A term such as "biodiesel
", The majority understands purely intuitively. But there is often a certain amount of confusion involved. It's okay, but it's still better to do without it and figure out what biodiesel is.

A bit of theory
When working in its cylinders, gasoline or diesel fuel is burned. Both are products of oil refining, the reserves of which are limited, in addition, when these types of fuels are burned, substances are formed that are harmful to people and the environment. One of the options to avoid this is the use of biodiesel as a fuel for engines. It is necessary to explain what it is. The fact is that the production of biodiesel is based on the use of animal fats and vegetable oil as raw materials. A simple analogy can be drawn - from oil, gasoline and diesel fuel are obtained, from oil or fat, it is possible to obtain fuel for the operation of an internal combustion engine.
A small clarification - different substances can be used as fuel for the operation of engines, for example, the same alcohol obtained from sawdust, but in this case we are considering fuel specifically for diesel engines, and the raw material for biodiesel, as this type of fuel is called, is oil or residual fat.
How to use biofuels?
The use of fat and oil as fuel can be done in the following ways: ✔ Directly by pouring oil into the tank. The disadvantage of this approach will be its incomplete combustion, mixing with the lubricant and deterioration of its lubricating properties, as well as the appearance of deposits on nozzles, rings, pistons due to the increased viscosity of vegetable fuel. ✔ By mixing it with kerosene or diesel. ✔ By converting vegetable oil, the source of which can be rapeseed, corn, sunflower, etc., and ultimately obtaining biodiesel. The most complex of these is considered to be the oil conversion technology, but nevertheless, it is so simple that it is easy to implement, thanks to which it is possible to obtain biodiesel at home.
What is biodiesel?
In fact, biodiesel is a mixture of ethers, mainly methyl ether, as a result of a chemical reaction. Its advantages include: ✔ plant origin, thanks to the possibility of growing plants, we get a renewable source of fuel; ✔ biological safety, biodiesel is environmentally friendly, its release into the environment does not cause any harm to it; ✔ lower level of emissions of carbon dioxide and other toxic substances; ✔ insignificant sulfur content in the exhaust gases of engines using biodiesel; ✔ good lubricating properties.
Essentially, vegetable oil is a mixture of esters with glycerin, which gives it its viscosity. The biodiesel production process is based on removing glycerin and replacing it with alcohol. It should be noted that the disadvantage of such fuel is the need to heat it at low temperatures or to use a mixture of biodiesel and conventional diesel fuel.
Equipment for the production of biodiesel
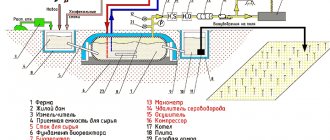
On the Russian market, there is a large number of proposals for the sale of biodiesel production units from domestic and foreign manufacturers. The equipment differs depending on the feedstock and the planned production volumes. Consider a set of equipment made in Russia for the production of methyl ester (biodiesel) from vegetable oils.


The area of the ready-to-use installation is about 15 sq. m.This area does not include the space reserved for containers, since their number depends on the needs of a particular enterprise. The biodiesel plant is compact and mobile, can be placed in a container (20 feet) and transported. The performance of the equipment depends on the selected raw material, therefore it can be indicated approximately: 2 cubic meters. m. in 1 hour equipment operation.
For 1 cubic meter m. of biofuel, 1 ton of oil is consumed, 110 liters. methanol and 10 kg. caustic soda. There are no pressure vessels in the methyl ether production unit, therefore no special permission is required for operation. The standard set of equipment includes:
- a mixing reactor for biofuel production;
- set of connections;
- shut-off valves;
- control cabinet;
- pumps;
- container.
Optional equipment:
- containers for raw materials and finished product;
- diesel generator of autonomous power supply (runs on its own biofuel);
- filters for cleaning oils from impurities (if necessary, such cleaning);
- equipment for vegetable oil refining.
Video: Automatic modules for the production of biodiesel
Production technology
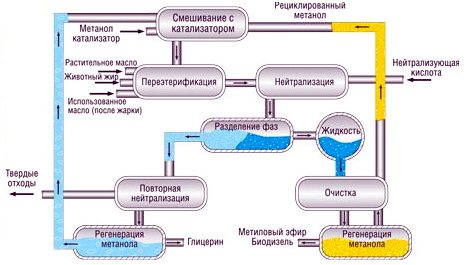
Biodiesel production technology is quite simple. It is usually made from various types of vegetable oil. For this, rapeseed, soybeans, corn, etc. can be used, the general list of substances suitable for obtaining raw materials is quite significant. Leftover oil from cooking is also suitable for biodiesel production. A diagram of a similar process can be seen in the figure below.


Since we are considering fuel of vegetable origin, then the technology of its manufacture should cover the process of growing the raw material. The most suitable for this is considered to be rapeseed, as it requires less production costs. Although now there are great prospects for biodiesel from algae. At the same time, land is not used for growing crops for fuel, and the cost of biodiesel will be lower than in other cases. So, the seeds (rapeseed, soybeans, sunflower, etc.), after quality control, go to the churn. The meal remaining after the production of oil can be used by the feed industry, and the resulting oil, as provided by the technology, goes for further processing. It is called esterification, and after it, methyl esters in biodiesel should contain more than ninety-six percent. The technology itself is simple, which makes it possible to organize the production of biodiesel at home. Methanol (9: 1) is added to the oil, and a small amount of alkali is used as a catalyst. Methanol can be obtained from sawdust, and it is also allowed to use isopropyl alcohol or ethanol instead. The esterification procedure takes place at elevated temperatures and takes up to several hours. After the end of the reaction, liquid stratification is observed in the container - biodiesel on top, glycerin below. Glycerin is removed (drained from the bottom) and can be used as raw material in some other processes. The resulting biodiesel must be purified, sometimes evaporation, settling and subsequent filtration is quite enough. The industrial production process is shown in more detail in the video.
How is biofuel diesel produced?
The raw material for this type of fuel can be any crops from which a large amount of vegetable oil is obtained. Most often these are rapeseed and soybeans, their processing gives the maximum yield of raw materials and, accordingly, the final product in the form of biodiesel.


Animal fats, which are wastes from meat processing plants, tanneries and other enterprises, are also used. Burnt vegetable oils from restaurants and other food service establishments are also suitable.


It should be noted that biodiesel from vegetable and animal oils is produced using a relatively simple technology. The main stages of the technological process are as follows:
- rough and fine cleaning of raw materials (oil) from the smallest impurities;
- mixing oil and methyl alcohol with the addition of an alkaline catalyst in the reactor. The proportions of raw materials and methanol are 9: 1, the catalyst is sodium or potassium hydroxide;
- heating to 60 ° C and stirring at this temperature for about 2 hours. The stage is called esterification;
- the resulting substance is settled in a separate container and stratified into 2 substances - a glycerin fraction and biodiesel itself;
- Substances are separated in a separator, after which the fuel undergoes thermal treatment in order to evaporate water from it.

Technological equipment for the production of biodiesel is also not very complex and consists of several tanks connected by pipelines, as well as pumps - the main one and several dosing pumps. Since at the enterprises all stages are automated, the reactor and other tanks are equipped with temperature and level sensors, and the pumps are controlled by the controller. All data about the ongoing process are displayed on the operator's display.
Biodiesel at home
As can be seen from the description presented, the production technology is quite simple and allows you to make biodiesel with your own hands, to the point that you can get fuel at home, and sometimes not only for your own needs. The reasons why you can take on such work may vary for everyone, but without touching them, it is worth noting that the consumption of biodiesel is only growing all over the world. When biodiesel is made at home with your own hands, the main problem will not be the issue of its production, but the quality assurance of the finished product. The suppliers of raw materials can be catering establishments that have a sufficient amount of used oil and can be bought at an affordable price. Rapeseed cultivation is worth pursuing when biodiesel is consumed in large quantities, for example, for sale on the side or having a large fleet of equipment. When organizing production at home, the most pressing problems will be: ✔ Poor output, i.e. no more than ninety-three percent of the finished product is obtained from the initial raw materials. This may be due to the features of the installation used at home or the re-esterification modes. ✔ Poor filtration. Such a process is quite complicated, and in order to obtain high-quality biodiesel at home, special attention should be paid to it. For this, special technologies or adsorbents are used. Directly with the installation for the production of such fuel can be found in the video. There are other industrial biodiesel plant options available.
How to make a Recycling Farming Module?
In order to make a system for processing waste into biofuel, at least one must be aware of the principle of operation of such devices, as well as have an idea of the circuitry.
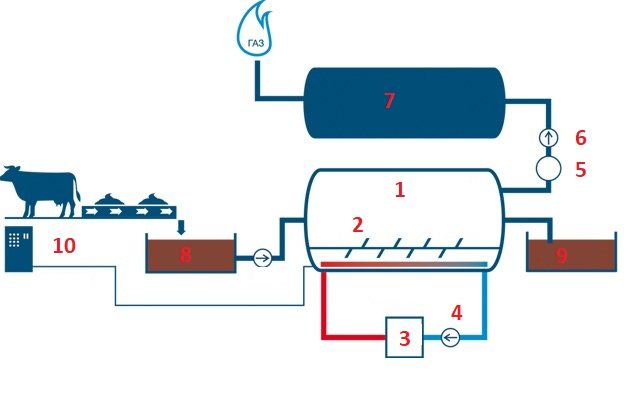

Diagram of the bioreactor unit: 1 - bioreactor; 2 - stirrer; 3 - heater; 4 - pump; 5 - filter element; 6 - gas compressor; 7 - gas holder; 8 - a collection of manure; 9 - the output of fertilizers (sludge); 10 - heating control panel
Let's consider both, but it should be noted: the construction of a full-fledged installation is a rather troublesome and costly business. At home, as a rule, it is possible to do only something similar to processing stations. However, some attempts have been successful.
The principle of operation of the biological plant
Biofuel production technology usually supports the following systems approach:
- The bioreactor (tank) is loaded with manure.
- For a certain time, the fermentation process takes place inside the reactor.
- A gaseous environment is formed.
- The gases are removed from the reactor.
- The gas mixture is purified and sent for use as fuel.
The composition of the gas mixture obtained at the outlet is characterized by a sufficiently high saturation with various substances. Methane (60%), carbon dioxide (35%) and other substances, including hydrogen sulphide (5%), are most present in the percentage.
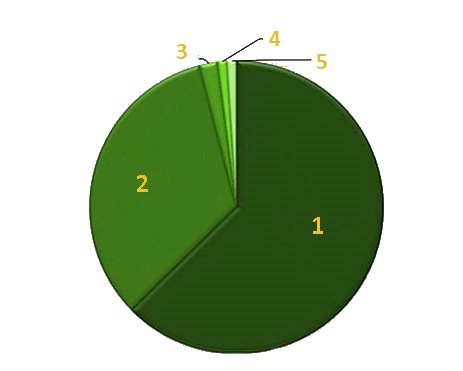

This is how the gas distribution diagram of the mixture looks like: 1 - methane content about 63-65%; 2 - the content of carbon dioxide is about 30-33%; 3 - the content of hydrogen sulfide is about 2%; 4 - the content of ammonia is about 1%; 5 - hydrogen content about 1%
Meanwhile, for the efficient operation of a gas-generating station of home production, significant reserves of waste from the representatives of the animal world are required.
Therefore, the first thing that should be paid attention to in solving the problem of obtaining biofuel in home (country) conditions is the availability of sources of raw materials for the processing plant.
Making a bioreactor with your own hands
Having decided on the sources of raw materials, then you need to decide on the site for the placement of the home (or country) bioreactor. The reactor itself is a sealed vessel, sufficiently strong, having a volume based on the daily intake of manure raw materials for processing (for reference: to obtain 100 m3 of a gas mixture, approximately 1 ton of manure is needed).
Table of the ratio of the type of manure and the amount of biogas produced
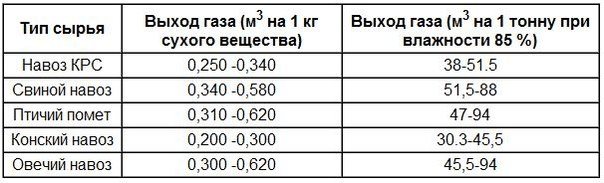

A table showing the efficiency of a particular type of biological waste in terms of the volume of gas produced. As can be seen from the table, the most efficient is pig manure, which can produce the largest amount of biofuel.
Such a container will have to be installed on a solid foundation, equipped with shut-off valves and other technical attributes according to the classical scheme. It is advisable to make the upper part of the vessel removable, with bolted fasteners and a sealing gasket.
To ensure the continuity of the cycle, the storage tank must be equipped with an artificial heating module. If in summer the efficiency of manure fermentation and the rate of gas formation are fully provided by external temperature conditions, in winter the situation changes.
For the winter operation of the bioreactor, artificial heating is required, given the cessation of the activity of fermentation bacteria already at 4-10 ° C above zero. Accordingly, the container must have high-quality thermal insulation. For this, the classic method of insulating with mineral wool is well suited.


An illustrative example of isolating a bioreactor for its winter operation. Mineral wool was used here as an insulating material. The top layer of cotton wool is covered with foil material
There are several options for organizing heating. For example, the use of electric heaters or a water-based heating system (water jacket).
The power of the heating circuit should be calculated based on the optimal temperature norm inside the reactor of 25-40 ° C, necessary to achieve an effective biomass fermentation process.
In addition to heaters, the degree of stagnation affects the fermentation activity of biomass. In fact, inside the tank, the raw manure must be constantly in motion. The movement of biomass enhances the fermentation process and reduces the time for obtaining the gas component.
Option for a summer installation for manure processing and biofuel production. In this case, the heating is made in the form of a concrete water bath, into which the reactor vessel is immersed.However, this installation cannot be operated during the winter period.
The problem of organizing the movement is solved by introducing a special mechanical stirrer into the design of the bioreactor. The shaft of this device is connected to the shaft of a low-speed motor, which carries out the rotation action. Turning on and off the mixing process can be done manually or automatically.
We have another article on our website, which provides instructions on how to install a biogas plant for the needs of a private house.
Biogas and fertilizer production process
The design of the biofuel production system at home technologically provides for loading the vessel with manure by about 1/3 of the capacity. For loading manure, a loading hatch with a hermetically closing door is made. The remaining free upper area of the bioreactor is used for the accumulation of emitted gases.


Homemade miniature bioreactor based on a conventional 200-liter barrel. In principle, to meet the modest needs for biofuel, it is quite suitable for use in private households. This is the very design that can actually be made at home for biofuel production.
Outlets must be made at the upper and lower levels of the vessel. Above is a gas outlet, below is an outlet for draining processed manure (fertilizers). Also, in the area of the upper region of the vessel, it is advisable to mount a viewing window to monitor the process.
The branch pipe for the outlet of the gas mixture is connected by a sealed pipe with a device that simultaneously performs the functions of a separator and a hydraulic seal. For communication, a pipe (metal or polyethylene) of small diameter (25-32 mm) is used.
The separator itself is a vessel of relatively small capacity, filled with water. Gas passing through the water column is purified, discharged into a gas tank and then supplied to consumers.
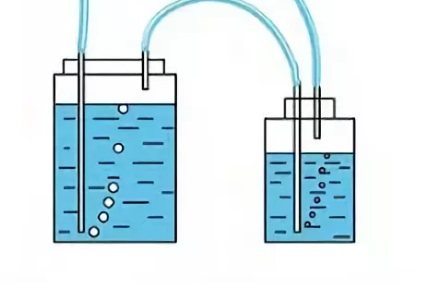

An example of a two-stage separator device - a hydraulic seal for supplying a gas mixture coming from a bioreactor. This filtration option allows you to get a high-quality purified product
The lower branch pipe on the reactor (for the outlet of spent manure - sludge) should preferably be made as large as possible. Shut-off valves (gate valve) are connected to it and a branch is made to the tank for collecting sludge. The spent mass on the farm can be successfully used as fertilizer.
Detailed information on determining the required volume of the tank, as well as on calculating the efficiency of the bioreactor and the feasibility of using biogas, we considered in the next article.
Perspectives
As already noted, the production of such fuel is only growing. And although vegetable oil serves as the raw material for this, it is obtained in different places from different cultures. In Europe - rapeseed, in Indonesia - palm oil, in America - soybeans, etc. However, the most promising is the production of biodiesel from algae. For their cultivation, both separate ponds and special bioreactors, as well as sections of the sea coast, can be used. In addition, this not only increases fuel production, but also frees up land for growing food. Although biodiesel is made from vegetable oil rather than sawdust, it is an excellent substitute for conventional diesel fuel. Especially with limited oil reserves. And besides, such dignity as the possibility of production at home cannot be ruled out. Despite the fact that in industrial production it turns out to be more expensive than diesel fuel, nevertheless, it is an excellent alternative fuel for diesel engines.
The chemical process for producing biodiesel
To obtain biodiesel, all types of vegetable oils are used - sunflower, rapeseed, linseed, etc. At the same time, biodiesel obtained from different oils has some differences.For example, palm biodiesel has the highest calorific value, but also the highest filterability and solidification temperature. Rapeseed biodiesel is somewhat inferior to palm biodiesel in terms of calorie content, but it tolerates cold better, therefore it is most suitable for European countries and Russia. Chemically, biodiesel is methyl ether, which is a product of the esterification reaction of vegetable oil at a temperature of about 50 C in the presence of a catalyst. The process itself is, in principle, quite simple. It is necessary to reduce the viscosity of the vegetable oil, which can be achieved in various ways. Any vegetable oil is a mixture of triglycerides, i.e. esters combined with a glycerol molecule with a trihydric alcohol (C3H8O3
). It is glycerin that gives the viscosity and density to the vegetable oil. The challenge in biodiesel preparation is to remove glycerin by replacing it with alcohol. This process is called
transesterification
... The general reaction looks like this:
CH2OC = OR1 | CHOC = OR2 + 3 CH3OH> (CH2OH) 2CH-OH + CH3COO-R1 + CH3COO-R2 + CH3OC = O-R3 | CH2COOR3 |
Triglycerides + methanol> glycerol + ethers, MA "Navigator" Technologies and equipment for the production of biodiesel 10 Where R1, R2, R3: alkyl groups. As a result of the use of methanol, methyl ether is formed, as a result of the use of ethanol, ethyl ether. From one ton of vegetable oil and 111 kg of alcohol (in the presence of 12 kg of catalyst), approximately 970 kg (1100 L) of biodiesel and 153 kg of primary glycerin are obtained. As an alkali, potassium hydroxide KOH or sodium hydroxide - NaOH is taken. NaOH is recommended for beginners.
Benefits of biodiesel
The main advantage of biodiesel
- this is that it is produced from resources that are quickly restored (oil reserves, for example, are practically irreplaceable). For example, this issue is very relevant for collective farms that are engaged in oil processing, everyone has a sore point of where to get diesel fuel by the beginning of the season. The answer is simple, make biodiesel from your own raw materials and be completely autonomous in fuel consumption.
Plant origin
... We emphasize that biodiesel does not have a benzene odor and is made from oils, the raw material for which are plants that improve the structural and chemical composition of soils in crop rotation systems. The raw materials for the production of biodiesel can be various vegetable oils: sunflower, rapeseed, soybean, peanut, palm, cottonseed, linseed, coconut, corn, mustard, castor, hemp, sesame, waste oils (used, for example, in cooking), and animal fats.
Ecology
... The strong point of biodiesel is also that it emits much less harmful gases into the atmosphere during combustion (biodiesel, in comparison with its mineral analogue, contains almost no sulfur (Biological harmlessness. Compared to mineral oil, 1 liter of which is capable of contaminating 1 million liters of drinking water and lead to the death of aquatic flora and fauna, biodiesel, as experiments show, when it gets into water does not harm either plants or animals.In addition, it undergoes almost complete biological decomposition: in soil or water, microorganisms process 99% of biodiesel per month , which allows us to talk about minimizing pollution of rivers and lakes when transferring water transport to alternative fuels.
Less CO2 emissions
... When biodiesel is burned, exactly the same amount of carbon dioxide is released that was consumed from the atmosphere by the plant, which is the initial raw material for the production of oil, over the entire period of its life. However, it should be noted that it would be incorrect to call biodiesel an environmentally friendly fuel. It emits less carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than conventional diesel fuel, but still it is not zero emissions.
Good lubricating properties
... It is known that mineral diesel fuel, when sulfur compounds are removed from it, loses its lubricating ability. Biodiesel, in spite of the significantly lower sulfur content, is characterized by good lubricating properties. This is due to its chemical composition and oxygen content. For example, a truck from Germany made it into the Guinness Book of Records, having traveled more than 1.25 million kilometers on biodiesel with its original engine.
Increased engine life
... When the engine is running on biodiesel, its moving parts are simultaneously lubricated, as a result of which, as tests show, an increase in the service life of the engine itself and the fuel pump is achieved by an average of 60%. It is important to note that there is no need to upgrade the engine.
High flash point
... Another technical indicator of interest to organizations that store and transport fuels and lubricants: the flash point. For biodiesel, its value exceeds 150 ° C, which allows us to call biofuel a relatively safe substance. However, this does not mean that it can be treated with negligence.

DIY biofuels: biofuel production, pros and cons of self-production
Interested in information on how to make biofuels with your own hands and how much is it possible? Then read below about what biofuels are, what raw materials it can be obtained from, and what technologies are used for this.
The issues of providing your personal household with the energy resources necessary for its functioning is a problem that, to one degree or another, arises before any owner. Often, difficulties even lie in the impossibility of bringing the appropriate communications, for example, in the absence of gas distribution networks in the area of residence. But all the same, if we consider everything in a complex, then the main problems are high tariffs for energy carriers, which often call into question the profitability of the household economy. Unfortunately, even the fall in prices for the main sources of energy in the world market does not in any way affect the end consumer - tariffs remain at the same level and even tend to grow.


DIY biofuel
Naturally, in such a situation, more and more owners begin to think about the possibilities of using alternative energy sources. In particular, there is a lot of talk now about biofuels - high-calorie energy carriers (liquid, solid or gaseous), which are obtained by processing raw materials, often literally "lying underfoot". In particular, many are interested in the question of how realistic it is to make such biofuel with their own hands, in a small private economy.
There are a lot of opinions on this matter, up to such that it is literally "a pair of trifles" to establish such a mini-production. Can you believe such optimistic assurances? Most likely not - any biofuel will require special, often very expensive equipment, the necessary knowledge and skills, and a constant source of raw materials. Let's understand in more detail ...
What is biofuel and where does it come from?
Almost all the energy resources produced on the planet are the product of many years of natural processing of organic matter. Complex biochemical processes that took place in the layers of obsolete plants and in the remains of animals, under the influence of external factors (temperature, pressure), over time led to the formation of coal deposits, oil-bearing layers, to the accumulation of combustible gases in the soil. It is these natural resources that are to this day the main energy sources used by man.


Energy extraction is often carried out under the most extreme conditions
The problem is that all these resources are not unlimited, and their quantity is decreasing from year to year. They practically do not recover (this takes many millions of years). All of them, in the overwhelming majority, lie at great depths, often in hard-to-reach places (in the Arctic regions or on the sea shelves), their production requires the use of complex technologies, and in addition to this, transportation issues are also quite difficult.
In a word, such problems, obviously, will only grow over time, and mankind has no choice but to consider the possibilities of alternative energy sources. Bioenergy is currently being considered as one of the most promising areas.
Indeed, the laws of biochemistry do not change, organic matter is a renewable type of raw material, so why not artificially, in a short time, carry out the very processes of obtaining energy carriers? Moreover, as raw materials, you can use not only specially grown crops, but also a variety of biological and technological waste, along the way solving the issue of their disposal.


Raw materials for the production of biofuels are often literally lying underfoot.
The table below shows schematically the main directions in the production and associated use of biofuel. I must say that such approaches can be applied both on a large scale and in rather isolated, autonomous systems, for example, medium or small agricultural complexes.
| Raw materials for processing | Technological lines | Received product | Recycled or recycled product |
| Agricultural livestock waste, fodder residues | Biogas plants | Biogas (biomethane) | Providing livestock complexes with "free" electricity |
| Providing autonomous heating | |||
| Environmentally friendly organic fertilizers | |||
| Industrial crops with a high oil content (sunflower, rapeseed, soybeans, corn, etc.) | Processing lines | Bioethanol (alcohol) | |
| Vegetable technical oil | Biodiesel | ||
| Agricultural waste (crop and food production) | Distillation and pyrolysis plants | Gaseous fuels (pyrolysis gases) | Electricity |
| Thermal energy | |||
| Liquid fuels (alcohols) | |||
| Waste from the wood processing industry | Pyrolysis plants | Gaseous fuels (pyrolysis gases) | Electricity |
| Thermal energy | |||
| Granulation plants | Fuel briquettes (pellets) |
Some countries with developed agro-technical infrastructure are elevating the production of biofuels to the rank of global national programs. A striking example is Brazil, where the introduction of technologies for the production of alternative fuels is proceeding by leaps and bounds, and it is likely that this country will soon be able to claim the title of one of the largest suppliers of such energy carriers.


In Brazil and many other countries, biofuel dispensers are no longer surprising.
However, let's return to our "native lands". In our conditions, it is also quite possible to produce almost any type of biological fuel, using either raw materials specially grown for these purposes, or using technologies for processing waste from agricultural, food production, logging or woodworking industries. In particular, we can consider the process of creating liquid biofuel (biodiesel) and solid (fuel pellets).
Prices for fuel blocks and biofuels for biofireplaces
Fuel blocks and biofuels for biofireplaces
Biodiesel production
The advantages of biodiesel and the basics of its production
Is it possible to obtain diesel fuel - diesel fuel, a product obtained by rectification, that is, direct distillation of oil - from vegetable raw materials? It turns out, quite, since the molecular structure of vegetable and animal oils is very similar to classic diesel fuel.
These are, in fact, the same "long" hydrocarbon molecules, but not in a free linear state, but linked into "triads" by a transverse framework of fatty acids - glycerol. This means that in order to extract exactly the energy combustible component from the oil, you need to clean it from glycerin. This is what the technological process for producing biodiesel consists of.
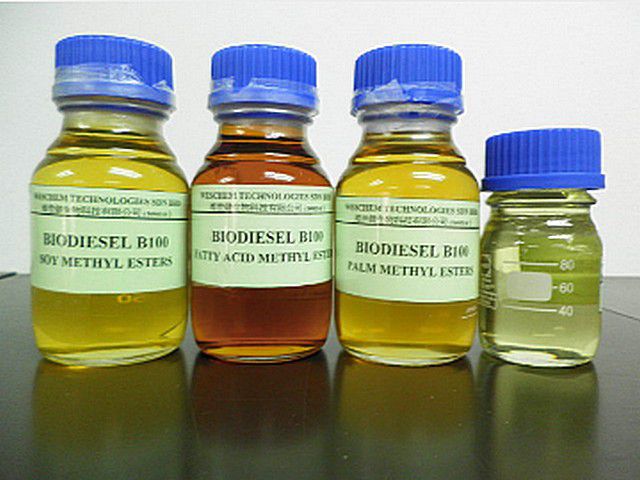


Biodiesel from different grades of oil
As a result, you should get a yellow (with a possible tint variety) liquid that does not have that specific smell that is characteristic of the usual diesel fuel. Nevertheless, this is a ready-made fuel that can be used both in its pure form and as an additive to "classic" diesel fuel. Interestingly, conventional diesel engines do not need any modification when switching even to pure biodiesel.
(Most often, due to the high freezing point temperature, biodiesel is used in a mixture with ordinary diesel fuel, and the resulting fuel is usually indicated by the letter "B" with a number that indicates the percentage of the biological component of the fuel from the total volume. For example, the most common fuel "B20" - 20% biodiesel and 80% diesel fuel).
At the same time, such biofuel, while keeping up with its calorific value, even differs in many ways from an oil refined product for the better:
- Such fuel has a pronounced lubricating effect, which significantly prolongs the life of diesel engine parts.
- Such fuel contains practically no sulfur, which oxidizes engine oil, quickly removing it from a state of suitability, and "eats" rubber seals, and is simply extremely harmful to the environment, where it gets as a result of exhaust.
- The flash point of biodiesel is significantly higher than that of conventional diesel fuel (about 150 ° C). This means that biofuels are much safer to store, transport and use. The toxicity of such fuel is much lower than that obtained from oil refining.
- One of the basic metrics of diesel fuel is the "cetane number", which is the ability of hot to ignite when compressed. The higher it is, the better the fuel is, the smoother the engine runs and the less wear out of its parts. If for ordinary diesel fuel this indicator starts from 40 - 42, then for biodiesel the cetane number is lower than 51 and does not occur (by the way, according to European quality standards, the cetane number in any diesel fuel used in the European Union must be brought to no lower than 51) ...
The disadvantages of biodiesel include a higher temperature of the onset of crystallization (usually such fuel requires preliminary heating) and a relatively short period of possible storage of the finished product (usually up to 3 months).
High-yielding oil-containing crops - for example, sunflower, soybeans, corn - are used as raw materials for the industrial production of technical vegetable oil, and then - biodiesel.


Products for the production of technical vegetable oils - raw materials for the production of biodiesel
Recently, rapeseed has begun to gain particular attention from farmers, due to its extremely high yield, unpretentiousness, and besides, it depletes the soil to a much lesser extent of all the listed crops.


One of the most promising industrial crops is rapeseed
However, the trends in the development of biodiesel production are such that it is considered inappropriate to occupy valuable cultivated areas for it, which may be more in demand for food purposes.Farms for growing green algae of special species, which grow extremely quickly and provide biological material with excellent energy content, are becoming the most promising direction.
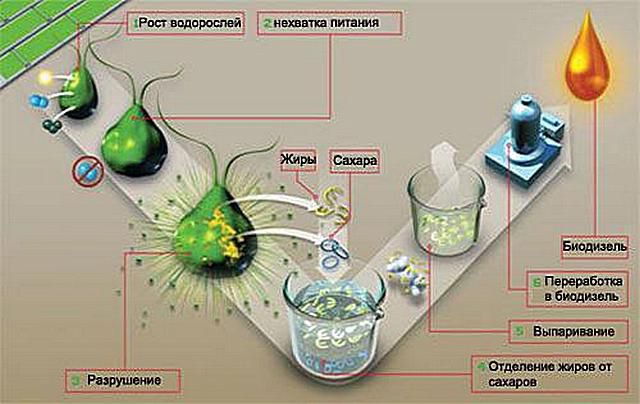

From green algae to complete fuel
When certain conditions are created for the growth and life of algae in artificial reservoirs (bioreactors), they actively accumulate vegetable fats and sugars, which then, during processing, become the initial product for obtaining a combustible hydrocarbon. By and large, only the equipment itself is high in price, and algae need only water, sunlight and carbon dioxide for active growth.


This is what plants for the production of biodiesel from green algae will look like
Used for the production of biodiesel and other oils - palm, coconut, as well as animal fats, as a rule - in the form of waste from the processing or food industries.
What is the process of "breaking" the hydrocarbon chain from the unnecessary glycerin base? You just need to replace this dense binder with another, more chemically active and volatile. Methanol (methanol) is best suited as such a reagent. It is itself a highly flammable substance and even in some cases can be used as a completely separate type of fuel, therefore it will not in any way reduce the properties of biodiesel.
The chemical process of displacing the glycerol component (in the scientific literature, this procedure is called peresterification) should go on by itself, but it is not irreversible - the substance can go both into the required state and again into the initial state. In order to avoid such instability and to speed up the process, a catalyst is used. Alkalis (NaOH or KOH) are most often used as it. For maximum uniformity of the exchange process, the processed mixture is subjected to constant stirring and heating to a temperature of about 50 degrees.
Usually, depending on the volume and quality of the initial products, the process can take from 1 to 10 hours. As a result, the mixture should give a pronounced stratification. In the upper part of the reactor (the vessel where the process took place), a light fraction remains - in fact, the biodiesel itself. At the bottom there is a pronounced dense mass - a glycerin component.
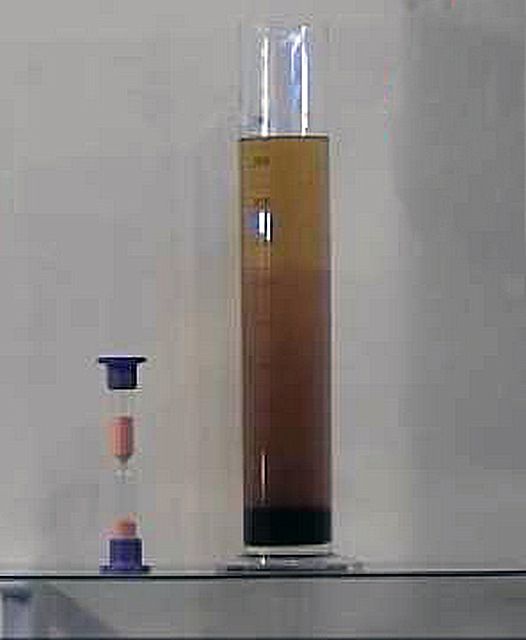


Layering of the composition after transesterification
Now it remains to separate the biodiesel, clean it up from excess methanol and catalyst residues. The remaining glycerol fraction is also subjected to a purification process, since glycerol itself is a very valuable product with a wide range of applications.
Expert opinion: A.V. Masalsky
Editor of the "construction" category on the Stroyday.ru portal. Specialist in engineering systems and drainage.
The optimal dosage of the components is considered as follows: to process a ton of vegetable oil, 111 kg of methyl alcohol and about 12 kg of a catalyst - sodium or potassium hydroxide are required. If the process technology is followed, the output should be approximately 970 kg (or 1110 liters) of finished purified biodiesel and 153 kg of glycerin.
You can, of course, describe a complex chemical formula, but it is unlikely to say anything useful to the reader. It is better to give a visual flowchart of the production process, so that it becomes clear how difficult it is to carry out all operations with high quality.
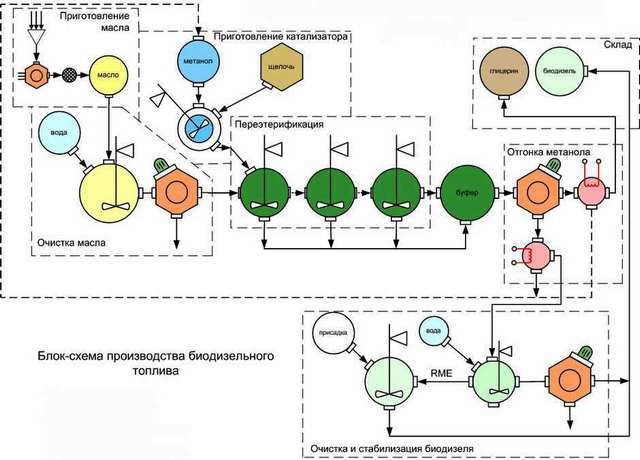

Flow chart of a typical biodiesel production process
Vegetable oil is either squeezed in place, or comes in finished form, or fatty waste from food production is used. After the purification process, it enters the transesterification reactors. A prepared mixture of catalyst and reagent, methanol, is supplied there through its own channel. Further, there are technological cycles of separation of fractions and their multistage purification.As a result, biodiesel and refined glycerin are delivered to the warehouse as the final product, and the recovered methanol surplus is returned for reuse.
Is it possible to produce it yourself?
It would seem that everything is simple and clear, but it is in a well-thought-out technological line. But is it possible to make biodiesel yourself?
1. First, one must immediately clearly realize that this organization of such a mini-production will be justified only if there is a reliable and practically inexhaustible source of raw materials - vegetable or animal fats of the required degree of purification. For example, if there is an opportunity at food enterprises or in public catering establishments for a very low amount to buy up the remains of used oil. To produce oil on their own by growing the appropriate crops for this or by purchasing seeds for pressing - on the scale of a personal economy, such a prospect should not even be considered, since the business will be deliberately unprofitable.
2. The next important aspect is the considerable difficulties in working with chemical components.
- Alkaline compounds are very hygroscopic, instantly absorb moisture, that is, their storage becomes a considerable problem. This is also taking into account the fact that sodium and potassium hydroxides are extremely "aggressive" substances and easily react with most metals. Therefore, they can only be stored in stainless or glass containers, or polypropylene containers.
- Methanol will also create a lot of problems. First of all, you need to constantly remember about its highest toxicity - poisoning with such alcohol is often fatal. (Special attention if there are people in the house with an addiction to alcohol - methanol in appearance and smell differs little from ethyl, "wine" alcohol). All work with methanol must be carried out with mandatory protection of the respiratory system, eyes, skin, mucous membranes.
Of course, the reaction can be carried out with safer ethyl alcohol, but in the end the fuel is denser and more viscous, its quality for refueling engines is significantly lower.
- By handicraft, "by eye", it is very difficult to maintain the correct dosage of the starting components and determine their quality.
- It is usually assumed that the above ratio of methanol and oil for the normal course of the reaction may be insufficient - it largely depends on the biochemical composition of the purchased raw materials. Therefore, methanol is always added in excess, about 1: 4 by volume to oil. Alas, it is impossible to calculate more precisely without laboratory research.
- Earlier, it was not for nothing that it was mentioned that the raw materials should be of a certain degree of "purity" - if you use at random any obtained fat or oil waste, you can not only not get the desired biodiesel at the output, but also seriously "screw up" the equipment. For example, if the oil contains too much water, then it will simply destroy the catalyst, the process will get out of control, and soap will begin to form in the reactor instead of the expected biodiesel (the so-called saponification). Moreover, if NaOH was used, then, most likely, it will be possible to "catch a glop" - the soap quickly thickens and fills the entire volume of the reactor, completely absorbing the unreacted oil.
In enterprises, special drying agents are used to remove excess water, which are then, after processing, removed by filtration. Water can be removed at home, of course, by the usual preheating of the oil to 110 ÷ 120 degrees - the water should evaporate and evaporate. However, heating the oil often leads to another "nuisance" - an increase in the concentration of free fatty acids. This is the next point.
- The second vulnerability of the feedstock is the concentration of free fatty acids (FFA) - there are certain technological limitations on their content. Such a disadvantage - an increased concentration of FFA, is usually characteristic of food waste, that is, oils that have already been heat-treated, since these acids themselves are a product of the thermal decomposition of oils. When reacted with a catalyst, FFAs are converted into water and soap, the dangers of which have already been mentioned above. On technological lines, this issue is solved by analyzing the incoming raw materials and developing an appropriate formulation for the optimal percentage of the catalyst.
So, the oil for processing should contain a minimum amount of water and FFA. But at home, it is hardly possible to carry out the necessary laboratory research. That is, the manufacturer risks very much both the quality of the product and the safety of its own equipment.
3. The third "block of problems" is the equipment required for the process. Although there are descriptions and photographs of self-made "lines" for the production of biodiesel on the web, call them successful, convenient, etc. - does not work.
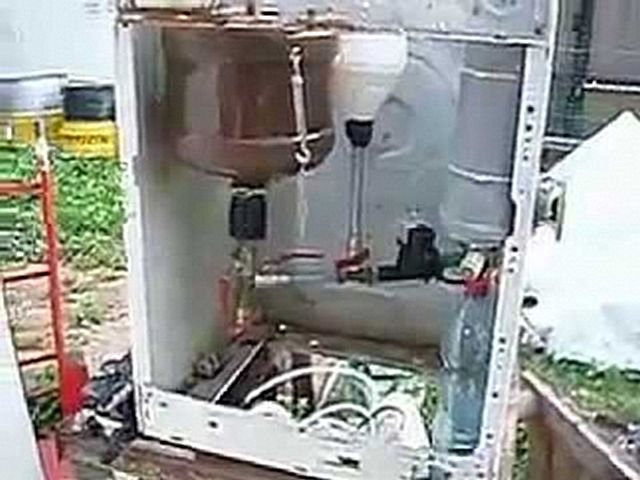


Unfortunately, handicraft devices are still very far from perfect.
You can pay tribute to the authors for originality, for the use of the most unexpected parts and assemblies, for example, old washing machines or refrigerators, for interesting solutions to the problems of separation and cleaning of the final product, but still claim some kind of "breakthrough" model of the installation recommended for self-production, it is impossible.
Video - An example of a home-made installation for producing biodiesel
One of the most difficult and laborious processes is the separation of the glycerin-containing fraction from biodiesel, and then - cleaning the fuel from soap residues, alkaline constituents, and excess methanol. By the way, methanol is a very expensive raw material, and simply evaporating it into the atmosphere is extremely unprofitable. This means that with its increased volatility, special purification sealed chambers are needed, allowing the distillation process to be carried out without losses.
The soap component is separated by settling, water washing, followed by filtration and evaporation of excess. To remove alkalis, acidified compounds (for example, acetic acid) are used.
Some home craftsmen prefer the installation of a special aeration column, in which biodiesel is settled and, with the help of air bubbles artificially created by a compressor, it is cleared of chemical impurities. A similar example is shown in the continuation of the video:
Video - How to make biodiesel
In a word, it is hardly necessary to talk about the high (or at least some) profitability of such handicraft production. The productivity of such installations is low, it is impossible to organize a continuous cycle, home-made equipment requires almost constant monitoring by a person. And the quality of the resulting biodiesel is difficult to control. That is, for the needs of a personal economy, for refueling your own car (at your own peril and risk), this can be used, but won't such fuel become more expensive than ordinary diesel fuel?
And if you consider the organization of biofuel production as your own business, then in this case you cannot do without the acquisition of special technological units.
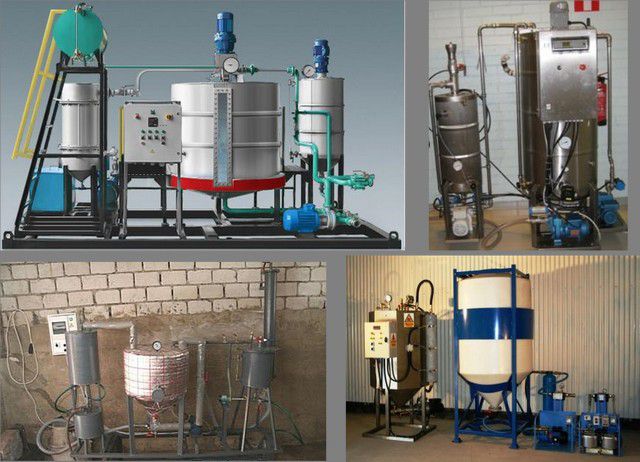


Many models of mini-lines for the production of biodiesel are presented to the attention of interested people.
If you set a goal, it will not be so difficult to find the necessary production mini-complex that is optimal for the available space. There are many similar technological installations on Internet sites, differing in power consumption, productivity, degree of automation, the number of operators required to service them, and, of course, in the cost of equipment. Both domestic and European companies have mastered the production of biodiesel production lines.
Video: automated modular biodiesel production line
Solid biofuel - pellets
Recently, there are a lot of various rumors or even a kind of "legends" that one of the most promising and highly profitable types of small business can be the production of fuel pellets - a special type of biological fuel. Let's take a closer look at the merits of solid granular fuel and the process for its production.
Why and how are fuel pellets produced?
Logging, woodworking enterprises, agricultural complexes, some other production lines necessarily produce, in addition to the main products, a very large amount of wood or other plant waste, which, it would seem, no longer have any practical value. Not so long ago they were simply burned, throwing smoke into the atmosphere, or even wastefully decomposed by huge "waste heaps". But they have a huge energy potential! If this waste is brought into a state that is convenient for use as a fuel, then, along with solving the problem of disposal, you can also make a profit! It is on these principles that the production of solid biofuel - pellets is based.
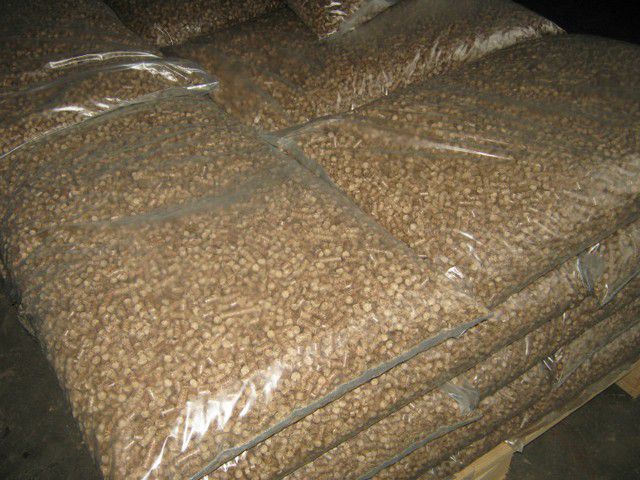


Pellets are extremely convenient to store, transport, use
In fact, these are compressed cylindrical granules with a diameter from 4 ÷ 5 to 9 ÷ 10 mm, and a length of about 15 ÷ 50 mm. This form of release is very convenient - the pellets are easily packed into bags, they are easy to transport, they are excellent for automatic fuel supply to solid fuel boilers, for example, using a screw loader.
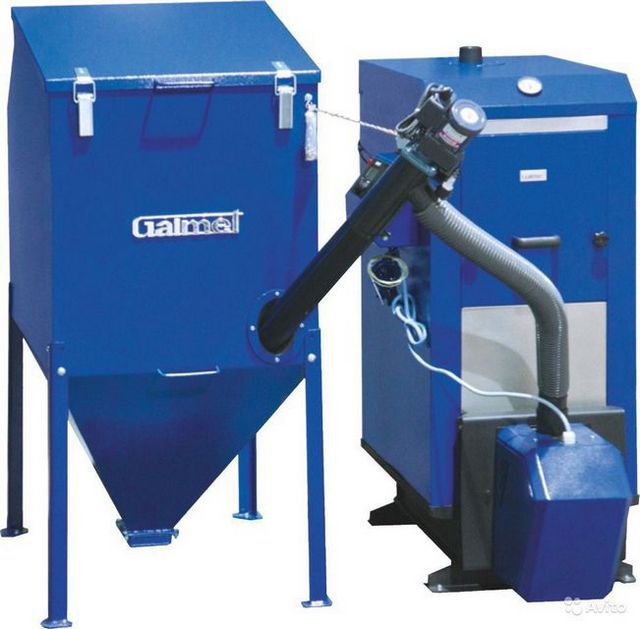


Pellet boilers have the ability to automatically feed fuel from the bunker
Pellets are pressed both from natural wood waste and from bark, branches, needles, dry leaves and other by-products of logging. They are obtained from straw, husk, cake, and in some cases even chicken manure is used as raw material. In the production of pellets, peat is started up - it is in this form that it achieves maximum heat transfer during combustion.


Pellets can be produced from a variety of materials.
Of course, different raw materials give different characteristics of the resulting pellets - in terms of their energy output, ash content (the amount of the remaining non-combustible component), humidity, density, and price. The higher the quality, the less hassle with heating devices, the higher the efficiency of the heating system.
Some pellets can be used not only as fuel, but also as fertilizer or composition for mulching the soil. Nevertheless, their main purpose, of course, is fuel for boilers, and here they have many pronounced advantages over other types of solid fuels. So, for example, this is an absolutely clean type of fuel from the point of view of ecology. No chemical additives or molding sands are used in the pellet production process.
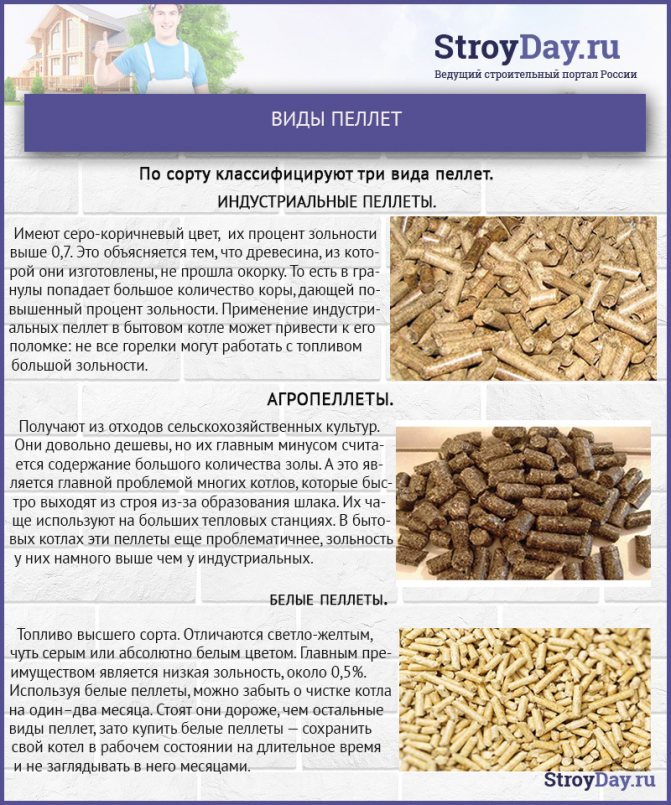

Pellet types and description
Expert opinion: A.V. Masalsky
Editor of the "construction" category on the Stroyday.ru portal. Specialist in engineering systems and drainage.
According to their specific caloric content (in terms of volume), pellets leave behind all types of firewood and coal. The storage of such fuel does not require large areas or the creation of any special conditions. Compressed wood, unlike sawdust, never begins to decay or debate, so there is no risk of spontaneous combustion of such biofuel.
Now - to the issue of pellet production. In fact, the whole cycle is simply and clearly depicted in the diagram (agricultural raw materials are shown, but this applies equally to any wood waste):


"Short course" on the production of pellets
First of all, the waste goes through a crushing stage (usually up to a chip size of up to 50 mm in length and 2 ÷ 3 mm in thickness). This is followed by a drying procedure - it is necessary that the residual moisture does not exceed 12%.If necessary, the chips are crushed into an even finer fraction, bringing its state almost to the level of wood flour. It is considered optimal if the particle size entering the pellet pressing line is within 4 mm.
Before the raw material enters the granulators, it is lightly steamed or briefly immersed in water. And, finally, on the pellet pressing line, this "wood flour" is pressed through the calibration holes of a special matrix, which have a conical shape. This configuration of the channels contributes to the maximum compression of the crushed wood with, of course, its sharp heating. At the same time, the lignin substance present in any cellulose-containing structure reliably "glues" all the smallest particles, creating a very dense and durable granule.
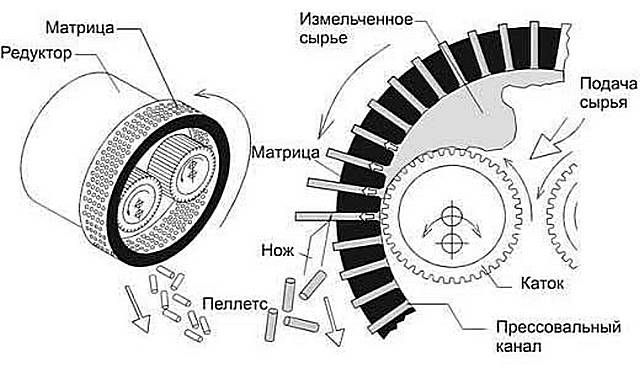

Formation of pellets in a cylindrical matrix
At the exit from the matrix, the resulting "sausages" are cut with a special knife, which gives cylindrical granules of the required length. They go to the hopper, and from there to the receiver of finished pellets. In fact, all that remains is to cool the finished granules and pack them into bags.
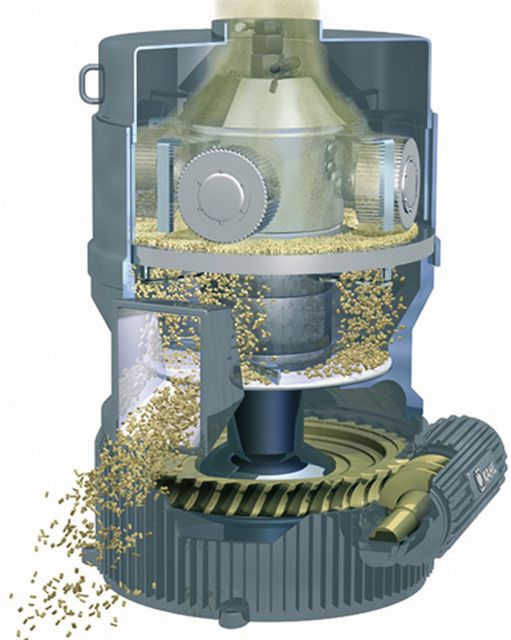


The scheme of the apparatus with a flat matrix
Matrices can be cylindrical or flat. The first ones are more productive, they are used mainly in powerful industrial installations. On small granulators, which are more often used on individual households, they are usually flat.
Video: small production for processing wood waste into pellets
But what about a "private owner"?
So, everything seems to be simple. But this "simplicity" is for streamlined production, but is it worth starting such a process yourself?
1. First of all, you need to very carefully "look around" from the point of view of the source of raw materials for private production.
- If there is any woodworking plant (large workshop) nearby, and there you can get ready-made sawdust on a regular basis at “ridiculous” prices or even free of charge, in the order of self-pickup, then it is worth trying. Most likely, all the initial costs will soon be justified - there will be an opportunity not only to fully provide themselves with granular biofuel, but also to realize the surplus.


If you manage to find such a supplier - then it will work!
It is quite clear that the presence of a pellet line will be very beneficial if the owner himself deals with woodworking issues, and sawdust on the farm, as they say, "is not transferred."
- It is worse if only large wood waste is available - in this case, you will have to think over the issue of crushing it, and this is already unnecessary costs for equipment and electricity.
- If the calculation is based on voluntaristic assumptions - “what I find, I will process it”, then, most likely, nothing good will come of it. Equipment for pelletizing is not cheap, and it is unlikely that it will ever justify itself with this approach.
When assessing the possibilities of obtaining raw materials, it is necessary to evaluate the species of wood. It is hardly worth getting in touch with poplar or willow - not only is the wood itself low in calories, it also does not sinter well into granules due to its low lignin content. Linden is also not a good choice. But sawdust from conifers, due to the high resin content, is suitable for everyone, without exception.
2. The next big issue is the hardware problem.
Actually, there are no special problems with this - there are many installations of various capacities and performances, domestic, European or Chinese assemblies on sale. Calling them cheap is probably impossible. Which of them is better or worse is also difficult to judge, it is better to delve into this topic in the Internet forums.
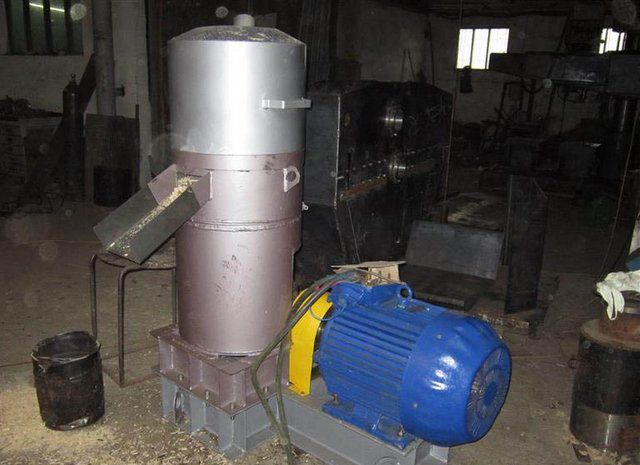


Prefabricated Pellet Machine
In the same place, on the forums, you can find the proposals of the masters who are engaged in the manufacture of custom-made granulators. They have proven schemes, their own drawings, experience in assembling and setting up installations.It is possible that such a device will be much more attractive for the price than the factory one.
Video: 4 kW fixed flat die pellet mill model
But about self-production - a very controversial issue. First of all, it is almost impossible to get ready-made drawings of such products - except perhaps to copy from the assembled device. Craftsmen who have mastered the production of such installations are unlikely to share all the nuances of design and assembly.
The second difficulty is that moving and stationary parts in the granulation chamber experience enormous loads, and it is almost impossible to correctly calculate them without the appropriate knowledge of strength materials and applied mechanics. To do it "by eye" - will not work.
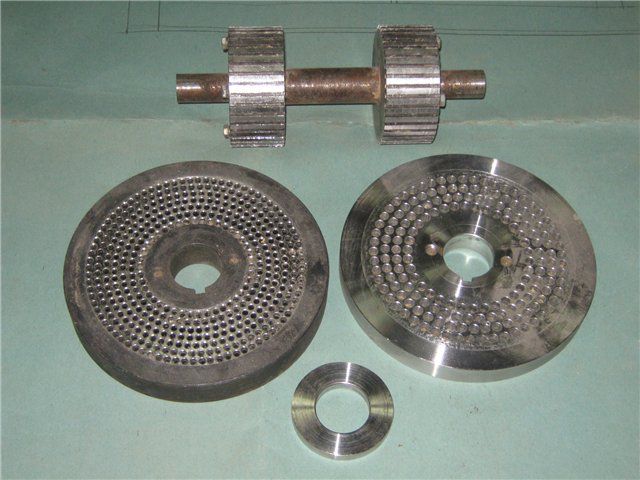


The main parts of the granulator are die and crushing rollers
The main parts - die and crushing rollers - can be purchased ready-made. But to execute the body itself, mount it on the bed, install an electric drive, think over a transmission system with the required gear ratio, precisely adjust all parts and assemblies - this requires the extraordinary abilities of a locksmith, mechanic, milling machine operator, turner ...
Of course, if you have complete confidence in your abilities, then you can try - there are examples on the Internet in which home craftsmen boast of their successes. Moreover, some even manage to get away from conventional schemes and change the design, making it simpler, but without losing the installation possibilities.
Perhaps the video below for someone will be the starting point in the development and manufacture of your own pellet granulator:
Video: how a compact pellet granulator works
In conclusion, the following can be noted.
On the scale of one publication, it is simply impossible to even briefly go through all the modern methods of making biofuels. Thus, the issues of the production and use of biogas from animal waste, the production of bioethanol from plant raw materials deserve separate articles. If the reader has interesting information on these issues, we will be happy to publish it on our portal. In any case, these topics will also not be left without consideration.
Stay tuned!