| Name | Key Features |
| Liquid | The most common. It is used for thermal insulation of various structures, for repairs. Fills cracks and gaps. Can be cooked on site. |
| Granular (thermovata) | It is made by crushing the polymer into fractions of 10-15 mm. Economical during installation. Penoizol in granules in volume is 2 times higher than the amount of sheet polymer obtained during production. They fill the cavities between the walls when laying the floor. |
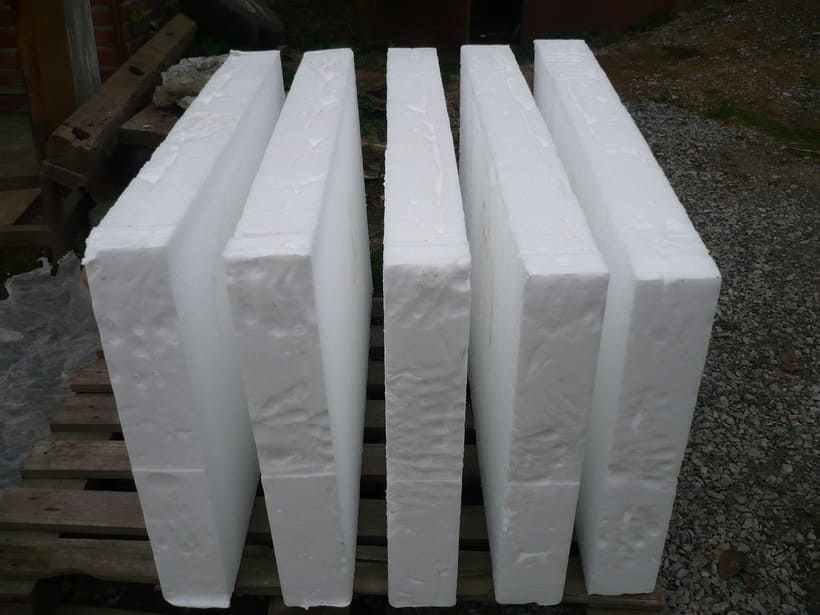
| Sheet | Insulation is poured into a special form, cut when ready, dried and further processed. It is mounted on the outside of the walls of houses, fastened with dowels. It can also be laid on the floor (between the joists). |
Indicators and advantages of penoizol
The popularity of urea foam is due to its low price and characteristics:
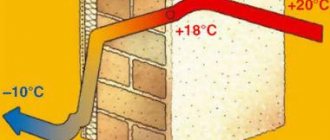
- Low thermal conductivity (0.041 W / m2 * K). To ensure good thermal insulation, a narrow layer of foam insulation is sufficient (at least 10 cm).
- High noise absorption, up to 65%. Even a narrow layer of building material solves the issue of sound insulation.
- Good fire resistance. The insulation belongs to the G-1 flammability group with the B-2 flammability category. The polymer does not melt, but evaporates without releasing harmful toxins. Smokes weak.
- Hygroscopicity. Air can pass through the foam, the vapor permeability property allows the walls to "breathe".
- Chemical neutrality to various components, including organic solvents.
- Biostability. Fungus and mold do not grow on penoizol, mice / rats do not gnaw it.

Thermal insulation with liquid foam - penoizol.
The scope of application of urea foam - foam ash as a heater is very wide:
- insulation of hollow walls: timber frame houses, timber houses with insulation for siding, hollow pockets in brickwork;
Video: Thermal insulation of the wall of a frame house with liquid foam - penoizol.
- floor insulation, for example, if the house is on piles with a ventilated underground;
- insulation of attics;
Video: Filling the floor and attic with liquid foam - penoizol.
- insulation of the attic roof;
- insulation of industrial refrigerating chambers and containers;
- insulation of industrial premises.
disadvantages
Penoizol has the following disadvantages.
First, it absorbs moisture and does not give it away. Penoizol is quite resistant to moisture, but this feature does not allow the use of insulation when screed the foundation.
Secondly, the material gives a sediment in the range of 0.1-5%.
Thirdly, penoizol tears easily - it has low tensile strength.
Fourthly, it is possible to put insulation only at a positive temperature (at least + 5 ° C). Only in this case will you get high-quality foam for filling cavities.
If sheet and granular penoizol does not emit hazardous substances, then in liquid form it can evaporate harmful toxins. Workers are better off having protective equipment.
What is penoizol
It is a porous material that resembles foam. But unlike it, penoizol is elastic: after pressing it is able to take its original shape. It also contains smaller porous cells. The new polymer is called liquid foam because of the similarity in structure and external data, but the process of its creation is fundamentally different.
The composition of penoizol includes chemical components: phosphoric acid, urea resin and a foaming agent. These compounds in certain proportions enter the compressed air device intended for synthesis. As a result of chemical reactions, a mass in the form of foam is obtained.Increasing in volume, it fills any cracks, cracks, spaces between structures.
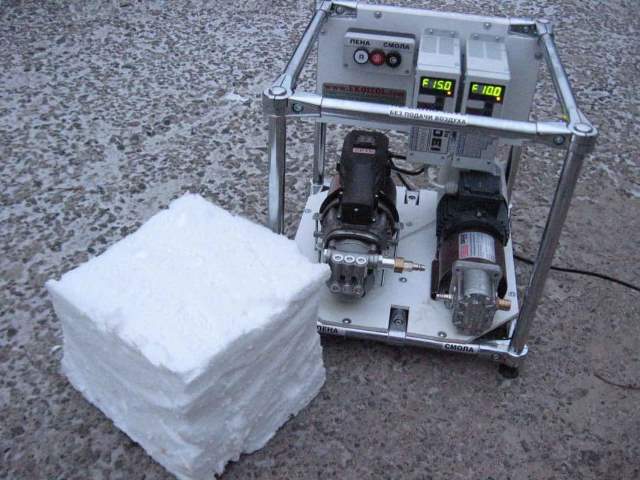


Equipment for the production of penoizol and the appearance of the material obtained
White clots and jelly-like consistency resembles expanded polystyrene, but differs in a fine-meshed structure. Possesses:
- excellent thermal insulation capabilities;
- resistance to moisture and fire;
- environmental friendliness;
- elasticity;
- the ability to tightly close any holes and gaps.
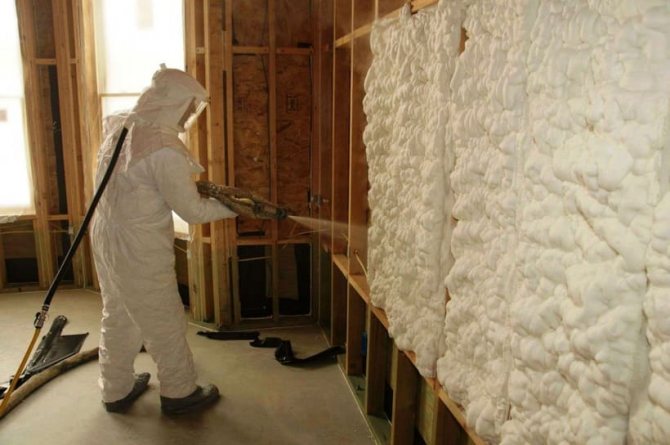
Installation of insulation is carried out by spraying using a special device. With a small amount of work, penoizol is used in cylinders. The new polymer is used for thermal insulation of walls, floors and ceilings, filling of ceilings between floors.
When the components are combined in the required ratios, penoizol does not harden immediately. The process goes gradually:
- after 10-15 minutes, the foam sets a little;
- after 1-4 hours it hardens;
- after 2-3 days it becomes thoroughly solid and acquires the necessary qualities.
When applied to the surface, it resembles polyurethane foam. The spraying technology assumes a seamless layer of thermal insulation, which makes it possible to process any geometric structures.
Important! The new material is used in construction in many countries, since high thermal insulation is combined with low costs for its manufacture. The installation of the insulation is carried out quickly, the speed of work increases by 4-5 times, and the use in lightweight, lightweight structures makes the material even more in demand.
Penoizol manufacturing technology
- In a separate container, 3 ingredients are mixed: water, a foaming agent and a reaction catalyst. Urea-formaldehyde resin is poured into the second container. Subsequently, it enters the mixture under the influence of compressed air.
- The components are thoroughly mixed until a mixture is formed, similar in consistency to a soufflé. The resulting material is called liquid penoizol, that is, it is already suitable for use on construction sites.
- The liquid mass is poured into molds of various sizes. Curing takes place at room temperature, lasts up to 3 hours (depending on the shape, size and specific recipe), on average - 30-40 minutes.
- The resulting sheets of insulation are cut into separate slabs in accordance with the required dimensions.
- Urea foam is coated with a protective compound that increases strength and fire resistance.
- The finished product is packed and stored.


Description of liquid foam - penoizol.
Urea insulation - foamed plastic consisting of 98% air and 2% of urea-formaldehyde resin with approximately the same number of both open and closed pores. The structure of its liquid foam is similar to the well-known meringue-type soufflé, and from afar many people confuse it with expanded polystyrene (polystyrene), but upon closer inspection, a material completely different from foam is guessed. Other names for insulation are mipora, liquid foam - penoizol, liquid insulation, urea foam, bipor and mettemplast.
Video: Appearance of liquid foam - penoizol and its mechanical properties.
What you need to get started
A penoizol business can be started without serious investment. The equipment is inexpensive, and the main expenses every month will be spent on the purchase of raw materials and remuneration of personnel.
Table 1. Initial Costs for the Penoizol Business.
| Consumable item | price, rub. |
| check in | 20 thous. |
| Premises for rent, 90 sq. m | 25 thous. |
| Equipment | 200 thous. |
| Raw materials (for a month at full load) | 230 thous. |
| Salary, 6 people | 190 thous. |
| Additional expenses | 100 thous. |
| Total | 765 thous. |
The calculations are relevant for a city with a population of up to 1-1.5 million people. Additional costs include utility bills, advertising promotion, premises preparation, etc.The amount of tax deductions is not included in the calculation.
So, let us consider the classic scheme for the production of penoizol using a GZhU installation.
Resin is poured into one tank.
In another tank, a solution of OFA and surfactant. The proportions are approximately equal: 1% OFA and 1% surfactant (depends on the setting and on the hardness of the water).
The solution is fed into the foam generator by a centrifugal pump. Compressed air from the compressor also enters there. The foam concentrate is a tube filled with metal or plastic mesh, shavings, balls from bearings, and other rubbish that serves one purpose - to create the largest possible surface area. Air bubbles are formed precisely at the border of the environments. Remember the childhood experience with a ring, which we dipped in soapy foam and then blew into it to get soap bubbles.
At the outlet of the foam generator, a stream of soapy foam is formed, into which the resin is injected either in a jet or aerosol. The resin is also supplied by a centrifugal pump. Then the mixture of soapy foam and resin moves along a hose with a diameter of 35 to 45 mm and a length of 10 to 20 m and is mixed at the same time. The soap foam already contains a catalyst (CFC), which accelerates the polymerization of the resin that has got on the walls of the bubbles. After exiting the hose, the foam will polymerize.
Disadvantages of installation:
a) foam generator:
1.In the foam generator under a pressure of 2-2.5 atm. solution and compressed air are supplied, which gradually compress the filler, which in turn leads to deterioration of foam formation. It is necessary to constantly monitor that the filler is evenly distributed throughout the foam generator (this does not apply to the balls from the bearings).
2. In case of clogging of the outlet hose, kinking, or back pressure of the foam when pouring into the cavity, high pressure can build up in it and some of the resin can get into the foam generator. There it will polymerize safely and you will get such a tang that it is quite difficult to clean.
3. Basically, this type of foam generators use tangled metal mesh, which is strongly influenced by the OFC. If you took the equipment seriously and put in the tubes an imported mesh, resistant to OFC, which served for a long time, now, because. is no longer on the market You run the risk of seeing the filler crumbled into dust after 2 months of work.
b) PUMPS: centrifugal pumps are used in installations of the GZHU type. These pumps create a maximum pressure of 4 atm. and at the same time their productivity drops to zero.
1. The biggest drawback of these pumps is the dependence of performance on back pressure. Moreover, if back pressure is created at the outlet of the hose, for example, you accidentally bend the hose, decide to raise the hose by 2-3 meters when filling voids, etc. , then the pumps on the solution line and on the resin line will change their performance unevenly, because these fluids have different viscosities. That is why you can guarantee that you will NEVER achieve the right proportion between mortar and resin. The proportion will always float. In practice, this means that in some places you will have light and brittle foam (from a lack of resin and an excess of OFA), and in some places it will be heavy and soft (from an excess of resin and a lack of OFA). And in some places the foam will fall due to the large lack of OFK. (The polymerization reaction is slow and the bubbles have time to collapse).
2. "METTEM" produced an impeller and a pump head along the line with a solution of stainless steel. If you nevertheless decide to buy a fake for GZHU, and since no more, all other sold by GZHU are fakes and plagiarism, demand the head of the centrifugal pump along the line of the stainless steel solution. Otherwise, the OFK will quickly "eat" your pump.
c) Poor mixing.
d) Uneven foaming.
I will dwell on these two points later.
Now let's move on to the installations of the FOAM-2000 type.
The main advantage of installations of this type over GZhU is the absence of a foam generator. In them, foam is created due to turbulent flows of water and air in the hose when rubbing against the walls of the hose. Then, resin is injected into the foam stream, as well as in the GZHU, and mixing takes place in the outlet hose. And since there is no foam generator, then there are no disadvantages associated with it.
Due to the fact that centrifugal pumps are used in PENE-2000, the disadvantages of maintaining the required proportion and sensitivity to backpressure are identical to those of GZHU.
The Ukrainian installation "Standard" works according to the same principle as "PENA-2000". The guys who make and sell it claim that this is a new generation unit. I have to disappoint. The only difference between this unit and "FOAM-2000" is the use of a gear pump along the resin line.
Is it good or bad?
On the one hand, it's good. At every moment you know how much resin is spent in a unit of time. And that's all. There are no other positive aspects here. The density and quality of the foam is determined by the proportion between the amount of water, air and resin. Changing the back pressure in the outlet hose will not change the resin flow. And what about the solution? After all, there is a centrifugal pump. And if in a system with two centrifugal pumps, with an increased back pressure, the productivity of both pumps decreased proportionally (with an error due to the different viscosity of liquids), then in the "Standard" the change in productivity will occur only along the solution line, i.e. the disproportion will be greater.
In fact, the pitch line has been tried to be fixed more than once. The NST company has a unit under the PENA-2000 brand with a screw pump along the resin line. Vladimir (director Andrey Konovalov) has been working for many years at his own plant with a gear pump in the resin line. But if Andrei used an asynchronous motor with a gearbox as a drive for a gear pump, then the Ukrainian brothers followed a simple path - they supplied an electric drill as a drive. I am familiar with this drive. We used in the installations "STREAM 6". A brushed motor is much more sensitive to voltage surges. Even by setting the potentiometer to a certain position, you cannot be sure that the next time you turn it on, you will get the required number of revolutions. Therefore, the inventors were forced to put a tachometer on the electric drill and use a stabilizer (which, by the way, is not included in the kit). Unfortunately, there is no feedback there. Those. When the engine speed changes, the device will faithfully show you the numbers. The question is, how often will you look at the screen during operation?
So, they are trying to give us a forced measure when using collector motors (installation of a tachometer), for a new word in the production of penoizol. Just like Dale Carnegie: “If you got a lemon, make lemonade out of it.” The standard is advertised as a variable capacity unit. AWESOME. Especially for a beginner.
I will reveal a terrible secret. In the production of penoizol, variable productivity is not needed, and even very harmful. If you want to receive normal material, you must strive to maintain the stability of ALL PARAMETERS. That is why the highest quality material is obtained in the workshops, and not at the construction site.
I apologize to the reader for giving so much attention to the Standard installation, although it does not deserve it. It's just that the creators of this installation are conducting very aggressive advertising, which people who first decided to start producing penoizol can easily succumb to.
How the problems of stable supply of components at the Potok plant were solved
Firstly, we decided that in the production of penoizol, the most important thing is the stability of the supply of components through the Resin line and the Solution line. This solves a lot of problems.
First of all, it is easy to pre-select the minimum required concentration of foaming agent and acid, which in turn:
1. It has a beneficial effect on the quality of the produced foam.
2. Makes the density of the product predictable.
3. Reduces the cost of material.
For this purpose, at the Potok-6 unit, we used power peristaltic pumps of our own design. They showed good results, but did not solve some of the problems. The maximum pressure they could create was 6 atm. Considering that this is the working pressure with our method of foaming, the pumps made it possible to fill only in the horizon with the installation, with a maximum excess of 3-4 m. In addition, the quality of the consumable material (rubber tubes) left much to be desired. It was possible to follow the path of selecting better quality tubes, for example, reinforced silicone or polyurethane, but this did not solve the problem of lack of working pressure. Therefore, peristaltic pumps had to be abandoned.
In the Potok-7 and Potok-9 units, we use high-pressure dosing plunger pumps with an asynchronous motor. We take the standard German ones. We make a plastic head for them ourselves. These pumps allow you to work from the ground, lifting only hoses to the floors. In Chita, the Potok-9 unit was used to fill the 14th floor, while the unit was at the bottom.
The main idea: the proportions of all components are selected in advance, when mixing the solution. During operation, the supply of components through the resin line and through the solution line are unchanged. Density is regulated by air supply. Of the instrumentation, only the air line pressure gauge will show you the density of the foam.
Now let's move on to mixing and foaming, those processes that I omitted at the beginning of the article.
So the mixing quality.
I will repeat myself. One of the components required for the production of urea foam is a catalyst (UFC). The better we distribute the catalyst molecules over the volume of the resin, the less we will need it and the better the material will be. The chemical reaction will proceed at the same rate, the polymer chains will be of approximately the same length, and during polymerization there will be no internal stresses leading to additional shrinkage. How much acid is needed? The foaming agent keeps the foam bubbles for about 15-20 minutes, after which they begin to burst, which means that the polymerization should take place in 10-15 minutes.
In installations GZHU, "Foam-2000", "Standard", first a flow of foam is formed, then resin is injected into it and stirred mechanically using compressed air.
In the Potok units, the solution is first mixed with the resin using compressed air, without the formation of bubbles, and only then this mixture is foamed. Which is easier?
Imagine that you need to distribute a viscous liquid evenly over the thinnest walls of sticky bubbles (the wall of one bubble is simultaneously the wall of three or four adjacent ones) by mechanical stirring without destroying the foam. Not an easy task. Most likely impracticable in principle.
On the other hand, mix the two liquids.
Compare yourself.
But this is a speculative comparison. If I'm right, there should be digital confirmation. So how much acid do different plants use? When comparing, I will indicate two ratios: the percentage of acid in the solution (taking into account the different hardness of the water) and the ratio of the supplied solution to the resin (taking into account the viscosity of the resin). Those. with the same percentage of acid in the solution, if more solution is supplied in relation to the resin, then accordingly more acid will be needed per unit mass of resin.
GZhU, "Foam-2000" - 1-2% acid in solution, 1.5-2.5 / 1 solution / resin ratio.
"Standard" - 5% acid in solution, 1.5-2.5 / 1 solution / resin ratio.
"Stream" - 0.5-1% acid in solution, 1-1.5 / 1 solution / resin ratio.
Further comments, I think, are superfluous.
Let's talk better about foaming.
I have already told you how foam is obtained in GZhU installations. But if there was no secondary foaming, then penoizol could not be obtained. What is secondary foaming? When resin is added to the foam stream (either jet or aerosol) and further mechanical stirring with compressed air, some of the bubbles burst. In this case, the solution contained in the wall of the bubble is mixed with an aqueous polymer solution (resin) and creates a new bubble. This is done by friction against the walls of the hose. For example, think about making lather in a shaving cup using a brush. Compressed air acts as a brush, and a hose wall acts as a cup. The more bubbles burst and form again, the better will be the mixing of the solution with the resin, i.e. the longer the supply hose, the better. But there are limitations here. The limitation is the compressor capacity. At a certain length of the hose, the air loses energy, overcoming friction against the walls of the hose, and stops mixing the foam with the resin, but simply moves the foam along the hose to the outlet. In this case, the destruction of bubbles at the hose / foam interface continues, i.e. we just lose some of the foam. In this case, the liquid formed on the walls of the hose does not form new bubbles, and does not move at the speed of the foam flow, but slowly flows down in a trickle if there is a natural slope, polymerizes and clogs the hose. The recipe seems to be simple. You just need to put in a more powerful compressor. But this is not the case. With an excess of air, air pockets appear in the foam, which degrades the quality of the foam. Ideally, we need only as much air as we want to get foam.
The units "Foam-2000" and "Standard" operate on the principle of secondary foaming.
The quality of the foam depends on the size and uniformity of the bubbles. The longer and with more energy we mix the foam, the smaller and smoother the bubbles. But in any case, no matter how much you stir the foam with a brush, you cannot get foam that would be compared with the foam that is contained in shaving cans. For this it is necessary to change the method of foaming.
On the Stream settings, we have changed the way. We first mix two fluids with air under pressure without foaming, and part of the air is dissolved in the fluid. When moving along the hose, the pressure decreases and the liquid boils with the formation of tiny bubbles throughout the entire volume at the same time. The rest of the air adds foam to the liquid by secondary foaming. Moreover, the air has more kinetic energy than in other installations, because supplied with great pressure. Therefore, we need a compressor with a lower air consumption and we have the opportunity to build it into the unit (“Stream-7).
Documents
First you need to register a form of activity. You can work in the form of an individual (individual entrepreneur) or a legal entity (LLC). It all depends on the plans of the entrepreneur, the scale of production. Each form has its own capabilities and limitations, however, work in the form of an LLC will allow you to cooperate even with large construction companies and wholesale and retail chains.
When registering, OKVED-2 codes are indicated.
23.99.6 "Production of mineral heat and sound insulating materials and products".
22.23 "Manufacture of plastic products used in construction".
22.29 "Manufacture of other plastic products".
32.9 "Manufacture of products not included in other categories".
Certification is not required to launch a business project. The polymer is produced in accordance with TU 2254-001-33000727-99 “Heat-insulating foam insulation. Technical conditions ".
Benefits of using penoizol
A feature of penoizol, which is a liquid foam, is the ability to be pumped into any cavity.After that, the liquid polymerizes, dries, takes the desired shape and begins to perform certain functions.
Excellent performance is not the only plus of this material. Its composition ensures biological stability, which means that it is guaranteed that it will be free from mold, fungi, insects and mice throughout its entire service life. Compared to foam and glass wool, it retains heat by about 10% better. It does not burn, therefore it is ideal from the point of view of fire safety. It is also vapor-permeable, which means that it makes it possible to leave excess moisture outside.


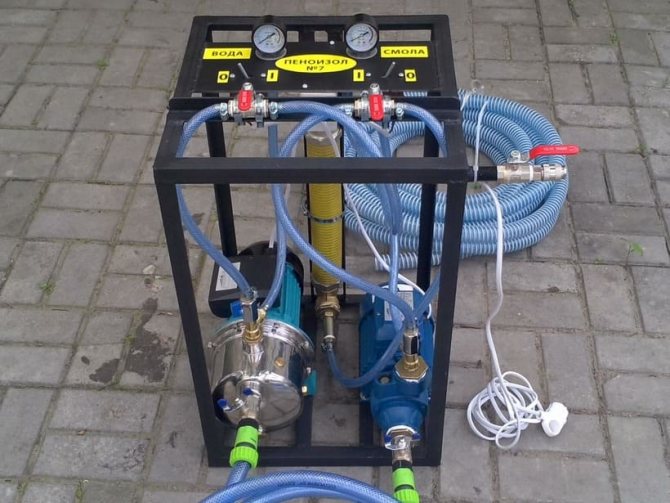
Equipment for penoizol
For the industrial production of insulation, you need to buy the following equipment:
- compressor and power supply;
- a gas-liquid plant for liquefied gas, including a pumping system for supplying foam and solution;
- collapsible forms for filling;
- containers for making a mixture;
- large table for packing material.
In this configuration, it is possible to produce sheet and liquid penoizol.


On sale there are equipment of Russian, Ukrainian and foreign production. The models differ from each other in price, technical characteristics - including the degree of process automation. There are mobile and stationary installations.
Equipment and components for the production of penoizol., UPG plants, VPS-G resin, ABSK foaming agent, orthophosphoric acid.
Negotiated price Buy
The equipment can be made by yourself - the necessary drawings and diagrams are on sale.
When choosing a technique, it is better to look for a seller who trains the customer's personnel on the installation. The equipment must be guaranteed.
Composition and application
The main component of penoizol is a polymer - urea resin.
For the manufacture of penoizol use:
- polymer urea resin;
- hardener;
- foaming agent;
- water specially prepared for the process.
The finished penoizol is very similar to the souffle. Coming into contact with air, it solidifies, filling voids in building structures, which creates the effect of heat and sound insulation of the room.
The production of penoizol can be started on the existing ready-made equipment or assembled by hand according to the drawings. Ease of use allows you to work with penoizol all year round, not depending on climatic conditions. Roofs, ceilings, walls, foundations and partitions can be insulated with this material.
The manufacturing process itself is not very difficult, so you can prepare the insulating material at home. Having modest experience in construction, the necessary knowledge and high-quality installation, making penoizol with your own hands is a real task.
Equipment for the production of penoizol consists of:
- solution pump;
- foam pump;
- foam generator;
- compressor;
- power supply.
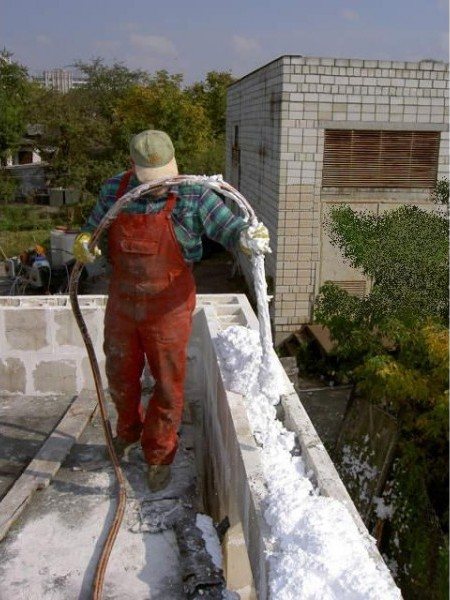
The production of penoizol for sale to third-party organizations or customers can be set up indoors, but an effective option (saving on transport services) would be to produce it directly at the construction site using a foam generator.
Equipment for the production of penoizol on the modern market is represented by different manufacturers. A wide selection of Russian and Ukrainian equipment (Pena-2000 DMU, Pena-2000 10 / UM, Pena-2000R) is presented to the attention of an entrepreneur who decided to start producing penoizol.
Foam-insulating unit Foam 2000 DMU Immediately it is necessary to decide what the unit is being purchased for. If you plan to insulate your house and several objects for your relatives and friends, then it is not necessary to purchase expensive equipment, but try to keep within a small budget.
Alternatively, you can make yourself a gas-liquid or pneumohydraulic installation.
You may be interested in an article on how to insulate walls with penoizol.Read the article on home insulation with penoizol here.
Raw materials
The product is produced by foaming a polymer resin according to a developed recipe. Depending on the formula, additives may be added to the composition, but the main components are the same.
- Synthetic urea-formaldehyde resin.
- Foaming agent. Required for stable foam formation.
- Catalyst (hardener). Accelerates the hardening process.
- Water with a temperature not lower than + 20 ° С.
Finding and buying the necessary raw materials will not be a problem.
There are generally accepted standards regarding the recipe, but a businessman may well create his own insulation formula. It is better to contact a construction expert, although you can find information yourself - there are enough online resources and forums on this topic on the Runet.
Initial components for the production of penoizol


By its composition and structure, Penoizol belongs to the class of urea foams with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.035 - 0.047 W / mK and a density of 8 - 28 kg / m3. The composition of the components used for its production is quite simple:
- urea polymer resin;
This is the main component. It is not uncommon and is quite often used in the production of chipboard and fiberboard. The resin looks like a suspension of light brown color and consists of 55% dry matter, 0.25% formaldehyde and water. Refers to non-combustible materials.
- foaming agent;
There are quite a few varieties of it (Morpen, ABSK, Penostorom, etc.), so almost any can be used. By its composition, it is a low-combustible, viscous brown substance with a sulfuric acid content of about 2%.
- orthophosphoric acid;
This component, in essence, performs the functions of a hardener. It is a combustible material and has a density of 50 to 90%.
- water.
The water is used with regular tap water.
Penoizol production workshop
To organize a business, you will need a room with an area of 70-90 sq. m, divided into a production workshop, a warehouse, a staff room, an administrative office and a bathroom. It should be located away from residential areas. It is necessary to carry out communications on the territory of the mini-plant.
The workshop is equipped with a 220V current supply and a good ventilation system. The latter is necessary, because when drying sheets of insulation, substances harmful to health are released (phenol-formaldehyde is present in the composition of the synthetic resin).
The warehouse will store raw materials and finished goods. It is worth placing metal racks in the room.
The premises should be equipped with a car entrance for unloading and loading operations.
How to equip a workshop?
Mini-production of penoizol as a business will require the purchase of technical equipment. The standard line for the production of sheet material includes the following set of equipment:
- compressor,
- gas-liquid installation,
- collapsible forms,
- containers for components,
- packing table.
The purchase of a drying chamber is not required, since the mixture solidifies under normal conditions.
To make penoizol right on the construction site, you will need almost the same set of machines - with the exception of tables for packaging and forms. A mobile gas-liquid plant and compact raw material mixing tanks perform all the necessary technological steps. In terms of costs, the technical equipment of the offsite business will require less finance.
The price of equipment for the production of penoizol is low. You can fully equip the workshop for 100,000 rubles. Even powerful equipment will cost no more than 300,000 rubles. It is possible to organize activities for the production of a heat insulator at construction sites without spending even 70,000 rubles.
Staff
To service the production, you need to hire 3 people, one of whom will be the senior in the shop. The latter is responsible for coordinating the rest of the workers, monitoring their activity and training. It is the senior worker who needs to be sent on an internship to the equipment seller.


A sales manager is required to organize sales. He will meet and negotiate supplies with representatives of construction and wholesale and retail companies.
A driver is needed to deliver raw materials to the plant and finished goods to customers.
The accountant will deal with paperwork and preparation of papers for tax authorities. It is better to hire him for outsourcing (contacting an accounting firm).
Advantages and disadvantages
Outwardly, penoizol is similar to marshmallow cookies. Pleasant to the touch, lightweight porous white material retains its elasticity and strength for several decades. Construction experts note the following advantages of the material:
- Low coefficient of thermal conductivity. This indicator makes Penoizol one of the best heaters on the market.
- High adhesion to most building materials and excellent foam penetration. These factors facilitate the application of insulation both over large areas and in various hard-to-reach places, including hidden cavities in walls and roofs. The material fits well on horizontal, vertical and inclined surfaces.
- The estimated service life is 55-75 years. The result was obtained by calculations and large-scale tests, but the analysis of control samples that served for 10-20 years confirms it.
- High vapor permeability. This property allows the insulation to "breathe", removing excess moisture from its volume. This prevents the accumulation of moisture - a breeding ground for mold and pathogenic microorganisms. At the same time, a comfortable microclimate is maintained in the premises.
- Unattractiveness to pests: insects and rodents. Penoizol becomes a natural barrier to their spread.
- Resistant to open fire and high temperature. When heated, penoizol does not emit toxic substances, unlike other foam materials.
- Resistant to solvents and other active chemicals.
There are a number of disadvantages inherent in the insulation.
- Over time prone to volumetric shrinkage;
- May give off an unpleasant odor when applied and dries. This indicates the low quality of the solvents and binders used, but does not affect the final quality of insulation. Just for the duration of the work on thermal insulation, the dwelling will have to be left.
It is better to pay attention to the smell before buying a composition for spraying.
Who should we sell the finished product to?
3 main groups of urea foam consumers:
- construction companies, repair and construction companies;
- retail stores and wholesale and retail chains selling construction products, construction markets;
- private persons.
At the initial stage, it is important to use all possible distribution channels - it is necessary to attract the attention of potential buyers to the new product. However, the most convenient option is to get a contract for large supplies of insulation. Therefore, great attention should be paid to negotiations with construction companies.
Penoizol business is seasonal. Construction is actively carried out in the warm season. Of course, large construction projects are carried out in winter, but in general, the volume of construction work in the cold drops noticeably.
Stages of technology for the production of sheet penoizol
- Preparation of forms.
- Pouring liquid penoizol.
- Exposure for 2-3 hours.
- Dismantling the forms and holding the "cubes" of the material for 3 hours.
- Primary cutting into sheets.
- Drying.
- Finishing, packaging, warehousing, shipping.
It would seem that everything is simple and clear. Nevertheless, the production of sheet penoizol is a more complex technology than pouring on site, which requires careful adherence to the consumption of components, temperature and drying regime.
Approximate consumption rate of penoizol components for filling a form, volume 1m3
- Urea-formaldehyde resin - 22 kg.
- Foaming agent - 0.2 kg.
- Curing catalyst (phosphoric acid) - 0.3 kg.
- Tap water or industrial water - empirically.
The first thing you need to start producing sheet penoizol is a suitable room. If industrial production volumes are planned, a room with an area of 250-500 m2 will be required, which should accommodate the following production areas:
- Raw material warehouse.
- Area for filling forms.
- Drying section.
- Site for preliminary and finishing cutting and packaging.
- Finished goods warehouse.
Features of the production process
To implement the technological process (pouring, disassembling forms, cutting, stacking on racks, cutting to size, packaging, etc.), personnel in the amount of three people will be required.
In addition, the production area must be "warm". Special requirements for the temperature regime are imposed on the drying section. So, at the pouring site, a temperature of at least 15 degrees Celsius must be maintained, and at the drying site at least 20-28 degrees Celsius.
Since the drying process lasts three days, the temperature in the drying compartment should rise gradually, starting from 20 degrees on the first day and reaching 28 degrees on the last day. Pouring and drying areas should have effective supply and exhaust ventilation.
When drying on racks, ready-made penoizol boards should not have "closed" zones. That is, air access is provided from all sides of the plates. High-quality drying is necessary so that later shrinkage does not appear, and the smell of formaldehyde is completely disappeared. Its duration depends on the air temperature in the room, relative humidity, the degree of air exchange and the amount of water used for the production of penoizol.
Molds for pouring slabs are four walls of galvanized steel, connected to each other by means of quick-release locks. The bottom of the mold is a pallet on which a sheet of galvanized steel is laid, after which the walls are installed on it. Inside, the mold is not smeared with anything.
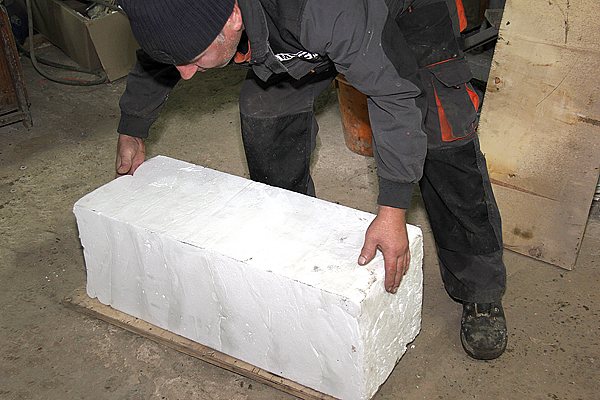
Penoizol has one drawback - in the process of intensive drying, shrinkage is possible, therefore, initially the “cube” of the finished material is cut into sheets of larger sizes than required. And after final drying, each sheet is passed through a special cutter, adjusted "to size", which removes "tolerances" (excess) with an accuracy of one millimeter.
Thus, from the initial block, about 7 sheets of 1200x600x100 millimeters are obtained - 0.5 m3 of finished insulation, which are packed in thermal film in packs of 7 pieces.
Scraps and other residues generated during the cutting and manufacture of foam sheets are crushed into crumbs, packed in bags and used for thermal insulation backfill. That is, it is possible to characterize the production of sheet penoizol. How completely wasteless.
It should be noted that if liquid penoizol can be used, including in the repair and reconstruction of buildings and structures, then sheet material is used mainly in the construction of new buildings.