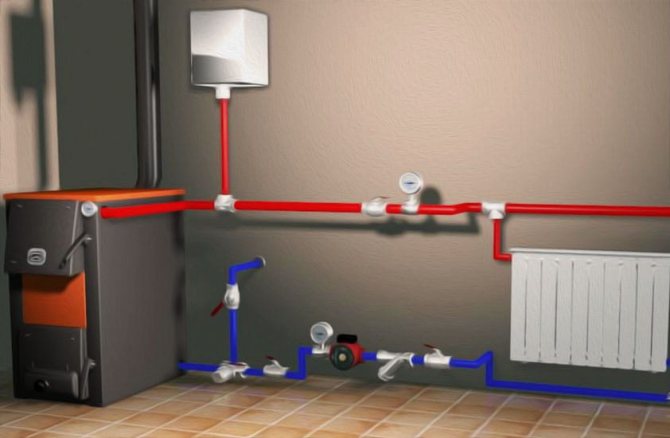
Water flow through the pipe at the desired pressure
The content of the article
The main task of calculating the volume of water consumption in a pipe by its cross section (diameter) is to select pipes so that the water consumption is not too large, and the pressure remains good. In this case, it is necessary to take into account:

- diameters (DN internal section),
- head loss in the calculated area,
- hydraulic flow rate,
- maximum pressure,
- influence of turns and gates in the system,
- material (characteristics of the pipeline walls) and length, etc.
The selection of the pipe diameter according to the water flow rate using the table is considered a simpler, but less accurate way than measuring and calculating the pressure, water velocity and other parameters in the pipeline, done locally.
Pipe circumference
Where does the determination of the diameter of the pipeline by flow rate begin? If you are new to laying networks, then this process begins by understanding what diameter is.
So, the diameter is a segment connecting two extreme points on a circle located on opposite sides of the structure. The diameter of the pipeline is calculated depending on the flow rate, it is one of the significant overall dimensions of the system.
The wisdom of calculation
What is taken into account at the time of calculations, what parameters need to be taken into account?
- The thickness of the wall of the structure.
- Internal dimension of the line.
- Outer dimension of mesh elements.
- The nominal diameter of the structure, often referred to as DN in formulas.
- An indicator characterizing the conditional passage, referred to in the calculations as Du. Measured in millimeters.
In addition, one should take into account what will move in the system, under what pressure, and the length of the route. It is also necessary to take into account what type of pipeline the calculations are for. The parameters for the heating system and water supply differ.
Previously, the size of structures was calculated and indicated in inches, but over the past few years, it has been increasingly practiced to make calculations in centimeters, millimeters. But even if you calculated everything in inches, it doesn't matter - just use one of the measurement conversion tables generously posted on the Web.
Standards for determining the flow rate
Water consumption
An important point is to correctly determine the water flow in the pipeline.
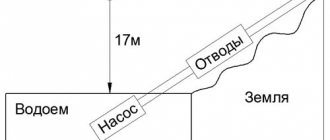
Let's take a country house. To determine the size of the structures used to supply water to the structure, the maximum consumption must be calculated. This point is important not only for understanding what elements are needed for the route, but also for the correct conduct of drilling processes, when the size of the casing is important.
Let's consider the situation with an example. Private house of average size. This means that it has a kitchen where water should be supplied, a bathroom (toilet, bathroom, which will also house a washbasin). In addition, washing machines are now used, which also need to be connected to the system. In the summer, you will need irrigation of the beds and flower beds. Based on such input data, it can be concluded that to supply water to this economy, a water supply system with approximate parameters of 3 cubic meters per hour will be needed.
For such a load, three-inch pumps are suitable. The unit itself has a diameter of 75 cm. When installing the pump, it is important to remember that the device should not come into contact with the walls of the casing, which means that you must take care that there is free space between the elements - inside the pipeline.
As a rule, a three-inch pump is sufficient to supply water to a private house.
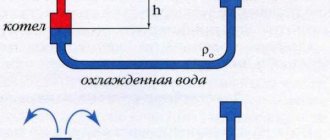
Reducing pressure and calculating hydraulic resistance
To determine the head inside the pipes and the correct selection of equipment that helps to pump liquid or gaseous media, it is necessary to calculate the pressure drop. In the absence of access to the Internet network, calculations are made according to the formula:
Δp=λ·(l/d1)·(ρ/2)·v²
Δp - voltage drops in the pipeline section, Pa l - length of the pipeline section, m λ - resistance coefficient d1 - pipe cross-section, m ρ - density level of transported media, kg / m3 v - movement speed, m / s
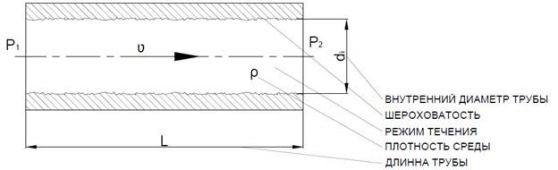

Hydraulic resistance is formed under the influence of 2 main factors:
- frictional resistance;
- local resistance.
The first option is provided for the formation of irregularities and roughness that impede the movement of the pumped media. To overcome the inhibitory effect, additional energy consumption is required. With a laminar flow and the corresponding low Reynolds exponent (Re), characterized by uniformity and the exclusion of the possibility of mixing adjacent layers of liquid or gaseous media, the effect of roughness is minimal. This is due to an increase in the parameter of the extreme viscous sublayer of the pumped media, relative to the formed irregularities and protrusions on the surface of the pipes. These conditions allow the pipes to be considered hydraulically smooth.
With an increase in the Reynolds value, the viscous sublayer has a smaller thickness, which ensures the overlap of irregularities and the effect of roughness, the level of hydraulic resistance does not depend on the Reynolds exponent, and the average height of the protrusions on the pipe coating. A subsequent increase in the Reynolds value makes it possible to transfer the pumped media into a turbulent flow mode, where the destruction of the viscous sublayer is formed, and the friction formed is determined by the value of the roughness.
Friction loss is calculated by data substitution:
HT = [(λ · l) / de] · [w2 / (2g)]
- HT - head loss with friction resistance, m
- [w2 / (2g)] - velocity head, m
- λ - resistance coefficient
- l - length of the pipeline section, m
- dЭ - equivalent value of the cross-section of the pipeline line, m
- w - speed of movement of media, m / s
- g - acceleration due to gravity, m / s2
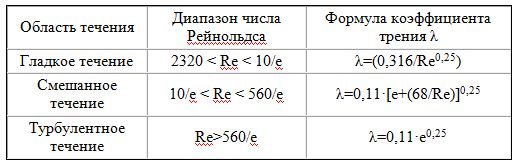

Methods for calculating the dependencies of water flow rate and pipeline diameter
Using the formulas below, you can both calculate the water flow in the pipe, and determine the dependence of the pipe diameter on the water flow.
In this water consumption formula:
- q is the flow rate in l / s,
- V - determines the speed of the hydraulic flow in m / s,
- d - internal section (diameter in cm).
Knowing the flow rate and d of the section, it is possible, using inverse calculations, to set the speed, or, knowing the flow rate and speed, to determine the diameter. In the case of an additional supercharger (for example, in high-rise buildings), the pressure generated by it and the hydraulic flow rate are indicated in the instrument's passport. Without additional injection, the flow rate most often varies in the range of 0.8-1.5 m / s.
For more accurate calculations, head losses are taken into account using Darcy's formula:
To calculate, you must additionally install:
- pipeline length (L),
- loss factor, which depends on the roughness of the pipeline walls, turbulence, curvature and sections with stop valves (λ),
- fluid viscosity (ρ).
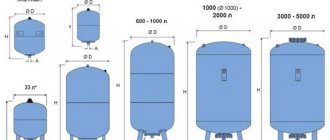
The relationship between the D value of the pipeline, the hydraulic flow rate (V) and the water flow rate (q), taking into account the slope angle (i), can be expressed in a table where two known quantities are connected by a straight line, and the value of the desired quantity will be seen at the intersection of the scale and the straight line.
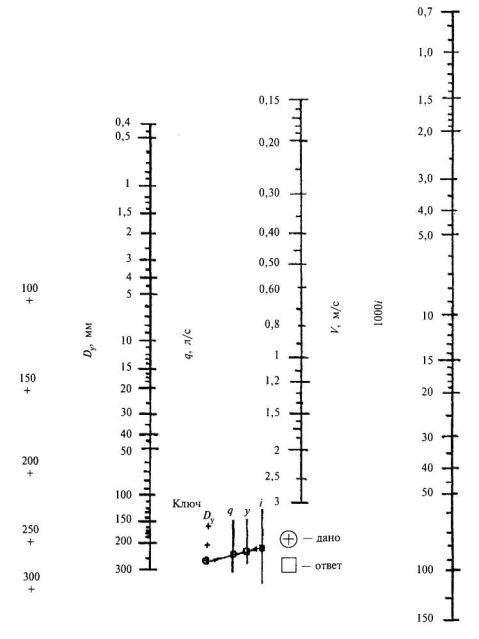

For technical justification, graphs of the dependence of operating and capital costs are also built with the determination of the optimal value of D, which is set at the intersection of the curves of operating and capital costs.
The calculation of the water flow through the pipe taking into account the pressure drop can be carried out using online calculators (for example: https://allcalc.ru/node/498; https://www.calc.ru/gidravlicheskiy-raschet-truboprovoda.html). For the hydraulic calculation, as in the formula, you need to take into account the loss factor, which implies the choice:
- method of calculating resistance,
- the material and type of piping systems (steel, cast iron, asbestos, reinforced concrete, plastic), where it is taken into account that, for example, plastic surfaces are less rough than steel and do not corrode,
- inner diameters,
- section length,
- pressure drop for each meter of the pipeline.
Some calculators take into account additional characteristics of piping systems, for example:
- new or not new with bituminous coating or without internal protective coating,
- with external plastic or polymer-cement coating,
- with external cement-sand coating, applied by different methods, etc.
How to calculate the diameter of a gas pipe
The gas pipe is calculated slightly differently than the water pipe. Here the fundamental values are:
- gas velocity and pressure;
- pipe length with pressure loss on fittings;
- pressure drop within acceptable limits.
The calculation of the diameter of the gas pipe can be carried out using the formula:
where di is the inner diameter of the pipeline, m;
V´ - volumetric consumption of compressed air, m³ / s;
L is the length of the pipeline, adjusted for fittings, m;
Δp - permissible pressure drop, bar;
pmax - upper compressor pressure, bar.
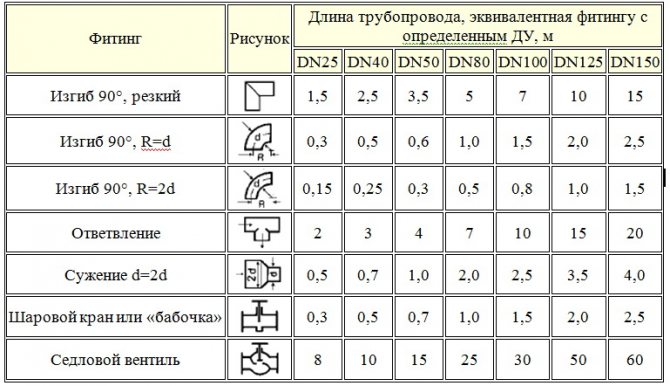

Thus, when choosing a pipe diameter, an important parameter is the throughput, which depends on the cross-section and internal size of the line. Therefore, it is imperative to measure such data as permissible pressure, wall thickness, pipe inner diameter, properties of the heat carrier or gas.
How do you size the pipeline? Tell us, by what parameters did you calculate the pipes for your own home?
When laying water mains, the most difficult thing is to calculate the throughput of pipe sections. Correct calculations will ensure that the water flow rate is not too large and its pressure does not decrease.