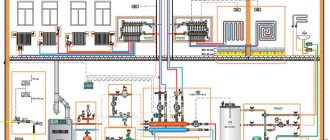
Heat consumption for ventilation
To find out how much heat is lost in a private house as a whole, it is necessary to add up the losses of all its rooms. But that's not all, because it is necessary to take into account the heating of the ventilation air, which is also provided by the heating system. In order not to go into the jungle of complex calculations, it is proposed to find out this heat consumption using a simple formula:
Qair = cm (tв - tн), where:
- Qair - the required amount of heat for ventilation, W;
- m is the amount of air by mass, defined as the internal volume of the building multiplied by the density of the air mixture, kg;
- (tв - tн) - as in the previous formula;
- с - heat capacity of air masses, taken equal to 0.28 W / (kg ºС).
To determine the heat demand of the entire building, it remains to add the value of QTP for the house as a whole with the value of Qair. The power of the boiler is taken with a margin for the optimal operating mode, that is, with a coefficient of 1.3. An important point must be taken into account here: if you plan to use a heat generator not only for heating, but also for heating water for hot water supply, then the power reserve must be increased. The boiler must work effectively in 2 directions at once, and therefore the safety factor must be taken at least 1.5.
Nuances and subtleties
Those who have a desire to make homemade heating should remember that only those types of pipes should be used that have a small diameter, since only they can maintain a high water temperature and effectively create and maintain the required temperature regime in the Russian climate.
However, they also have their drawbacks. In particular, the installation of hot water heating, due to the small diameter of the pipes, cannot be carried out without preliminary overhaul of the entire room. In addition, as for the water heating system itself, it requires constant heating of the coolant.
Therefore, if you forgot to drain the water from the pipes of your private house in the winter season and left it for a long time, then you should expect trouble, because under the influence of low temperature the pipes can simply break. As a result, upon your return, you will be forced to repair the entire water heating system, since the main part of the pipeline will be damaged.
But even if you do not forget to drain water from heating pipes with a small diameter, they can still suffer from the effects of corrosion, since the presence of air will take place, which will lead to the formation of internal condensation on the walls of the pipeline.
Water heating of a country house is an affordable cost of materials for installation and further operation, as well as good results in creating warmth and comfort in the house.
Basic ship systems. Appointments.
Previous85Next
Ship systems are a set of specialized pipelines with mechanisms and apparatus, instruments, devices and containers, etc., intended for the movement and storage of liquids or gases in order to ensure production activities, create habitable conditions, to fight for the survivability of the vessel. The number of ship systems can be different and depends on the size of the ship, its type and purpose.
Classification of ship systems by purpose and character, functions performed by them.
| System group | Composition | Appointment |
| Bilge | Drainage Ballast Drainage | Removal of small masses of water accumulating in the compartments of the vessel. Change in draft, roll and trim of the vessel.Removal of large masses of water entering the ship's hull as a result of a breach. |
| Fireproof | Fire alarm Water fire Steam extinguishing Foam extinguishing | Fire source detection Fire extinguishing Fire extinguishing Fire extinguishing with chemical and air-mechanical foam |
| Sanitary | Water supply Wastewater | Supply of drinking, washing and sea water to the places of consumption. Removal of faecal and waste water from sanitary facilities and premises |
| Artificial climate | Heating Ventilation Air conditioning | Heating of residential and office premises. Creation of the necessary air exchange in the premises. Maintaining the specified air parameters in the ship's premises. |
Bilge systems.
Dehumidification system
The purpose of this system is to remove moisture accumulated there from the bottom of the hull, from bilges through leaks of various joints, as a result of sweating, water spills during cleaning and for other reasons. Seawater inflow can be caused by the appearance of leaks in the hull of the ship, therefore control over the water level in the bilges is an important responsibility of the watch service. In bilges, inlet pipes are located at the aft bulkheads of the compartments and end with safety nets - snoring. The use of non-return valves in the drainage system eliminates the possibility of flooding the compartments through the drainage system.
In case of emergency water flow, more powerful drainage means are activated. There is also a system for bypassing water from rooms or compartments where there are no drainage or drainage means to other rooms where such means are available.
The drainage pipeline runs outside the double bottom space inside or over the cheekbones. In the latter case, it is protected by a wooden casing. The discharge line is led overboard at a height of about 300mm above the load waterline.
Bilge systems are serviced by piston, vane and centrifugal pumps, and on small ships - by ejectors. Each transport ship must have at least 2 autonomous bilge pumps. All bilge pumps are included in the bilge system so that each of them can pump water from any compartment. On the pipelines of this system, a distinctive sign in the form of a narrow black ring is applied.
Previous85Next
Date Added: 2016-09-26; views: 9272; ORDER WRITING WORK
Similar articles:
Types of water heating systems in a private house
There are several types of hot water heating for private houses. Here we mean standard heating systems with radiators, underfloor heating and baseboard heating. Individual types can be combined with each other, which allows you to achieve efficient heating. For example, ordinary radiators are installed in bedrooms and living rooms, and heated floors are often installed in bathrooms and toilets - an excellent solution for those who cannot stand the cold and do not like cold tiles. Let's take a look at the individual types of heating and their advantages.
Radiator
Radiator heating systems are timeless classics. The principle of their operation is to transfer heat from the coolant through the radiators installed in the premises. Such heating systems are installed in the overwhelming majority of buildings for various purposes - in residential, industrial, administrative, business and many others. They are relatively easy to install - just stretch the pipes and connect radiators to them.
Previously, water heating in a private house provided for the installation of bulky cast-iron radiators. Over time, they were replaced by lighter and thinner steel radiators made of corrosion-resistant steel.Later, aluminum batteries were born - they are lightweight, cheap and durable. For a private house, this is the most ideal battery option.
The main advantage of radiator systems is that no concrete screeds need to be poured to install them. The entire installation is reduced to the installation of the boiler and radiators with their subsequent connection. Radiators provide effective heating of the premises and do not violate the interior design, especially if they are modern aluminum multisectional batteries.
Warm floor
Water floor heating in a private house can work both independently and in auxiliary mode. In an independent mode, the need to lay pipes with radiators disappears, and all the heat is emitted by the floors. Thanks to this, children can play safely on such floors, they will not be blown through and will not go through. Are your feet constantly freezing? Then you will definitely like the always warm floors. In auxiliary mode, they work as an addition to radiator systems.
Underfloor heating systems are good in kitchens, bathrooms and toilets. where the ever-cold tiles often lie on the floor. Heating pads will help keep your floors warm and comfortable. For example, in the bathroom, you no longer have to stand with bare feet on cold tiles. The same goes for the toilet. If you have a tiled floor in your kitchen, feel free to install underfloor heating systems here too. Another place where a warm floor will become an attribute of comfort is the bedroom - you must admit that it is not pleasant to crawl out from under a warm blanket and become your heels on cold floors.
Underfloor heating is characterized by a low coolant temperature, not exceeding +55 degrees, which allows you to create economical heating systems. But the need to make concrete screeds and pass through walls and door frames is a significant disadvantage. It is best to consider the need to install the system even at the stage of building a house.
Skirting boards
Modern heating systems, built on the basis of classic aluminum radiators, differ in that the heat from them spreads only upwards - due to natural convection. As a result, all the warm air rises, and cold air enters its place. There is nothing surprising in the fact that households start to feel cold feet. The only plus is the lack of cold from the windows, as it is carried away by convection to the ceiling. But what about heating? Do not lower the radiators to the floor?
The way out of the situation is skirting heating systems. Small-sized radiators made of brass or aluminum are used here. The coolant is supplied using small diameter plastic pipes. The system is complemented by taps, air drains and other necessary accessories.
All this is laid in a special plastic skirting board - the air that gets here heats up and heats the walls on top. Further, the room is warmed by infrared radiation from heated walls and floors. There are no drafts blowing across the floor in heated rooms. Here, not only the walls are warmed up, but also the floors themselves, making the rooms warm and comfortable.
The advantage of skirting board heating is that it can be installed at any stage, even after the completion of construction. Disadvantages - the high cost of installation and a bunch of requirements for the placement of baseboards and other elements. Simultaneous installation of all types of the described systems is also allowed.
Diy heating schemes in a private house
How effective the heating will be depends on the characteristics of the circuit being mounted. The heating scheme in a private house with your own hands can be implemented in different ways. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the possible options in order to choose the best option.
You can always choose the right option
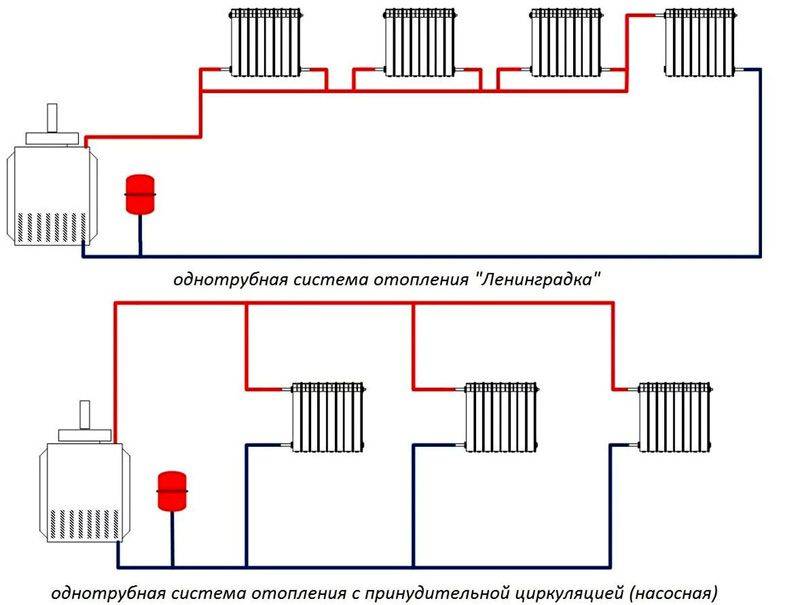
Diagram of a one-pipe heating system of a private house with your own hands
The one-pipe scheme assumes that the coolant from the boiler begins to move along a single line, and then returns along it. Radiators are connected to the line at both ends. A properly mounted one-pipe heating system of a private house with your own hands works as follows:
- the coolant heats up to + 75 ÷ 85 ° C and begins to move through the pipeline. Having reached the first radiator, part of the hot water fills the battery, and the rest continues to move through the pipes;
- passing through the radiator and giving off heat to the surrounding space, the water mixes with the coolant, reducing its temperature by a couple of degrees;
- on the next radiator, the situation is repeated. As a result, significantly cooled water is supplied to the last battery, which reduces the amount of heat given off.
The scheme and procedure for installing one-pipe heating involves building up a section of radiators, starting from the second from the boiler, in order to ensure uniform heating of all rooms of a private house. Water heating works quite efficiently if it contains no more than 5 batteries. In a multi-storey building, several risers are often mounted. Such a vertical scheme assumes the presence of stable working 3 ÷ 4 batteries.

One-pipe model is not always effective
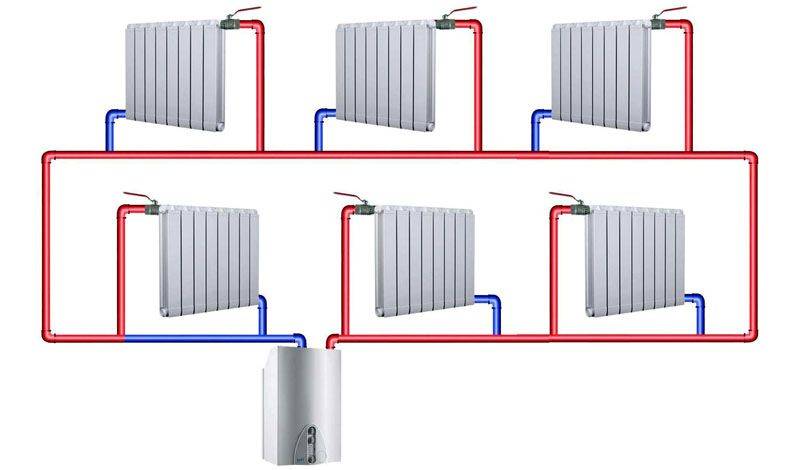
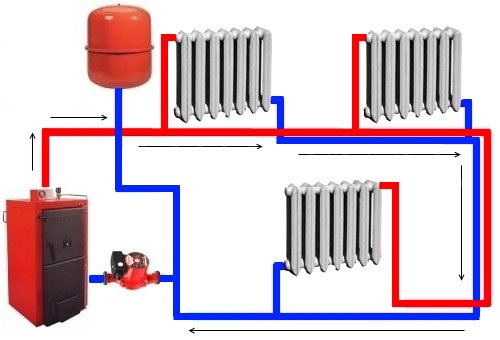
Diagram of a two-pipe heating system
A stable and reliable option that provides a heating medium heated to the same temperature to radiators located in different rooms. Heated water moves through one pipe, and cooled water returns through another.
Depending on the selected wiring, a two-pipe scheme can be:
- Dead-end. The coolant supplied through the corresponding branch fills all radiators, and returns on the reverse. Balancing ensures uniform heating of all batteries;
- Passing. Loop-shaped heating scheme of a country house.When performing installation with your own hands, you should ensure that the coolant moves along the main and return branches in the same direction. Suitable for a sufficiently long contour;
- Collector. A suitable option for a large private house. For powering each radiator, a separate two-pipe branch is used, connected to the distribution manifold.

A double-circuit circuit allows you to better warm up all rooms
Scheme of water heating of a two-story house
When installing a system in a two-story building, a gravity flow scheme is rarely chosen. Here, the best choice is water heating in a private house with forced circulation. The contour can be one-, two-pipe or radial.


The scheme is selected individually
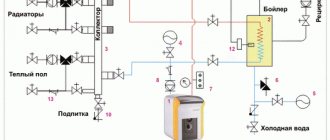
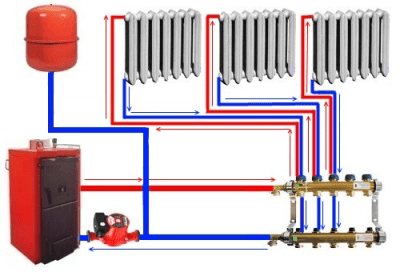
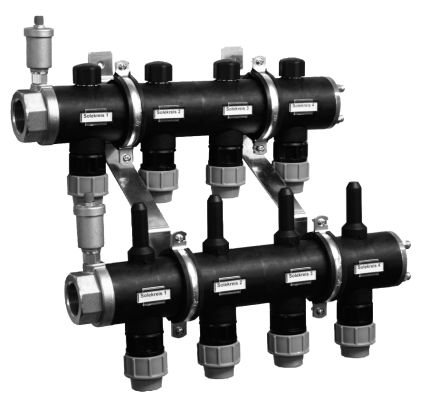
Collector circuit for heating a one-story house with forced circulation
The collector (beam) water heating system includes a collector, which is a device used to collect the coolant. Two pipes are connected to each radiator: direct and return. Such a heating scheme with forced circulation of a one-story house makes it possible to best hide the pipes being laid. Moreover, each room may have its own temperature.
A special cabinet is used to accommodate the collector. The disadvantage of this scheme is the increased cost due to the need to purchase new equipment.
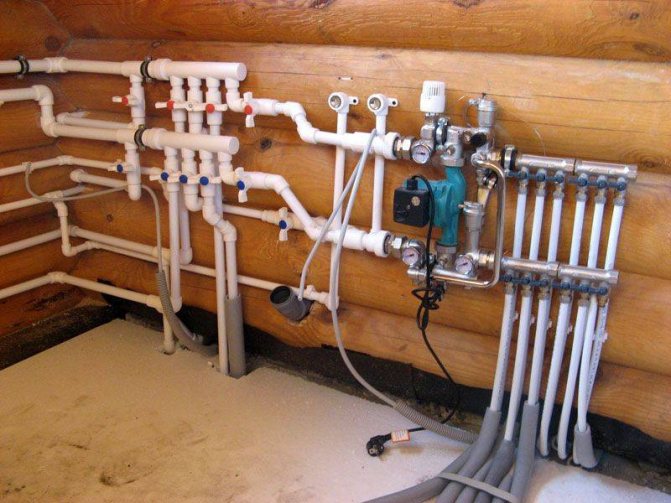


The collector circuit is expensive
The main types of wiring for water heating
Today, there are several main options for routing piping around the house when using water heating:
One-pipe. The so-called "Leningrad", in which one pipe connects all heaters in the house in the direction of movement of the coolant. Such a scheme is chosen for its simplicity, minimal financial (the cost of highways is generally lower) and labor costs.

But at the same time, the heating of the radiators is uneven, and it is impossible to regulate the temperature in each of the batteries;
- Two-pipe
... The heating radiators are connected by two pipes laid parallel to the movement of water in the system. The advantages include the ability to quickly adjust the temperature, quick and uniform heating of the premises, accessibility; - Manifold arrangement of pipes
... It has its own supply and return pipelines, connected together by means of special distribution manifolds. Feature - beautiful appearance, full control over all batteries in the house from the switch cabinet.
The main advantages of water heating of a cottage
As you can see in the photos and videos of country houses on our website, water heating schemes are used quite often in our country.
There are a lot of reasons for this widespread use:
- The ability to perform installation work on the arrangement of heating the house at any stage of construction. In addition, even in a finished house, water heating is installed without any problems;

- The water itself is of excellent quality when used as a heating medium. High thermal conductivity, availability and low cost, along with unique heat capacity, make water the best choice;
- Versatility, the ability to use various types of fuel for heating the coolant in the heating circuit;
- A wide range of pipe routing options for water heating schemes. You can choose a certain type depending on the mass of parameters, ranging from the area of the cottage and ending with financial capabilities;
- A variety of equipment for home heating arrangement;
- Accurate and quick regulation of the air temperature in each of the rooms of a private house. Provided by the installation of special equipment, namely thermostats and shut-off valves.


Installation diagrams of a heating system in a private house
In practice, two types of systems are used - schemes (or types of pipe routing), namely:
- one-pipe;
- two-pipe.
Each of them has its own advantages, disadvantages and is used in different cases.
One pipe system
This type of wiring is cheaper and simpler. The system is built in the form of a ring - all the batteries are connected in series with each other, and hot water moves from one radiator to another, then enters the boiler again.
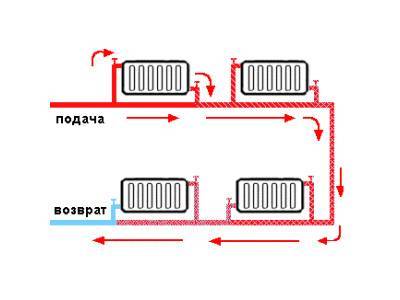

As you can see in the figure, all the batteries are connected in series, and the coolant passes through each of them.
This heating scheme is very economical in its execution, it is simple to install and design. But it has one significant drawback. It is so weighty that many refuse such a wiring and prefer the more expensive and complex two-pipe. The problem is that as the coolant advances, it will gradually cool down. Until the last battery, the water will flow slightly warm. If the power of the boiler is increased, then the first radiator will heat up the air too much. This uneven distribution of heat makes it necessary to abandon a simple and cheap one-pipe system.
You can try to get out of a difficult situation by increasing the number of sections of the last radiator, but this is not always effective. Hence the conclusion that one-pipe wiring can be used when the number of batteries connected in series is no more than three.
Some get out of the situation as follows: they connect a pump to the boiler, thereby forcing the water to move forcibly. The liquid does not have time to cool down and passes through all radiators, almost without losing temperature. But even in this case, some inconveniences await you:
- the pump costs money, which means that the costs of installing the system increase;
- electricity consumption increases, since the pump is powered by electricity;
- if the electricity is cut off, there will be no pressure in the system, which means there will be no heat either.
Output. The one-pipe system is effective only for small houses with 1-2 rooms, where a small number of radiators are used. Despite its simplicity and reliability, it does not justify itself in country houses, where it is necessary to install more than three radiators for the entire living space.
Two-pipe system
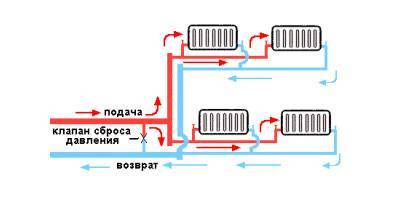

Hot water is supplied through one pipeline, and cooled water through another. This ensures an even distribution of heat across all batteries.
Such a heating distribution in a private house will be much more efficient and better than a one-pipe one. Although it is more expensive to perform and more difficult to install, it allows you to evenly distribute heat across all batteries, which will help create a comfortable environment. Unlike a single-pipe, in this wiring, a hot water pipe is supplied under each radiator, and the cooled liquid goes down the return line to the boiler. Since the coolant is supplied to all batteries at once, the latter heat up equally.
This system is not much more complicated than the first one; you will have to buy more materials, since pipes will have to be supplied to each radiator.
A two-pipe system can work in two ways:
- collector;
- ray.
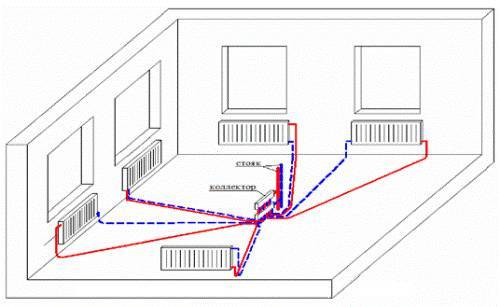

The beam layout is older. In this version, the supply pipe is installed at the top of the house, after which pipes are laid for each battery. Thanks to this design, the circuit was named - ray.
The first scheme works as follows: in the attic it is necessary to install a collector (a special device consisting of many pipes), which distributes the coolant through the heating pipes. In the same place, you need to install shut-off valves that will cut off the circuits. This design is quite convenient, it facilitates the repair of the entire line and even a separate radiator. Although the scheme is reliable, it has one significant drawback - a complex installation with a large amount of materials (shut-off valves, pipes, sensors, control devices). The collector layout of heating pipes is similar to the radial one, but more complex and efficient.
Unlike a one-pipe system, a two-pipe system does not need additional forced circulation of the coolant. It shows high efficiency even without a pump.
Disadvantages of a ring heating system.
The main disadvantage of "Leningrad" is that for its installation in one-story private houses, a special device is needed - a booster manifold, which will circulate water through the heating pipes. An autonomous heating system must be installed in rooms where ceilings reach 220 centimeters. This is necessary to accelerate the water, as well as to be able to connect the supply tank of the heating system. However, natural circulation is now increasingly not used, but a pump is installed that disperses water through pipes. With the help of it, pressure is created and it is possible to adjust the radiators depending on the needs.
As the features of the system, for any installation method, it can be noted:
- The batteries that are at the end of the system circle in front of the boiler must be installed multi-section. The fact is that while the coolant passes a full circle, cooling occurs.
- When overhauling the system, it is quite difficult to dismantle radiators with a large number of fins.
The above features are considered by many to be a disadvantage of the system, however, it is popular among owners of private houses and those who are just building them.
Boiler selection
for water heating in the country depends on the variety of energy sources available in the summer cottage.If the dacha association has a gas main, then the boiler, respectively, is better to choose a gas one - this is the most economical option. Also, the boiler can be electric, or run on diesel fuel, or coal.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that boilers are single-circuit - designed only for heating the room, and double-circuit - they can cope not only with heating a country house, but also used to heat water
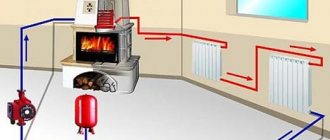
An example of a solid fuel heating boiler with a water circuit.
In a country house, the wiring can be made open, or hidden under the floor, which will help to equip the heated floors that are very popular nowadays. If the house is only at the construction stage, then it is preferable to place the heating system under the floor. And if the house is already ready, then the pipelines are mounted along the inner walls.
Installation
Effective water heating in the country can provide for two types of piping:
with a vertical riser - all systems are connected to a single riser;
with horizontal drain.
The horizontal scheme is better than other options in terms of self-installation, and cheaper to install, but there is a threat of air accumulation and air congestion. The horizontal type is also used for the installation of warm water floors.
Features of the installation of water heating
The use of water as a heat carrier is due to the fact that this liquid has a very good heat capacity and is able to effectively receive and give off heat. Water heating has been used in homes for a long time. Since then, the principle has remained the same, but the heating element connection diagrams have undergone major modernization. Nevertheless, for the construction of water heating, all the same materials and devices are used as a hundred years ago, only improved ones:
- power plants. They can be stoves or boilers that run on electricity or gas;
- pipes of various diameters. Today, in addition to metal pipes, plastic and metal-plastic pipes are actively used;
- heating radiators, which are made of cast iron, steel or aluminum;
When buying radiators, choose trusted manufacturers
- various shut-off valves, without which it is impossible to build water heating in a private house with your own hands. Its connection diagram is quite simple;
- expansion tank to compensate for excess pressure in the system;
- circulation pump, which is included, for example, in the heating circuit of a one-story house with forced circulation.
This is an almost exhaustive list of the equipment that will be needed in order to make water heating of a private house with your own hands. There are three schemes for installing and connecting radiators:
- Using one pipe.
- Using two pipes.
- Using collectors.
One-pipe heating system with circulation pump
According to the type of coolant supply, all schemes can be divided into heating with a natural water flow and forced. Natural circulation is carried out due to changes in water temperature. The hot liquid rises, since it has a lower density, and the cold one flows downward. Forced circulation occurs due to pumps that are installed in the pipeline or located directly in the boiler.
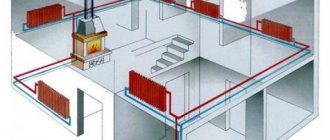
A stove with a water circuit for heating a house: implementation options. Stove heating, heating and cooking stoves, fireplace stoves, advantages, design, implementation options. Calculation, materials, installation.
Vertical wiring of the heating system
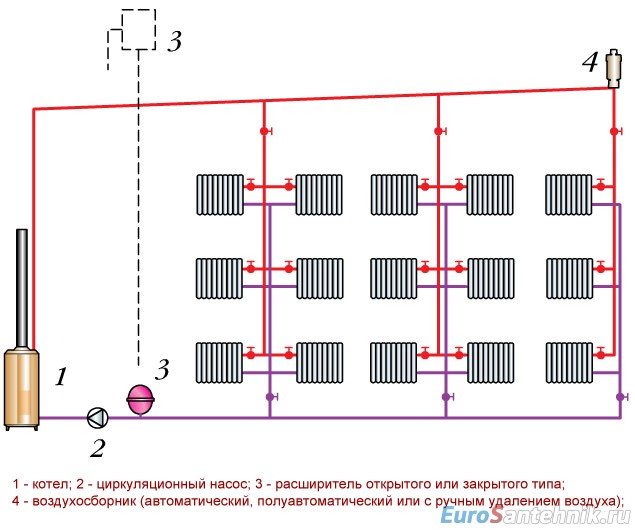

This type of wiring is still used in apartment buildings, since this type is most suitable for heating a large number of floors. Also, vertical routing saves materials and is easier to install. This type of circuit is available as one-pipe or two-pipe, and two-pipe is preferred.The two-pipe heating system of a vertical type also allows you to change heating devices without stopping the entire heating system. The heaters can be equipped with automatic or manual temperature control valves.
The vertical single-pipe scheme does not allow you to turn off the radiators separately, but on the other hand, much less pipes are needed for the installation of such a system than for a two-pipe scheme. The vertical type of wiring allows you to evenly distribute heat throughout the room, but the heated area of the rooms is somewhat limited. It is advisable to use vertical wiring if the building has three floors or more.
Vertical wiring also allows you to organize a heating system that will not be equipped with a circulation pump. This technical solution is applicable to private housing construction. The main disadvantage of a vertical heating scheme is that it cannot be scaled. It can also cause inconvenience the fact that it will not be possible to regulate the temperature in each separate room.
The vertical type heating distribution can be top or bottom. These two types have some peculiarities. If a single-pipe vertical wiring of the upper type is used, then it is supplied from the attic, where a special reservoir (lounger) is installed. Further, from the reservoir, the coolant is distributed along the risers, which supply heat to the heating devices.
The vertical distribution system with bottom feed is equipped with a reservoir in the basement, from which water flows into the risers. The coolant moves up along the risers, passing along the way through the heating devices in each apartment. If the vertical wiring is mounted in a two-pipe scheme, then adjustable heating devices can be used in its circuit. Also, heat metering devices can be connected to such a system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Vertical System
With a two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring, the supply and return main pipelines pass in the floor of the lower floor of the building or in the basement, and the coolant flows independently into each radiator.
Benefits: good regulation of the heating system, the possibility of separate shutdown of each heating device, no overspending of heating devices.
Disadvantages: the length of the pipelines increases in comparison with the one-pipe scheme, the practical impossibility of installing apartment heat meters.
Reasons for the impossibility of installing apartment heat meters in houses with vertical heating distribution
- Metrological problem... The heat meter is considered to be working correctly when the temperature difference of the heat carrier between the inlet and outlet (supply and return) is more than 3oC. Heat consumption of 1 radiator, depending on the standard size, fins ratio and heating area, ranges from 0.5 ° C to 2 ° C.
- The need to install heat meters for each riser, which is expensive and very troublesome. In the future, the user will have to manually take readings from each of the meters, add them up and submit them to the heat supply organization. Risk of mathematical error and human error. High verification costs, which partially offsets installation savings and increases return on investment.
- The scope of application of the device is written in the passport of the heat meter... For example, for Ultraheat T-230 - “The meter is used to meter the energy consumption in apartments, cottages, apartment buildings and small business facilities ... the temperature is measured in the supply and return pipelines .... etc.". Nowhere is there a word about the battery, and there is no supply and return pipelines on the battery.
All of the above reasons are arguments for heat supply organizations not to take into commercial accounting heat meters installed in houses with a vertical distribution of the heating system.
The only way to organize heat metering in a vertical heating distribution scheme is with heat distributors.
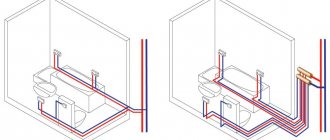
One pipe connection
Installation of heating using the one-pipe method is the least costly, at the same time, wiring in two pipes will be most effective, especially if the rooms in the house have a large area. The advantages of this scheme are as follows:
- Ease of installation and repair;
- Profitability;
- Possibility of laying the line at floor level;
- Use of the system in a one-story and two-story house;
- Possibility of forced or natural circulation.
With a one-pipe system, water moves from one radiator to another through the pipe, and upon reaching the last radiator it cools down a lot. Such a system does not lend itself to adjustment.
Connection options.
Installation of a one-pipe system and its features.
In a two-story building, the system does not need to use a booster manifold or pump, the movement of water is carried out due to the height of the system. For the appearance of a temperature difference and the beginning of water circulation, a high vertical pipe is mounted immediately after the boiler. Such a heating line will be silent.
Radiators cut into the line in the same way as with any other system. There can be two ways to connect heating batteries:
- Bottom, in this case, radiators are connected to the heating system using pipes located below.
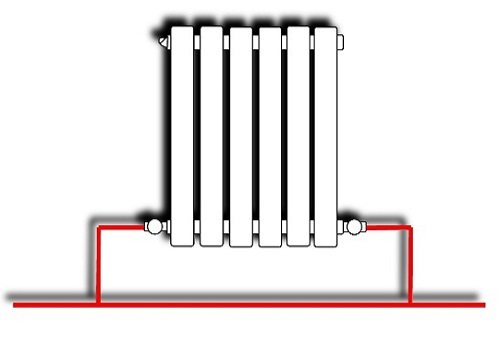

Lower radiator connection
- Full bore or diagonal. In this case, the input to the radiator is made through the upper pipe, and the output is made through the lower one.


Diagonal radiator connection
In order to save resources, various taps, valves and balancing valves are installed in the heating main. However, during installation, it is necessary to ensure that additional elements do not affect the temperature of the system elements located after the radiator equipped with these structural elements.
To make the system more perfect, heating radiators with taps are installed in such a way that it is possible to isolate the battery for repair or complete replacement without stopping the entire system.
Depending on the type of expansion tank in the system, the design can be divided into closed or open. Closed-loop heating is isolated from the "atmosphere" by means of a diaphragm expansion tank. If the expansion tank has a branch pipe connected to the ambient air, then the system is called open.
Application of gas boilers
Boilers used in a water system can use a variety of fuels. The most common and convenient to use is gas equipment - although it can be installed only when the central gas supply is connected to the house. In addition, among the disadvantages of gas boilers can be called the need for their regular monitoring by the relevant utilities.
But such a system has the following advantages over the others:
- Easy to install and operate.
- High efficiency in the use of energy resources. On average, gas costs are 30–40% lower than using liquid fuels or electricity.
- Rapid heating of premises with a heat carrier. Within an hour, the temperature in rooms with a hot water heating system, the source of heat in which is a gas boiler, will increase markedly.
- Environmental friendliness of gas use.
- The ability to automate the process, including programming the required temperature and heating hot water.
General advantages of a two-pipe heating system
- All radiators receive a coolant of the same temperature
- You can install a thermostat on each radiator and maintain a comfortable temperature in each room, and this will not affect the operation of the entire system.
- Low pressure losses
- The flow of the coolant on each radiator can be stopped and this will in no way affect the operation of the entire system. This plus allows you to carry out repair work without turning off the heating in the whole house or apartment.
- Can be installed and operated in a house of any size and number of storeys.
How to make water heating of a private house with your own hands - a step by step diagram
Step 1: Project
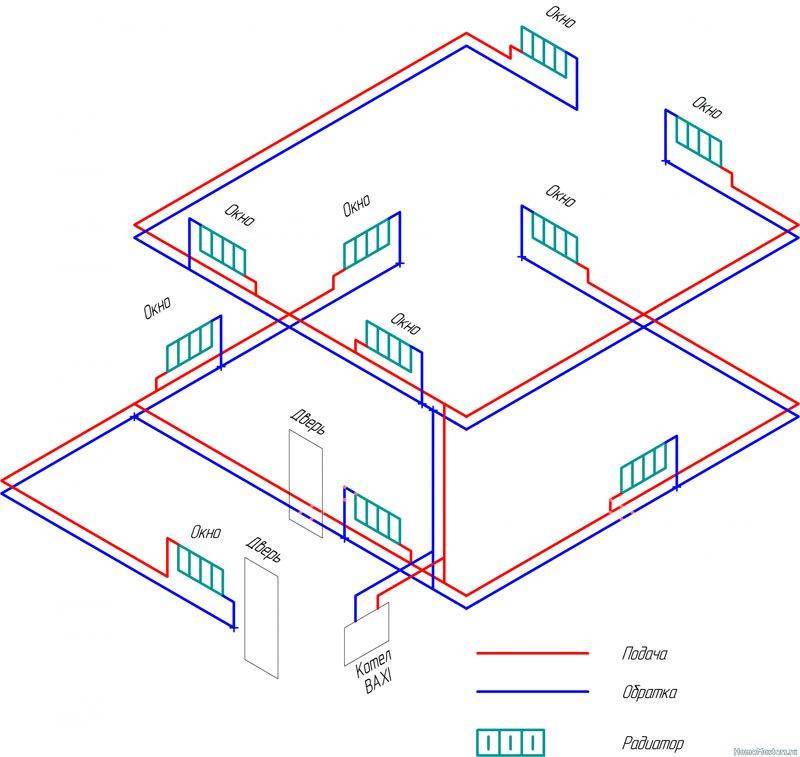
To begin with, we select a suitable scheme and display it on paper. Consider the area of the rooms, the position of the radiators, piping, their dimensions, etc. Such a sketch will help to correctly calculate the amount of consumables. Special programs will greatly simplify all calculations.
Step 2: accessories
Let's briefly consider what a boiler, batteries and pipes can be. The types of heating units, depending on the fuel used, are gas, electric, solid fuel and combined. The favorite among these options can rightfully be called gas devices. Water boilers come with a pump (for a forced heating circuit of a private house) or without it (natural circulation), and both types can be easily installed with your own hands. The double-circuit unit has proven itself perfectly, providing not only heat in the house, but also hot water.
Steel batteries will please the price, but at the same time they are susceptible to corrosion, and if you plan to drain the coolant, then the operating life will be significantly reduced. Cast iron, on the other hand, can be said to be an eternal material. It heats up for a long time, but it also keeps warm for a long time. But the large weight, not very attractive appearance and high cost have significantly reduced the popularity of this material. Cast iron batteries were replaced by aluminum ones. Their appearance is very attractive, they heat up quickly and are resistant to corrosion. However, aluminum does not tolerate sudden changes in pressure. Bimetallic resistors are famous for their excellent heat transfer, however, the anti-corrosion properties remain the same as those of aluminum.
The steel pipeline has lost its former glory due to its short operating life. It was replaced by modern polypropylene. Easy installation, the ability to create a "one-piece" structure, reasonable cost and reliability - all these are indisputable advantages. Copper pipes also have good characteristics, but their cost is far from affordable for everyone.
Step 3: boiler
Water heating in a private house is built in such a way that the medium is heated by a boiler. This scheme is the most optimal in the absence of a centralized supply. Therefore, when choosing a place where to install a boiler, one should take into account the location of the gas pipeline inlet or the presence of electrical wiring. If we are talking about a solid fuel unit, then it is necessary to carry out additional installation of the chimney. If you prefer the natural circulation of the coolant, then position the heating unit so that the return flow inlet is as low as possible. In this case, the basement is ideal.
Step 4: Installing the radiators
The batteries are placed under windows or near doorways. The design of the mount depends on the material of the resistors and the number of sections. The heavier they are, the more reliable fixation they need. A gap of at least 10 cm should be left between the radiators and the window sills, the floor should be more than 6 cm. By installing shut-off valves on each element, you will be able to regulate the amount of coolant in the radiators, and the air valve will help to avoid unwanted traffic jams.
Step 5: Layout
The boiler will be the starting point for piping installation. In this case, one should adhere to the scheme chosen and sketched on paper. If the pipes are visible, then we are talking about open wiring.On the one hand, the aesthetic side suffers, but on the other hand, any leak will remain visible, and in order to replace the damaged element, you do not need to disassemble the box. The pipeline can also be hidden, walled up in the wall, made of plasterboard cladding, etc. At this stage, batteries, additional equipment (pump, filters, security unit, expansion tank, etc.) are connected.
§ 39. Basic elements and classification of systems
Ship systems is a complex of pipelines with fittings, service mechanisms, tanks, apparatus, instruments and means of control and monitoring over them.
Ship systems provide on ships:
the fight for the unsinkability of the ship - removing water from flooded compartments, receiving or pumping water ballast
for the purpose of straightening the damaged vessel;
fighting fires on board;
maintaining the required temperature and humidity in the living and service premises of the vessel - living conditions;
supply of fresh and outboard water for the crew's household needs;
removal of dirty water from the vessel;
compressed air supply;
loading and unloading operations on tankers.
Ship systems must include reliable automation elements.
Systems serving ship power plants: cooling systems for mechanisms, lubrication, fuel supply, production and supply of compressed air to engines, etc., are discussed in the corresponding courses.
It is customary to classify ship systems by the type of medium transported in pipelines or by purpose.
By the nature of the medium transported in the pipelines, the systems are divided as follows:
a) water pipes of cold and hot, sea and fresh water;
b) air ducts of cold dry and warm moist air;
c) steam lines;
d) brine pipes of aqueous solutions of salts (serving mainly for cooling rooms);
e) gas pipelines of carbon dioxide, ammonia, freon, etc. It is more convenient to study ship systems, classifying them by purpose and function. According to this principle, all ship systems are combined into the following groups, during the operation of which common elements are used, which simplifies individual systems and their operation.
Bilge group
, including the following systems:
1) drainage, designed to remove masses of water from flooded compartments after filling a hole, as well as for pumping filtration (flowing through loose connections) waters;
2) drainage - for removing bilge water, as well as for draining double bottoms and side compartments that do not have a special purpose;
3) ballast for changing the heel, trim and draft of the vessel by receiving or draining special compartments or tanks.
IN fire fighting group
includes the following systems:
1) water (water extinguishing and water spraying) —for extinguishing a fire with a water jet from fire hoses and from sprinkler heads, for driving ejectors and other systems, for extinguishing fuel fires in engine-boiler rooms with sprayed water;
2) steam extinguishing - to extinguish a fire in fuel compartments by filling them with water vapor;
3) liquid - for extinguishing a fire of fuel in MKO and at power plants by supplying fire-extinguishing liquid to these rooms;
4) foam extinguishing - for extinguishing a fire with non-combustible foam, which isolates the fire from the access of air oxygen;
5) gas extinguishing - to extinguish a fire in rooms by filling them with carbon dioxide;
6) irrigation and flooding of ammunition cellars - to cool the ammunition stock and flood it to prevent an explosion and extinguish a fire in the cellars.
Sanitary group
includes systems for the following purposes:
1) fresh water — for supplying drinking water to catering units, fresh, cold and hot water to baths, showers, laundries, washstands and other consumers;
2) seawater — for supplying seawater to sanitary facilities and for washing decks;
3) waste water - to remove dirty water from baths, washbasins, baths, etc.;
4) funnel and fecal - to remove fecal water from latrines and toilets; to collect dirty water from the sewage and sewage systems into fecal tanks and discharge this water into a special vessel or overboard outside the territorial waters or to a landfill;
5) scuppers - for removing water from decks, bridges, etc.
Air conditioning unit
includes systems of winter, summer and general air conditioning to maintain the specified air parameters in the premises in winter and summer: temperature, relative humidity and CO2 concentration. In winter, the supplied outside air is heated and humidified, and in summer it is cooled and dehumidified with automatic control. This group also includes systems:
1) steam heating, heating rooms with steam heaters;
2) electric heating, heating rooms with electric heating pads;
3) ventilation - for air exchange in rooms: supply of fresh outside air and removal of polluted air;
4) aero-refrigeration - to maintain the set temperature in the premises by removing warm and supplying cooled air;
5) refrigerated - for cooling the provision chambers and supplying chilled brine (coolant) to various consumers;
6) regeneration — to restore the amount of oxygen required for the human body in the air environment of the premises, and to remove excess amounts of carbon dioxide and other harmful gases from the premises.
Compressed air group
consists of air systems of low, medium and high pressure, supplying air for the operation of ship devices or mechanisms, as well as for the operation of pneumatic drives that do not have their own compressors.
Special group of systems for tankers
consists of the following systems:
1) cargo, carrying out loading and unloading operations with liquid cargo in tanks of tankers;
2) stripping, providing cleaning of tanks of tankers from the rest of the cargo, sludge and dirt;
3) a gas outlet, which discharges gases emitted by the cargo in the tanks through the safety valves into the atmosphere;
4) heating of viscous cargo - for heating cargo in tanks when they are discharged from a ship or when reloading between tanks or tanks;
5) tank washing - for supplying steam or hot water to tanks after their unloading for washing and gas-safe processing.
Group of control systems for ship mechanisms and devices and on-board communication
, including systems for specific purposes:
1) control (hydraulic and pneumatic) —for changing the operating modes of mechanisms at a distance from central posts;
2) air measurement (pneumatic system) —for remote measurement from central stations of the ship's draft or the amount and level of liquid cargo in the compartments;
3) communication pipes (communication) —for voice communication and oral transmission of commands between control posts in different rooms of the ship.
Forward Table of Contents Back
DIY heating system installation
Installation work should begin with the installation of the heating boiler. If the power of the equipment does not exceed 60 kW, you can put the device in the kitchen, if it is higher, a separate room should be allocated for the boiler. To heat sources that burn different types of fuel, you need to ensure the flow of air. In addition, it is necessary to ensure the removal of combustion products. This can be done using a properly equipped chimney.
When installing a heating boiler, certain rules must be observed. The distance to the nearest equipment and walls should be at least 0.7 m. The piping of units that run on different types of fuel is practically the same.The figure shows a variant of piping a gas boiler with a forced circulation system.
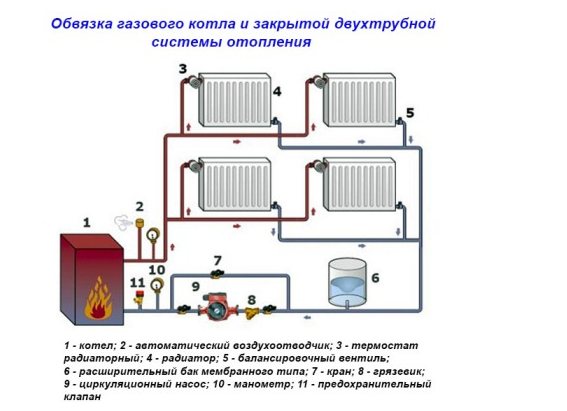

This strapping method is used most often. Other schemes provide for the presence of their own pumps to ensure continuous circulation of the heated coolant.
If solid fuel heat generators are used to service the heating system, when connecting them, the following nuances must be taken into account: due to the inertness of the device, the coolant may overheat and boil. To avoid unpleasant situations, it is necessary to install a circulation pump on the return. An additional security system is also mounted, which consists of the following elements:
- safety valve;
- automatic air vent;
- pressure gauge.
An important function is performed by a safety valve, because it is he who is responsible for relieving excess pressure in cases where the coolant overheats. The most effective piping scheme for a solid fuel boiler is shown in the figure below.
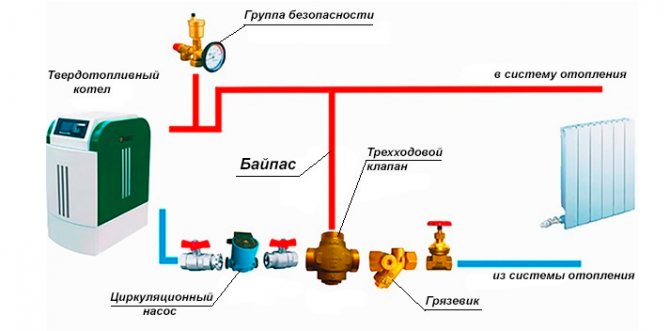

Another problem that is often encountered when operating a heating system on solid fuel boilers is the accumulation of condensate on the elements of the unit. This happens due to the ingress of cold water with a hot cut. To prevent condensation of the coolant, a three-way valve and a bypass are installed in the systems.
Installation of heating pipes
It is impossible to equip a heating system in a private house without a pipeline. In old houses, there are cast iron pipes from the last century. They boast a long service life, durability and reliability. However, today such products are used extremely rarely, because they are almost completely replaced by lighter, more convenient and cheaper pipes, which can be made from the following materials:
- steel;
- copper;
- stainless steel;
- polypropylene;
- polyethylene;
- metal-plastic.
Features of the gravitational heating system
The principle of operation is based on the property of water to expand with increasing temperature. The creation of a pressure difference in a closed loop of pipes is the basis for fluid circulation. Thanks to this effect, the gravitational closed heating system received another name - gravity.
Structurally, it should consist of the following elements:
- Boiler... A device designed to transfer the energy of burning fuel (wood, coal, gas, etc.) to a heat carrier (water, antifreeze). In a closed gravity heating system, this is done using a heat exchanger located as close as possible to the combustion chamber in the boiler;
- Pipelines... Necessary for the transportation of heated liquid from the heat exchanger to heating devices;
- Radiators... They are the main source of heat in the room. Their large area ensures maximum heat exchange between heated water and air in the room;
- Control and safety devices... These include an expansion vessel, a gravity valve for heating, valves and throttles.
During the heating of the water in the heat exchanger, it expands, which creates excess pressure. In turn, the cold heat carrier from the return pipe has a higher density and begins to displace the liquid with a high temperature. As a result, circulation occurs.
One of the main elements of the system is the booster manifold - a vertical branch pipe connected to the boiler. If a do-it-yourself gravitational heating system is made, he needs to pay special attention - starting from the material for making the pipes, and ending with their diameter.
The larger the volume of the boost manifold, the higher the speed of the coolant. To do this, you need to calculate its optimal section and height.
The gravitational heating system of a two-story house should be designed in such a way that the coolant can be distributed as evenly as possible over several circuits.