements of the heating system.
The latter includes a circulation pump, heat generator, expansion tank and pipes.
Why do you need pressure in the heating system?
The working medium circulates in pipes and radiators. In this capacity, water most often acts. In order for it to circulate evenly, a constant pressure is required. Differences can lead to malfunctions and a complete stop of the process. Only overpressure (PR) is taken into account. Unlike absolute (ABD), it does not take into account atmospheric (ABD). The higher its value, the greater the efficiency.
ISD = ABD - ATD
AD is not a constant value. It varies depending on the altitude and weather conditions. On average, it is one bar.
The values
What is the pressure difference between different parts of the heating system?
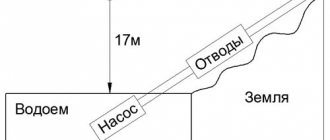
- Between the supply and return lines of the heating main, it is approximately 20 - 30 meters, or 2 - 3 kgf / cm2.
Reference: excess pressure in one atmosphere raises the water column to a height of 10 meters.
- The difference between the mixture after the elevator and the return pipeline is only 2 meters, or 0.2 kgf / cm2.
- The difference on the retaining washer between the circulation inserts of the elevator unit rarely exceeds 1 meter.
- The head created by a wet rotor circulation pump usually varies from 2 to 6 meters (0.2 to 0.6 kgf / cm2).
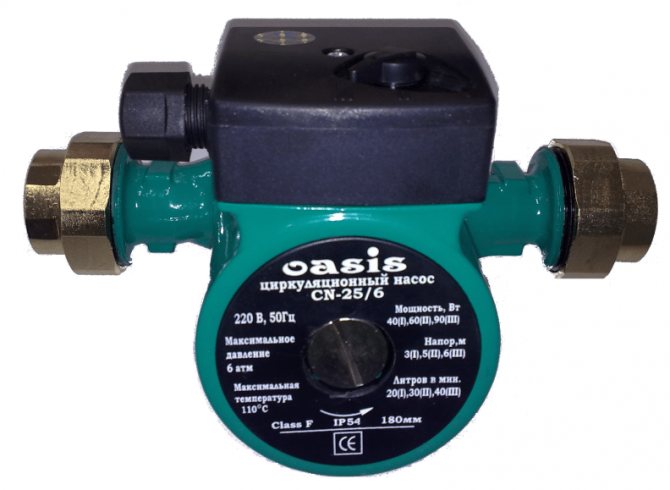


This pump generates a head of 3, 5 and 6 meters, depending on the selected mode.
How to create pressure in the heating system?
The pressure is static and dynamic.
Static systems are installed without the use of pumps. These are usually single-loop circuits. The pressure is created as a result of the height difference. Under its own weight from a height of ten meters, the water presses with a force of one bar.
Dynamic systems use pumps to increase the pressure in the heating system. These are more complex schemes that allow the installation of two and three circulation circuits. In other words, they simultaneously include:
- warm water floor;
- storage boilers.
The most important thing in heating is proper water circulation. In order for the liquid to move in the right direction, check valves are installed. The check valve is a coupling with a spring and a damper. It passes the liquid in only one direction, ensuring its correct circulation and high pressure in the heating system.
Control methods
You can control the pressure in the system using a sensor
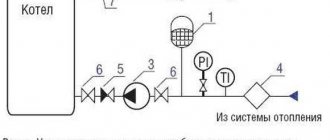
For monitoring, water pressure sensors are installed in the heating system. These are pressure gauges with a Bredan tube, which is a measuring device with a scale and an arrow. It shows overpressure. It is installed at the control nodal points defined by regulatory documents. With the help of the pressure sensor of the heating system, it is possible to determine not only a quantitative indicator, but also areas with possible leaks and other malfunctions.
The flow of the working medium does not pass directly through the pressure gauge, since the measuring device is installed by means of three-way valves. They allow you to purge the gauge or reset the readings. Also, this tap allows you to replace the pressure gauge by simple manipulations.
Pressure gauges are installed before and after elements that can affect losses and pressure rise in the heating system. Also, using it, you can determine the health of a particular unit.
Controlling pressure drops


Deformation pressure gauges with a Bourdon tube are most often used to measure pressure. When determining low pressure, their variety can also be used - diaphragm devices. After water hammer, such models should be verified, since during subsequent measurements they may show overestimated values.
In those systems that provide for automatic control and regulation of pressure, different types of sensors are additionally used (for example, electrocontact).
The placement of pressure gauges (tie-in points) is determined by regulations.
These devices should be installed in the most important areas of the system:
- at its entrance and exit;
- before and after filters, pumps, pressure regulators, mud collectors;
- at the exit of the main line from the boiler room or CHP and at the entrance to the building.
These recommendations must be followed even when creating a small heating circuit and using a low-power boiler, since not only the safety of the system depends on this, but also its efficiency, which is achieved due to the optimal consumption of fuel and water (read: "Safety system for heating"). It is recommended to connect pressure gauges through three-way taps - this will allow blowing, zeroing and replacing devices without stopping the heating system.
Key nodes
- , electric or solid fuel
Each of them has certain characteristics. The volume of the liquid that it is able to heat, as well as the allowable pressure, depends on these values.
- Expansion tank
Used in closed-loop dynamic systems. Consists of two chambers: in one air, and in the second liquid. The chambers are separated by a membrane. There is a valve in the air compartment through which, if necessary, a bleeding takes place. The main purpose is to adjust the pressure drops in the heating system.
- Electric pressure blower
- Heating control devices
- Filters
Fluctuations and their causes
Pressure surges indicate system malfunction. The calculation of pressure losses in the heating system is determined by summing the losses at individual intervals, which make up the entire cycle. Early identification of the cause and its elimination can prevent more serious problems that lead to costly repairs.
If the pressure in the heating system drops, this may be due to the following reasons:
- the appearance of a leak;
- failure of the expansion tank settings;
- failure of pumps;
- the appearance of microcracks in the boiler heat exchanger;
- power outage.
Expansion tank regulates differential pressure
In the event of a leak, all connection points must be checked. If the cause is not visually identified, it is necessary to examine each area separately. For this, the valves of the taps are sequentially closed. The pressure gauges will show the change in pressure after cutting off a particular section. Having found a problematic connection, it must be tightened, previously additionally sealed. If necessary, the assembly or part of the pipe is replaced.
The expansion tank regulates the differences due to heating and cooling of the liquid. A sign of a tank malfunction or insufficient volume is an increase in pressure and a further drop.
The calculation of the pressure in the heating system necessarily includes the calculation of the volume of the expansion tank:
(Thermal expansion for water (%) * Total volume in the system (l) * (Maximum pressure level + 1)) / (Maximum pressure level - Pressure for gas in the tank itself)
Add a clearance of 1.25% to this result. The heated liquid, expanding, will force air out of the tank through the valve in the air compartment. After the water cools down, it will decrease in volume and the pressure in the system will be less than required. If the expansion tank is smaller than required, it must be replaced.
A rise in pressure can be caused by a damaged membrane or an incorrect setting of the heating system pressure regulator. If the diaphragm is damaged, the nipple must be replaced. It's quick and easy. To configure the reservoir, it must be disconnected from the system. Then pump the required amount of atmospheres into the air chamber with a pump and install it back.
It is possible to determine the malfunction of the pump by turning it off. If nothing happens after the shutdown, then the pump is not working. The reason may be a malfunction of its mechanisms or a lack of power. You need to make sure that it is connected to the network.
If there are problems with the heat exchanger, then it must be replaced. During operation, microcracks may appear in the metal structure. This cannot be eliminated, only replacement.
Why is the pressure in the heating system increasing?
The reasons for this phenomenon may be incorrect fluid circulation or its complete stop due to:
- the formation of an air lock;
- clogging of the pipeline or filters;
- operation of the heating pressure regulator;
- continuous feeding;
- shutoff valves overlapping.
How to eliminate drops?
An air lock in the system does not allow fluid to pass through. The air can only be vented. To do this, during installation, it is necessary to provide for the installation of a pressure regulator for the heating system - a spring air vent. It works in automatic mode. The new design radiators are equipped with similar elements. They are located at the top of the battery and operate in manual mode.
Why does the pressure in the heating system increase when dirt and scale accumulates in the filters and on the pipe walls? Because the flow of fluid is obstructed. The water filter can be cleaned by removing the filter element. It is more difficult to get rid of scale and blockages in pipes. In some cases, flushing with special means helps. Sometimes the only way to fix the problem is.
The heating pressure regulator, in the event of an increase in temperature, closes the valves through which the liquid enters the system. If this is unreasonable from a technical point of view, then the problem can be rectified by adjusting. If this procedure is not possible, the assembly should be replaced. If the electronic make-up control system breaks down, it must be adjusted or replaced.
The notorious human factor has not yet been canceled. Therefore, in practice, the shut-off valves overlap, which leads to the appearance of increased pressure in the heating system. To normalize this figure, you just need to open the valves.