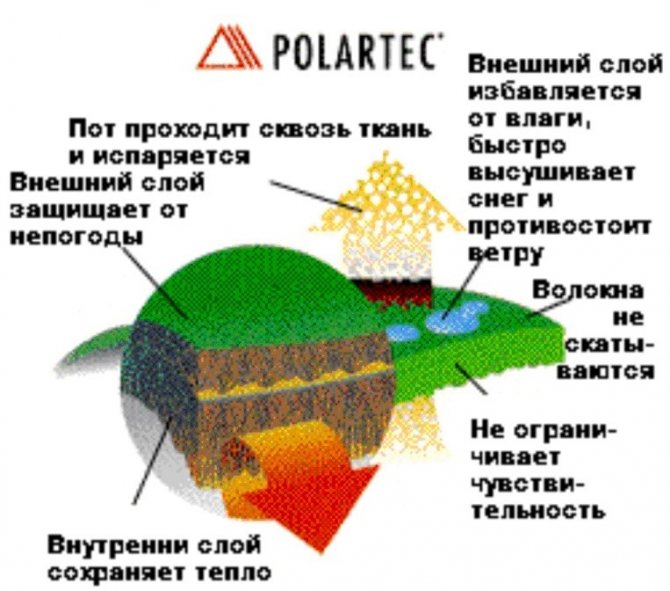
According to fire safety rules, the arrangement around stoves, fireplaces and fuel boilers should be carried out using refractory special materials that can simultaneously protect a residential or utility building (bathhouse) from possible fire hitting the walls, and at the same time not harm health.
Any stove or fireplace heats up to create a favorable home atmosphere, they radiate a strong heat, which in turn can be a source of ignition or fire. Therefore, it is important to carefully choose the right materials when arranging a heat source in a house, bathhouse or basement when it comes to a fuel boiler.
Types of materials
Refractory materials can be roughly divided according to the method of heat transfer:
- Heat-reflecting - aimed at reflecting infrared radiation into the interior of the room;
- Preventing loss due to their physical and chemical properties.
On the video of refractory materials for the walls around the furnaces:
But all of them can also differ in the type of raw materials from which they are produced:
- With organic ingredients, for example, polystyrene foam materials, although their refractory index is very low, they are best suited for walls near furnaces with low heating;
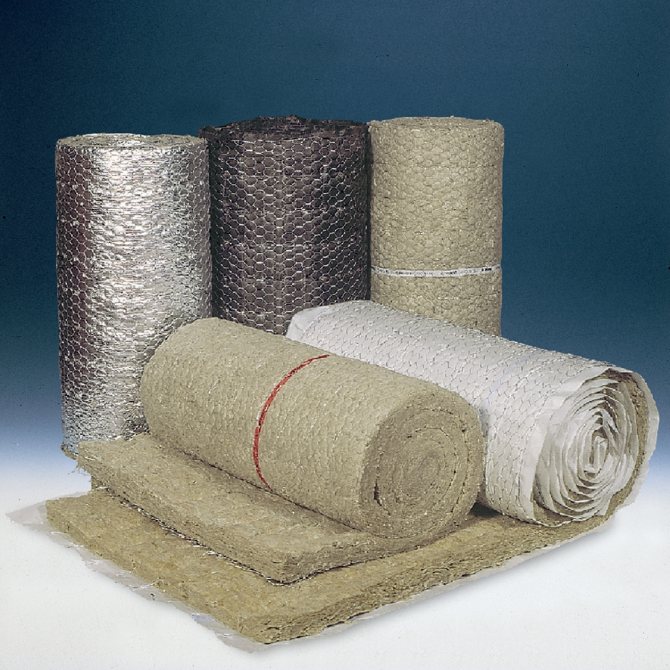
- Inorganic - This is an extensive class of non-combustible materials for insulation of walls of various fire resistance, including very flammable ones, such as wooden floors. These include stone and basalt wool, pressed into large slabs, fiberglass wool, lightweight cellular concrete slabs with fire retardant impregnations, honeycomb plastics, foamed perlite or vermiculite, polypropylene. However, such a beautiful decorative thing as Leroy Merlin plastic sheet is definitely not suitable.
- Mixed type - these include asbestos-cement refractories, asbestos-lime or silica, foamed from a variety of inorganic substances.
Basic requirements for refractory materials
Many suburban buildings are erected from wood, whether it is a cylinder or frame house, without a stove or fireplace it is difficult to survive the frosty winter, therefore they are very careful about their arrangement, and such materials are chosen around the stoves so that they are:
- Effectively and reliably prevented any attempt at fire;
- Environmentally friendly, so that when heated, they do not emit harmful substances into the home air.
What is the composition of the kiln plaster solution that exists and is most often used, the information from this article will help to understand.
But what are the dimensions of the standard kiln brick, you can see here.
You may also be interested in knowing what kind of brick is used for laying stoves.
For walls around ovens
A long time ago, people used asbestos sheets to cover the walls around stoves, but it turned out to be very harmful to health and the environment - its microparticles can get into the lungs or settle on things, which leads to serious ailments, and when heated, they are also released carcinogenic substances. Therefore, the best materials can be considered:
Fire resistant gypsum board. can serve as the basis for wall cladding around hot-heated stoves, and for decoration you can use porcelain stoneware tiles of the most unusual colors.
Sheets have the following characteristics:
- Fire-resistant indicator - up to 30 minutes of resistance to fire;
- Does not ignite until 1 hour of time even after the formation of a fire center;
- Slab parameters - 120 x 250 x 1.25;
- On the front and back sides, gypsum-treated cardboard, inside there are fiberglass threads that will resist fire;
- The ends of the sheets are covered with cardboard material, along which there is a joining chamfer;
- Fasteners can be carried out both on adhesives and on self-tapping screws.
Refractory minirite slabs. The material is distinguished by excellent heat-resistant properties, it is made exclusively from environmentally friendly substances, including:
- Compositions of white or gray cement make up up to 90% of the total material;
- Mineral fiber materials included;
- Fiber reinforcement plates are used for strength and durability.
Asbestos fiber is absolutely excluded from the composition, which improves the quality of the material for the home stove. It is easy to fix it to the wall with screws close to the wall itself; for reliability, you can mount 2 sheets of minirite each. Note! Leave a small distance during installation, as the material may increase in size when heated. For other walls, you can choose a similar decorative brick finish.
Protective stainless sheets - a little expensive, but reliable refractory material, with which you can protect not only the walls of the house, but also the basement, when installing a heating boiler. But in order to provide the greatest protection, special fiberglass with thermal protective properties should be laid under the stainless steel - the structure will reliably protect the house from any attempts to start a fire. Choose a substrate carefully so that it does not contain harmful phenolic resins; when heated, they release substances that are too hazardous to health.
Heat Resistant Basalt Fiber Material, pressed into mats - is characterized by hygroscopicity, a high degree of resistance to fire, can remain unchanged at temperatures up to 900 degrees Celsius.
Superisol sheets for wall insulation - a practical and versatile thermal insulation material, with a low specific weight and excellent strength and durability.
Wall insulation with heat-resistant terracotta tiles... The main advantage is the complete environmental friendliness of the material, they do not contain any chemical coloring compositions, they have excellent vapor permeability and fireproof properties. Glazed ceramic tiles for interior wall cladding also look beautiful.
For wall decoration under the boiler
A gas or steam boiler heats up very much in order to provide heat transfer to the house at the desired temperature of the carrier. Therefore, experts recommend equipping the walls with porcelain stoneware tiles with a high degree of fire resistance. The characteristics are the most reliable - it can withstand high temperatures without visible signs of fire.
It is also allowed to use sheets of fibers impregnated with gypsum, installation is very easy by sticking on walls, but plastic panels for brick for interior wall decoration are not recommended, since they do not meet fire safety requirements.
Recently, a sheet of xylolite fiber has begun to gain popularity, since it meets all environmental properties in terms of purity and the absence of any harmful emissions, even at elevated temperatures of about 1000 degrees. Also, the material is very flexible, these properties allow you to sheathe the most curved wall surfaces. It can perfectly withstand humid and damp air, its main characteristics do not change.
Manufacturers and prices
- Basalt fiber panels cost of 1 sq. meter - from 390 to 690 rubles, depending on the decor of the front side, produced by ESCAPLAT;
Roll refractory nonwoven fabric - cost of 1 running meter from 112 rubles, production of OgneuporEnergoHolding, LLC, Moscow;
- Non-flammable composition for plastering walls with a volume of 20 liters at a price of 410 rubles a bucket, produced by a company from Perm.
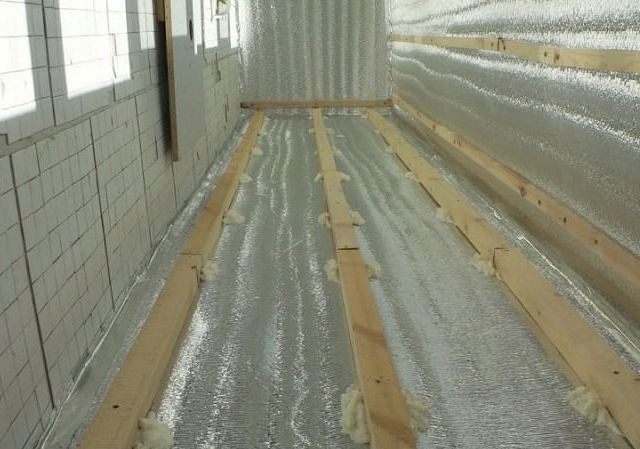
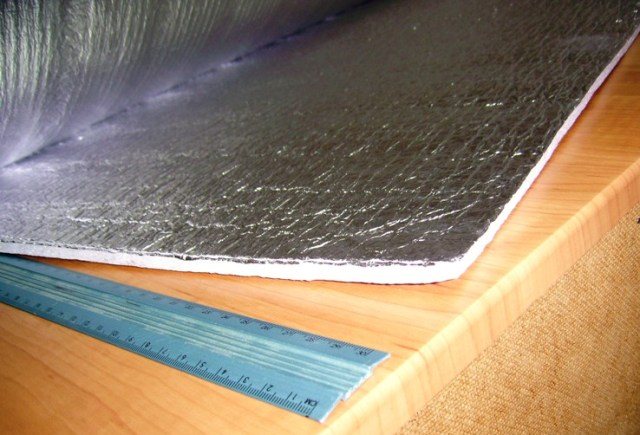
Reflective insulation is a roll-up material that consists of a base layer and a reflective layer. The latter is represented by a foil with a high reflectance from 90%. Any insulating material with good physical and mechanical properties can be taken as a basis, and reinforced meshes are used to enhance the qualities.
Principle of operation
To understand the principle of operation of such insulation, consider the main methods of transferring heat from one coating to another:

Thus, heat loss is inevitable. It turns out that in order to create the effect of thermal insulation, it is necessary to minimize heat loss from radiation. But traditional TIMs are not able to protect a building from this type of heat transfer. And the optimal material was found - foil insulation, known for its reflective and low emitting ability.
Reflective insulation works on all heat transfer processes: radiation, convection and heat conduction, inhibiting heat loss.
Advantages of using insulation Izolon
- this insulation is environmentally friendly and does not harm human health, even in direct contact with the skin;
- the material is vapor-proof and non-hygroscopic, resistant to moisture;
- is a high-quality heat insulator and successfully copes with noise reduction;
- you can work with the material in a wide temperature range: from -60 to 125 ° С;
- withstands any environmental conditions and is resistant to UV radiation;
- a thin layer of material does not "steal" the interior space of the room;
- practically weightless Izolon does not make the structure heavier.
Nuances of use
So, there are several nuances of using such heaters:
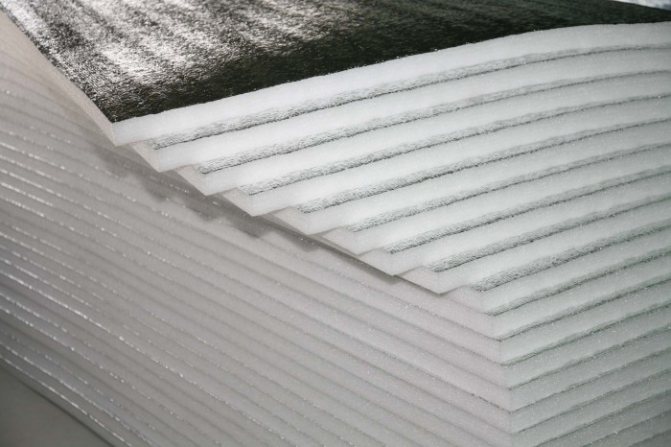


- deposited aluminum spraying on a polyethylene or lavsan film does not reflect infrared heat waves;
- a thick layer of foil is needed for the radiation to really reflect;
- for weak heat waves, a thin sprayed layer of 20-30 angstroms is enough;
- it is impossible to determine the thickness of the layer by eye.
The vapor permeability of foil-clad TIM is 0.001 mg / m * h * Pa. The technical resistance parameter must be indicated in the documentation of the reflecting TIM. In the absence of it, this means that the material has not been tested for reflectivity, which means that it cannot be used as insulation.
Advantages and disadvantages
The performance characteristics of such material are as follows:
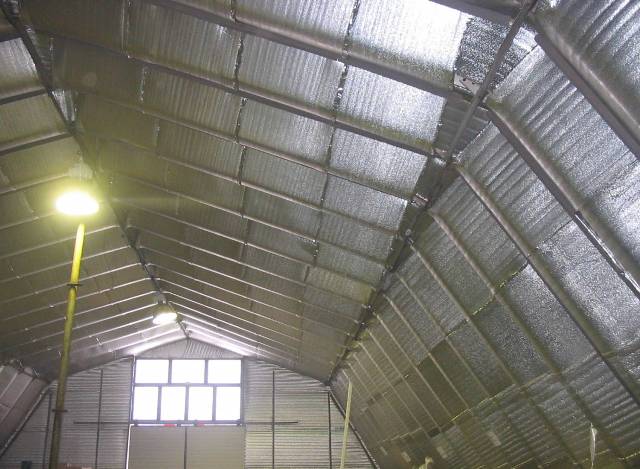


- for production, polyethylene and foil are used, which are acceptable for the food industry, and therefore the material meets hygienic standards;
- polished aluminum foil reflects up to 97%, emitting no more than 5% of thermal energy;
- a layer of air bubbles in polyethylene foam provides additional thermal resistance, which does not transmit heat according to the principle of thermal conductivity;
- insulation is fireproof, non-flammable and refers to hardly flammable materials;
- low weight and compactness of rolls make it convenient to transport and store them;
- reducing heat loss reduces heating costs, the cost of thermal insulation of the room in comparison with the cost of other materials.
Minuses
Reflective insulation has the following disadvantages. Firstly, its softness - the lack of rigidity makes it impossible to finish the insulation with plaster and wallpaper.Secondly, fastening is carried out easily only with materials on an adhesive basis (type C), and for the installation of other models, you will have to stock up on adhesive.


Thirdly, nailing the material degrades the thermal insulation qualities. Finally, when insulating external walls, it can only be used as an additional layer that reflects heat and protects against moisture.
The most popular brands of such insulation today are Porileks NPE-LF, Ekofol and Penofol, BestIzol. Manufacturers Ursa, Isover and Rockwool produce reflective insulation based on mineral wool of various densities and thicknesses. The modern market offers foil-clad TIM in the form of mats and cylinders, with which it is convenient to insulate pipelines.
BestIsol
BestIzol is a vapor, heat and sound insulation material with a reflective ability, in the production of which closed cell polyethylene foam and aluminum foil are used. The thickness of polyethylene foam can vary from 2 to 10 mm, and the thickness of the foil - from 7 to 14 mm, depending on the brand.


There can be several modifications:
- type A - polyethylene foam with one-sided foil;
- type B - with double-sided foil;
- type C - foil is applied on one side, and glue with a layer of anti-adhesive material on the other.
This type of reflector is effective not only for insulating residential buildings, but also for insulating ships, ventilation ducts, vans, and metal structures.


Lightness and strength allows this TIM to be built into metal structures by fixing it to the frame. This will not require additional expenses for the construction of temporary structures, gratings for securing the insulation.
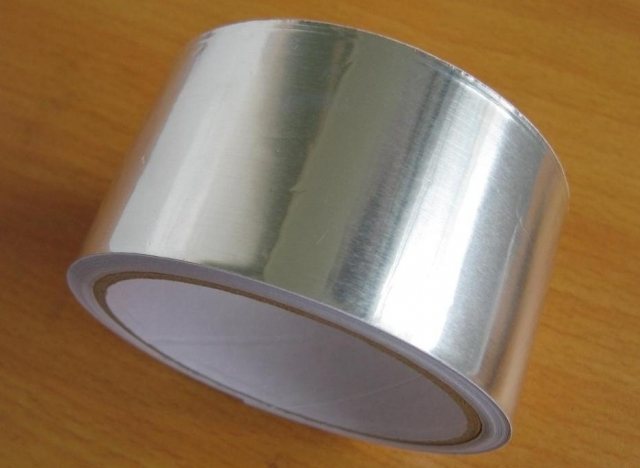
Aluminum tape
Adhesive tape is used for seams of reflective insulation elements. Types F-20 and F-30 are foils with a thickness of 20 and 30 microns, respectively, with an adhesive coating and permanent stickiness. Protection of the adhesive layer is provided by a material with anti-adhesive characteristics.


FL-50 type - combined from 20 µm aluminum foil and 20 µm polyethylene film, also with adhesive application and anti-adhesion material. In addition to foil, film and glue, the reinforced adhesive tape contains a fiberglass mesh. The characteristics of aluminum tape are as follows:
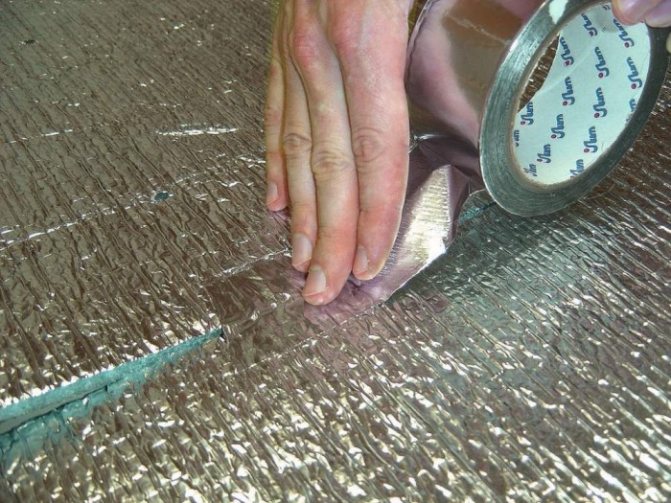


- high strength, wear resistance and reflection of UVF rays and infrared rays, which makes it effective;
- durability of the adhesive layer, which gives a high-quality connection;
- the material can be used at temperatures up to 350С;
- has high moisture resistance.
The use of thermal insulation [edit | edit code]
Thermal insulation is used to reduce heat transfer wherever it is necessary to maintain a given temperature, for example:
- In construction, thermal insulation is used for internal and external insulation of external walls of buildings, roofs, floors, etc. This reduces energy consumption for heating and air conditioning.
- In the production of clothing and footwear. Due to the heat-insulating properties of clothing, a person can stay outdoors for a long time in extreme cold or in cold water without active movement.
- In housings or enclosing structures of refrigeration equipment, ovens. Thanks to thermal insulation, it is possible to significantly reduce the energy consumption for maintaining the required temperature inside.
- Heat pipelines are surrounded by thermal insulation to reduce cooling or heating of the transferred heat carrier. Protects against corrosion. Thermal insulation has vapor barrier (not always) and soundproofing properties.
- Insulation of tanks, reservoirs, boilers.
- Insulation of pipeline fittings, where removable heat-insulating structures are used.
The main types of insulation
Modern thermal insulation materials for use in construction and repair are divided into many varieties: industrial and household, natural and artificial, flexible and rigid thermal insulation materials, etc.
For example, in terms of form, modern thermal insulation is divided into samples such as:
In terms of structure, the following types of thermal insulation are distinguished with their own unique feature:
By the type of raw materials, such products of various quality classes are distinguished:
- Organic, natural or natural insulation materials are cork bark, cellulose wool, expanded polystyrene, wood fiber, foam plastic, paper granules, peat. These types of building insulation materials are used exclusively indoors to minimize high humidity. However, natural building thermal insulators are not fireproof.
- Inorganic thermal insulation materials - rocks, fiberglass, foam glass, mineral wool insulation, foamed rubber, aerated concrete, stone wool, basalt fiber. A good heat insulator from this category is distinguished by a high degree of vapor permeability and fire resistance. Insulation with a product with water-repellent additives is especially effective.
- Mixed - perlite, asbestos, vermiculite and other insulation made of foamed rocks. They are distinguished by the best quality and, of course, increased cost. These are the most expensive brands of the best thermal insulation materials. Therefore, premises are covered with such insulation much less often than with more economical materials.
If you need to make thermal insulation of the pipeline in the wall, then special "sleeves" of increased density are used for this.
Determining the best product does not only depend on the price. They are chosen for their quality characteristics, ergonomic properties and environmental friendliness.
How to choose thermal insulation materials?
When they talk about a house in which comfort reigns, one of the first places they mean is a comfortable temperature. When it comes to the thrift and economy of the owner of the home, they mean, first of all, his concern for the thermal insulation of the walls, floor and ceiling.
Modern heat-insulating materials make it possible to combat heat loss and cold penetration into premises with great efficiency. Choosing the best option among the variety of heat insulators is a guarantee against excessive consumption of heat carriers, a guarantee of the optimal temperature as a component of comfort in your home.
Of course, the most accurate advice is within the power of only specialists who know the intricacies of not only heat engineering, physics of substances and the structure of all insulating materials. We will try, in an accessible and understandable form, to conduct an excursion into the world of thermal insulation and help an ordinary buyer in the optimal choice.
What parameters should you pay attention to when choosing?
The choice of quality thermal insulation depends on many parameters. They take into account both the installation methods, and the cost, and other important characteristics, which are worth dwelling on in more detail.
Choosing the best heat-saving material, you must carefully study its main characteristics:
- Thermal conductivity. This coefficient is equal to the amount of heat that in 1 hour passes through 1 m of an insulator with an area of 1 m2, measured by W. The thermal conductivity index directly depends on the degree of surface moisture, since water passes heat better than air, that is, the raw material will not cope with its tasks.
- Porosity. This is the proportion of pores in the total volume of the heat insulator. The pores can be open or closed, large or small. When choosing, the uniformity of their distribution and appearance are important.
- Water absorption. This parameter shows the amount of water that can be absorbed and retained in the pores of the heat insulator in direct contact with a humid environment. To improve this characteristic, the material is subjected to hydrophobization.
- Density of thermal insulation materials. This indicator is measured in kg / m3.Density shows the ratio of mass to volume of a product.
- Humidity. Shows the amount of moisture in the insulation. Sorption humidity indicates the balance of hygroscopic humidity under conditions of different temperature indicators and relative humidity.
- Water vapor permeability. This property shows the amount of water vapor passing through 1 m2 of insulation in one hour. The unit of measurement for steam is mg, and the temperature of the air inside and outside is taken as the same.
- Resistant to biodegradation. A heat insulator with a high degree of biostability can withstand the effects of insects, microorganisms, fungi and in high humidity conditions.
- Strength. This parameter indicates the impact on the product will have transportation, storage, installation and operation. A good indicator is in the range from 0.2 to 2.5 MPa.
- Fire resistance. All parameters of fire safety are taken into account here: the flammability of the material, its flammability, smoke-generating ability, as well as the degree of toxicity of combustion products. So, the longer the insulation resists the flame, the higher its fire resistance parameter.
- Heat resistance. The ability of a material to resist temperatures. The indicator demonstrates the level of temperature, after reaching which the material's characteristics, structure will change, and its strength will also decrease.
- Specific heat. It is measured in kJ / (kg x ° C) and thus demonstrates the amount of heat that is accumulated by the thermal insulation layer.
- Frost resistance. This parameter shows the ability of the material to tolerate temperature changes, freeze and thaw without losing its main characteristics.
When choosing thermal insulation, you need to remember about a whole range of factors. It is necessary to take into account the main parameters of the insulated object, conditions of use, and so on. There are no universal materials, since among the panels, bulk mixtures and liquids presented on the market, you need to choose the type of thermal insulation that is most suitable for a particular case.
The main types of insulation [edit | edit code]
In practice, according to the type of feedstock, thermal insulation materials are usually divided into three types:


- Organic - obtained using organic substances. These are, first of all, a variety of polymers (for example, expanded polystyrene, expanded polyethylene (NPE, PPE) and products based on it (including reflective thermal insulation). Such thermal insulation materials are made with a bulk density of 10 to 100 kg / m 3. the disadvantage is low fire resistance, therefore they are usually used at temperatures no higher than 90 ° C, as well as with additional structural protection with non-combustible materials (plaster facades, three-layer panels, walls with cladding, cladding with gypsum board, etc.). Also as organic insulating materials use recycled non-business wood and woodworking waste (fiberboard, fiberboard, and chipboard, chipboard), cellulose in the form of recycled paper (ecowool insulation), agricultural waste (straw, reeds, etc.), peat (peat) and etc. These heat-insulating materials, as a rule, are characterized by low water and biological resistance, and are also susceptible to decomposition and are used in construction. e.
- Inorganic - mineral wool and products made from it (for example, mineral wool slabs), monolithic foam concrete and aerated concrete (aerated concrete and gas silicate), foam glass, glass fiber, expanded perlite, vermiculite, honeycomb products, etc. rocks or metallurgical slags into glassy fiber.The volumetric weight of products made of mineral wool is 35-350 kg / m 3. The thermal conductivity of mineral wool is in the range of 0.035-0.040 W / m * K and strongly depends on the density of the material. During operation, the thermal conductivity increases by an average of 50% over 3 years due to moisture penetration. Vapor permeability (υ-factor of resistance to diffusion of water vapor) is equal to 1 in the absence of a vapor barrier layer. Also, if the area of the holes in the vapor barrier layer is more than 0.2 mm 2 per m 2. A characteristic feature is low strength characteristics and increased water absorption, therefore the use of these materials is limited and requires special installation techniques. In the production of modern heat-insulating mineral wool products (TIM), the fiber is hydrophobized, which makes it possible to reduce water absorption during transportation and installation of the TIM.
- Mixed - used as installation materials, they are made on the basis of asbestos (asbestos cardboard, asbestos paper, asbestos felt), mixtures of asbestos and mineral binders (asbestos diatomaceous, asbestos-asbestos, asbestos-lime-silica, asbestos-cement products) and on the basis of exfoliated rocks (weathered rocks) and