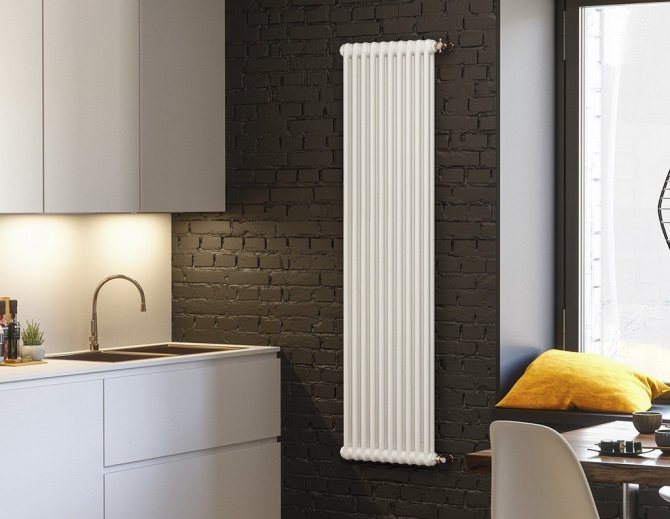
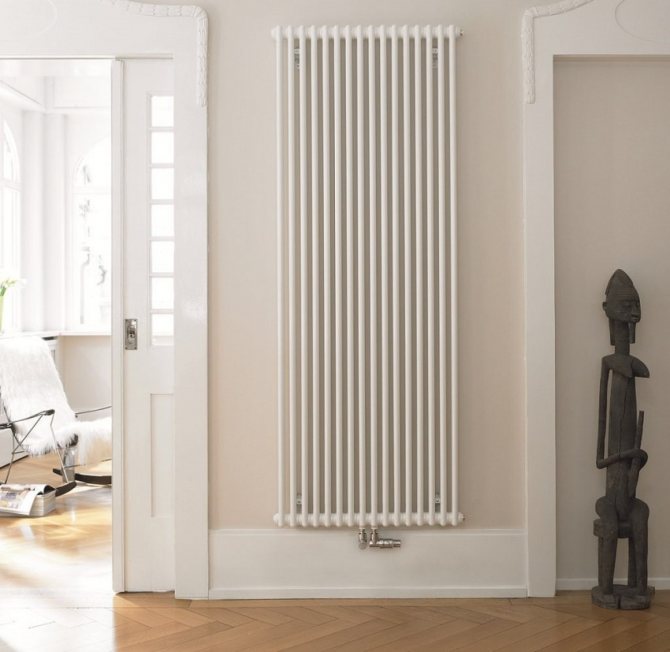
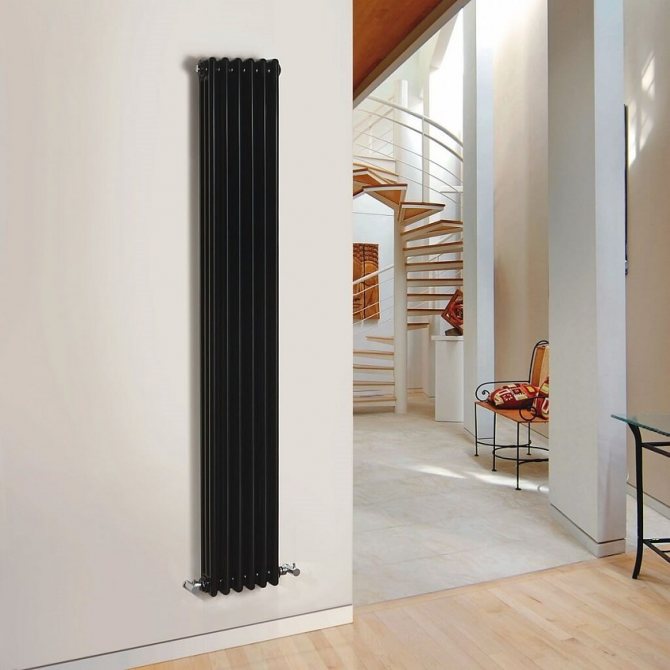
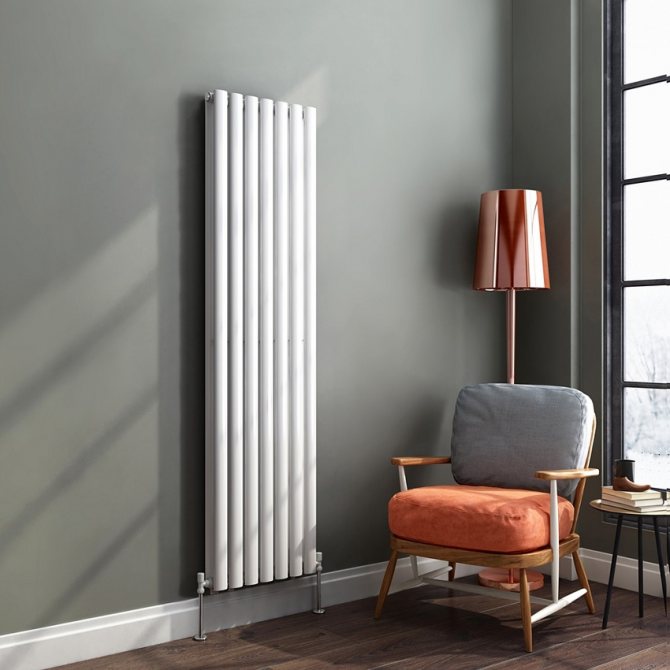
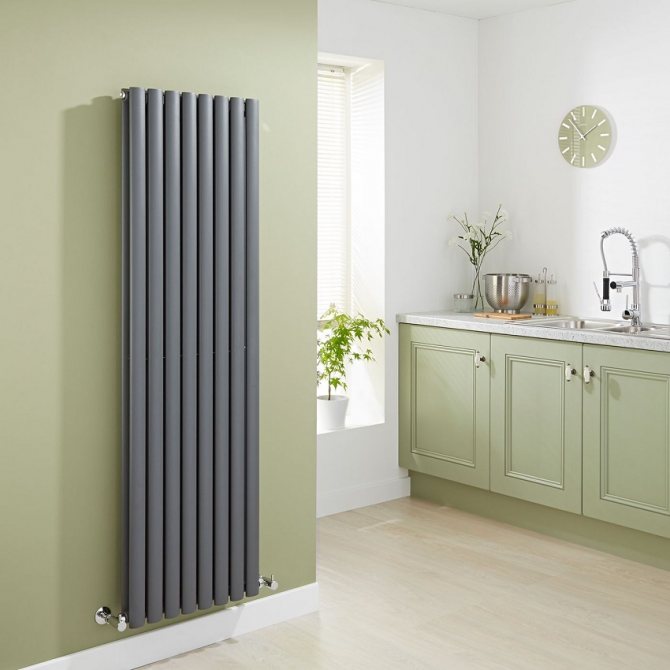
Varieties of vertical radiators
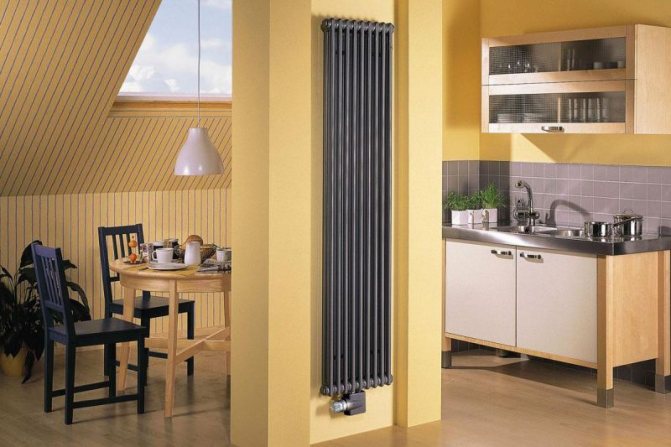
The main difference between vertical radiators is their height, which is several times larger than standard options. This design feature allows the heater to be installed in narrow wall spaces. For example, between the openings of panoramic windows.
High heating radiators differ in the material of manufacture, according to which the following models are distinguished:
- • steel • bimetallic • aluminum • convector type
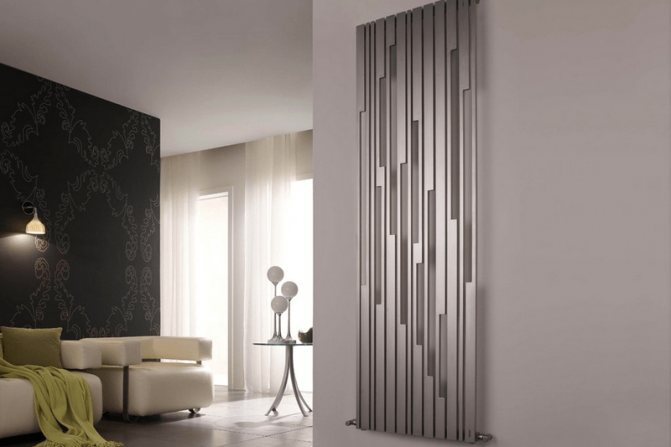
In addition, all vertical radiators differ in their design. In appearance, they are divided into sectional, tubular and panel. Tubular models belong to the classic version, which cannot be said about sectional and panel ones, presented in an unusual design. It is among them that you can find devices that will be a real decoration of the interior.
Types of vertical batteries

A vertical wall-mounted radiator does not differ structurally from a traditional heater. The difference lies in its proportions - the height (1-3 meters) is much greater than the width. Such models can be divided into several types according to the material of manufacture, design solution and type of coolant.
Types of heating radiators, and which batteries are best for an apartment
Classification by material of manufacture
Since vertical radiators have impressive dimensions and considerable weight, they are not made of cast iron, so as not to further increase the load on the walls of the room. After all, the cast-iron sections, together with the coolant, are the heaviest. Another argument in favor of abandoning cast iron is that this metal is poorly processed, so it will be difficult to give it a decorative shape.
High and narrow heating radiators are made of the following materials:
- The bimetallic structures have a steel core and an aluminum body. The result is a durable and durable device with good heat dissipation. Due to the ease of processing aluminum, aggregates of different shapes can be made. Also, the body can be painted in any color. The disadvantage of bimetal aggregates is their high cost.
- Strong steel sections have the lowest heat dissipation. In addition, this metal is difficult to process, so refined instruments are not made of steel. Another drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion. Usually, panel steel heating appliances are bought, which are inexpensive.
- Aggregates made of aluminum have the best thermal conductivity. This plastic material can be used to make devices of exquisite shape and original design. Aluminum heats up quickly, but also cools down quickly. These designs are not designed for high working pressure, but are cheaper than bimetal.
Varieties of design
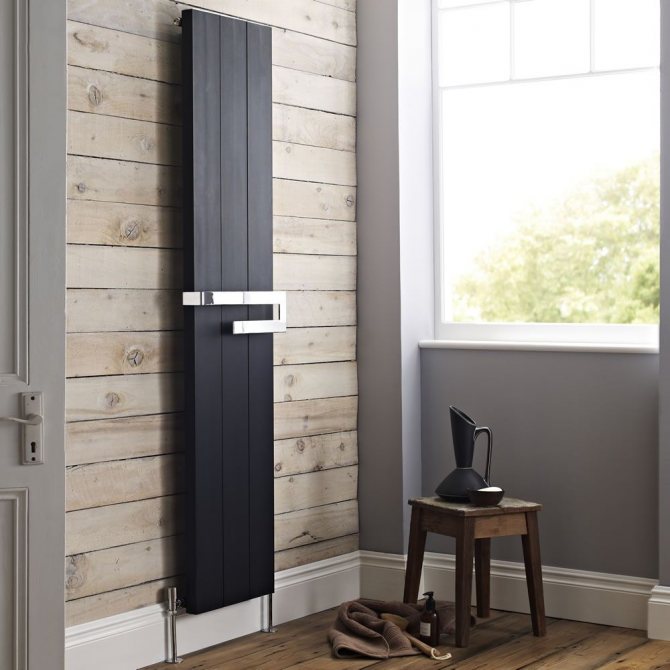


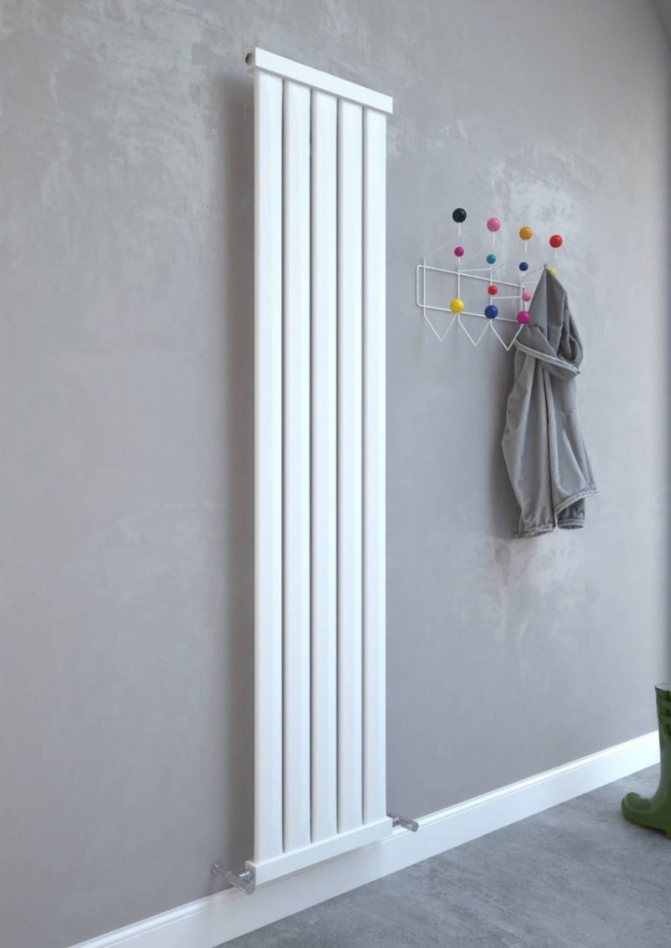
Its heat transfer largely depends on the constructive solution of the battery. By design, all vertical radiators are divided into three types - sectional, panel and tubular. Sectional batteries differ from traditional units of this type only in the height of the sections. They are easy to look after, they are outwardly attractive and stylish.
Sectional units have the following features:
- they are usually made of bimetal or aluminum;
- consist of separate sections with threaded connections;
- are more expensive than other varieties;
- the number of sections can be reduced or increased to change the thermal power;
- work using convection principles.
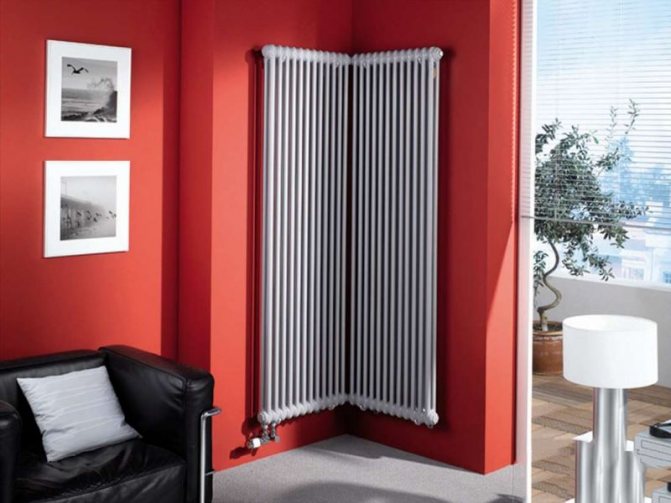
Tubular vertical radiators consist of two horizontal collectors connected by long vertical tubes.To obtain the original shape, vertical tubes are sometimes bent. Tubular structures have the highest heat dissipation. Steel tubes are welded to the manifolds.
Panel type devices are one-piece construction. The faceplate is a sheet steel or mirror surface. Smooth smooth surface fits well into any room. The color of the panel can be any. You can apply a drawing on it. The price of panel radiators is the most reasonable.
The best bimetallic heating batteries and radiator characteristics
Heat source classification
Most often, vertical wall-mounted water heating radiators are used, that is, water circulates in them as a coolant, which heats the boiler. But there are also models that run on electricity. They use special oil as a coolant, and the design resembles models that work with water.
Important! Since vertical electrical appliances absorb a lot of electricity, they are used only as an additional source of heating in the house. To save energy, a thermostat is installed.
Dignity
In addition to various design solutions, high radiators have several more advantages:
- at a low temperature of the medium, they provide the highest possible heat transfer;
- due to their light weight and the use of a small volume of water, the devices reduce energy consumption;
- radiators are equipped with regulators that allow you to independently set the temperature regime;
- when installing devices with a lower piping of communications, the aesthetic appearance of the room is preserved.
The advantages of these models include the fact that, while saving space, several heating devices can be installed in one room at once.
Advantages and disadvantages
Assessing the advantages and disadvantages of this kind of heating devices, you immediately need to clearly determine that this is a separate class of radiators and cannot be compared with other types of heating batteries.
The second point to pay attention to is that the vertical radiator - this is one of the options for arranging a heating system and it has its pros and cons.
The positive aspects of such a heating element include:
- Compact placement in the interior of the room.
- Relatively light weight (except for cast iron versions or large massive radiators).
- Originality of the idea.
- Fast and efficient heating premises.
- Possibility of choice different mounting options.
- Simple and easy installation equipment.
- Ease in service.
Disadvantages:
- For aluminum batteries - a small resource due to the peculiarities of the reaction of metal with hydrogen inside the battery.
- High price products.
Features of mounting high radiators
Installing a vertical view of radiators differs little from installing a conventional battery. They can also be used with underwater pipes made of steel, polypropylene or polyethylene. But still, there are small subtleties of the installation. Since the coolant has a large area, and hence its mass, it must be fixed only on a main wall that can withstand a large weight of the product. In addition, when choosing a radiator with top piping, it should be borne in mind that the pipe will run along the entire height of the battery and spoil the overall aesthetics of the room with its appearance.
You can choose and buy vertical radiators for heating in the Dom-Termo online store. You will be surprised by the variety of models and their affordable cost.
Convectors with natural convection Klima TK
Free-ventilated floor convectors operate on the principle of natural air movement. Used for secondary space heating. Thermal power, depending on the size of the convector, ranges from 0.3 kW to 4 kW. They work silently.
Advantages of Klima TK convectors:
- high thermal power;
- simple connection to a one- or two-pipe system;
- at low water consumption - rapid warming up of the room;
- mounted under the floor, so it does not take up much space;
- numerous control equipment;
- the possibility of combining forced and natural convection; the ability to manufacture special models (corner, various grilles);
- simple installation and maintenance.
All IMP Klima convectors are equipped with sealed plugs and ventilation plugs in accordance with the product series.
Technical features:
- Convector heights: 70, 105, 140 mm
- Convector length: 800 to 5000 mm
- Convector widths: 200, 300, 400 mm
- Working pressure: 10 atm.
- Maximum pressure: 25 atm.
- Maximum temperature of the heating medium: 100 ° C
- The heat exchanger for built-in convectors IMP Klima TK is made of copper pipes 16 × 1.0 mm, on which there are ribbed aluminum plates 83 × 50 mm
- Connection to water pipes is carried out by means of a connecting nut with an R ½ "female thread
- Thermal output is indicated for a temperature regime of 90/70/20 ° C
- Certificate of conformity: ROSS SI.AB28.B06253
Operating principle and adjustment of Klima TK convectors Klima convectors work due to the natural movement of air: the air from the room is lowered into the convector box and, warming up in the heat exchanger, rises. It is recommended to place convectors near windows with or without low sills (no further than 10 cm). With this arrangement, warm air will heat the glass, preventing condensation from forming on them. Also, the heat flow effectively prevents the formation of drafts from a cold window.
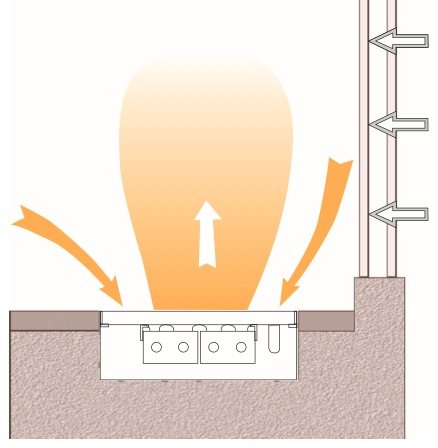

In most cases, IMP Klima TK convectors are used as an additional source of heating - only for windows, since their thermal power is rather low in comparison with radiators. Therefore, these convectors are often installed with limited adjustment, being limited at best by a manual valve, which can be reached by lifting the grill. If more precise operation of the convector is required, then both thermo valves with servo drives and a remote liquid thermostat can be used, which can be placed on the wall next to the convector. Contact our company and we will help you choose the most optimal option for connecting Klima convectors, based on your needs.
Convectors with forced convection Klima TKV
TKV floor convectors operate on the principle of forced ventilation, i.e. the air flow is intensified by a fan. Designed for primary and secondary heating of premises where it is necessary to use devices with a high heat output. Thermal power, depending on the size of the convector, from 0.4 kW to 8 kW. In convectors with forced convection "Klima TKV" air movement is provided by a built-in tangential fan. The cold air accumulating at the floor is sucked in by the fan and warming up when passing through the heat exchanger enters the room. Forced air circulation and its increased volume, involved in the movement, contributes to the rapid and uniform heating of your room. Compared to heating devices operating on the principle of free convection, the Klima convector significantly improves overall comfort.
Klima TKV specifications:
- Convector heights: 82, 105, 140 mm
- Convector length: 800 to 5000 mm
- Convector depth: 200, 300, 400 mm
- Working pressure: 10 atm.
- Maximum pressure: 25 atm.
- Maximum temperature of the heating medium: 100 ° C
- The material of the heat exchanger for built-in convectors IMP Klima is made of copper pipes 16 × 1.0 mm, on which there are ribbed aluminum plates 83 × 50 mm
- Connection to water pipes is carried out by means of a connecting nut with an R ½ "female thread
- The tangential fan for built-in convectors IMP Klima TKV consists of a low-power single-phase motor (220 V, 33 W, max 0.25 A) with propellers on both sides of the motor.
- The fan is protected by a protective mesh, which prevents mechanical damage
- The heat output is indicated for a temperature regime of 90/70/20 ° C (convector operating mode - NORM)
- Certificate of conformity: ROSS SI.AB28.B06253
The principle of operation of Klima TKV convectors Each convector has one or more tangential fans (their number depends both on the length of the convector and on the specific model - you need to specify when ordering), which pump air from the room directly to the heat exchanger, where the air is heated and goes directly to the window. This ensures better glass heating, which prevents the formation of icing and condensation on them.
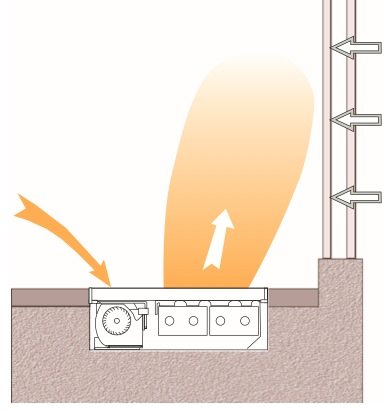

The fans can operate in three modes: with minimum, average and maximum speed, depending on the required power, they can also be turned off. To control the operation of the fans depending on the room temperature, it is necessary to additionally install a room wall-mounted thermostat Hidria 09T or 037. One thermostat can simultaneously control several fans or convectors if they are located in the same room - the complete set must be specified when placing an order.
Parameters and designs
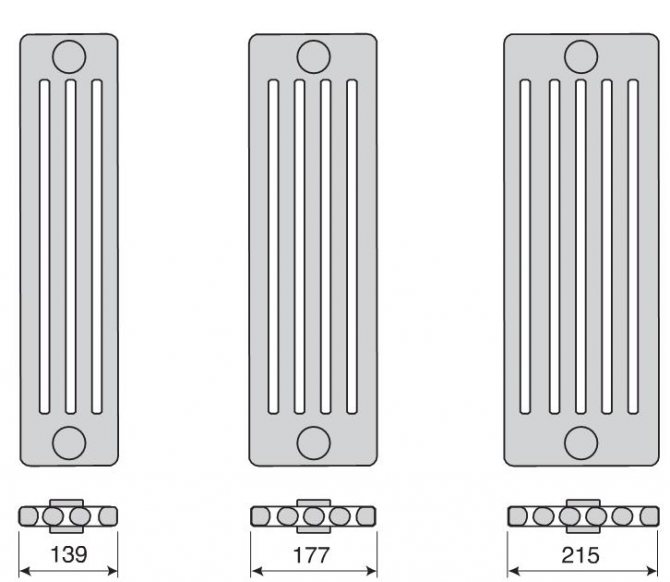
Bimetallic, aluminum and steel heating radiators: technical characteristics. Vertical radiators of various types can be up to 180 cm in height. And the width is determined only by the availability of free space and the required battery power. You can connect as many sections as you like.
With the same dimensions, aluminum will have the highest heat transfer, followed by bimetallic and steel radiators. In general, the power output depends on the design features and the number of mounted sections.
A structurally high battery can be of various shapes. That allows you to harmoniously fit it into the interior of any room. The coolant pipes can be located inside and vertically and horizontally.
Existing technologies for the manufacture of batteries allow you to give the heating device the most original shape. But for design delights, of course, you have to pay a lot. But this is the main advantage - the ability to give the room an individual style.
The main disadvantage of steel appliances is their high susceptibility to corrosion. Manufacturers try to smooth this out and coat the inside of the battery with various polymers. But on the other hand, steel is much easier to process and therefore vertical radiators of non-standard shape can be found on sale.
Plus, the spot welding used in the manufacture of steel devices does not tolerate water hammer, which is not uncommon in centralized urban systems.
Therefore, steel radiators are recommended to be used exclusively in private cottages with an autonomous boiler, which produces less coolant pressure and practically eliminates water hammer in the pipes.
Bimetal combines the advantages of steel and aluminum. The increased strength characteristics of the cast steel manifold and the high heat dissipation of the aluminum fins give an excellent heating device at the output.