Scope of application of vapor-moisture insulating membranes ↑
The basis of the film is polypropylene, which provides the coating with strength, tear and pressure resistance. The use of roll insulation extends the service life of multi-layer building structures and helps to achieve an optimal ratio of humidity and temperature in the house.
The use of Izospan modifications is the best solution in the following situations:
- protection of heat-insulating materials and internal parts of the structure from penetration of steam and moisture;
- arrangement of a "roofing pie";
- ensuring the vapor tightness of the attic, attic and interfloor floors;
- insulation of the structure from atmospheric precipitation, UV radiation in areas of insufficient joining of roof elements;
- additional waterproofing of different types of foundations;
- increasing the efficiency of the heat-insulating material.
High performance and affordable cost have become the main factors in the increased demand for materials.
Differences between vapor-permeable membranes and vapor barrier films
On the construction sites and forums, you can read, and from the lips of builders and private developers hear such terms as "Izospan waterproofing", "Izospan steam waterproofing" and "Izospan film". And sellers of building materials will tell you more about the "Izospan superdiffusion membranes".
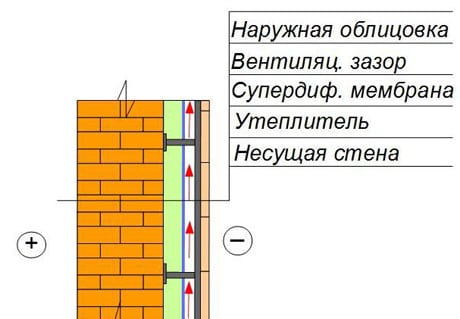
In the case when the walls of a stone building are insulated using the ventilated facade method, vapor barrier is not only not required, but also categorically not allowed. All you need is a vapor-permeable membrane that protects the insulation layer from the street side
It happens that the speakers themselves do not understand the difference between the materials or use the terms incorrectly. Often this confusion leads to the wrong choice of materials, as a result of which the thermal performance of the enclosing structures deteriorates and their service life decreases. To avoid such mistakes, you need to clearly understand how the Izospan materials and their analogues differ, as well as what they are used for. In accordance with their purpose, they are divided into two groups: vapor barrier films and vapor-permeable membranes:
Vapor barrier films ↑
Vapor barrier films are impervious to water, steam and wind. That is, they are practically sealed. They are made, as a rule, of polyethylene and more durable polypropylene, to increase strength they can be reinforced. They are also called "Izospan vapor barrier", but this definition is correct only to a certain extent. Indeed, the film is waterproof.
If it is used in the "pie" of a pitched roof, condensation water or a leak from a leaky coating will not penetrate into the attic. But for underground structures and flat roofs, the standard Izospan B waterproofing film is not the best, it is not strong enough and weather-resistant. True, the characteristics of Izospan B, the cheapest film, are low, there are better materials that can be used for waterproofing concrete floors. But nothing more.


Reflective Izospan sheet is laid as insulation under the heating floor
Application of vapor barrier films:
- Protection against high humidity of multilayer insulated structures is mounted from the inside, from the side of the room. These are frame walls, pitched roofs and wooden floors on the ground floors of buildings without basements.
- Protection against condensation and possible leaks of rafter structures in an uninsulated ventilated attic.In this case, the vapor barrier is placed on the outside, under the roof covering.
Please note: The vapor barrier can be placed in the "pie" of the pitched roof from the street side only if the attic is not insulated and well ventilated.
- In interfloor wooden floors, the Izospan film is placed under and above the insulation. Izospan for the floor in a wooden house plays the role not so much of a vapor barrier as it prevents the spread of the smallest fibers of mineral wool into the premises.
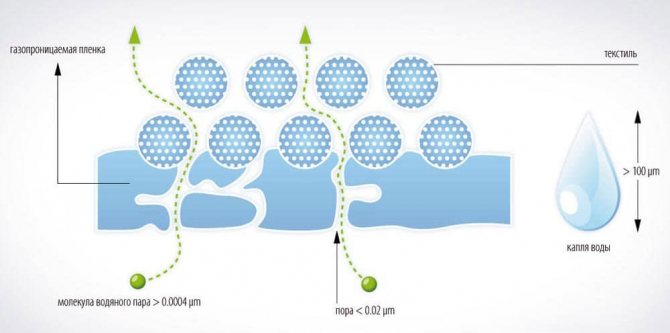

The holes in the vapor permeable membranes are large enough to allow water vapor to pass through, but too small for liquid water to enter. Membranes often have a rather complex multilayer structure and during installation it is important not to confuse the orientation: the canvas turns outward with a strictly defined side
Vapor-permeable membranes ↑
Vapor-permeable membranes are single or multi-layer nonwoven fabrics with tiny holes. The size of the holes and their number is such that the membrane is not blown by the wind, but with a difference in air humidity on the sides of the film, water vapor diffuses towards the side where the air is drier. This allows you to remove excess moisture from building structures, ventilate them. Liquid water, falling on a vapor-permeable membrane, is not able to penetrate the barrier, the surface tension force interferes. Of course, we are talking about a relatively small amount and pressure of water: individual drops or a little rain. If the membrane is left unprotected by a roofing or wall covering under heavy rain, water will flow through it.
Application of vapor barrier diffusion membranes:
- Ventilation of multilayer enclosing structures and their protection from liquid water (condensation). Located outside, from the street side. Frame walls, pitched roofs, wooden floors on the ground floors of buildings without basements.
- The membrane can be used in interfloor wooden floors, but Izospan film is cheaper.
Please note: A vapor-permeable membrane differs from a vapor barrier film in its ability to transmit water vapor. It is important to understand this difference.
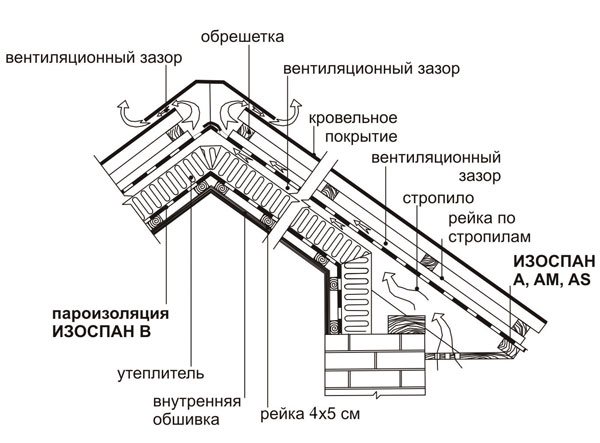

The general principle of using Izospan materials is clear from the diagram: from the outside - a vapor-permeable membrane, from the inside - a vapor barrier film
Classification and characteristics of roll insulation ↑
The manufacturer has developed a whole line of waterproofing materials. Some types of Izospan and their use are quite versatile. Other modifications of the product, on the contrary, are highly specialized and maximally reveal the protective qualities under certain installation conditions.
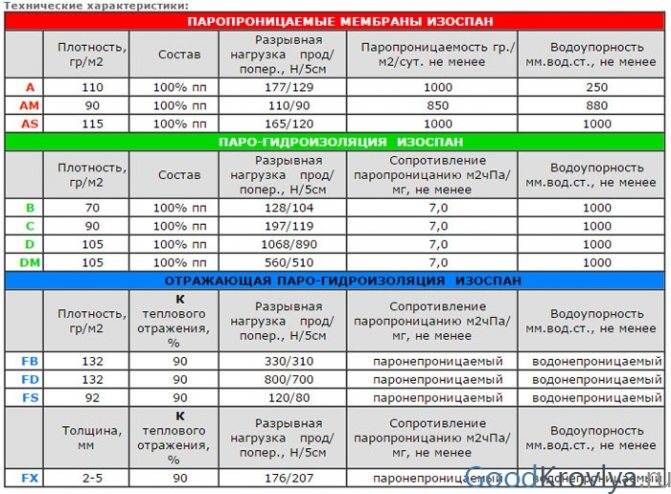

Types and characteristics of Izospan
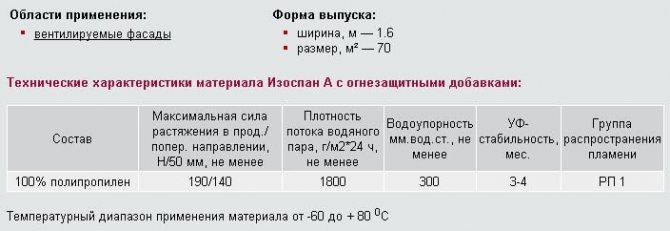
Windproof membrane category A ↑
Category A contains vapor-permeable polymer membranes designed to protect internal elements. The material facilitates the release of steam into the atmosphere. Insulation is used when arranging insulated roofs, frame walls and ventilated facades.
Izospan A has a smooth water-repellent outer surface and a porous base on the inner side. Due to this structure, moisture from the insulation is quickly absorbed into the membrane and removed to the outside. When laying insulating material of category A, two rules must be followed:
- Suitable for use on roofs with an angle of inclination of 35 ° and higher.
- Installation work is carried out in calm and dry weather.
- For high-quality steam extraction, an air gap must be provided. For this purpose, a control rail is stuffed onto the rafters.
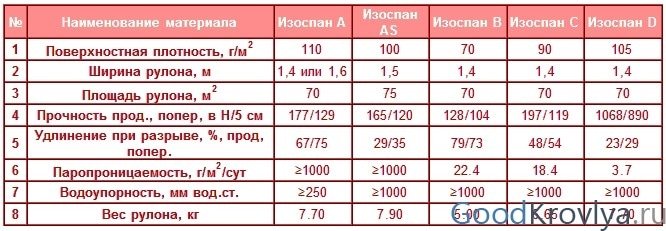

Specifications Izospan A, AM, AS
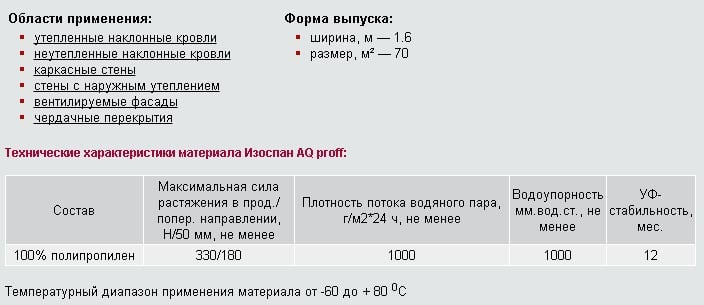
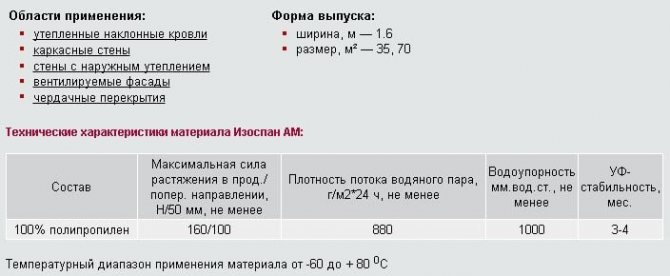
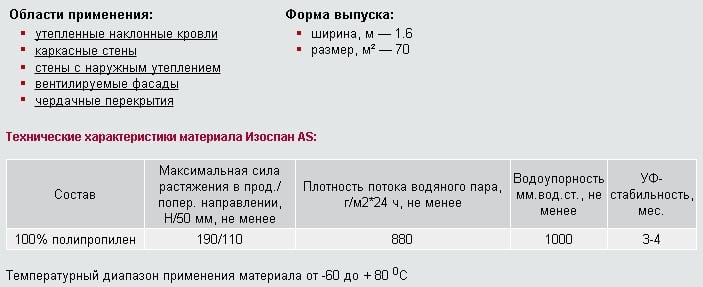
Izospan AM and AS modifications are three-layer diffuse membranes. They differ from their counterpart in reduced vapor permeability and the possibility of laying without crate.
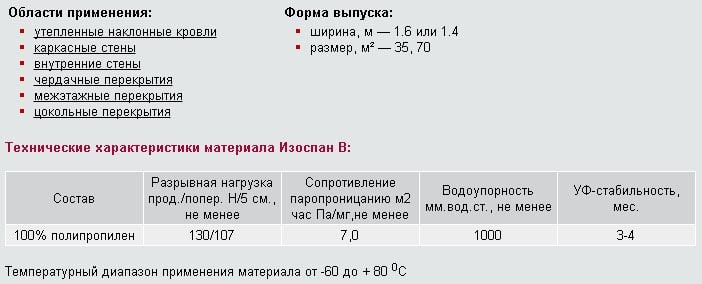
Waterproofing films of grades B and C ↑
Film insulation of category B has a design similar to materials of group A. The main difference is increased water resistance (at least 1000 mm of water column). The vapor barrier does an excellent job with the task - it protects wooden, metal elements from the effects of condensation and moisture from inside the structure.
Izospan B is considered universal and is suitable for insulation of walls, roofs and internal ceilings. Possesses the following technical characteristics:
- breaking longitudinal and transverse load - 130/107 N / 5 cm;
- density - 72 g / m2;
- temperature range of application - from -60 ° С to + 80 ° С.
Group B vapor-waterproofing films are installed with an air gap of 5 cm above the fleecy side of the vapor barrier. It is the rough side that prevents condensation from flowing to the finish. Improved vapor barrier properties explain the demand for this material when laying laminate and parquet flooring.


Vapor barrier under a wooden floor - scheme
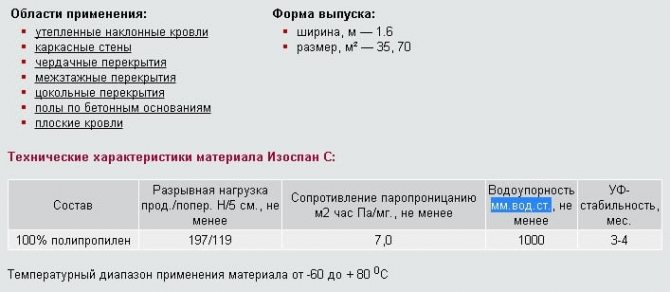
Izospan S has a similar structure and characteristics. A distinctive feature of insulation is a large margin of safety and, as a result, high reliability and durability. The breaking load is 197/119 N / 5 cm and the density is 90 g / sq. m. The cost of type C waterproofing is higher than that of group B.
Izospan category C completely isolates the structure from capillary moisture and condensation.
Main functions:
- protection of "cold" and insulated roofs;
- steam and water insulation of a flat roof;
- moisture protection of wooden horizontal floors and concrete floors.
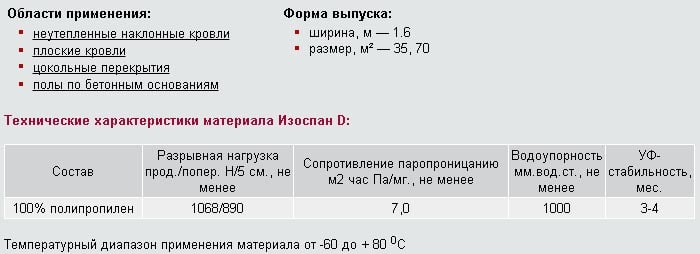
Heavy-duty canvases of category D ↑
Vapor barrier Izospan D is a two-layer woven fabric made of high-tech polypropylene. The multifunctional film is resistant to solar radiation and can withstand significant mechanical stress and snow load. Hydro and vapor barrier of the serial type D or DM is distinguished by its extra strength - a strip of fabric 5 cm wide does not deform under a weight of up to 106 kg.


Waterproofing category D
High technical and operational characteristics explain the versatility of category D film insulation. The material will adequately replace any of the above-described analogs and cope with more complex tasks:
- waterproofing floors on earth and concrete base;
- insulation of basement floors in rooms with high humidity;
- arrangement of a temporary roof and protection of the structure from precipitation.
New developments - energy-saving materials ↑
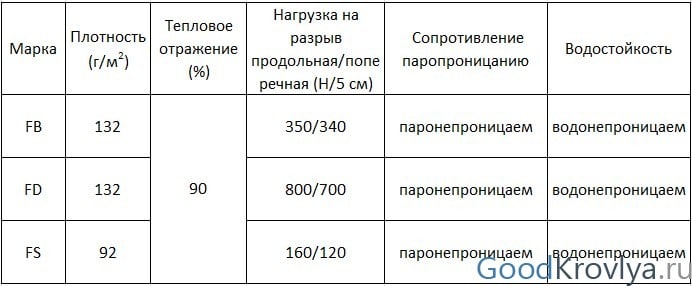
Izospan vapor barrier films of the FB, FD, FS and FX brands are modern high-tech waterproofing materials capable of reflecting 90% of infrared radiation. Progressive insulation acts as a reliable barrier against condensation, wind, moisture, and at the same time - increases energy savings.
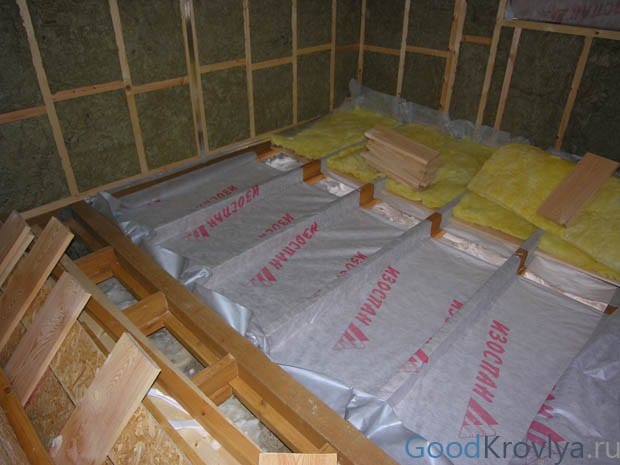


Attic vapor barrier
Thermal reflective insulation of FD and FS categories is made of two-layer polypropylene film. Izospan FX is based on foamed polyethylene of various thicknesses, and FB grades are made from kraft paper. Regardless of the type of insulation, one side is metallized. The reflectivity of materials is massively used in the arrangement of a "warm home", namely:
- as a backing layer for insulated floors;
- wall cladding behind heating radiators;
- thermal insulation of basement, attic and interfloor floors;
- construction of baths and saunas.

Energy-saving insulation characteristics
Important! Energy-saving films are completely impermeable to water vapor. Due to this feature, their use is possible only in buildings where a forced ventilation system is provided.
Instructions for the use of isospan
When using this material, the specific modification must be considered.If we talk about Isospane B, then with its help walls, roofs and ceilings are insulated. As a rule, the film is laid on top of the insulation. In this case, it is necessary to adhere to a certain sequence:
- roofing material;
- modification A or AS;
- counter-rails required to create a ventilation gap;
- isospan B;
- roof beams;
- finishing material.
Thanks to such a vapor barrier, you will be able to avoid the penetration of moisture or insulation particles into the room.
Izospan S differs significantly from other vapor barrier materials the possibility of using in the construction of roofs with a slope of less than 35˚... Thanks to this vapor barrier, an optimal microclimate is maintained in unheated attics. There is no condensation on the walls and ceilings of the basement floors, which means there is no mold or unpleasant odor.
This modification is laid as follows:
- a vapor barrier material is laid on the bottom of the roof, not pulling it too much and leaving free space;
- a membrane is fixed around the entire perimeter of the roof, and the joints are processed with construction tape;
- the overlap should be 15 cm;
- at the last stage, the material is fixed with counter-rails, which are fixed with self-tapping screws or nails.
If the roof slope is small, the modification is laid on a boardwalk fixed to the rafters.
Qualitative analogues or a brand: the nuances of choice ↑
In Russia, goods produced under the Izospan trademark are in great demand. However, there are also lesser-known analogues on the market:
- Megaspan specializes in the production of construction membranes and insulating films. The model range repeats the Izospan vapor barrier line for roofs, walls, ceilings, facades, etc. Megaspan materials are more affordable and are not inferior in quality to their main competitors from.
- "Keramospan" produces film insulation, the declared characteristics of which are similar to the original.
- Axton is a foreign manufacturer of building materials, including hydro-vapor barrier. The company pays special attention to the sanitary and environmental safety of its products.
For your information. Companies use uniform product labeling. For example, the properties of Megaspan B correspond to the technical characteristics of Izospan V.


Characteristics of Izospan class B
The difference in price between branded insulation and analogs is sometimes very noticeable. However, the reasons for the cheapness may be understated quality. Unscrupulous manufacturers use the following tricks:
- Reducing the density of the material. This is invisible to the naked eye, but water resistance and strength deteriorate.
- Lack of UV stabilizer - the film becomes vulnerable to sunlight.
- The use of recycled raw materials in production reduces the service life of the coating.
- Replacing polypropylene with polyethylene or adding chalk to the raw material leads to a "weakening" of the structure and a reduction in the life of the film.
The technology of laying roofing hydro-vapor barrier ↑
Installation technologies for various types of film insulation are similar to each other. The sequence of work depends on the finishing of specific structures. Below is a step-by-step instruction on the use of Izospan B vapor barrier when creating a "roofing pie".
Installation instructions ↑
Before proceeding with the installation, it is necessary to have an idea of the roof structure and the sequence of placing the layers of the "roofing pie". Insulation from above must be waterproofed, and a vapor barrier must be mounted from below. Both films are fixed to the roof rafter legs.
Important! The Izospan B vapor barrier is mounted in the direction from bottom to top. As a rule, one strip of roll is not enough to cover the roof slope. Therefore, first the film is rolled at the bottom of the roof, and then at the top.
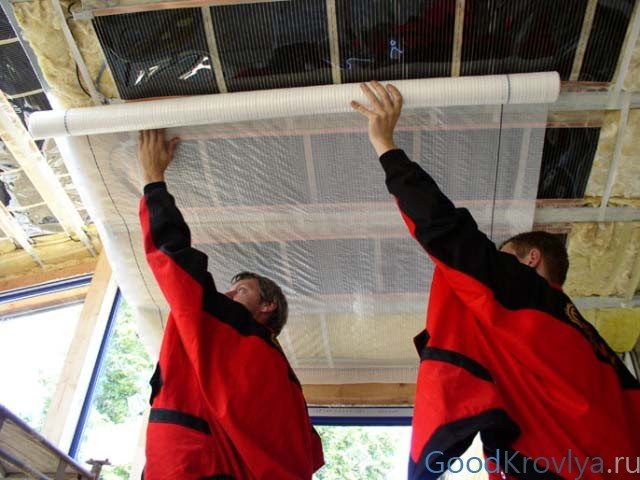


Installation of Izospan film
Algorithm of actions:
- Open the roll and fix the free edge of the film sheet to the outer rafter. Fixation with fasteners with a wide head. To speed up the work, you can use a construction stapler with staples.
- Expand the Izospan roll for the roof and stretch the canvas parallel to the floor to the opposite edge of the rafters. It is necessary to check that the vapor barrier film sags slightly. Under the influence of low temperatures, the material shrinks slightly and shrinks.
- Cut the foil with a slight gap and attach the edge to the rafter system.
- Additionally fix the vapor barrier on the intermediate rafters.
- Proceed with the installation of the second canvas. Izospan B is overlapped with a width of more than 10 cm.
- Fasten the strip to the truss structure.
- Glue the joints between the canvases with Izospan SL connecting tape or ML proff single-sided tape.
Important! Before using Izospan and finally fixing it to the rafters, you must make sure that the film is laid with the smooth side to the insulation, and the rough side to the inside of the building.
Roof vapor barrier: expert advice ↑
Roof vapor barrier is a crucial stage in the construction of a house. Builders' mistakes are costly for households. After taking a bath and cooking, vapors rise upward, penetrate the insulation and reduce its thermal insulation properties. Over time, this leads to wetting of the rafters, the formation of mold, freezing of the roof in winter and damage to the interior decoration.
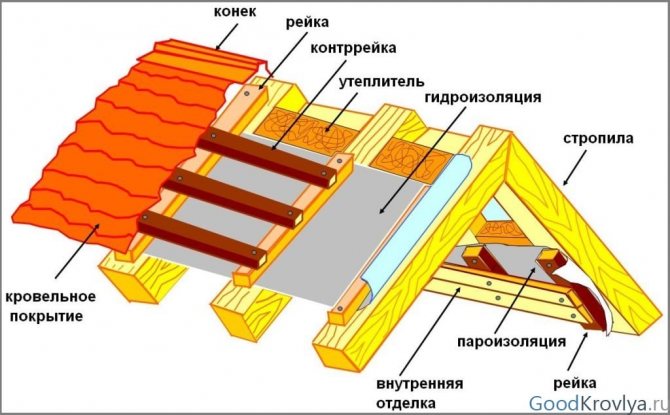

The structure of the "roofing pie"
To prevent negative consequences when installing a vapor barrier, it is important to take into account some of the nuances:
- Before starting installation work, you should carefully study the instructions for using Izospan for roofing. Izospan category A, B, C is fixed only indoors.
- When laying and attaching the protective film, it is necessary to avoid tension on the material, the appearance of holes and other defects.
- Steam and waterproofing on the roof of the attic room is fixed with counter-rails. In the future, the installation of interior decoration is carried out on this crate. In addition, the slats ensure the tightness of the joints between the rafter legs and the foil insulation.
- The allowances on the sides of each canvas must be at least 15 cm. This is enough to bring the vapor barrier onto the gables or adjacent slopes.
- It does not matter which side to lay Izospan AM on. The main condition is the installation of the membrane film directly on the insulation.
Multilayer building structures and moisture ↑
To understand how to use Izospan correctly, you will have to understand some issues of construction technologies:
Modern building technologies include various multi-layer structures. They are most justified and popular in low-rise construction. These are frame walls, pitched roofs, ceilings, ventilated facades. The supporting part of the structure - racks, rafters, etc., is often made of wood. The gaps between them are filled with an effective heat insulator. As a rule, fibrous materials are used: mineral wool, ecowool (fluff pulp).
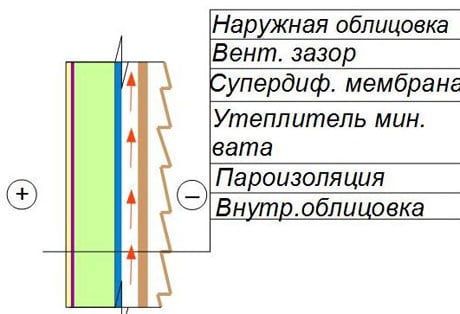

In a multi-layer frame construction, a vapor barrier from the inside and a vapor-permeable membrane from the outside are required.
Such heaters, along with useful properties, also have disadvantages: they are blown through when exposed to the wind and get wet in conditions of high humidity. As a result, their thermal insulation properties are noticeably reduced. The wooden frame is also "afraid" of moisture. It enters porous materials from the air, in the form of water vapor. For most of the year, the humidity inside the house is much higher than outside. Accordingly, from the inside of the house, it is necessary to prevent the penetration of steam into the multi-layer structure. Isolate from steam. Outside the building, the air is usually less humid, which makes it possible to ventilate and dry the insulation.
If you provide good ventilation, free moisture escape from the insulation and the wooden frame, their moisture will be minimal. Accordingly, in a multi-layer structure, vapor-permeable materials should be located on the outside. The above is true for heated homes. For unheated and well-ventilated buildings, vapor permeability does not matter.
Please note: In a multilayer heat-insulated structure, INSIDE - STEAM PROTECTION, and FROM OUTSIDE - VAPOR PROTECTION. Not the other way around. If, for example, Izospan A and Izospan B are confused, the wall or roof will become waterlogged, which will inevitably damage the building.
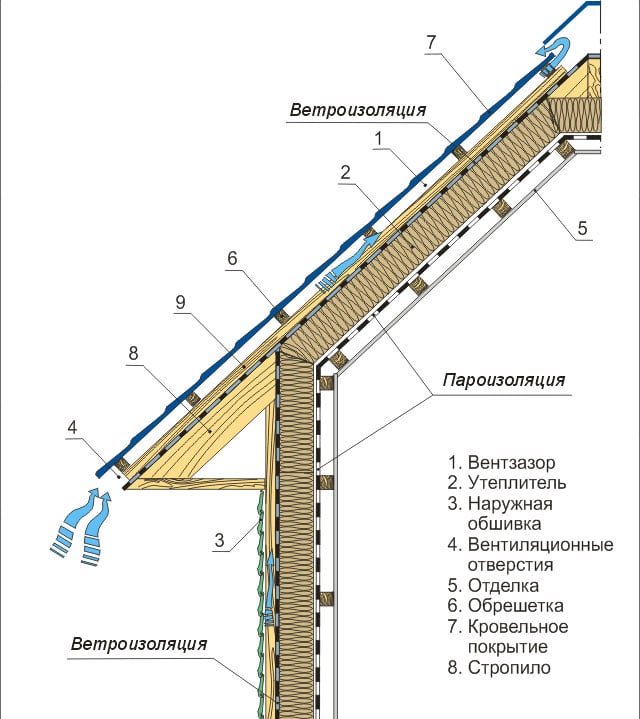

Recommended wall and roof construction of a frame house
From the inside, they are protected from moisture by a vapor barrier film (vapor barrier), and ventilation from the outside is provided by a vapor-permeable membrane (wind protection). Please note that the windscreen membrane must not come into contact with the roofing and wall cladding. To remove water vapor, there should be a ventilation gap between them with holes in the lower and upper parts of the walls and roof.
Vapor barrier of various structures: location schemes ↑
The vapor barrier of the floor must be performed in baths, saunas, swimming pools and in rooms located above the basement. The vapor barrier is laid over hydro and thermal insulation materials.
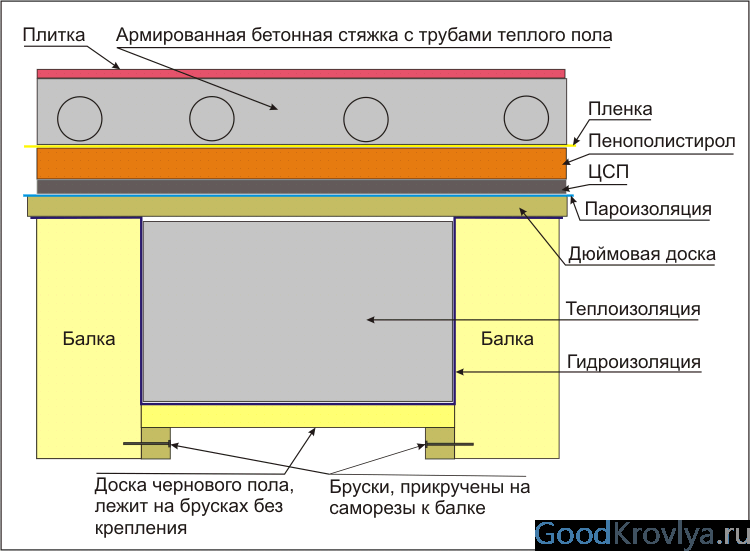

Vapor barrier for underfloor heating
Wall insulation against steam penetration can be performed both from the inside and from the outside of the building. The choice of method depends on the location of the insulation. With external thermal insulation, it is recommended to place the vapor barrier on both sides of the insulation - this measure will significantly reduce heat loss.
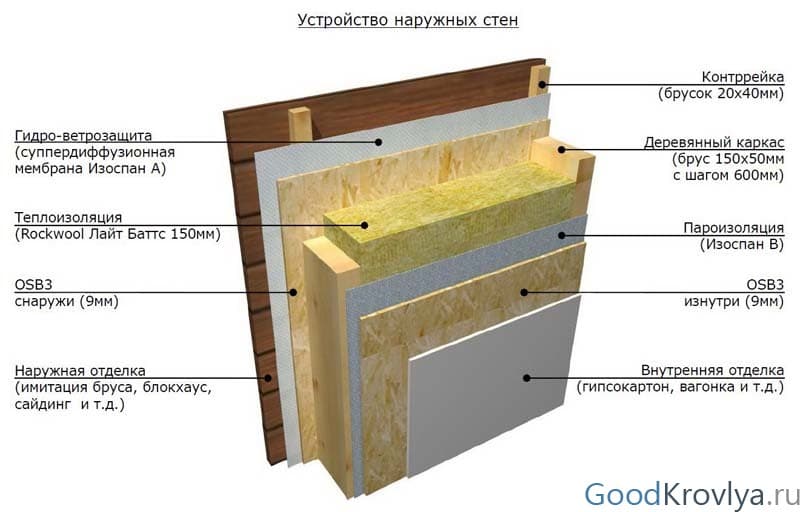

Vapor barrier in external walls
A monolithic concrete foundation has a porous structure and needs high-quality hydro and vapor barrier. The protective barrier is placed on top of the concrete base in front of the insulation. The dense film minimizes the penetration of ground moisture and prevents dampness in the basement.
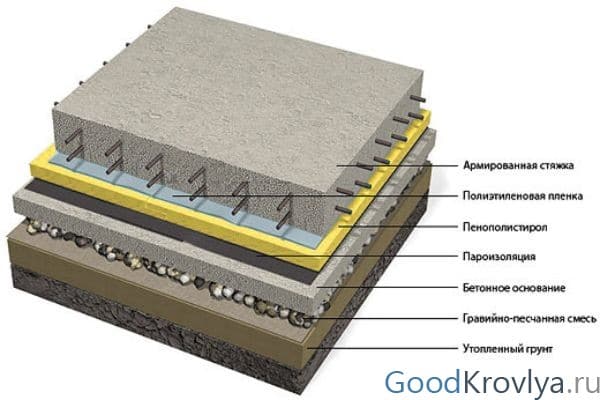

Monolithic foundation structure
Izospan is rightfully recognized as the leader of film moisture and vapor barrier for roofs.
In order for the material to realize its protective qualities as much as possible, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to the issue of choosing its modification and to carry out installation in accordance with technological requirements. The ideal option is to entrust this difficult work to professionals with a good reputation.