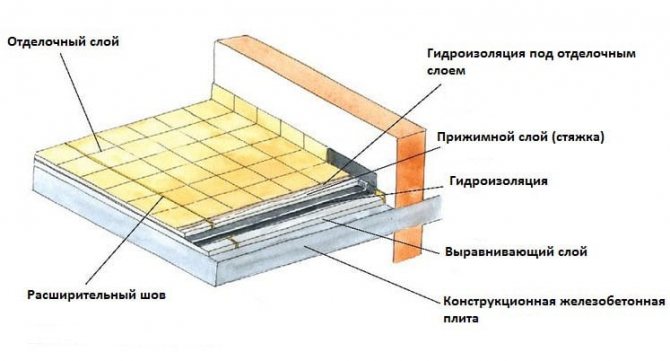
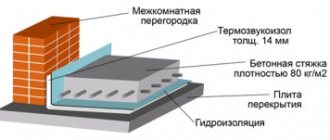
General principles of substrate organization ↑
Regardless of whether a strip recessed foundation with a basement will be used or the rough floor screed will rest on the ground, it is necessary to organize a substrate or backfill, i.e. a layer that will serve as a barrier to moisture rising from the ground, as well as perform the function of thermal insulation.
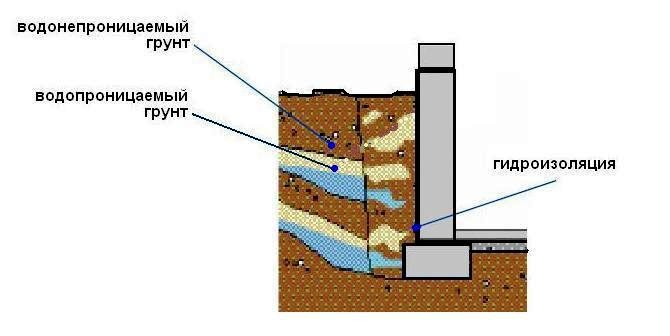
Water tends to spread in a vertical direction through the smallest capillaries existing in the soil. If the cross-sectional dimensions of these capillaries are increased to sizes exceeding 0.5 mm, then such propagation becomes difficult. Thus, in order to organize an effective barrier, we need to create a layer with significant air pockets and gaps, which moisture in the soil layer cannot overcome. Also, this layer will prevent the floor from freezing, which can occur with direct contact with the soil.
For the substrate, coarse crushed stone is used, sometimes the bottom layer is sprinkled with cobblestones. The crushed stone should be at least 30 - 50 mm, and its layer should be at least 10 cm. After filling, the crushed stone is thoroughly rammed using rollers or vibrating equipment.

First add rubble
Then, river or quarry sand is poured onto a layer of crushed stone in a layer of 7 - 10 cm, which is also rammed using a special tool. From how well the backfill layers are laid and tamped, their water repellency and bearing qualities will depend, which will affect the integrity of the subsequent concrete screed.
Sometimes a layer of fine gravel is poured onto the sand and closed with a liquid cement mortar. This is done in places where the groundwater table is too high.


Crushed stone is covered with sand
The substrate of large rubble or cobblestone creates a layer in which there are no small capillaries, instead of them there is a large number of volumetric air gaps or pockets, which water cannot overcome by capillary propagation. If the groundwater does not rise high, the composition of the substrate may include a layer of expanded clay, which will play the role of an excellent insulation.


Sometimes expanded clay is used as insulation
Sometimes measures are required to improve the waterproofing properties of the substrate. If, on the basis of measurements of the groundwater level and soil analysis, it is decided to carry out additional waterproofing measures, then the layers of sand and crushed stone are impregnated with bitumen or special polymer compounds, a rough screed must be performed and treated with mastics or penetrating waterproofing. Also, various materials are often combined.
Waterproofing polyethylene film ↑
Specifications and types ↑
According to the specifications of GOST 10354-82, the waterproofing film is made on the basis of low density polyethylene with various additives (stabilizers, dyes, modifiers). It is also made of high density polyethylene (GOST 16338-85). In construction, a film with a T marking (stabilized or unstabilized) with a thickness of up to 0.5 mm is used. The material is produced in the form of a canvas, a sleeve, a half-sleeve in rolls of various widths and lengths. Operating temperature from -50 ° С to +60 ° С.
Along with the usual polyethylene waterproofing, a reinforced one is used, in which a mesh frame is sealed between the layers of the film. The indicator of its strength is not thickness, but density.Sometimes a geomembrane is also referred to as a type of waterproofing polyethylene sheet. It is quite elastic, resistant to mechanical damage, has good chemical inertness (PH 0.5–14), and is environmentally friendly.


Waterproofing film is produced in rolls
Advantages and disadvantages of the material ↑
Pros of plastic wrap:
- Provides double-sided protection against moisture: the foundation is protected from the outside (from groundwater) and from the inside (concrete does not give off moisture, which guarantees good adhesion / hardening and uniform solidification).
- It is not subject to rotting, decomposition: bacteria cannot "process" polyethylene.
- Convenient to use: wide canvas covers a large area at once. Small thickness and a sufficient degree of elasticity make it possible to use the material in inconvenient places (corners, etc.).
- Allows you to create tight joints: the joints are soldered with a special machine for welding polymers or glued.
- Minimizes the cost of waterproofing: polyethylene film is an inexpensive material for protecting buildings from moisture.
- Non-slip during styling. Manufacturers produce textured (profiled) canvas.


A layer of reinforcing mesh significantly increases the strength of polyethylene
The main disadvantage of polyethylene is its low strength. The canvas can be easily damaged during repair and construction operations: a breakthrough negates the entire moisture insulation system. Therefore, usually plastic wrap is used in conjunction with other means of protection against moisture. The material is inconvenient to use for vertical moisture insulation. It is mainly used to protect the foundation, floors, floors, and roofs from water.
Correct waterproofing of the foundation ↑
Another source of moisture penetrating the walls and floor of the first floor of a private house is a foundation that is poorly insulated from moisture. No matter how high-quality the waterproofing of the floor in the house is, if the foundation is not processed according to building codes and regulations, dampness cannot be avoided. This is especially true of basements, which can even be heated in the off-season and moisturize partitions and walls of the house. We will not list all the negative consequences of the lack of waterproofing of the foundation structures, but will dwell only on how this affects the moisture content of the floor of the first floor.
If the foundation is strip, then its structures smoothly pass into the load-bearing walls of the building, which means that the capillary movement of water can reach the rooms of your house. Waterproofing of strip foundations should be carried out using roll, bituminous, and in the case of a monolithic foundation - penetrating insulating materials.


Correct waterproofing of the foundation is a prerequisite
The choice of one or another method of isolation depends on the geodetic and climatic conditions of the area and should be made by an experienced specialist. Also, between the walls of the house and the foundation, there must be an effective vertical cut-off using roofing material or PVC membranes, which, in the event of soaking underground structures, will not allow moisture to penetrate the walls of the building.


Vertical clipping is done with roll material
If such a cutoff was made poorly or deteriorated over time, you can restore it using injection isolation. Insulation of the vertical ends is also required.
If a columnar or pile foundation is used in the construction of a house, then its structures must also be carefully processed with mastics, pasting insulation or penetrating compounds. In addition, it is necessary to insulate the upper surfaces of the ends of the posts, on which the wooden logs will lie.Wood reacts extremely negatively to constant moisture, therefore, roll materials must be laid between the wooden elements and the foundation structures: roofing material, roofing felt, PVC or polyethylene. The logs themselves can also be treated with mastics based on bitumen-latex compositions or impregnated with special solutions that prevent decay.


Roofing material is placed under the lags
Materials to protect the wooden floor from moisture
Materials that do not allow moisture to pass through are called waterproofing materials. Applying them to a wooden surface to be protected is called waterproofing installation. Properly selected materials can not only save wood from moisture, but also maintain a healthy climate in the house.
When choosing waterproofing for a wooden floor, first of all, film and impregnating materials are used. This is due to the property of wood to absorb any liquid well. Wooden floors can be different: floorboards, parquet or plywood, etc. Therefore, when choosing, you need to focus on the type of floor.
The main types of waterproofing for wood flooring include materials:


Cast. Consists of polymers that are heated and applied to the surface. The resulting layer repels moisture well, but easily collapses under mechanical stress. There is another type of cast waterproofing, when the material is rolled out with an overlap and, with the help of a hairdryer, the seams are heated by gluing. But you need to use cast insulation only where there will definitely not be any loads, since the material is soft. Cast insulation includes, for example: Bituminous mastic, Bitumen.

Paintwork. This is one of the easiest ways to waterproof your flooring. Paints and varnishes have a special water-repellent property. But this coating needs to be carried out every 2-3 years, and it is not enough to protect the floor from the basement or underground. In country houses, where heating is used only from time to time, varnish and paint will quickly crack and lose their protective properties. Under furniture, without the use of linings, materials also wear out quickly. It is not recommended to wash a floor covered with varnish or paint often, therefore such waterproofing is not suitable in a house where there are children and animals. These include, for example, the protective varnish for Tikkurila wood.

Water-repellent impregnation. This is one of the safest ways to protect wood. The oldest methods of impregnation include impregnation: drying oil, liquid glass, tar, modern ones on an acrylic basis. Users love liquid glass for its low cost and good protective properties. It is still used today. Liquid glass is applied to a dry and pre-cleaned surface, but there is one big drawback. If you use liquid glass on an insufficiently dried surface or with a rotting process that has already begun inside, this will only aggravate the situation.

Gluing waterproofing of the floor. It is often confused with a cast. There are just similar materials of the pasting type, for example TechnoNIKOL. But he, like monolithic, protects well, but is afraid of any mechanical influences. One of the subspecies of pasting is Izospan film insulation. This is a special type of protective coating. Izospan not only protects against moisture, but also gives an additional thermal layer. Izospan is used most often in underfloor heating systems.
We will talk about how to make a waterproofing floor with your own hands using these materials below.
Waterproofing of the ground floor floor ↑
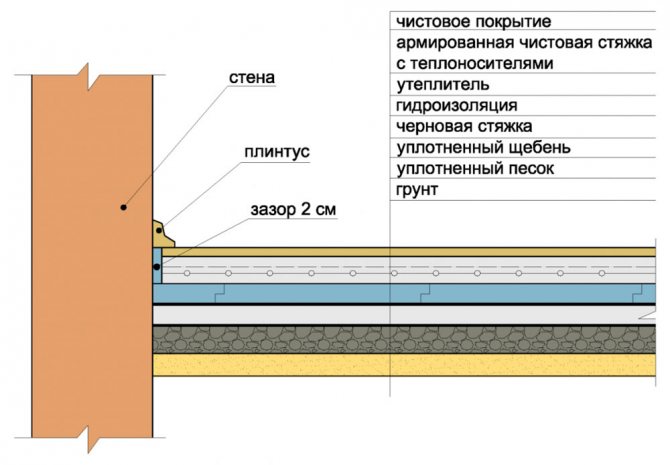
Now we will consider the activities that precede the construction of the screed. In the case of a basement structure, this will be waterproofing of the floor of the living quarters, in the case when a basement is built in the house - insulation of the basement floor.
After completing the appropriate damper filling or substrate, we proceed to the main work on waterproofing the floor before the screed.
For this, various materials are used:
- construction polyethylene films;
- PVC membranes;
- roofing material;
- bitumen-polymer roll products;
- polyisobutylene;
- waterproofing, etc.
From the choice of a specific material, the principle of work does not change. Let's just say that traditional polyethylene films are the cheapest and easiest method of waterproofing, however, membranes and bitumen-polymer materials, as well as other modern insulating carpets and coverings, have the best characteristics and performance, but far exceed polyethylene in terms of cost and installation complexity.


Roll materials are carefully glued
Roll material is laid on the sand. Separate strips are carefully welded or glued, in the case of polyethylene, tape is used. The polyethylene film should be 200 - 300 microns thick, it is better to use two layers with overlapping seams. The overlap of the strips should be at least 10 - 15 centimeters. In the case of using various modern diffusion membranes or other coatings, installation should be carried out in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions, since installation conditions can vary greatly for different materials.
If a rough screed or "skinny concrete" is not used, then when installing a reinforcing frame on the film, care should be taken to provide linings that will not allow the reinforcing elements to pierce the coating. However, a more practical solution would be to build a layer of "skinny" concrete 6 - 7 cm thick from a conventional cement-sand mixture with fine crushed stone, which is also covered with roofing material or membrane on top.


The rough screed is also covered with waterproofing
Next, a reinforcement cage is laid on the rough layer and a finishing screed is performed. A rough screed can be treated with bitumen or bitumen-polymer mastic, and a layer of extruded polystyrene foam or dense foam can be laid on top for insulation.
Materials (edit)
Today there are a lot of waterproofing materials for the floor. In addition to classic films, this includes modern membranes, liquid rubber and mastics.
They differ in cost, in the technology of work. However, the main difference is in the effectiveness of protection against moisture penetration.