His majesty is jute
What is jute? Initially, jute is a plant of the linden family, namely spinning (bast), which grows from the subtropical regions of Asia, Africa, South America and Australia. Most of the products sold on the domestic market are made from raw materials imported from Bangladesh.

Someone will ask, but after all, we have quite a good insulation growing here - flax, why do we need to export raw materials thousands of kilometers away? Yes, it can grow. However, in the Russian climate, it is not so easy to grow and preserve flax. Therefore, the factories for the procurement of raw materials almost all closed as one. The current situation has led to a shortage of raw materials for the production of linen insulation. A foreign solution came to the rescue - jute fiber.


The plant has a structure similar to flax. Flax is used for the production of textiles, while jute is used for the manufacture of technical equipment - bags, ropes and insulation. This application is due to the greater rigidity of the jute fibers in front of flax.
Plants gain their strength due to the high content of lignin, a resin that is a natural polymer. This substance promotes the hardening of other substances that make up the fibers and greatly increases their strength. Below in the table you can see a comparison of the characteristics of the lignin content in jute and other plants.
| Material | Lignin content% |
| Jute | 20 |
| Linen | 2 |
| Hemp | 4 |
It is not difficult to determine which material will be more durable and durable. But, here is the other side of the coin. Jute fiber is stiffer, making it more difficult to lay. The pluses include the absence of problems when drilling. Jute insulation does not wrap around the drill as it does with softer materials such as linen.
Heaters containing linen
The materials considered below are not much inferior in quality to jute, but they cost a little less. These include:
- linen felt;
- flax
The properties of heaters resemble jute, but at the same time they are cheaper. Linen felt, also referred to as "eurolene", is a needle-punched material. When pierced with a sharp object, the fibers of the plant become entangled, further strengthening the structure.
Flax is obtained in a slightly different way - needle-stitched, so it is not as dense as previously described. Both materials are not to the liking of birds, insects and rodents, although they are made from natural materials. As a mezhventsovy heater for timber it is used extremely rarely and is not recommended by specialists.
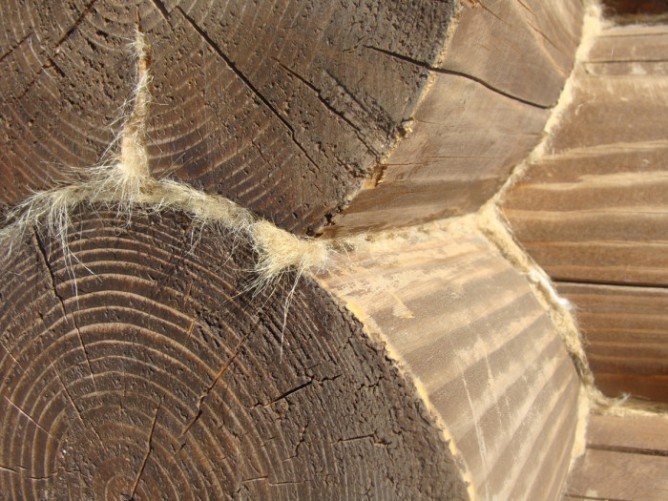


Is there an alternative?
Do you need it? We have already seen enough of the advantages of this material, although we have considered its disadvantages. Let's highlight the most significant ones:
- The cost is higher than that of flax;
- Rigidity - difficulty in laying;
- With low-quality raw materials, it is not environmentally friendly. For example, this will never happen with moss - no chemicals are added to it.
By the way, in order not to be distracted from the topic, in a separate article we talked in detail about mezhventsovy heaters, namely the 3 most popular, except for jute.
Types of mezhventsovy heaters
All existing materials for laying between the beams of the house are divided into two large groups:
- Made from artificial components;
- Made from natural fibers.
The first group has proven itself excellently when insulating walls (outside or inside), roofs, attic floors. These include:
- mineral wool (basalt, glass, slag);
- expanded polystyrene;
- foamed polyurethane foam;
- various sealants;
- foam rubber.
No matter how low the thermal conductivity of the listed materials is, they are not used as a mezhventsovy heater. For example, mineral wool or foam rubber, squeezing under the weight of the timber, are compacted and impede the normal circulation of air and liquid. Also, the space between the crowns, insulated with these materials, is easily blown through at low temperatures, and the room freezes over.


With moisture-proof insulation (polyurethane foam, foam, sealant), the situation is different - liquid vapors condense at the joints, causing premature destruction of wooden walls. Of course, you can close the seams tightly, eliminating blowing, but what's the point if another problem appears?
Most often, it manifests itself when laying the so-called "warm seam", when a foam tape is applied to the horizontal plane of the bar, then the seams (on both sides) are caulked with a polyethylene cord of a certain thickness, and then acrylic sealant is applied.
The consumer's expectations are only partially justified - air and moisture do not get inside the house, but the foam rubber will absorb moisture from the bars and will not be able to dry out. Moisture at the joint will inevitably lead to the gradual rotting of the wood. Summarizing the option with artificial insulation, one thing can be said - they do not allow the walls of the house to breathe fully, which is just necessary for buildings made of timber.
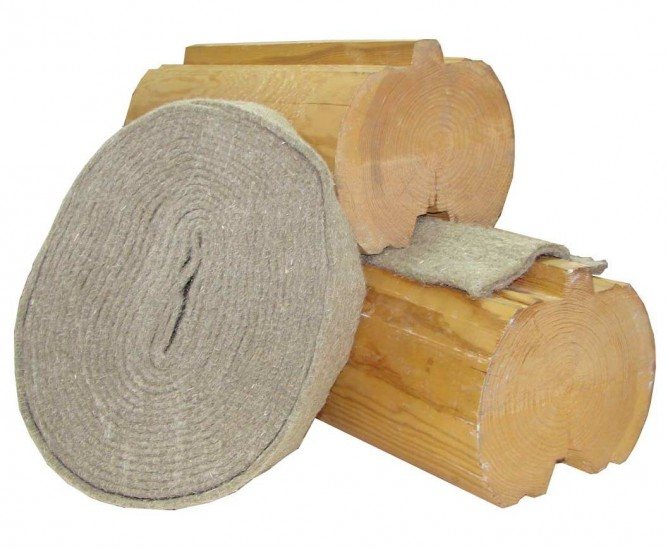
Natural materials are more preferable, with the exception of wool and cotton. The latter quickly absorb moisture, dry slowly, and are of genuine interest for insectoids. In order for a wooden beam to fully show its positive properties, it is better to choose a heater made of natural fibers. The most popular are jute (in the form of a ribbon), flax, moss. They have a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, prevent pests, quickly release moisture after being absorbed into themselves. The given materials differ in their characteristics from each other, so it is worth considering each of them in detail.
The best option
The experience of professional builders shows that the optimal solution in terms of price / quality is a combined option - it is flax-jute or jute felt with flax impurities (sometimes other components). Jute gives the structure the required rigidity, and linen gives elasticity and elasticity. The ratio can be 10/90 or 50/50.
There are standards for the use of flax jute for different types of timber:
- For example, for a 150 x 150 mm bar, the width of the jute insulation should be 152 mm with a thickness of 5-8 mm;
- For a chopped block, a wider felt with a width of 100-150 mm is used. In the case of a rarely seen log house with a thickness of 250 mm and more, you can find tapes of a similar width. For example, the website of one jute manufacturer states that, if necessary, you can cut ribbons up to 1600 mm wide.
Requirements for inter-crown insulation
In winter, the average daily air temperature always drops below zero. The warmer seasons are also characterized by frosts, especially at night. Therefore, the key requirement for inter-row insulation is to provide reliable protection from the cold.


This quality is a complex indicator that combines:
- density (gap closure by 100%);
- elasticity (the previously mentioned condition must be met even after the house has shrunk);
- low coefficient of thermal conductivity (approximately like that of a bar; the lower the insulation has, the better the heat is retained);
- absorption and quick release of moisture in the case of precipitation (to maintain normal humidity inside and protect the walls from decay or destruction);
- resistance to external mechanical influences (harm to rodents, birds, pulling apart insulation for nests, insects);
- durability (the ability to perform their functions for as long as possible without deterioration);
- ecological purity (absence of impurities harmful to human health that cause diseases or allergies);
- antibacterial properties (resistance to harmful microorganisms).
Almost any mezhventsovy heater for a bar, encountered by a consumer in a hardware store, to one degree or another meets the above stated requirements. However, choosing the best one for your own benefit will not be easy. To facilitate the task, it is worth familiarizing yourself with two large groups of materials for cladding wooden structures between tiers.


How much will jute cost
The price of jute flax depends mainly on the density. The density is selected according to the project and largely depends on the weight of the structure lying on the insulation.
For example, a well-known Russian jute felt is sold with a density of 250 g per m / p, thickness 2-4 mm (thin), 100 mm wide at a price of 4.5 rubles per meter, 150 mm wide at 6.5 rubles per running meter. With a thickness of 4-6 mm, prices will increase to 5.7 and 8.55 rubles, respectively.


If the width of the strip for the log house is insufficient, the material can be laid in 2 layers. Material consumption increases and the cost, of course, also increases.
Advantages and disadvantages
The mezhventsovy jute heat insulator is actively used in construction. This is facilitated by the low cost and useful qualities of the material. The advantages of jute include:
- saturation with lignin - a natural resin, due to which the fiber of the insulation and the wooden surface are reliably and hermetically glued;
- compliance with environmental and hygienic standards, production in accordance with GOST. Jute practically does not rot, has bactericidal properties, does not contain third-party and chemical suspensions;
- long-term thermal insulation. The material retains its given shape well and is minimally subject to compression due to its rigidity;
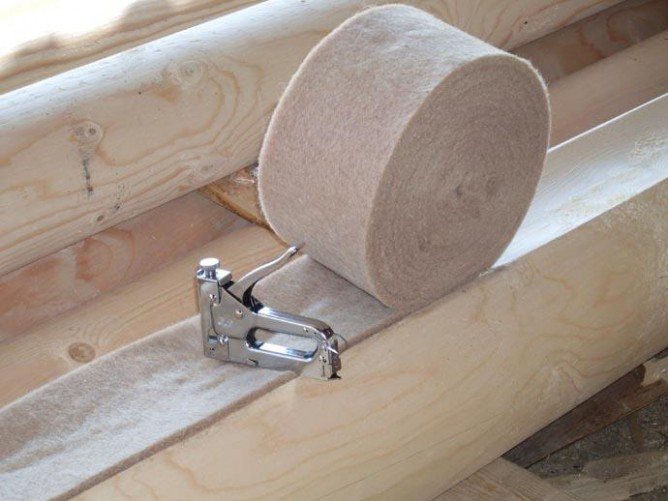
- ease of installation does not require specialized education and sophisticated equipment. Flax then easily fits into the gap between the crowns;
- multipurpose use. Jute is great for caulking and insulating external and internal walls, floors, windows, roofs and more;
- neat appearance. The caulked surface looks neat and aesthetically pleasing. The beige color of jute is in harmony with the wood.


Jute batting gives the structure a neat and stylish look
In contrast to all the positive qualities, jute has minor flaws that affect the operation of the insulation:
- jute service life is limited. Natural material deteriorates over time, therefore, the caulking of the log house must be periodically renewed;
- intolerance to getting wet. Jute fiber is quite moisture resistant, but prolonged contact with water leads to a deterioration in thermal insulation properties. Experts recommend laying jute batting only on a dry hike with low humidity;
- the installation of the insulation must be completed with a finishing caulk using a jute rope. This will help prevent cold air from entering the room.
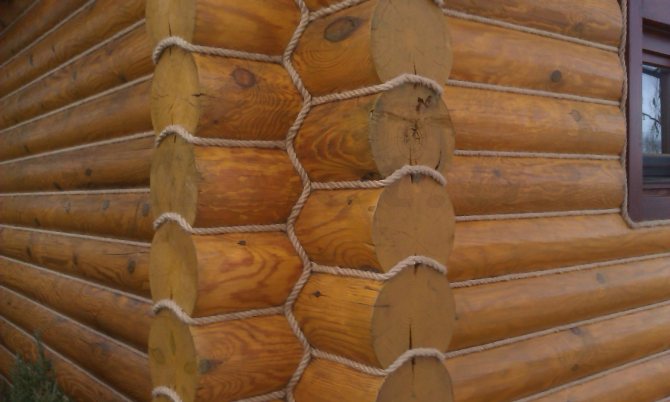


Finishing caulking is carried out with a jute rope
Jute batting is a versatile thermal insulation material that is used to maintain the internal microclimate in wooden houses and cars. Jute is widely used in light and furniture industry, in needlework. Due to its thermal insulation properties and environmental parameters, jute fiber can be safely used in almost all spheres of human life.