Comparison of thermal conductivity of heaters
The higher the thermal conductivity, the worse the material works as insulation.
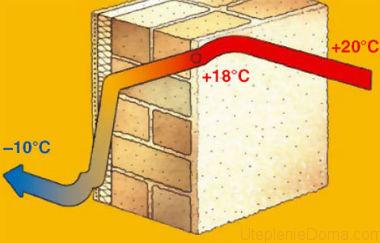
We start comparing thermal insulation materials for a reason, since this is undoubtedly the most important characteristic. It shows how much heat the material passes not over a certain period of time, but constantly. Thermal conductivity is expressed as a coefficient and is calculated in watts per square meter. For example, a coefficient of 0.05 W / m * K indicates that constant heat loss per square meter is 0.05 watts. The higher the coefficient, the better the material conducts heat, respectively, as a heater it works worse.
Below is a table comparing popular thermal conductivity heaters:
| Material name | Thermal conductivity, W / m * K |
| Minvata | 0,037-0,048 |
| Styrofoam | 0,036-0,041 |
| PPU | 0,023-0,035 |
| Penoizol | 0,028-0,034 |
| Ecowool | 0,032-0,041 |
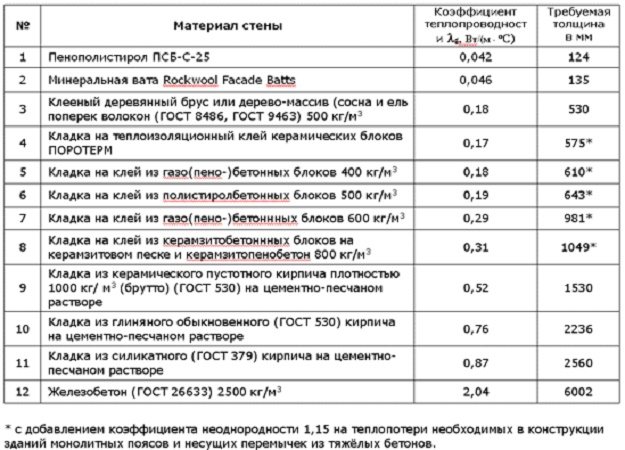
Having studied the above types of insulation and their characteristics, we can conclude that, with equal thickness, the most effective thermal insulation among all is liquid two-component polyurethane foam (PPU).
The thickness of the insulation is of paramount importance, it must be calculated for each case individually. The result is influenced by the region, the material and thickness of the walls, the presence of air buffer zones.
Comparative characteristics of heaters show that the density of the material affects the thermal conductivity, especially for mineral wool. The higher the density, the less air in the insulation structure. As you know, air has a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, which is less than 0.022 W / m * K. Based on this, with an increase in density, the coefficient of thermal conductivity also increases, which negatively affects the ability of the material to retain heat.
What you need to know about the thermal conductivity of foam
The ability of a material to transfer heat, conduct or retain heat fluxes is usually estimated by the coefficient of thermal conductivity. If you look at its dimension - W / m ∙ Co, it becomes clear that this is a specific value, that is, determined for the following conditions:
- The absence of moisture on the surface of the slab, that is, the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the foam from the reference book, is a value determined in ideally dry conditions, which practically do not exist in nature, except in the desert or in Antarctica;
- The value of the thermal conductivity coefficient is reduced to the thickness of the foam plastic of 1 meter, which is very convenient for theory, but somehow not impressive for practical calculations;
- The results of measurements of thermal conductivity and heat transfer are made for normal conditions at a temperature of 20 ° C.
According to a simplified technique, when calculating the thermal resistance of a layer of foam insulation, it is necessary to multiply the thickness of the material by the coefficient of thermal conductivity, then multiply or divide by several coefficients used in order to take into account the actual operating conditions of the thermal insulation. For example, a strong flooding of the material, or the presence of cold bridges, or a method of installation on the walls of a building.
For your information! The values of the coefficient of 0.37-0.39 W / m ∙ Co issued by SNiP and various reference books are the average ideal value. Instead of fiddling around taking into account the peculiarities of the insulation scheme, it is easier to use the average value.
How much the thermal conductivity of foam differs from other materials can be seen in the comparison table below.

In fact, not everything is so simple. To determine the value of thermal conductivity, you can make it yourself or use a ready-made program to calculate the parameters of insulation. For a small object, this is usually done.A private trader or self-builder may not be interested at all in the thermal conductivity of the walls, but lay insulation from foam material with a margin of 50 mm, which will be quite enough for the most severe winters.


Large construction companies that carry out wall insulation on an area of tens of thousands of squares prefer to act more pragmatically. The performed calculation of the thickness of the insulation is used to draw up an estimate, and the real values of thermal conductivity are obtained on a full-scale object. To do this, several polystyrene sheets of different thickness are glued to the wall section and the real thermal resistance of the insulation is measured. As a result, it is possible to calculate the optimal thickness of the foam with an accuracy of several millimeters, instead of an approximate 100 mm of insulation, you can put the exact value of 80 mm and save a considerable amount of money.
How profitable is the use of foam in comparison with typical materials, can be estimated from the diagram below.
Comparison of vapor permeability of heaters

High vapor permeability = no condensation.
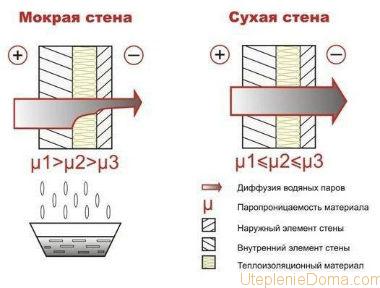
Vapor permeability is the ability of a material to pass air, and with it steam. That is, the insulation can breathe. Manufacturers have been focusing a lot of attention on this characteristic of home insulation lately. In fact, high vapor permeability is needed only when insulating a wooden house. In all other cases, this criterion is not categorically important.
Characteristics of heaters for vapor permeability, table:
| Material name | Water vapor permeability, mg / m * h * Pa |
| Minvata | 0,49-0,6 |
| Styrofoam | 0,03 |
| PPU | 0,02 |
| Penoizol | 0,21-0,24 |
| Ecowool | 0,3 |
Comparison of heaters for walls showed that natural materials have the highest degree of vapor permeability, while polymer heaters have an extremely low coefficient. This indicates that materials such as polyurethane foam and polystyrene have the ability to retain steam, that is, they perform the function of a vapor barrier. Penoizol is also a kind of polymer made from resins. Its difference from polyurethane foam and foam is in the structure of the cells that open. In other words, it is a material with an open cell structure. The ability of thermal insulation to pass steam is closely related to the next characteristic - moisture absorption.
Today, gas autonomous heating of a country house is the cheapest option for heating a home.
On the contrary, autonomous heating of a private house with electricity is the most expensive. Details here.
In what cases is Penoplex better?
If the protected structure will experience mechanical stress (the weight of the finish on the walls or the walking of people on the surface), it is better to buy Penoplex. The point is not that it is warmer - just its high rigidity in this case turns out to be the most demanded. But the lack of pressure, say, on the walls will force you to choose a more affordable foam.
Also, extruded polystyrene foam is out of competition when it is necessary to simultaneously perform high-quality thermal and waterproofing of objects. That is, in the case of the basement of a house or a damp basement, the low water absorption of Penoplex will only play into the hands. In frame buildings, EPS is also preferred if it is necessary to provide a sufficient level of sound insulation. The reason is that conventional foam not only does not stop noise, but also amplifies it.
The decision in favor of Penoplex is also made in the case of insulating too tight spaces from the inside, since its effective layer is about 25% thinner than when using foam. That is why for loggias, where every centimeter of area counts, it is better to choose extruded polystyrene foam.
Testimonials
“I would add to the disadvantages of foam plastic the fundamental impossibility of working with thin sheets.Even the standard 50 mm is too flimsy, and it is sometimes scary to mount them on a vertical. It is already easier and more convenient to operate from 100 mm, and in the case of Penoplex this thickness may not be necessary at all if the insulation is not too serious. "
Oleg Danilov, Kursk.
“I would not recommend fully attaching the EPSP to the outside of a residential building, otherwise moisture will condense in the wall itself. At my dacha, I glued Penoplex thermal insulation only along the plinth, so that no problems arose from soil movements and constant dampness. And the rest of the facade was simply covered with foam. For the money, it was the best option for me. "
Roman, Perm.
“At one time, the insulation of the walls from the outside did not give the desired effect, since no one performed calculations / calculations: they simply threw 100 mm mineral wool, sewed it up with siding and calmed down. Out of despair, I had to warm myself up from the inside. After reading the reviews, I stopped at Penoplex in order to somehow preserve the useful area. The third year everything is fine - no dampness or problems with the walls. As I understand it, the EPS now itself works as a vapor barrier for me ”.
Leonid, Moscow region.
“There are no questions: Penoplex is really more expensive than polystyrene, but do not forget that due to its low thermal conductivity in thickness (and in cubic capacity) less will be required. That is, the difference will no longer be so significant. And how many cans of foam do you need to pour out to collect a layer of ever-crumbling PSB? With smooth or L-shaped edges of the EPS, this question does not arise at all. "
Kirill Bannikov, Rostov-on-Don.
“To choose Penoplex for facades is an option from the category“ money has nowhere to go ”. It is good to use it for its intended purpose: under a screed (concrete or floating), underground or somewhere closer to the foundation. In all other cases, it is better to stay with foam. "
Mikhail, St. Petersburg.
“My father-in-law's house has been insulated from the outside with the most common foam plastic for 7 years now: nothing gets damp, does not grow moldy and does not fall off. We did everything with him alone: aerated concrete walls, PSB-S25-f on top. Judging by the reviews, with Penoplex it would have turned out much worse - it is very dense and completely impervious to air. "
Nikita, Moscow.
Penoplex and polystyrene actually differ slightly from each other, although some features of EPS make it necessary to choose it for certain types of work: insulation of structures experiencing mechanical stress in the ground or in conditions of high humidity. In all other cases, everything is decided only by the price - even the required thermal conductivity can be selected in terms of the density and thickness of the sheets. So if there are no special requirements for surface insulation, it is most reasonable to stop at ordinary foam, and Penoplex is better to purchase for serious work.
The first places among building materials for the insulation of houses and apartments are occupied by polystyrene and polystyrene foam. These types of building materials have a lot in common, but it is due to some differences that these heaters differ not only in cost, but also in quality, which affects their choice for carrying out insulation work.
Thermal insulation hygroscopicity overview
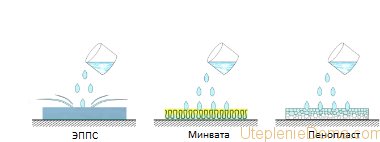

High hygroscopicity is a drawback that needs to be eliminated.
Hygroscopicity - the ability of a material to absorb moisture, measured as a percentage of its own weight of insulation. Hygroscopicity can be called the weak side of thermal insulation and the higher this value, the more serious measures will be required to neutralize it. The fact is that water, getting into the structure of the material, reduces the effectiveness of the insulation. Comparison of the hygroscopicity of the most common thermal insulation materials in civil construction:
| Material name | Moisture absorption,% by weight |
| Minvata | 1,5 |
| Styrofoam | 3 |
| PPU | 2 |
| Penoizol | 18 |
| Ecowool | 1 |
Comparison of the hygroscopicity of home insulation showed high moisture absorption of penoizol, while this insulation has the ability to distribute and remove moisture. Due to this, even when wet by 30%, the coefficient of thermal conductivity does not decrease. Despite the fact that mineral wool has a low percentage of moisture absorption, it especially needs protection. After drinking water, she holds it, not allowing it to go outside. At the same time, the ability to prevent heat loss is dramatically reduced.
To exclude the ingress of moisture into the mineral wool, vapor barrier films and diffusion membranes are used. Basically, polymers are resistant to prolonged exposure to moisture, with the exception of ordinary polystyrene foam, it quickly degrades. In any case, water did not benefit any thermal insulation material, therefore it is extremely important to exclude or minimize their contact.
It is possible to organize autonomous gas heating in an apartment only with all permits (the list is quite impressive).
The payback period for alternative heating of a private house with hydrogen is about 35 years. Whether it is worth it or not, read here.
What to choose for insulation
Despite the fact that the materials in question are intended for insulation, it is still recommended to insulate the walls of residential buildings with foam. The foam allows the walls to breathe by preventing condensation from forming inside the wall. If condensation forms constantly, it will cause the walls of the house to collapse. Avoid the accumulation of condensation inside the wall by laying a vapor barrier, which is unnecessary.
Penoplex is recommended to insulate non-residential buildings, as well as the foundation, ceiling and floor. In relation to these factors, penoplex is the best option for insulation. Penoplex has an important advantage - it is high strength. After the floor is insulated, the material does not need to be covered, as it is able to support the weight of a person.
A balcony or loggia insulated with polystyrene will have a low quality of sound insulation, but do not forget that the goal in view requires the preservation of heat, not sound.
Summing up, it is important to note the main technical characteristics of both materials for insulation:
- The strength of the foam is 0.5 MPa, that of the foam is 0.2 MPa.
- Significant difference in air and moisture resistance levels. For foam - 2%, and for foam - 0.4%.
- The degree of thermal conductivity for both materials is practically the same and amounts to 0.032 and 0.04 W / mK.
- The cost of polystyrene foam is 1.5 times more expensive than foam plastic, which is due to the laboriousness of manufacturing the material and its high strength.
Setting the goal - to insulate your balcony, it is important to weigh all the indicators and characteristics of the building materials in question, and then make a decision. Do not forget that not only the cost of the material plays an important role, but also the area of its application.
These materials have similar not only names, but their characteristics, as well as production technology. Why then should the producers of expanded polystyrene fool people's heads and produce almost identical materials? First, you need to understand the fundamental differences, why and why, and then draw conclusions.
Indeed, these materials are not only similar, they are almost identical. The main thing here is the first root "foam". He talks about the porous structure of both. Polyfoam and penoplex are easy to install, do not absorb moisture, weigh little, do not rot, they are not afraid of any kind of weather. True, the bad thing about them is that they do not tolerate solvents, for example, the same acetone. Well, and other chemically aggressive substances. Are burning. They have low strength and need protection.


The first difference between them is that the foam is white, and the foam is canary in color. Funny differences? Do not think that manufacturers of this artistic difference want to attract customers to buy more expensive penoplex.But this fact will still help in choosing a kettle.
Analysis by composition
These materials are actively used in the construction industry and, for the most part, precisely for thermal insulation, although they can also insulate sound. They are made using similar technologies - polystyrene foaming. Foam is understood to be an insulating material composed of 98% air and 2% polystyrene. This is why it is cheap: only 2% of the raw material is needed for the stove. Penoplex is a synthetic material for thermal insulation made from extruded polystyrene foam. It is also created by foaming raw materials, and the composition is approximately the same.
Heat transmission
Since we are talking about thermal insulation, that is, there is a small difference between them, since the thermal conductivity of the foam is 0.035-0.05 W / m * C, and the foam is 0.028 W / m * C. From this it follows that penoplex retains heat a little better. For example, a 25 mm foam board is identical in terms of thermal insulation to a 20 mm foam board. The first option is slightly inferior to the second. In large areas, this is a great space saving.
Water absorption
Penoplex does not like water at all, and absorbs no more than 0.4% in 30 days, but the foam has not gone far either. It absorbs less than 4% for the same three dozen revolutions of the planet around its axis. And again the penoplex is slightly ahead. It is also worth knowing and considering that penoplex is completely vapor-tight. What can not be said about the foam, which has a vapor permeability index of some kind, but there is, even if you just look in the specification.
About strength
By humiliation and compression of materials from expanded polystyrene, it was found that the foam withstands a pressure of 0.5 MPa, and the foam is only 0.2 MPa. Do you feel the difference? It is better to lay the first analogue on the floor, especially if it is a garage, a skating rink, or even an airstrip. True, it is worth taking into account that the density of the foam is lower, and ranges from 15 kg / m3 to 35 kg / m3, and the second has 28-45 kg / m3. This means that the specific gravity is also less.
Temperature
Here, the difference is almost imperceptible, both options feel great in explosive frosts, but at temperatures below -50 ° C they begin to lose their properties. The upper maximum is 70 ° C for polystyrene and 75 ° C for polystyrene foam. It is also better not to leave them at the mercy of direct sunlight. You can of course experiment by placing a piece of Styrofoam in the sun. The result will not keep you waiting for a long time.
The most painful question
Have you ever seen a material with the best properties sell for the same price as a losing competitor? Not to mention the lower one? Here the situation is very standard - due to the fact that penoplex has slightly pulled ahead in terms of indicators, it is one and a half times more expensive than polystyrene. Most choose Styrofoam only because of its lower cost. In some types of work, they really do not differ much in their properties, but it also happens in a different way.
Flammability of materials
Both pieces of expanded polystyrene burn well. Only foam makes it a little slower, and has the G3 category, and the foam is better and belongs to the G4 category.
G - combustible, NG - non-combustible. The numbers from 1 to 4 indicate the degree of flammability from low to high.
To prevent the material from burning, it is impregnated with fire retardants. But this does not mean that it will not ignite at all. It will burn, albeit worse, while also releasing toxic substances from fire retardants.
What is where?
- For facade insulation, it is better to take polystyrene foam. It is cheaper and more breathable. It will also reduce vapor barrier costs as it allows the wall to "breathe".
- It is better not to insulate the walls inside the house at all with the help of such materials. Although they are environmentally friendly in themselves, they can be impregnated with special solutions that release toxic substances just like that, at will.
- When insulating a balcony or loggia, it is better to choose a penoplex. It has less thermal conductivity, which means that it will not reduce the internal space so much.
- If you have a flat roof, and you decide to insulate it, then both options will work.
- The ceiling can also be insulated with any of your choice. But, if you are going to walk in the attic later, then it is better to choose a more durable analogue - penoplex.
- Both materials are also suitable for thermal insulation of the floor, if the subfloor is made along logs.
In construction, insulation is widely used with materials from polystyrene - thermoplastic polymers that turn into a viscous state when heated and amenable to molding. The plastics are filled with gas and acquire a cured foam structure. The resulting material is very light, which is good for installation, and has a low thermal conductivity due to the fact that it consists of more than 90% air. It is produced in the form of plates 1200x600 mm (Penoplex) or 2000x1000, 1000x1000, 1000x500 (polystyrene), with a thickness of 10 to 100 mm.
And one and the other insulation is obtained from polystyrene, which explains the similar characteristics. They are not subject to decay and biodegradation, lend themselves well to mechanical processing, do not absorb water and do not dissolve in it. But foam, like Penoplex, is destroyed by liquids such as acetone, benzene, dichloroethane, gasoline. When installing thermal insulation, it is important to choose the right accompanying materials: glue or paintwork. In addition, polystyrene and Penoplex deteriorate under the influence of ultraviolet radiation and during storage they must be protected from daylight. For the same reason, if the insulation is installed outside the building, further finishing work is required.
Polystyrene is a flammable substance; to reduce the fire hazard, flame retardants are included in its composition. Polyfoam is available in two types: with or without special additives to reduce flammability. According to GOST 15588-86, in the designation of the type of plate (PSB-S or PSB), the letter C symbolizes the presence of fire retardants. However, both polystyrene and Penoplex are unacceptable to use for thermal insulation of areas of premises near stoves, fireplaces, gas appliances and other sources of open fire. The following characteristics depend on the manufacturing technology of insulating materials:
- strength;
- water absorption;
- vapor permeability;
- thermal conductivity.
Polyfoam is produced from polystyrene granules in which a low-boiling liquid is evenly dissolved. Heating leads to its foaming and an increase in microparticles by 10–30 times; simultaneously, they are sintered and a block is formed, which is then cut into slabs of the required thickness. As a result, the foam consists of balls with an impermeable shell and micropores inside. However, voids remain between individual granules and the bond is not strong enough.
Penoplex (extruded polystyrene foam or EPS) is made in a different way: the particles of the initial substance, as a result of heating, turn into a homogeneous flowable mass, which, after foaming, is squeezed out through a forming extruder. It will be warmer in the room if the material obtained using this technology is used for insulation.
Installation and operational efficiency


Installation of PPU is quick and easy.
Comparison of the characteristics of heaters should be carried out taking into account the installation, because this is also important. It is easiest to work with liquid thermal insulation, such as polyurethane foam and penoizol, but this requires special equipment. It is also easy to lay ecowool (cellulose) on horizontal surfaces, for example, when insulating a floor or attic floor. For spraying ecowool on walls with a wet method, special devices are also needed.
Polyfoam is laid both along the crate and immediately on the work surface. In principle, this also applies to stone wool slabs.Moreover, it is possible to lay slab insulation on both vertical and horizontal surfaces (including under the screed). Soft glass wool in rolls is laid only along the crate.
During operation, the thermal insulation layer may undergo some undesirable changes:
- saturate moisture;
- shrink;
- become a home for mice;
- collapse from exposure to infrared rays, water, solvents, etc.
In addition to all of the above, the fire safety of thermal insulation is of great importance. Comparison of heaters, table of flammability group:
| Material name | Flammability group |
| Minvata | NG (not lit) |
| Styrofoam | G1-G4 (highly flammable) |
| PPU | G2 (moderately flammable) |
| Penoizol | G1 (slightly flammable) |
| Ecowool | G2 (moderately flammable) |
Table of thermal insulation properties of materials
| Material | Density in kg / m3 | Minimum layer, cm | Thermal conductivity | Hygroscopicity | |
| Bulk | Slag | 1000 | 30 | BUT | B |
| Expanded clay | 500 | 20 | B | D | |
| Glass pore | 15-120 | 10 | D | BUT | |
| Perlite, vermiculite | 40-100 | 10 | D | BUT | |
| Basalt fiber | 130 | 15 | D | B | |
| Roll | Glass wool | 75-175 | 10-15 | D | B |
| Minvata | 35-125 | 10-15 | D | B | |
| Stitching mats | 75-150 | 10-15 | D | B | |
| Plastiff | 50-60 | 2 | D | D | |
| Isover, URSA | 35-125 | 10-15 | D | B | |
| Penofol | 60-70 | 5 | D | AT | |
| Expanded polystyrene | 30-40 | 10 | D | AT | |
| Polyurethane foam | 30-60 | 10 | D | AT | |
| Plate-sheet | Styrofoam | 35-50 | 10 | D | AT |
| Mipora | 25-40 | 10 | D | AT | |
| Mineral and glass wool | 75-250 | 10-15 | D | B | |
| Wavy | 250 | 1.5-3 | B | BUT | |
| Foam blocks | Expanded clay concrete | 1000 | 40 | BUT | AT |
| Foam concrete | 600 | 25 | B | B | |
| Aerated concrete | 400-800 | 20-40 | B | B | |
| Aerated concrete | 400-800 | 20-40 | B | B | |
| Gas silicate blocks | 400-800 | 20-40 | B | B |
Legend:
- A - Very high.
- B - High.
- B - Average.
- D - Low.
- D - Very low.
Comparison of thermal conductivity and hygroscopicity of various materials allows for selection both in terms of quantity and quality.
Basement floors must be insulated with a material with the lowest possible hygroscopicity, such as plastic form. This is due to the fact that such ceilings are located in the dampest places.
It is quite possible to insulate ceilings, floors and other horizontal ceilings with any insulation.
For insulation of walls, partitions and other vertical planes, it is better to use plate-sheet insulation. They retain their shape and thermal insulation properties throughout their entire service life. Bulk and roll materials on vertical surfaces sag over time, which leads to uneven thermal insulation.
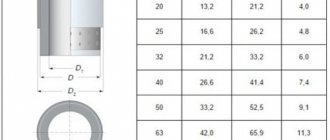
When designing thermal insulation, it is also important to correctly calculate the thickness of the thermal insulation layer. The dependence of the thickness of the insulation at the lowest external temperatures is given below.
Outcomes
Today we reviewed the most commonly used home insulation materials. By comparing different characteristics, we obtained data on thermal conductivity, vapor permeability, hygroscopicity and the degree of flammability of each of the heaters. All this data can be combined into one common table:
| Material name | Thermal conductivity, W / m * K | Water vapor permeability, mg / m * h * Pa | Moisture absorption,% | Flammability group |
| Minvata | 0,037-0,048 | 0,49-0,6 | 1,5 | NG |
| Styrofoam | 0,036-0,041 | 0,03 | 3 | G1-G4 |
| PPU | 0,023-0,035 | 0,02 | 2 | G2 |
| Penoizol | 0,028-0,034 | 0,21-0,24 | 18 | D1 |
| Ecowool | 0,032-0,041 | 0,3 | 1 | G2 |
In addition to these characteristics, we have determined that it is easiest to work with liquid insulation and eco-wool. PPU, penoizol and ecowool (wet installation) are simply sprayed onto the work surface. Dry ecowool is filled up manually.