If the question is being decided which is better - expanded polystyrene or polyurethane foam, you should compare properties of these materials. In addition, you need to take into account and terms of Use, because in different rooms it may be preferable to use one or the other option. To conduct a full comparative analysis, the following factors are taken into account: structure, service life, strength and thermal insulation characteristics, hygroscopicity, noise absorption efficiency, density and some other parameters. The cost of the product is also important.
Briefly about 2 materials
Expanded polystyrene (PSP) is a gas-filled, closed-cell material based on polystyrene, its cells contain natural or carbon dioxide, and there is also a vacuum version. There are 2 types:
- foamed;
- extruded (extrusion).


Polyurethane foam (PPU) is a group of gas-filled plastics. The material is based on polyurethane. It can be tough, elastic and self-foaming. If the characteristics of polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene are considered, you should be aware that both options are similar in most parameters.


Comparison of expanded polystyrene and polyurethane foam
To understand which of these two materials is better, let's compare them according to a number of important indicators in the form of a table.
| Expanded polystyrene (PPS) | Polyurethane foam (PPU) |
| Environmental friendliness | |
| Releases phenol at temperatures above 60 ° C. | The products comply with sanitary standards. PU foam can be used at temperatures up to 180 ° C without concern. |
| Fire hazard | |
| Is burning. Combustion separates the burning parts from the material, which can spread the fire. | Not flammable. |
| Durability | |
| Service life no more than 15 years. Decrease in performance occurs after 10 years of use. | UV protected polyurethane foam can last longer than the load-bearing structure of a building. |
| The material settles and shrinks, disrupting the geometry of the facade. | The properties of the material do not change throughout the entire service life. |
| Appearance | |
| The presence of joints between panels entails a high consumption of joint fillers. | There is no seam. |
| Limited choice of facing materials, as a dovetail is required. | A wide range of finishing materials of any shape. |
| Ease of installation | |
| Plates often deteriorate during installation or transportation due to their material fragility. | The material is not picky in transportation. Only a spray gun is needed for installation. |
| Sheathing of slabs is required. | The material does not need additional crate. |
| Not all adhesion materials are suitable for polystyrene, therefore it is necessary to use special formulations for EPS. | It has excellent contact with all types of bonding materials. |
| Specific installation of panels using dowels and other materials. | You don't need anything other than a spray gun for installation |
| Features of operation | |
| High humidity can cause mold and mildew to appear on the slabs, which will lead to an unfavorable indoor climate. | Moisture resistant. Not subject to rotting and mold formation. |
| When moisture gets on the panel, it is absorbed and when exposed to low temperatures it freezes and destroys the foam. | PU foam repels water from the surface, thereby preventing material destruction. |
| It is necessary to constantly inspect the thermal insulation for defects and their elimination. | No renovation or repair of thermal insulation is required throughout the entire service life. |
Comparison result
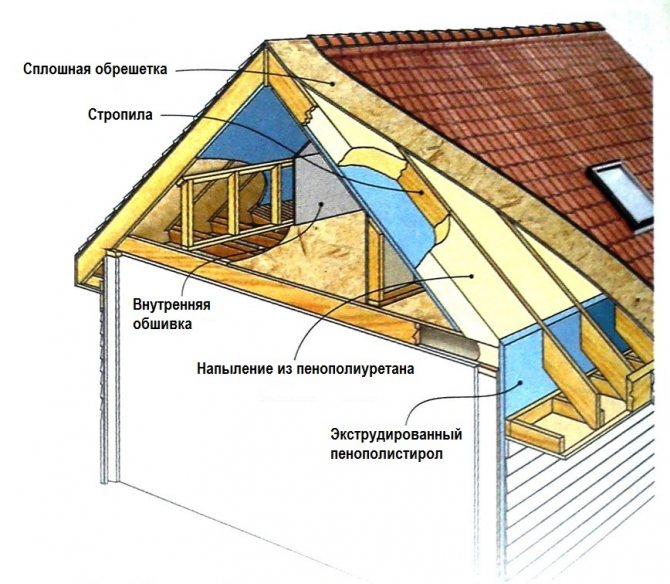

Roof insulation scheme with polyurethane foam.
It can be seen from the table that expanded polystyrene and polyurethane foam have both pros and cons, but most of all the disadvantages, of course, are in polystyrene. The service life of this material does not exceed 15 years. It is actively destroyed when exposed to the environment. Rodents often spoil the EPS slabs. Due to the fact that this material is a hydrocarbon polymer, adhesive and plaster solutions do not adhere well to it. But the most important thing is that expanded polystyrene is an unsafe material: it burns, scattering burning fragments in different directions, while emitting toxic substances. All this points to the unreliability of foam for thermal insulation at home.
Unlike foam, thermal insulation with polyurethane foam is a reliable and modern method of insulation. This material is lightweight and does not load the structure, but at the same time it is very durable. PU foam has low thermal conductivity and vapor permeability.
In our time, when all fuel resources are becoming more expensive, the question arises of high-quality thermal insulation. Undoubtedly, the best thermal insulation material today is polyurethane foam.
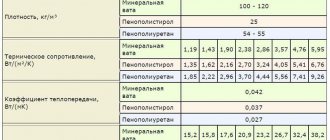
Comparative table of characteristics of PPU and EPS
These types of insulation are approximately equally popular due to their properties. If you are interested in the question, polyurethane foam or expanded polystyrene - which is better, it is recommended to compare them according to the main characteristics. The result can be seen in the table:
| Options | Polyurethane foam | Expanded polystyrene |
| Density, kg / m³ | 25-750 | 45-150 |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W / (m * K) | 0,019-0,028 | 0,04-0,06 |
| Structure | Closed-cell | Closed |
| Operating temperature, ° С | -160…+180 | -100…+60 |
| Environmental friendliness | Polyurethane foam retains its properties and does not emit harmful substances when heated to the maximum value (+ 180 ° C). | Expanded polystyrene at a temperature of + 60 ° C begins to emit a compound dangerous to human health - phenol. |
| Duration of operation, years | With proper installation, the service life is unlimited, in other cases it is 50 years. | 42278 |
| Fire hazard | Incombustible | More susceptible to combustion. In high temperature conditions, burning areas can be separated, which contributes to the spread of fire. |
| Hygroscopicity | Does not absorb moisture. | It is more exposed to liquids and is able to partially absorb them. |
| Appearance | Does not lose its properties throughout the entire period of operation. | Over time, it shrinks, undergoes deformation due to loss of properties. |
Do not insulate PPP and EPS …….
We invite you to study with us at the "school of construction"
Watch my channel school of construction on YouTube
Customer attention Live page shows Xella promotions for customers
Low-rise projects of any complexity from Itong aerated concrete with the calculation of foundations based on the IGI are made by WE. The prices are reasonable.
You can order a landscape design project for your site.
Do not insulate walls made of lightweight concrete and slotted bricks PPS and EPS
Quite often, building a house from Ytong, Grasse aerated concrete blocks or another manufacturer of aerated concrete blocks or aerated concrete, foam blocks, expanded clay concrete blocks, wood concrete or slotted ceramic bricks or ceramic stones, making a deliberately thin wall of a house or cottage, the developer then makes a constructive decision by insulating its PPS or EPPS- what, in principle, can not be done in any case for the following reasons: (on this page, for many years, a collection of information about the PPP of its modifications is presented)
The first of the reasons is the high fire hazard of expanded polystyrene PPS or EPS, so much has already been said on this topic and so many human lives have been paid, but the cheapness of EPS and EPS is very, very attractive, and a person thinks that this happened to them because they ... ...and then there are arguments for myself to justify my decision and the main argument that this will not happen to me - I will be careful in the operation of such a house ....
Second - in addition to the high fire hazard, the listed materials, namely, ytong or Grasse aerated concrete blocks, gas silicate blocks, foam blocks, expanded clay concrete blocks, wood concrete, slotted brick, porous ceramic stones possessing an important physical property - high vapor permeability from 0.14 to 0.25 according to the law of physics determining the movement of gases and liquids "take" increased moisture in the house and transfer it through their pores to the outside, but PPP and EPS are not vapor-permeable and it does not allow moisture to pass from a wall built of aerated concrete blocks of any manufacturer, at least Ytong or Gras, foam blocks, gas silicate blocks, as well as slotted bricks and ceramic stones - as a result, the process of moisture accumulation in the wall takes place, which in time in our middle lane lasts about 9-10 months, which leads to:
1- To moisten the wall and, as a consequence, aerated concrete block or foam block or expanded clay concrete block as well as slotted brick or ceramic stone, moistening, due to an increase in the coefficient of thermal conductivity, begins to lose more heat from the house and the insulation that the developer counted on due to moistening the wall is not only will receive, and even lose, more than before insulation, since every 5% moistening of the wall material increases the coefficient of thermal conductivity by 19-22%. Understanding what harm is done to the wall, the HENKEL corporation in its recommendations for the use of the CERESIT system in wet facades on the website prohibits the use of PPS and EPS on walls made of a number of porous stone materials, including aerated concrete walls made of aerated concrete blocks, slot bricks, porous stones, or wood concrete. The danger of the situation of humidification of a wall made of aerated concrete or foam concrete associated with its insulation with PPS or EPS is also that the period of moisture accumulation of the wall in our climatic zones of the central region is quite large - this period when the temperature inside the room is higher than from the outside lasts as already indicated above about 9-10 months and only two or three months on the contrary, when the temperature from the outside will be higher than from the inside. And these two or three months will not be enough to dry the wall, and accordingly the process of moisture accumulation progresses from year to year.
2- If in the middle lane the thickness of the insulation made of EPS or PPS is also less than 80 mm with a thermal conductivity of not more than 0.4, then the dew point will not be in the insulation, but at the border of the junction of the wall and the insulation, which will lead to mass condensation of moisture and in the case of high frosts will lead to defrosting of the wall. This we examined how the factor of low vapor permeability of EPS or EPS affects a wall made of aerated concrete blocks with high vapor permeability.
Below I cite a document of the Republic of Tatarstan, in which the use of PPP in buildings and structures with a planned durability of more than 50 years is prohibited due to other negative qualities of PPP, the reasons are also indicated in a generalized form there. Along with the PSP, the government of Tatarstan, for the same reasons, banned the use of MVP (mineral wool slabs) in the structures of these walls with a planned service life of the walls of more than 50 years. Now let's see what is a 50-year durability period? of stone materials, which are ceramic bricks, clinker bricks, porous ceramic stones such as braer or wienerberger, autoclaved aerated concrete blocks such as Ytong, Grasse, expanded clay concrete blocks with a density of over 1000 kg / m3, sand-lime brick, sand-concrete bricks made by vibration pressing ....
All that is determined by a service life of less than 50 years is the so-called time, that is, temporary buildings and structures. As a rule, in housing construction today, these are buildings, the service life within the walls of which determines the period of work on the effective thermal protection of heaters based on polymers PPS and MVP, where phenol-formaldehyde resins are the binder of mineral wool fibers. As soon as this polemer, according to the laws of chemistry, began to decompose into monomers, so the heat-shielding properties, it began to lose ... Russian experts estimate this at 30 years old, German at 15-20 years, depending on the density of the PPP or MVP (mineral wool plate)
Sincerely S. Korostelev


Decision of the Collegium of the Ministry of Moscow Oblast Construction of April 28, 2008 No. 4/7 "On the use of three-layer wall enclosing structures ..."
… ..Applied in recent years in the construction of frame-monolithic multi-storey residential buildings, three-layer external wall structures with an inner layer of effective slab insulation and a front layer of brickwork have significant damage on a significant number of buildings in use ……
…… In order to prevent possible negative consequences of using such solutions in enclosing structures, the Board decided:
To prohibit the municipalities of the Moscow Region, developers, design and contractors from using three-layer wall enclosing structures with an inner layer of effective slab insulation and a facing layer of brickwork for buildings and structures in the territory of the Moscow Region ...
Chairman of the Board, Minister of Construction
Moscow Region Government
E.V. Seregin
Cost comparison
Surface protection by means of polyurethane foam insulation is a more expensive technology. So, thermal insulation of 1 m² will cost 150-1500 rubles. In this case, the price is formed taking into account the thickness of the material: from 10 to 100 mm. This means that in order to insulate the surface of 1 m² with a layer of polyurethane foam 50 mm thick, you need to prepare about 850 rubles. The high price of this type of thermal insulation is due not only to the production technology of the material, but also to the high cost of equipment.
If the question is being decided which is better - polyurethane foam or expanded polystyrene, you should know that the latter of the options is offered at a lower cost. For comparison, insulation of an area of 1 m² with EPS boards will cost several times cheaper - 300 rubles, provided that the thickness is 50 mm. Good polystyrene foam boards, characterized by large dimensions and high density, are more expensive.
Application area
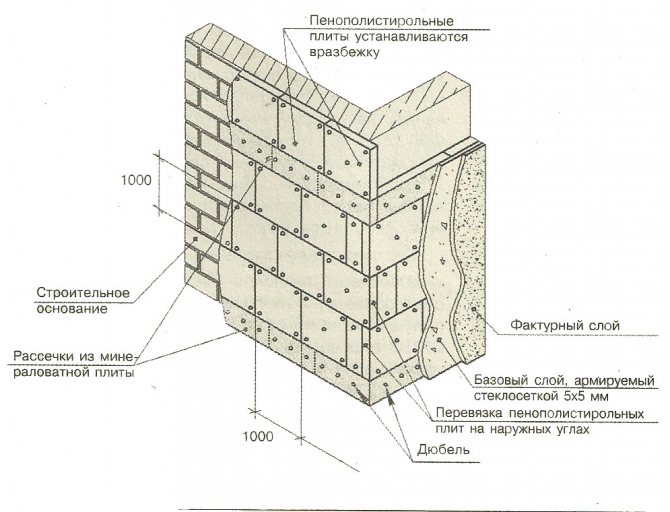

Facade insulation scheme with expanded polystyrene.
Expanded polystyrene, or polystyrene, is used in various fields of activity: from electronics packaging to individual construction. Polyfoam, as a building material, has become widespread for all types of thermal insulation work:
- it is used for roof insulation. Simplicity and ease of installation makes it possible to carry out work in any weather conditions. In addition, expanded polystyrene is used for the reconstruction of flat roofs;
- expanded polystyrene plates are used for floor insulation in houses, this is simultaneously not only good thermal insulation, but also waterproofing;
- foam is used as insulation for a warm floor, which significantly reduces costs;
- this material can be used to insulate the walls of buildings, both outside and inside, they insulate loggias and balconies;
- expanded polystyrene has become widespread not only for internal insulation of a house: it is used for thermal insulation of the foundations of buildings and pipelines.
But not only expanded polystyrene has become so widespread in construction, along with it, polyurethane foam is also in great demand.It is easy to use, and its main feature is that this heat-insulating material is presented not in the form of plates and rolls, as usual, but in the form of a special composition that is sprayed onto the surface. This feature makes polyurethane foam a universal insulation, which is why it is widely used in construction, where polyurethane foam is used in various directions:
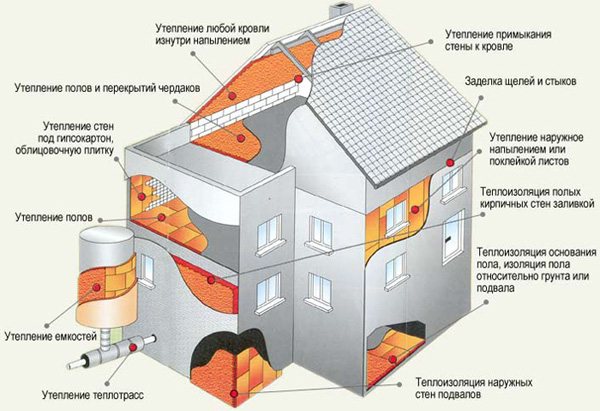

House insulation scheme with polyurethane foam.
- due to the chemical resistance of this material, it is well suited for thermal insulation of tanks, for example, swimming pools;
- polyurethane foam is excellent for thermal insulation of pipelines, because it has a high reaction rate, which avoids foam dripping;
- the adhesive properties of this material make it possible to widely use polyurethane foam for insulating building foundations;
- it is used for roof insulation;
- this material is great for insulating walls of buildings, both outside and inside.
The areas of application of expanded polystyrene and polyurethane foam are in many ways similar, but still they are two different materials with different properties.
For what purposes is it better to use?
PPU and PPP have their advantages over each other, for this reason, in some conditions, it is preferable to use one or another version of the insulation. For example, it is better to use PPU, if there are such tasks:
- it is necessary to create an effective wind protection;
- you need to implement the requirement of high adhesion;
- creation of a seamless heat-insulating structure;
- short terms of installation.
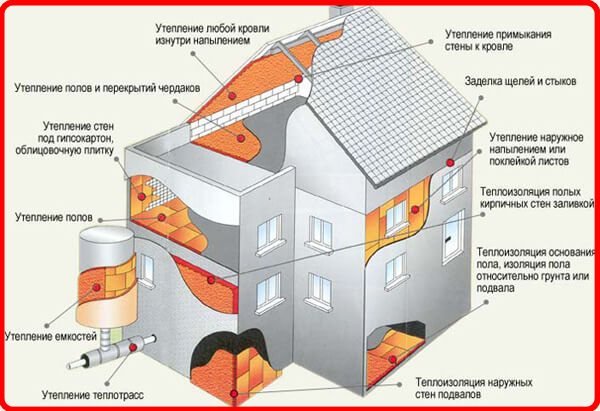

When polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene are considered, the comparison is made not only in terms of parameters, it is also necessary to take into account the operating conditions. For example, if it is planned to use PPS, it is necessary to provide high-quality moisture protection, which is facilitated by film materials. Expanded polystyrene and analogs similar in structure (polystyrene) need to create conditions in which the risk of fire will be small.
PPU is a fire hazardous material. Is it so?
Let's start with what we mean by combustible and non-combustible material. To do this, let us refer to GOST 30244-94 “Building materials. Flammability Test Methods ". In this document, building materials are divided into combustible (G) and non-combustible (NG). Non-combustible materials include metal (and even then not all alloys), stone, glass, expanded clay, basalt, etc. All wood-based or polymer-based materials are flammable and are divided into flammability groups:
- G1 - slightly flammable
(for polyurethane foam, this means that it is not capable of ignition, is resistant to the effects of open fire and thermal radiation, but under the influence of the flame it loses mass, smolders) - G2 - moderately flammable
(resistant to open fire and heat radiation, does not support combustion, in the absence of a flame extinguishes on its own) - G3 - normally combustible
(in the absence of a flame, it self-extinguishes and cannot be a source of ignition) - G4 - highly flammable
(supports combustion and may be a source of ignition)
In addition, other factors are taken into account during the tests - flammability, smoke emission, weight loss, flame propagation speed, decay time, release of toxic substances and a number of other factors. After such comprehensive studies, a conclusion and a fire safety certificate are issued, which regulates the scope of application of a particular material in construction.
Polyurethane foam is good because, depending on its composition (type and amount of fire retardant used), it can belong to all four groups of flammability. And the choice depends directly on the scope and wishes of the Customer. So, for example, polyurethane foam with a flammability group G1 and G2 can be used as insulation in residential and industrial facilities with open access to the insulation (roofs, facades, plinths, etc.).While the use of polyurethane foam with a flammability group G3 and G4 is justified for refrigeration units, when the polyurethane foam is concluded between other non-combustible building structures, etc.
In the section "certificates" on our website you can see examples of fire safety certificates for PPU: / products / certs / napylitelnye /
A couple of reviews about EPS
Leonid, 35 years old, Omsk: I used expanded polystyrene for wall insulation in a dacha. The house is small, it is heated in winter, so there were no problems with the appearance of moisture inside the heat-insulating "pie". I carry out repairs every 5-7 years, which means that the insulation during this time will not have time to sink and lose its qualities.
Vitaly, 45 years old, Khabarovsk: Expanded polystyrene does not make the structure heavier, retains heat well, so I chose this material. I heard that it is flammable, but the house uses a minimum amount of fire hazardous coatings, mostly concrete, brick, plastic, metal everywhere.
Extruded polystyrene foam


Pack of EPS sheets. Click on the photo to enlarge.
Expanded polystyrene can be divided into regular (foamed) and extruded (aka extrusion - EPS, English version - XPS). It is believed that conventional PPP lasts only 15 years, and extruded much longer - 45 years. The strength of the extruded polystyrene foam is much higher than that of the conventional one. I would use EPSS to insulate only "cold bridges" - window lintels, plate ends, etc. Of course, only outside and with the obligatory plastering of the entire surface of expanded polystyrene.
Different companies produce polystyrene foam under different brands. Some manufacturers claim the same strength characteristics for conventional EPS.
To choose a high-quality EPS, you need to pay attention to its properties. It should be homogeneous, the structure on the cut should be fine. When pressed, high-quality EPPS should not crack, leave significant dents, because this material is even used for road construction. You can check the water absorption of an EPSP test piece by immersing it in water for a day; EPS has a minimum water absorption by volume, usually no more than 0.4%.
Before laying the EPS, it is recommended to hold it for 2-4 weeks without packaging, so that all excess gases come out of it. Although usually the manufacturer should do this.
It must be remembered that EPSP has a very low vapor permeability, which limits the scope of its application. If used improperly, it can cause moisture buildup.
EPPS is resistant to many substances: water, weak acids, alcohol, bitumen, cement, alkalis, gypsum. It is not resistant to many hydrocarbons (including gasoline and diesel) and some acids.
Polyurethane foam
What is the difference between penoizol and polyurethane foam, which is a distant relative of penoizols?
Polyurethane foam is a polymer material that is a type of plastic, which was also discovered in Germany in 1947 by a German chemist named Bayer. This insulation is obtained through the reaction of two or sometimes more components. Among polyurethane foams, there are rigid, elastic and integral ones. However, for us, in this case, it is the rigid polyurethane foam that is of interest, which has become widespread as a reliable building insulation for buildings and private houses. Rigid polyurethane foam, as well as foam isols, have a fine cellular structure, but have a higher density - from 25 kg / m3 and more, as well as increased elasticity, which makes it more durable, for example, it does not crumble or crumble.
Comparison of polyurethane foam and penoizol
Impact on human and animal health
Penoizol, according to manufacturers, has passed numerous safety tests and is completely neutral in terms of its effect on the body for both humans and animals, as evidenced by numerous certificates.However, in some states of America and Canada, legislation prohibits the use of CPF as a material potentially hazardous to health. There is a similar ban in a number of European countries. The fact is that during the polymerization of urea foam, formaldehyde is released, which is harmful to the health of both humans and animals. It must be said that the disputes between scientists and manufacturers regarding the safety of urea-formaldehyde foam still do not subside and therefore there is no definitive answer to the question of the safety of KPF. The only thing that can be said is that the possible risks of emission of formaldehyde vapors can be reduced by applying a vapor barrier layer on the inside of the wall.
If we talk about polyurethane foam, then in matters of safety, it has certificates and conclusions that prove its harmless effect on living organisms, as well as on the environment. In terms of the use of polyurethane foam, no country in the world has such bans as Penoizol.
Fire safety
If we talk about fire safety, then penoisols belong to the G2 flammability class, that is, they are not able to ignite spontaneously. Polyurethane foams belong to the flammability class G3 and G4, which means that in the area of open fire they are slow-combustible and self-extinguishing.
Water permeability
The percentage of moisture absorption in penoizols is quite large, approximately 18-20%, from which it can be concluded that such heat insulators are afraid of moisture. With excessive moisture, penoizol begins to collapse, so additional steam and moisture insulation is needed for it.
Polyurethane foams have minimal water permeability due to their structure of closed pores, therefore, thermal insulation from polyurethane foam will not only perfectly retain heat, but will also be a good anti-corrosion protection, protection from moisture, mold and fungi. It is also worth noting that condensation does not form on polyurethane foam surfaces.
Thermal insulation of penoizol and polyurethane foam
High-quality penoizol has good thermal conductivity - up to 0.030 W / m K, but the thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam is about 0.021 W / m K.
Strength of polyurethane foam and foam insulation
In terms of strength, penoizol is inferior to polyurethane foam, since it is a much more fragile material. But polyurethane foam is quite durable and at the same time elastic material that is perfectly able to withstand, for example, building shrinkage, walking and other mechanical influences.
Prices for penoizol and polyurethane foam
If we compare penoizol with polyurethane foam in terms of cost, then here the first place will be for carbamide foam, which is an order of magnitude cheaper than polyurethane foam technology, however, its physical and chemical qualities are lower than that of polyurethane foam ...