Heating design prices
| № | Job title | Description | unit of measurement | Price in rubles |
| 1 | Heating system design | Project composition:
| m2 | 80 |
| 2 | Underfloor heating system design | Project composition:
| m2 | 80 |
| 3 | Design work on the water supply system | Project composition:
| m2 | 50 |
| 4 | Design work on the sewerage system | Project composition:
| m2 | 50 |
| 5 | Ventilation system design work | Project composition:
| m2 | 60-120 |
| 6 | Design work on the air conditioning system | Project composition:
| m2 | 70 |
| 7 | Boiler room project | Project composition:
| set | from 7000 |
| 8 | Low-current systems project. | Project composition:
| m2 | 70 |
| 9 | Visualization of the boiler room project in 3D | Project composition:
| set | from 9600 |
| 10 | Departure of the designer to the object | At the conclusion of the contract, the amount is counted towards the payment for design work. | 2100 | |
| 11 | Heat engineering calculation | Calculation of the heat loss of the building. | m2 | 25 |
| 12 | Transfer of drawings from paper to electronic form | m2 | 25 |
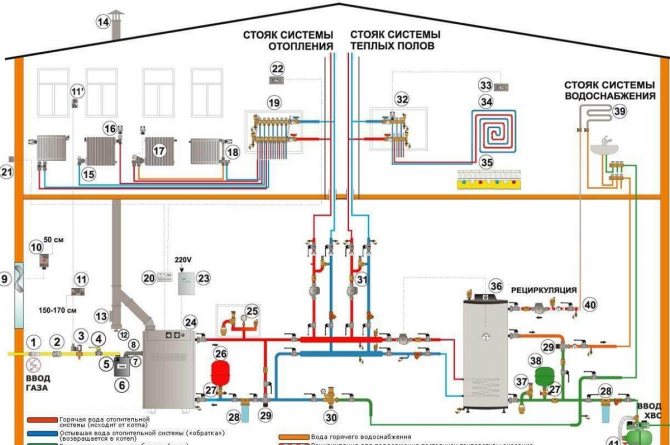
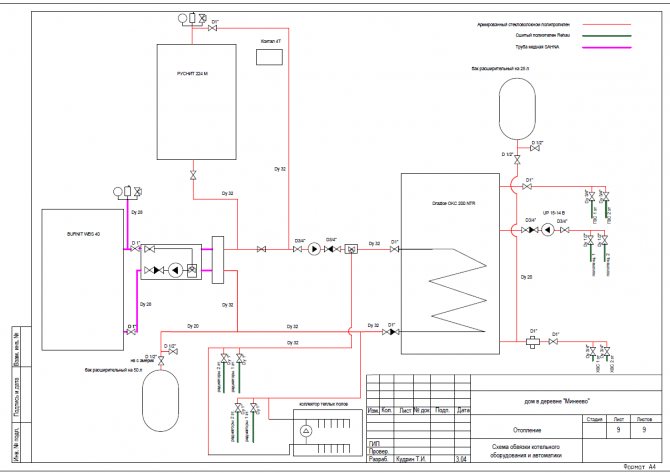
Two-story house heating system project
Object: two-storey house
Address: Moscow region, Mineevo village
Area: 150 sq. meters
Design temperature of the outside air: in winter -28 С; in summer +26.3 C
Estimated air temperature of a residential building: +22 С
Heat consumption for heating (heat loss at home): 32 kW
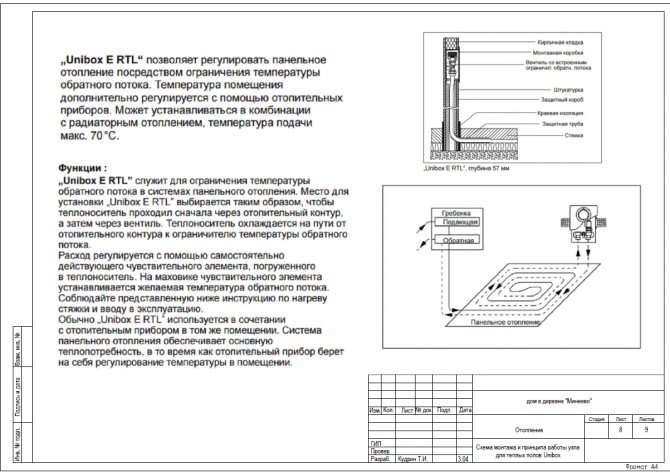
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
The system is designed to use a temperature regime of -75 / 55 C.
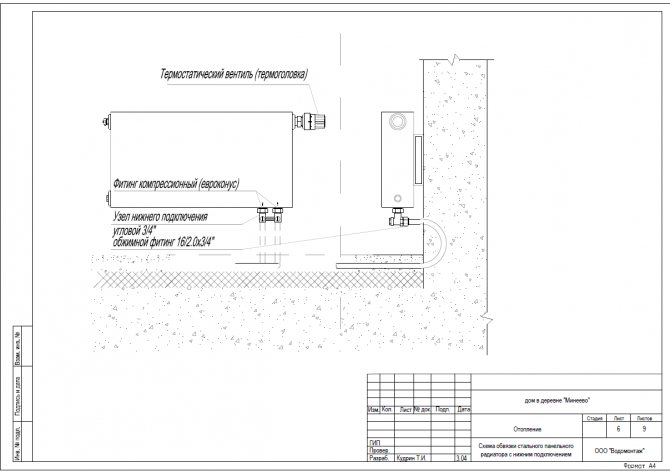
Steel panel radiators Kermi with bottom connection are offered as heating devices.
Luxor thermostatic heads are installed for radiator automatic power control.
The layout of the distribution pipelines is adopted as a two-pipe sequential. The piping of the radiator heating system is designed from pipes made of foil-clad cross-linked polyethylene Rehau Rautitan stabil.
The heating system is controlled by thermostatic valves. Each heating floor has its own route from the boiler collector. Balancing between floors is carried out using balancing valves installed on the return of each floor. All heating pipelines are designed to be laid in a hidden way on the floor. All pipelines should be laid in Thermaflex Super insulation to avoid heat losses.
The pipelines of the heating system are laid in accordance with the working drawings, taking into account the necessary slopes (min i = 0.002), to ensure complete air removal when filling and emptying the system.
Install pipelines in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions for installing the pipeline system. Air separation is carried out using automatic and manual air vents installed in the boiler room and radiators. Fastening the pipelines according to the manufacturer's instructions according to the diameters used.
After completing the installation work, the system should be tested for tightness at a constant water temperature, individual equipment tests, with the preparation of relevant acts.
Hydraulic testing of pipelines with their hidden laying should be carried out before their closure with the drawing up of an act of inspection of hidden works. Testing of insulated pipelines should be carried out before applying insulation to the joints.
At the end of installation, the heating system must be flushed with water until it comes out without mechanical suspensions.
INSULATION INSTRUCTIONS
On the overlap of the first floor, lay insulation made of expanded polystyrene of the Penoplex type in 2 overlap layers. The thickness of each layer must be at least 50 mm.
Insulate the roof with mineral wool insulation with a thickness of at least 200 mm.
General project data |
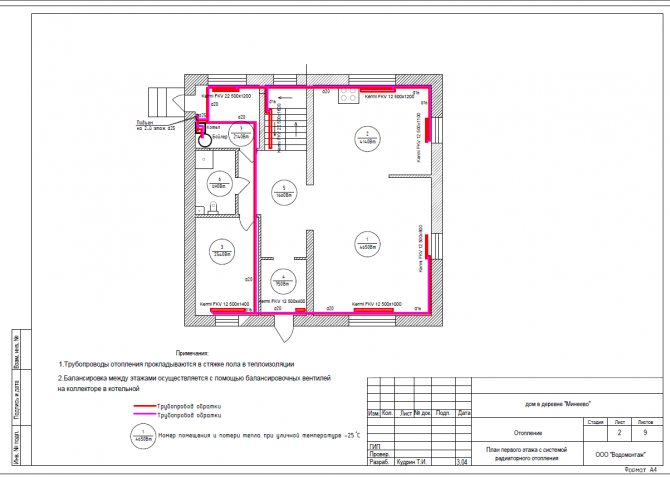
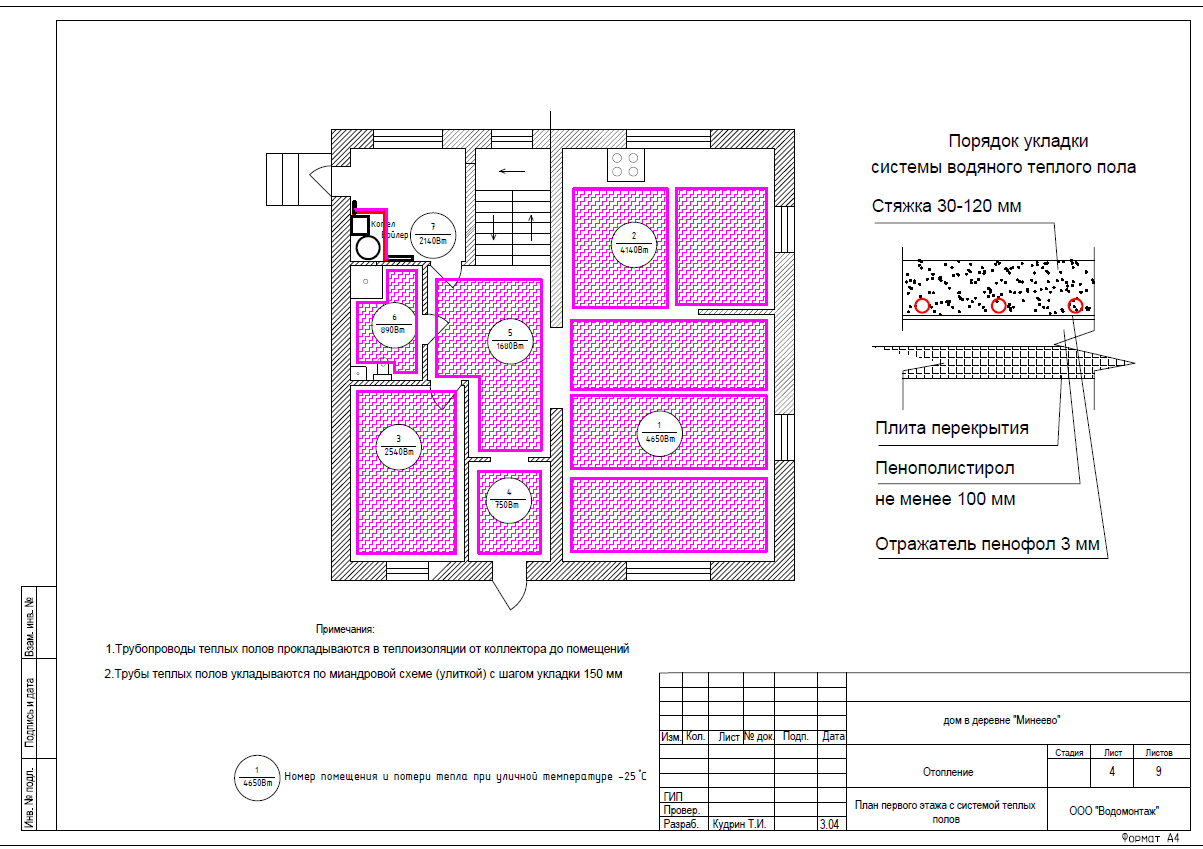
Ground floor radiator heating plan |
Second floor radiator heating plan |
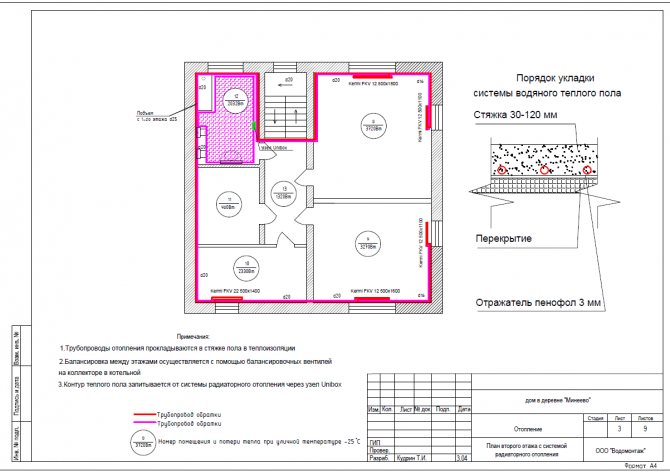
Underfloor heating plan of the first floor |
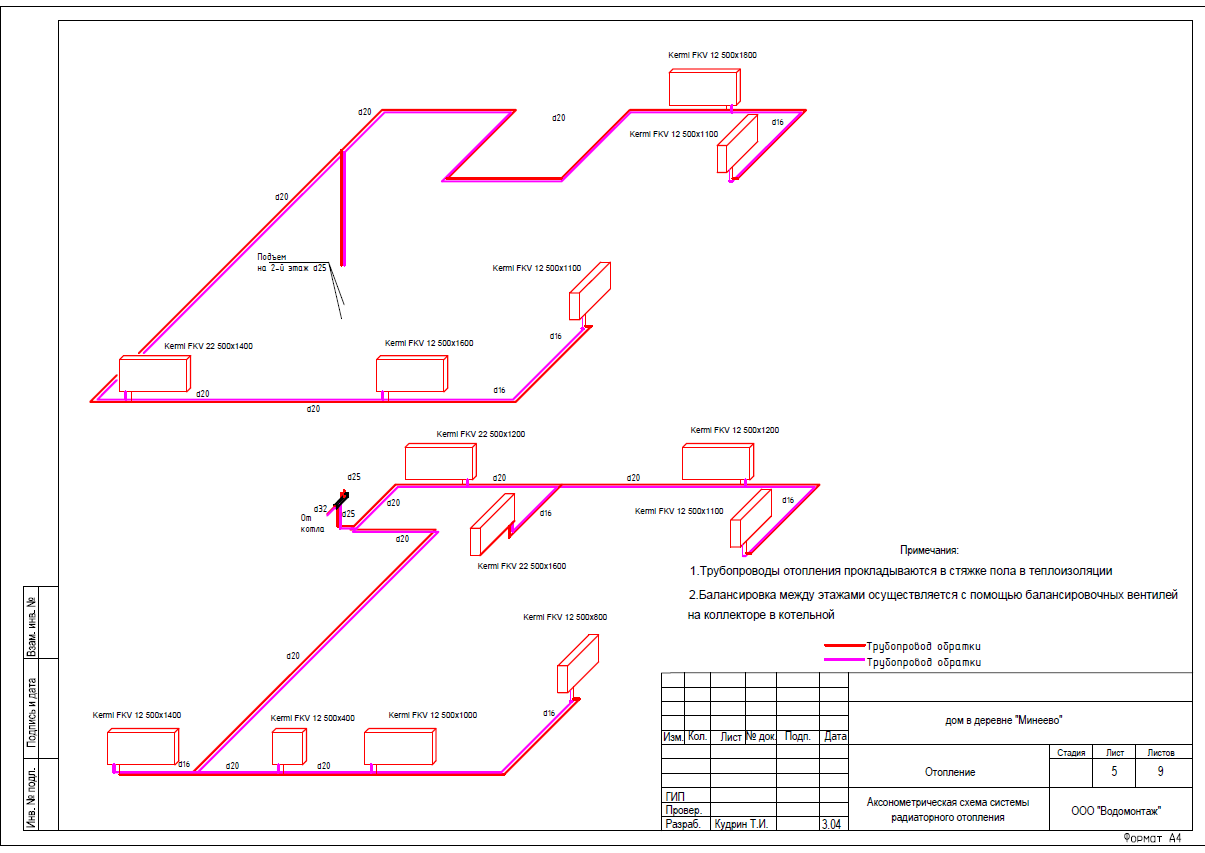
Axonometric heating diagram |
Radiator connection diagram |
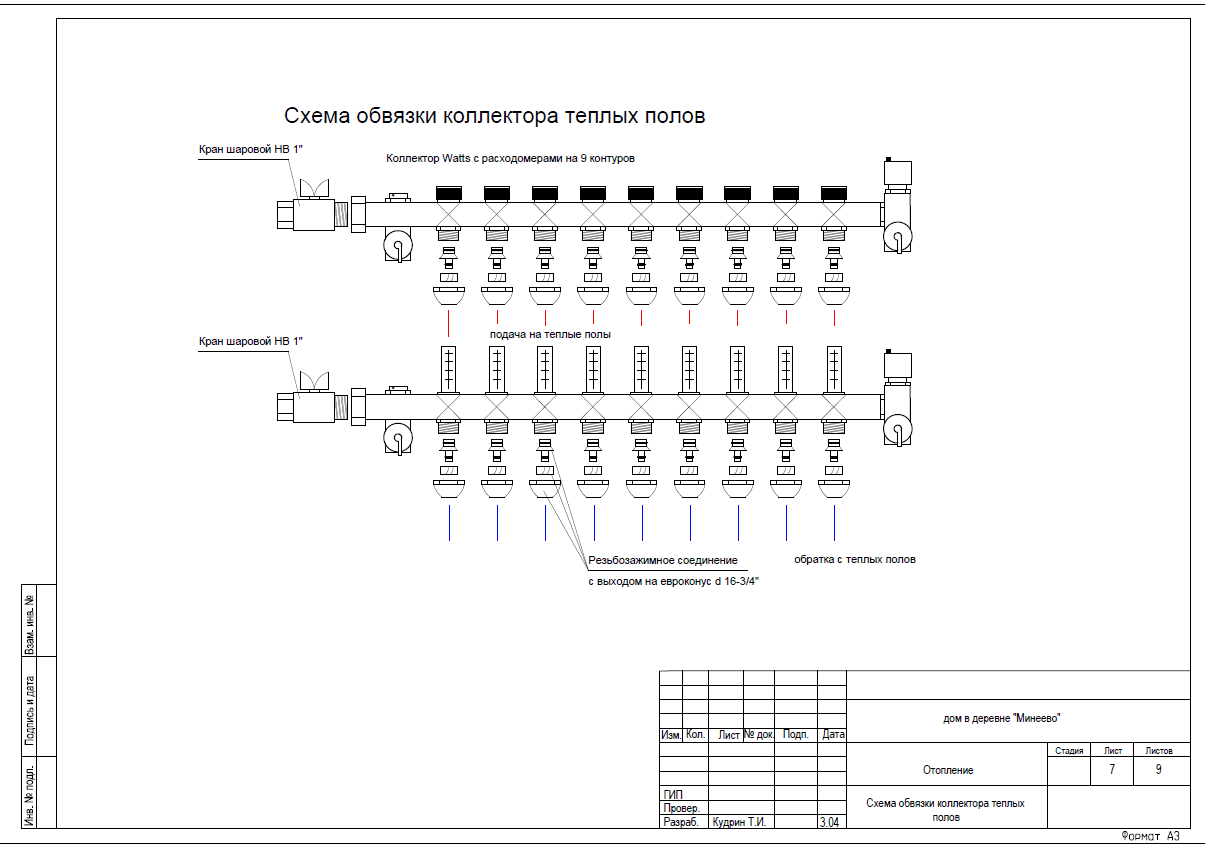
Connecting a collector for underfloor heating |
Unibox assembly diagram |
Boiler room installation diagram |
Preliminary design
The draft design (ED) of the heating system is intended to determine the requirements for the solutions of the object and to confirm the possibility of its creation. Sometimes the conceptual design stage is skipped, and all the work foreseen at this stage is performed at the feasibility study stage. We do not take this approach.
Our company is ready to offer several options already at the ES stage. The draft design is carried out with the preparation of an explication of the main equipment, equipment brand and manufacturer. That allows you to choose the optimal and less costly way to solve the problem at the earliest stage.
Terms of reference and commercial proposal
At the second stage, on the basis of the approved draft design and preliminary calculations, the following are developed:
- a document containing a textual description of the heating system being created - terms of reference (TOR);
- and possible investment costs for its creation - commercial proposal (KP).
Customers often turn to us with the question: "How much does the services of your specialists cost and how much will the heating system of my house (workshop, enterprise, etc.) cost me?" At the same time, the person who asked this question does not have any project for the desired heating system, and sometimes there is no answer to the question to himself: "What do I want myself?" Naturally, we cannot give an answer to such a question “in flight”, and we have to explain for a very long time why we cannot do this. Therefore, below we give a standard form of technical specifications for the design of a heating system, from which it is clearly seen how many questions the designer needs to answer in order to complete the design work. And this is not a complete range of all questions. And only on the basis of the finished project, the estimator already has the opportunity to issue an estimate for the object. And for us, as specialists, one thing is unambiguously clear that if someone "in flight" says the price, then this is just a shameless deception of the customer and nothing more. Miracles don't happen.
Heating project - a complete package of project documentation
The fourth stage is the execution of work on the preparation of complete specifications for heating equipment and materials, as well as the design of project documentation in a form that meets the established norms and rules.
Performing work on all four stages allows you to create a complete package of project documentation, which is called a heating project. The proposed projects of heating systems allow us to perform all further installation work on the installation of equipment with high quality.
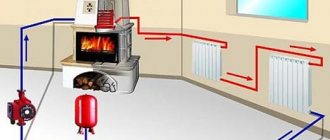
Heating scheme of a private house
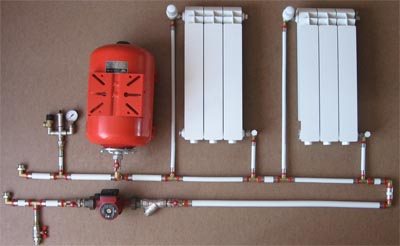

To understand the heating scheme of a private house erected with your own hands, you need to know some rules. They relate to the installation work, as well as the competent selection of heating equipment, piping and the type of heating system. In this article, we will analyze all the schemes and find out what nuances must be taken into account in order for the system to work efficiently.
Immediately, we will decide that we will consider only water heating using boilers and pipes. Firstly, this system is considered to be the simplest and most reliable. And, secondly, you can choose such a scheme and build such a system that its work will be effective, and the practical side of the matter will be observed.
The principle of operation of such a heating system is as follows. The coolant in the heating boiler heats up and flows through the pipeline to heating devices - radiators. Here it gives off heat and returns along the return circuit to the boiler. And the whole process is repeated anew. It turns out that water heating is a kind of cyclical technological process.
Types of heating schemes
So, what is the best heating scheme for a private house? There are two of them:
- One-pipe.
- Two-pipe.
One pipe system
Of the two above, this is the cheapest and simplest system. It is a ring in which heating radiators are installed in sequential order. The coolant moves from the radiator to the radiator until everything passes and returns to the boiler. Very simple.
It would seem that such a scheme should be optimal, because it is simplicity and economy that are often the fundamental factors influencing the choice.
But not everything is as simple as it seems at first glance. Judge for yourself. The heat carrier, heated to a certain temperature (usually +75 C), moves to the first heating device. He gives him a certain amount of heat, while cooling down by several degrees.
One-pipe heating scheme
In the second radiator, it is not yet clear that the coolant has cooled down. But already in the fourth or fifth it will be noticeable.
Having reached the last radiator, the coolant will have a temperature of approximately +45 C. And the room cannot be heated at such a temperature.
What to do? There are two ways out:
- Increase the number of sections of the last radiators, thereby increasing the heat transfer area.
- Increase the temperature of the heating medium leaving the heating boiler. And this will require more fuel consumption.
Both options have an economic component, which, unfortunately, is not distributed in the direction of reducing costs, but, on the contrary, in the direction of increasing. And here you have to choose what is best for you.
There is another option. This is a scheme with forced circulation of the coolant. What it is?
This is when there is a unit in the heating system, usually a circulation pump, which creates a small pressure inside it. It ensures an even distribution of the coolant over all radiators. In addition, hot water moves through the system at a low speed, and this affects the inertness of the system, so that rapid heating occurs.
This option is more effective than the first two, but the circulation pump installed in the system operates from the electric current network. What is the inconvenience?
- Firstly, it consumes a little electrical energy, but this is an additional cost.
- Secondly, if there is no electricity, then there is no pressure inside the heating. And in winter, turning off the power supply in suburban villages is not uncommon.
Two-pipe system
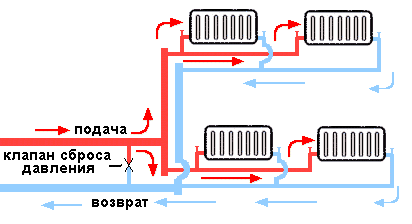

Two-pipe heating system of a residential building
To say that she is better than the first is to say nothing. This scheme works much more efficiently, because each radiator has its own separate pipe with a coolant. But they have only one reverse circuit. And from each radiator a separate pipe goes down to the return, through which the coolant is removed.
In general, this system is not complicated. It is only necessary to choose how the coolant will be supplied to the radiators - according to the beam or collector scheme.
In the first case, the supply pipe rises up to the ceiling into the attic, where its own individual pipe is diverted from it to each pipe. It turns out a kind of contour, similar to the sun, where in the center there is a pipe from the boiler, and the rays of the pipes diverge to the radiators to the sides. Hence its name - ray.
The collector circuit is considered more modern. A special device is installed in the attic, which is called a collector. It consists of a pipe structure through which the coolant is distributed throughout the system. Shut-off valves are also installed here, cutting off each circuit.
This makes the system convenient to operate, and also simplifies the repair process, if necessary. So, you can repair not only a separate supply circuit to the room, but even a free-standing radiator.
In all respects, the collector circuit is superior to the others. But a two-pipe system, and even more so a collector system, has one significant drawback. This is a large amount of material used to build this circuit. This includes pipe, shut-off valves, monitoring and control devices and sensors. Therefore, you will have to fork out here. But if you want your home to always be warm in all rooms, then just such a scheme will help you do this.
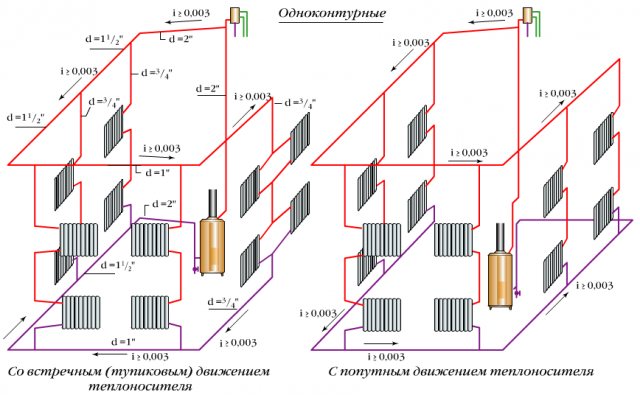

Single-circuit systems with natural circulation
Can a circulation pump be installed in a two-pipe heating system? How relevant is it? There is no great need for this, because the two-pipe system with natural circulation works efficiently. So there is no need for extra expenses.
Now he returns to the question of whether it is possible to build a heating system in a private house with your own hands.Here, as elsewhere, a lot will depend on the skills of using various tools and experience in carrying out installation work. If you do not have either one or the other, the consequences may not be very rosy.
First of all, the boiler will boil, and the batteries will be cold. If the slope of the upper piping is incorrectly made, it will be cool in the rooms, even with a hot boiler. The same applies to the return loop.
If you install a circulation pump in the wrong place, it will work for one season and stop, start leaking, that is, problems will appear. Well, if you put the expansion tank incorrectly, you will get a shortage of coolant in the system.
And there are many more such nuances. So, ideally, the installation of a heating system is the work of craftsmen. But if you want to save money and your budget is tight, then you have to learn.
Designing a heating system for an apartment building
Continuing the topic of engineering systems, consider the design of heating an apartment building. Like water supply or electricity, this system is complex in design. Even two apartments of the same size, one of which is corner and the other in the middle of the building, are different in terms of heating the apartment.
Heating standards for apartment buildings allow each of the residents to feel comfortable. For example, for living rooms, an adequate minimum is a temperature of + 20˚С. For the kitchen and the bathroom, the optimal temperature is considered to be in the range from + 19˚C to + 21˚C, the bathroom - from +24 to + 26˚C, inter-apartment corridors - from +18 to + 20˚C.
Types of heating systems
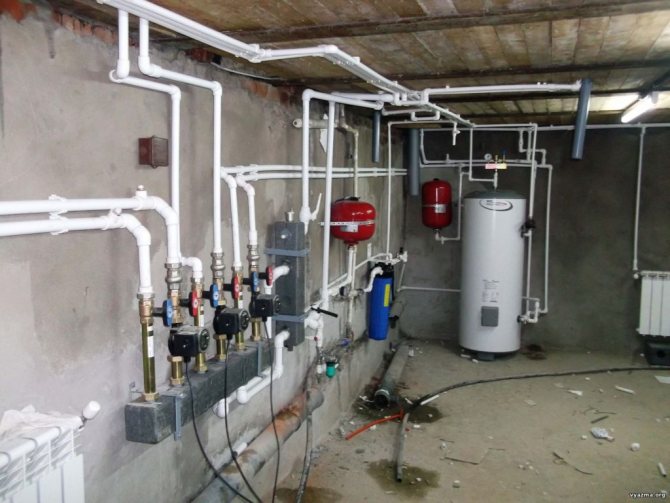
In most cases, houses in cities are heated with a centralized heating system. Its essence is as follows: at a heating station, heating boilers heat water to a temperature above 100˚С (therefore, in order to avoid boiling and evaporation of water, the pressure in the pipes is about 10 kgf). Further, water is supplied to all buildings connected to the heating main. When a house is connected to a heating plant, input valves are installed to control the supply of hot water to it. A heating unit and various specialized equipment are also connected to them.
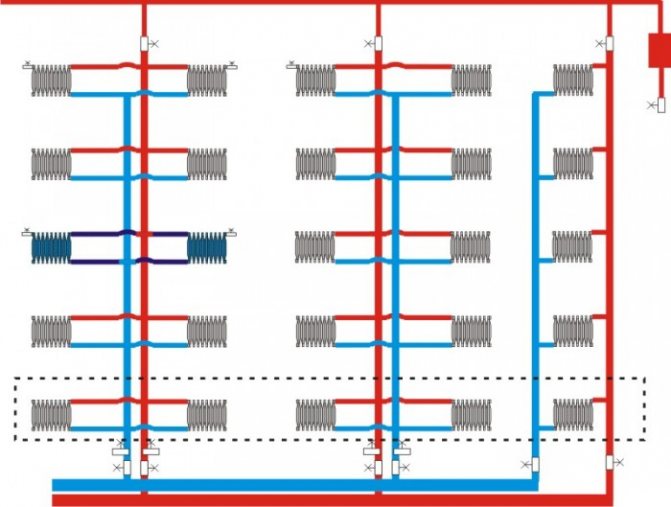

In the case of individual heating, the installation of its own boiler room is provided, with the help of which autonomous heating of the house takes place. Such systems have a number of advantages:
- Effective temperature control in rooms and its maintenance at a given level, regardless of the external network;
- More economical, stable and reliable.
Among the disadvantages is a significant start-up investment for the creation of individual heating.


Top and bottom piping
Depending on the location of the heating pipes, water can be supplied both top-down and bottom-up (when using a one-pipe system), or simultaneously to all apartments (with a two-pipe system).
With the upper wiring, the supply pipe is arranged either in the attic or on the top floor (in the absence of an attic). It is used if it is not possible to carry out the lower wiring. The advantages of the top wiring are that:
- Heat loss is minimized;
- Easy installation;
- A minimum of twists and turns.
The main disadvantage of such a wiring is the need for more materials and the mandatory presence of Mayevsky taps on the radiators (or, in another way, the STD7073V air release valve).
With bottom piping, the supply pipes are located in the basement. The main advantage is the ability to regulate the heating process of the coolant using a thermostat.
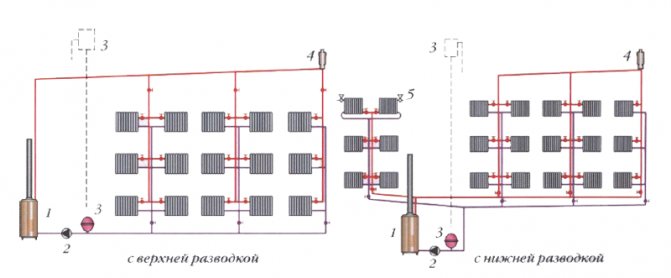

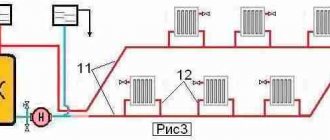
One-pipe and two-pipe heating system
Despite the fact that you can choose the pipe layout, as well as the heating method (from the central main or your own boiler), there is not much choice when designing the heating system of an apartment building. All houses are heated in about the same way.Each room has a radiator (mostly cast iron, the dimensions of which depend on the area and purpose of a particular room), into which the coolant coming from the thermal station is supplied.
The difference in water supply is only in what kind of heating system is provided in a particular building: one-pipe or two-pipe. Each of them has its own pros and cons. Therefore, briefly about each.

One-pipe heating system: simple, reliable and relatively cheap design. However, such a system is not very much in demand. The heat carrier (hot water), getting into the heating system of the house, must pass through all the radiators before leaving the return channel (or "return"). By heating the radiators one by one, the coolant loses its temperature and, as a result, the batteries are barely warm on the upper floors. Therefore, such a system is rarely used.
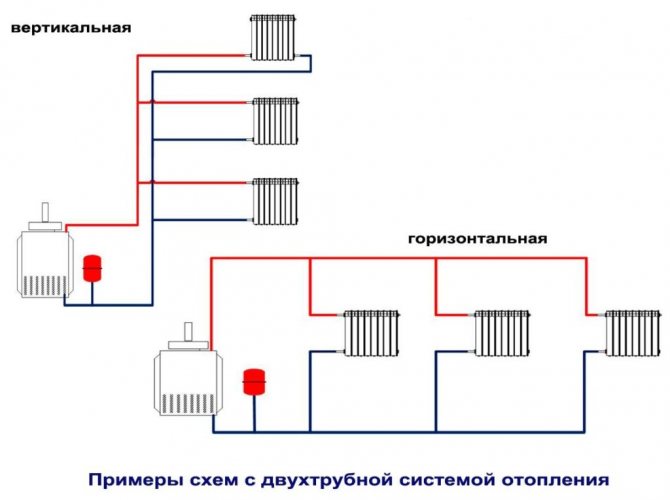

Two-pipe heating system: the one-pipe system is devoid of the disadvantages. The design differs significantly from the previous system. Hot water, passing through the heating radiator, enters the return duct, and not into the pipe leading to the next radiator. From there - immediately back to the heating station, where it heats up again to the desired temperature. Such a system is more costly to install and maintain. At the same time, a two-pipe heating system ensures the same temperature in all heated buildings. And it allows you to install a heating meter (placed on the radiator), so that the owner of the apartment can regulate the heating level of the radiator himself and save on heating bills.
Types of radiators for space heating
Considering the heating of an apartment and a house as a whole, one cannot but tell about radiators, because they are the main suppliers of heat to the premises. Most people are used to cast iron radiators, which began to be installed almost a century ago. Someone paints them, hides them behind special screens, draws up curtains. Such measures help to reduce the temperature. That is why many apartment owners prefer to install modern radiators made of different materials. Let's take a look at some of them.


Aluminum: lightweight material with high thermal conductivity. Aluminum radiators look sleek. No need to paint, heats up quickly and gives off heat in a matter of minutes. Disadvantages: Over time, acidic water can cause irreparable harm. In addition, aluminum is a fairly plastic and soft material, and high pressure (often on the first floors of 12-16 storey buildings) can simply rupture batteries.


Steel: just like aluminum, it heats up quickly and gives off heat to the room. Due to the high strength of the material, miniature radiators can be made that can maintain the desired temperature. And high strength is a guarantee that radiators will not be damaged at high pressure. Minus: - high oxygen content in the water can negatively affect the inner wall of the battery.


Cast iron: no, it has not left the world of heating irrevocably. Modern technology makes it possible to produce miniature and attractive cast iron radiators. They are not only highly durable, but also not afraid of high acidity of water or high oxygen content. Another plus of such radiators: they do not heat up quickly, but they also slowly cool down. Therefore, such radiators are able to protect against temperature changes that negatively affect human health.
Requirements for heating systems of apartment buildings
When designing a heating system for apartment buildings, the following requirements must be observed:
- Providing living quarters with a sufficient amount of heat;
- Taking into account the parameters of window structures, ventilation system and other parameters affecting the operation of heating. In this case, the heating system must be fully consistent with the work of other engineering systems. Therefore, it is best to develop all the engineering support of buildings in the complex;
- The heating system should fit into the image of the building without disturbing it;
- The heating system must be safe, regardless of its type. The most stringent requirements apply to individual heating devices in each apartment. Focus on fire safety and carbon monoxide leak prevention;
- Accounting, management and dispatching: accurate metering of consumed heat (special meters) and the ability to control, including remote control.
Features of the design of the heating system of an apartment building
In the process of designing a heating system for a residential building, a set of issues is being resolved. When composing the calculated part of the project, the following features must be taken into account:
- Heat loss of the building: in this case, it is necessary to take into account not only heat loss through windows and walls, but also losses as a result of the operation of the ventilation system;
- Determination of the required temperature of the coolant at the entrance to the system or the power of the boiler room in the individual heating of residential premises;
- Calculation of heating of a dwelling in a building, implying the calculation of the power of the radiator in each of the rooms;
- Development of temperature charts to help determine the minimum and maximum loads on the heating system at home.
The heating system design process is laborious and requires a lot of time and care. Miscalculations will lead to an increase in operating costs, uneven heating of premises, possible interruptions in heat supply and high repair costs due to increased accidents.
The specialists of the V-GRAND company will develop a home heating system according to your terms of reference. Just call us or leave a request on the website. V-GRAND - quality, efficiency, result!
Which heating boiler to choose?


It is no secret that there is a fairly large selection of modern heating boilers. They are divided into types according to the fuel on which they work. Which one to choose depends on the circumstances. It is based on the fuel that is easiest to find in your area, and which is cheaper than everyone else.
Manufacturers are now offering dual-fuel combination models. For example, gas and firewood, gas and electricity, coal and electricity, firewood and diesel fuel. When one fuel runs out, it can be replaced with another. Therefore, the advice is to choose the boiler that is convenient for you both in terms of fuel supply, and in terms of operation and maintenance.
How to order the design of a heating section and not be mistaken
] Smart Wei [/ anchor] is always interested in long-term cooperation, values its reputation. Therefore, we offer each client to familiarize themselves with examples of previously performed work, we will select the most effective option for placing the heating system and other utilities. This will save you time and money on approvals, contract work, commissioning and network maintenance. Call us, we will advise you on all your questions free of charge!
Heating pipes


REHAU metal-plastic pipe
Which pipes are best? For hot water heating, the best option are metal-plastic pipes that can withstand high temperatures. But if a solid fuel boiler is installed in the heating system of a private house, then it is better to use metal pipes. Indeed, sometimes the temperature of the coolant leaving the boiler can be more than + 100C, and the plastic cannot withstand it.
When choosing schemes for installing heating in a private house, you need to think carefully about everything, weigh and approve the budget exclusively for heating at the family council. It is from the money that you will have to dance. If the budget is large, then you can install a two-pipe scheme, and even with a collector and a pump. If it is small, then you can do with a one-pipe scheme.But if you add a little money and buy a circulation pump, then even this system will work well.
- Example 1. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a two-pipe scheme
- Example 2. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a one-pipe scheme
- Example 3. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a collector circuit
After a hydraulic calculation, it may turn out that the resistance of the heating system is too high. You can, of course, purchase a more powerful circulation pump. It is possible, as already suggested in the previous article, to increase the diameters of the pipes. But there is another option: change the way of connecting radiators. Therefore, I decided to add this article, which considers examples of heating systems projects for the same house.
In the previous materials, I performed calculations for a two-pipe heating system. You can replace it with a one-pipe one and perform all calculations on a new one ...
Well, not all, of course: the heat loss does not need to be re-counted. And also there is no need to re-count the sections of the radiators. It's only about the hydraulic calculation.
So, as I said, below are three examples of the project of the same house, but in each example the radiators are connected in a different way. All these schemes have already been sorted out, but I think it will be useful to refresh your memory.
Wiring
- How to separate the heating system from the boiler?
In my opinion, two types of wiring deserve attention:
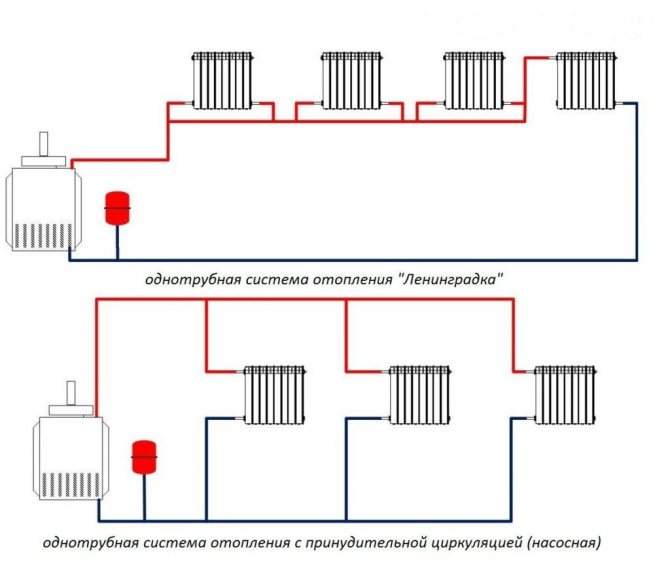
- One-pipe Leningrad (bottling along the perimeter of the floor with radiators connected in parallel to its pipe). It is extremely easy to install, has a minimum material consumption (there is only one filling) and maximum fail-safety: as long as there is at least a minimum pressure drop at the ends of the filling, the heating circuit will function;
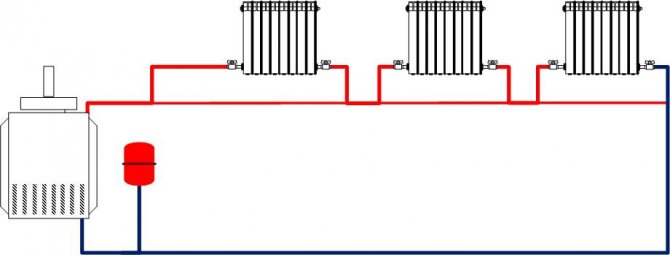

The simplest and most reliable heating system is one-pipe Leningrad.
- Associated two-pipe system (Tichelman loop). Unlike dead-end systems, it does not require balancing (throttling of the radiators closest to the boiler) and provides the same temperature for all heating devices.
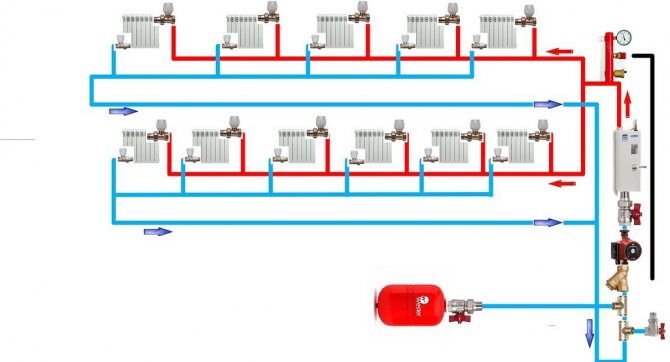

Tichelmann hinge version for a two-story house.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the underfloor heating system - underfloor heating. The pipes laid in the screed turn the entire surface of the finished floor into a heating device.
The maximum length of one circuit of a water underfloor heating is limited to 100 - 120 meters, since the pipes have a small diameter and, accordingly, a sufficiently high hydraulic resistance. That is why, to heat a large room, it is necessary to form several parallel circuits with the same coolant temperature, which implies collector wiring.
Each collector outlet is equipped with its own throttle to regulate the temperature of the circuit.
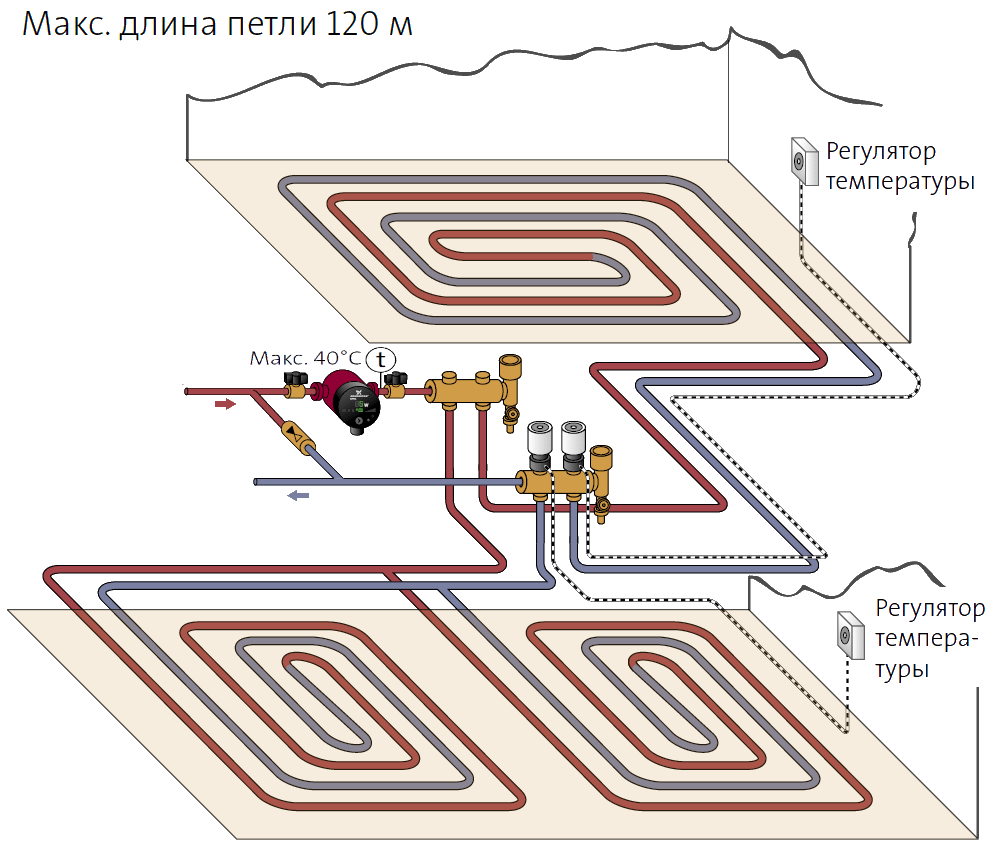

Low temperature heating circuit with multiple circuits.
Example 1. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a two-pipe scheme
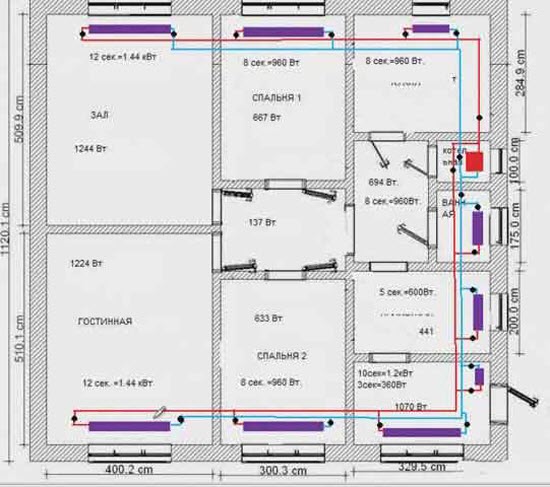

There is a boiler in the boiler room (red rectangle). Moreover, it is immediately worth making a reservation: if the boiler is wall-mounted, then it is not necessary to install it in the boiler room, it is allowed to install it both in the kitchen and in the hallway. But when designing, you need to remember about the chimney.
So, back to the heating system.
Radiators, as expected, under the windows; on the diagram radiators in purple.
In order not to pull pipes around the perimeter of the entire house, the pipeline is designed with two loops.
The supply pipe is marked in red, the return pipe is blue. Black dots on the supply and return are shut-off valves (radiator taps, thermal heads, etc.). Shut-off valves must be installed - in case the radiator for any reason fails, and it will need to be disconnected from the system for replacement or repair without stopping the entire system.
In addition to shut-off valves on each radiator, the same valves are on the supply for each wing, immediately after the boiler.
Why are shut-off valves installed here? As you can see from the diagram, the length of the system loops is not the same: the “wing” going up from the boiler (if you look at the diagram) is shorter than the one that goes down. This means that the resistance of a shorter pipeline will be less. Therefore, the coolant can go more along the shorter wing, then the longer "wing" will be colder. Due to the taps on the supply pipe, we will be able to adjust the uniformity of the coolant supply.
The same taps are installed on the return flow of both loops - in front of the boiler.
Example 2. Project of a heating system with connecting radiators according to a one-pipe scheme
The diagram below shows the same house design, but the heating system is one-pipe.
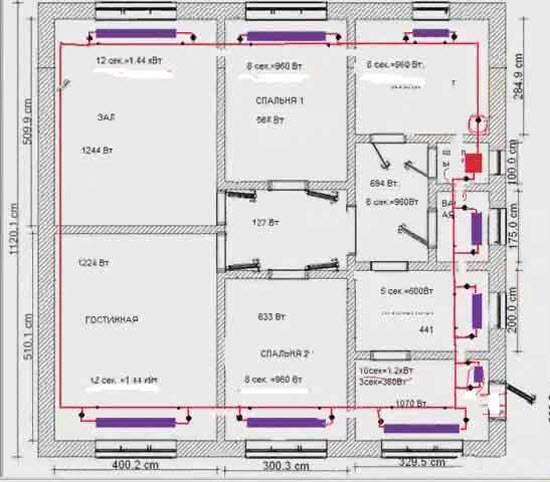

In principle, the requirements here are the same (shut-off valves on each radiator, on the supply and on the return).
The only difference is that the pipe runs along the entire perimeter of the house, and not in separate circuits, as in the example with a two-pipe system. In addition, it must be remembered that with a one-pipe system, a pipe of a smaller diameter should be placed under the radiators (in the diagram, such areas under the radiators are marked with dots). This is necessary for uniform heating of the radiators. You can read more about the nuances of a one-pipe heating system from a separate article.
Example of a collector heating system
The figure below shows a simpler manifold system (manifold assembly):
Manifold unit of the heating system
Here, as in the previous version, separate pumps are installed on each collector circuit. But in fact, this is done only if the system itself is very large (two-, three-story houses with large areas). If you do not have such areas, then there are enough bends in the collector with its own shut-off valves, and the circulation pump is set to one common for the entire system (usually on the return line).
Well, and a few more projects of heating systems.
Collector system:
House plan with heating system diagram (collector heating system)
The circuits are shown, in each of which the coolant is supplied to its own radiator. But it is necessary to make a reservation here that there can be more than one radiator in each circuit. Everything else is easy to follow according to the scheme, additional comments are superfluous.