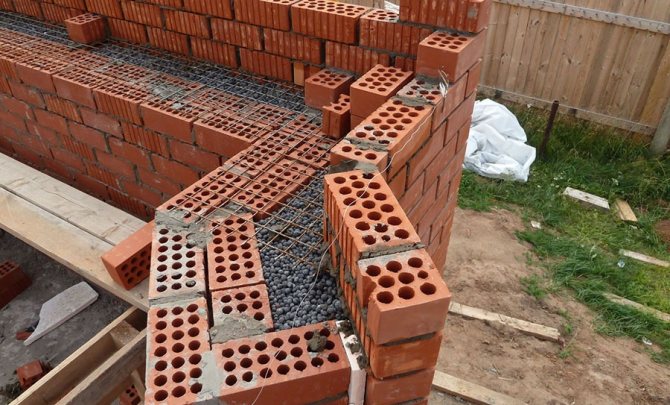
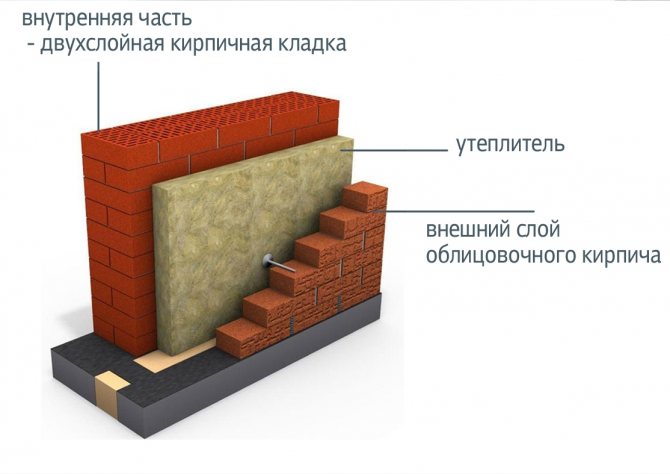
Brick building options include different types of masonry. The more and more popular is the well masonry of brick walls, which allows:
- save costs on expensive bricks;
- simultaneously solve the issue of thermal insulation at home;
- reduce the weight load on the foundation of the building;
- reduce costs for external and internal finishing (without insulation).
The construction of multi-storey buildings by the method of well masonry in places with an increased humid climate is prohibited.
What is it?

The masonry got its name from the cavities (wells) that are laid out in the process. When forming the walls, they are filled with heat-insulating materials, increasing the thermal stability of the structure. The thickness of the walls decreases, but thermal insulation, when properly installed, allows you to save not only during construction, but also on heating during the operation of the house. At the same time, two parallel walls are being conducted, which, according to different methods, in certain places connect the diaphragms - brick lintels. The lintels are a connecting link and take on the function of stiffeners.
Additionally, reinforced mesh or reinforcement is used to strengthen the structure. All metal parts must be coated with a durable anti-corrosion compound.
Well brickwork allows you to combine and thereby significantly save on building materials. For example, expensive ceramic facing bricks are used for external walls, and white silicate bricks or gas silicate blocks are used for internal masonry.
Thermal insulation and wall cladding technology
In order to insulate the walls outside the building, it is not at all necessary to be a professional builder, the main thing is to follow the recommendations exactly.
Preparation of tools and materials
The choice of materials for house insulation is dictated by the local climate. Having decided on the insulation, you can choose the tools - it can be a square, a building level, a trowel, a toothed trowel, etc.
Preparing the wall
Before starting work, it is necessary to prepare the facade for installation. To do this, the masonry is cleaned of dust and dirt, it is also necessary to seal the cracks and level the masonry surface, if necessary. After that, we process the facade with a primer.
Pre-cleaning the facade
It is necessary to take care of leveling the walls, because after the installation of the insulation, the voids formed at the place of cracks can become a place of deformation of the insulation - for this, a small mechanical effect is enough. Also, the insulation cannot be tightly glued to the pits and bumps.
Wall insulation
The technology of three-layer masonry with insulation and facing bricks contains the following steps:
- We lay out the inner wall - there is nothing difficult in this, since the masonry technology is the same as the masonry of any load-bearing wall. For it, either aerated concrete blocks or solid bricks are selected. The thickness to the straight line depends on the minimum winter temperatures in the area and can be either 1 or 1.5 bricks.
- The next stage is laying out the outer wall with cladding. It is carried out in such a way that a gap is formed between the walls - insulating material is inserted into it. If granules are used, wells are formed for them. For strength, the walls are interconnected by ties made of reinforcement and die-cutting. Alternatively, you can make a brick dressing at regular intervals.
- Waterproofing is an important step that will help protect the insulation from moisture, which inevitably penetrates the brick layer. As an insulator against moisture, you can use a dense film or roofing material.
- The backfill thermal insulation material is poured into a niche as soon as the wall height reaches 1 m. If a roll or sheet facing insulation is used, then it is attached to the inner wall - for this, mushrooms with a plastic cap of a large diameter are used. After fixing the insulation, we close it with external facing masonry.
- For normal gas exchange, it is necessary to leave ventilation ducts every 0.5-1 m - the so-called vertical seams between bricks, which are not deliberately filled with mortar.
As practice shows, three-layer masonry allows you to achieve several results at once and significantly improves the operation of the building in the winter.
You can do it yourself, but it is better to turn to professionals, since errors in the technical process negate all the advantages of this option for facade insulation.
Advantages and disadvantages


In each type of work there are positive aspects and problematic points that turn into tasks, required solutions. Lightweight well masonry has its advantages:
- significant reduction in brick consumption (up to 20%);
- reduction of construction time;
- a large selection of heaters in the price range;
- reducing the load on the foundation;
- the wall with a small width has good thermal conductivity.
The quality of the work performed should always be monitored in order to avoid possible problems:
- In seismically active zones and on difficult soils, it is necessary to carefully calculate the distance between the diaphragms, since the walls have an inhomogeneous structure.
- After the lapse of time, it is not possible to supplement or replace the settled layer of thermal insulation.
- Temperature changes lead to the destruction or subsidence of low-quality insulation.
- Condensation on the walls is likely.
- Uninsulated metal reinforcement leads to the formation of cold bridges and loss of heat transfer.
Perfume
In the case of a system device with an air gap of 2-5 cm wide, for ventilation, air vents (holes) are arranged in the lower and upper parts of the wall, through which vaporous moisture is removed to the outside. The size of such holes is taken at the rate of 75 cm2 per 20 m2 of wall surface.
The upper ventilation ducts are located at the cornices, the lower ones at the plinths. In this case, the lower holes are intended not only for ventilation, but also for water drainage.
- Air gap 2 cm
- Lower part of the building
- Top of the building
For ventilation of the layer in the lower part of the walls, a slotted brick is installed, placed on the edge, or in the lower part of the walls, bricks are laid not close to each other, and not at some distance from each other, and the resulting gap is not filled with masonry mortar.
Types of masonry
The main thing that characterizes well masonry is the voids that are filled with insulation, but the types of masonry play an important role in it.


Brickwork can be 2 bricks, 2.5 bricks, or modified. Each type of masonry has the right to be sold, depending on the purpose of the building and the climatic zone in which it is located. Since the main task of each type is to insulate the house, recently bricks with hollow cavities have been successfully used in well masonry. Air in the sealed space of a brick, laid in any type of masonry, also retains heat.
HOW TO BUILD A HOUSE
Air-spaced walls
The thickness of the brick enclosing structures at an external temperature of -30 ° C should be 64 cm (2.5 bricks) in order to provide adequate thermal protection.An economical brickwork made of solid bricks is obtained by forming closed air gaps with a width of 5-7 mm.
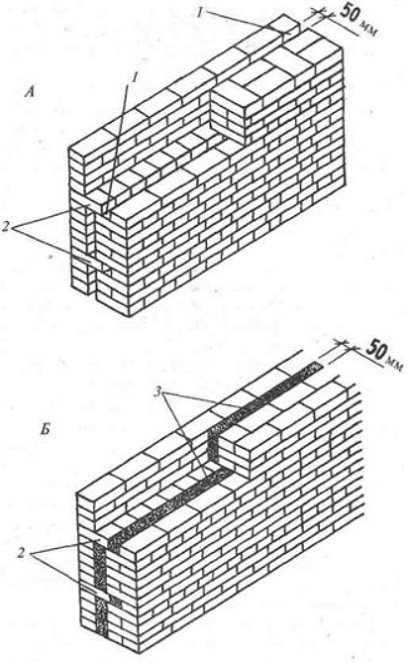

air-spaced wall structure
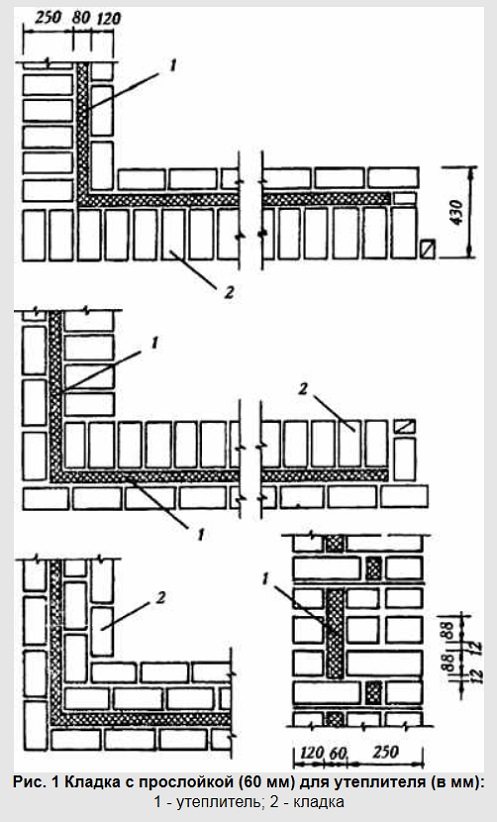
Such masonry not only reduces the consumption of bricks per unit volume of the wall, but also increases its thermal properties. This technique allows, among other things, to reduce the thickness of the walls in comparison with solid masonry, without reducing their thermal insulation properties. The benefits of this type of masonry are obvious. The volume of the masonry is reduced not only by the voids inside the masonry, but also by reducing the thickness of the walls. Figure 1 - air gap; 2 - brick; 3 - lightweight concrete.
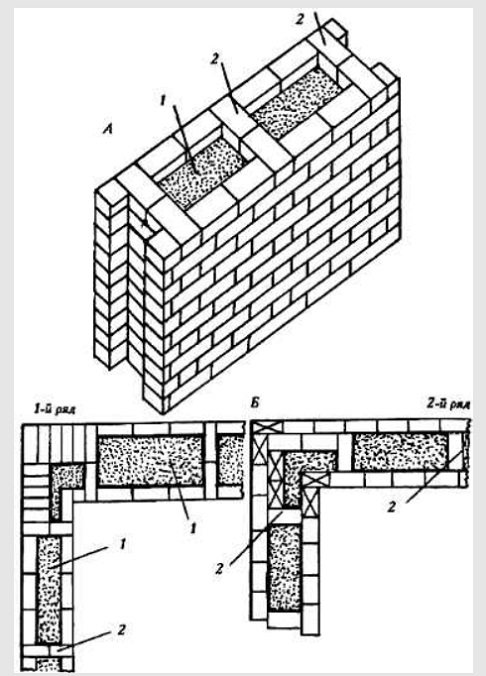

well masonry 1 - insulation, 2 - brick
Well masonry is one of the most common types of economical brick wall construction for low-rise buildings. This construction technique allows you to reduce brick consumption by 15-20% compared to solid brickwork. Well masonry options are characterized by different capitalization and stability. The layers in the well masonry are connected by vertical diaphragms, the distance between which should not exceed 1170 mm. In fig. below is a plan of masonry with an abutment of the inner wall.
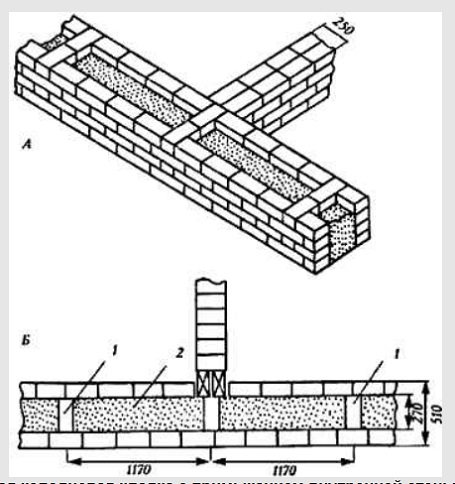

Lightweight masonry with an abutment of the inner wall, 1 - brick, 2 - insulation
It goes without saying that the strength of the wall decreases with the well masonry. Therefore, at the lower level of the floor slabs and two rows below the window openings along the entire perimeter of the outer and bearing walls, horizontal mortar diaphragms are arranged.
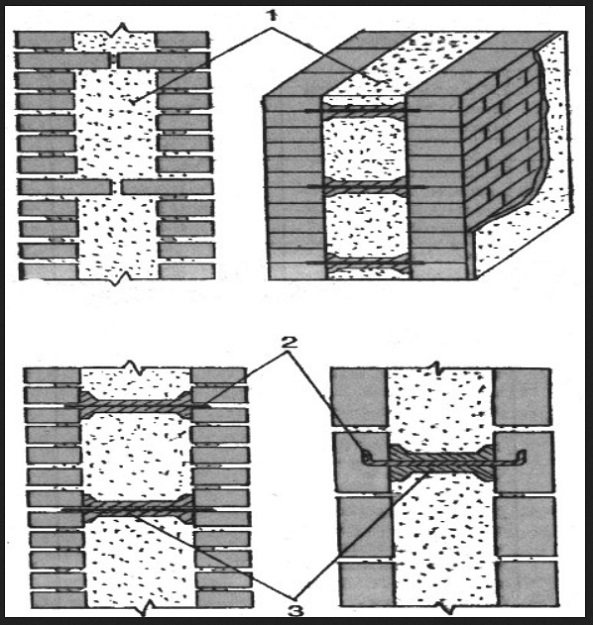

mortar diaphragms
Such diaphragms are formed by a reinforcing mesh, which is inserted simultaneously into the inner and outer layers of the masonry and protected with a layer of sand-cement mortar. A feature of these walls is solid masonry in the corners.
Anchor and brick-concrete masonry
Brick-concrete masonry
These are two parallel walls, between which a layer of lightweight concrete is laid. Bricks, laid with a poke and protruding into the masonry, provide anchoring of longitudinal walls with concrete (in the figure on the left 1 - brick; 2 - concrete).
The laying of the walls begins with the laying of two three-quarters in the first row of the outer and inner versts. Next, a brick laid with a poke is alternated with two bricks laid in spoons. In the second and third rows of masonry, bricks are laid with a spoon. The cavity between the walls begins to be filled with concrete after the construction of 3-5 rows of masonry. The space between the verst rows can be filled with lightweight concrete or other fillers that increase the heat-saving properties of the enclosing structures. In walls with transverse vertical walls, lightweight concretes of grade 10 and below are used, made on local binders without the use of Portland cement.
The walls are tied together with bonded rows, which go into the concrete by 1/2 brick, and located every three or five spoon rows of masonry. Dagger rows are laid out in one plane or staggered in a checkerboard pattern, depending on the accepted wall thickness. It is possible to connect the longitudinal walls with separate bricks laid in the longitudinal walls with pokes in two rows in height. The walls are erected in belts, the height of which is determined by the location of the stitch rows. If the stitching rows are placed in the same plane, then the laying begins with the stitching row. Then two spoonfuls are laid out: first from the outer, then from the inner verst. The gap between the walls is filled with lightweight concrete or insulation.
Modern construction technologies use foam plastic slabs as insulation, which halves the thermal conductivity of the walls, and the use of foam concrete for this purpose makes it possible to further increase the physical and mechanical characteristics of the wall.
Multilayer walls
A characteristic feature of brickwork is its high thermal inertia.A brick wall takes a long time to warm up and also slowly cools down. For residential buildings, this quality of brick walls is positive, since the temperature of the internal premises usually does not have large fluctuations. But for houses of periodic residence (usually summer cottages), the thermal inertia of a brick wall already plays an important role, since during the absence of the owners, the temperature of the walls decreases and it takes fuel and time to warm them up. To reduce this negative phenomenon, multilayer wall structures are used, consisting of layers of different thermal conductivity and thermal inertia. But this does not mean that multilayer structures can only be used for country houses. The high thermal efficiency of this type of wall masonry has found its application in all areas of construction, including in the construction of residential buildings.
Multilayer systems are called systems where the brick acts as a facing material. There are two types of multilayer systems. In the first form, the facing (brick) layer is self-supporting and does not perceive loads from floors and roofs - Fig. below:
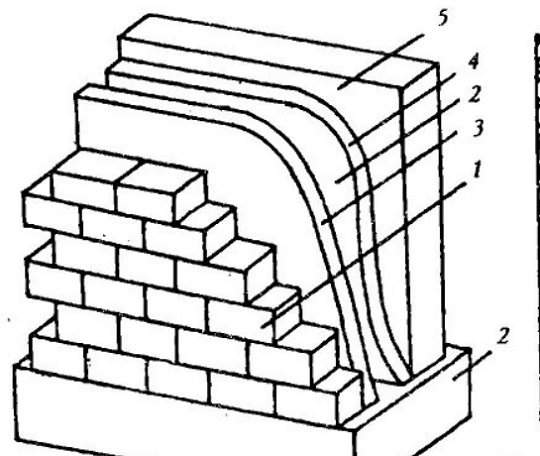

Multi-layer wall construction
Where: 1 - exterior cladding (brickwork); 2 - ventilation gap; 3 - wind protection; 4 - thermal insulation; 5 - load-bearing wall; (-) - outer plane of the wall; (+) - inner plane of the wall
With this type of masonry, the main wall built from traditional materials (solid bricks, blocks, slag or expanded clay concrete, etc.). She carries the main load. Heat-insulating plates are laid along the wall, and then an external facing layer of brick is built. The layers are connected by flexible Z-shaped ties made of stainless or galvanized steel, while the bearing and facing layers are connected to each other at the floor level with a reinforced concrete belt.
In the second variant, the inner and outer layers have a rigid binding, and the wall fully absorbs the load from the roof and floors. Various blocks made with advanced technology can be used as the inner layer.
The use of multilayer structures in the construction of walls made it possible to protect them from alternating freezing and thawing, to even out the temperature fluctuations of the main wall mass. In addition, multilayer structures favor an increase in the durability of the bearing part of the enclosing structures, shift the dew point into the outer heat-insulating layer. At the same time, favorable vapor permeability of the walls is created, the area of the premises does not decrease, and additional opportunities appear in the design of the facade of the building.
Sequence of works with lightweight masonry
The laying of walls of lightweight structures is performed somewhat differently than conventional ones. Before the start of the laying of lightweight walls, angular and intermediate orders are installed, moorings are pulled along the outer and inner sides of the walls in order to ensure the straightness of the masonry of two thin verst walls and the horizontality of the rows. First, 4-6 rows of the outer verst wall are laid, after which the inner verst wall is laid out to the same height. The laying is carried out in a press with the obligatory filling of horizontal and transverse vertical seams.
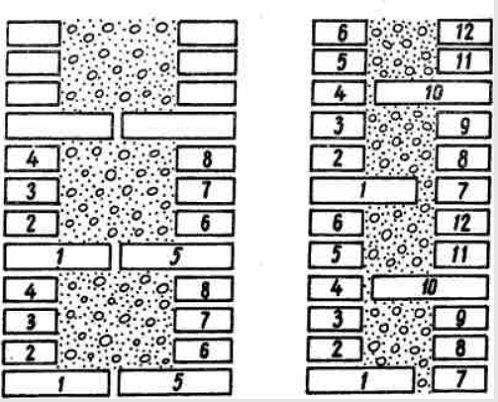

The sequence of laying a wall in 2 and 1.5 bricks
If the masonry of the inner walls lags behind the masonry of the outer ones, a slash in the outer wall is done with the release of every fourth bonded brick. In order not to chop a whole brick into three-quarters, it is sunk with one end into backfill or lightweight concrete. The sequence of brickwork of a lightweight wall is shown in Fig. below:
At the section of the masonry breaks, they make surety punishments. To prevent the backfill from falling out of the trenches (a section of the wall in height from one diaphragm to another), they are temporarily closed dry with a brick, and when the sections are closed, the brick is removed.
Lightweight wall design options
There are several options for constructive solutions for the masonry of external walls of lightweight construction.
Option 1 - brickwork with the formation of an air or insulation-filled layer 5-7 cm wide, Fig. below:

laying brick walls with a layer
With this option, brick consumption is reduced by 15-20% compared to solid brickwork of a 51 cm thick wall and 35-40% - 64 cm thick walls.The heat transfer resistance of the wall when using mineral wool as a heater increases by 60% when using expanded polystyrene - by 100%, solution consumption is reduced by 35% and labor costs are reduced by 10%.
For the construction of such walls, both solid and effective (hollow) bricks can be used. The front rows of masonry are tied to the main wall after 4-6 rows. The outside of such walls is usually plastered to reduce the likelihood of blowing.
Option 2 - brickwork with external or internal insulation. Compared to the previous version, this method is simpler, since it allows you to carry out work on wall insulation in the second place. In addition, this option makes maximum use of the strength characteristics of the brickwork.
To insulate the walls from the inside, you can use fiberboard, wood concrete, sawdust concrete, aerated concrete, soft fibreboard, mineral wool slabs, expanded polystyrene. Plates made of organic materials are installed on the beacons on the relative, while the air gap serves as an additional insulation of the wall. Inorganic insulation is attached directly to the wall using mortar or inorganic adhesives.
A variant of the wall construction with internal insulation can be successfully applied in houses of intermittent residence, in which the temperature inertia of the walls is undesirable, especially in the cold season. A large mass of cooled walls requires significant fuel consumption every time, and sudden changes in temperature inside the premises lead to moisture condensation on the internal surfaces. In this case, waterproofing must be provided on the outer side of the insulation, and the drainage of the formed condensate is organized in the wall structure.

External wall insulation
External insulation provides for mandatory wall cladding. For external insulation, it is better to use mineral wool slabs or polystyrene rice. left:
As a water-repellent layer, you can use a sheathing of boards laid horizontally in a quarter or tongue. The thermal and humidity regime of such a wall is better than walls with insulation located on the inside of the masonry. Special metal panels with various polymer coatings are very effective for external wall cladding. They are supplied by manufacturers of profiled metal with a wide range of colors and profile types. The steel cladding will not only reliably protect the walls from the weather, but also serve the architectural design.
Curtain wall structures are lightweight panels that consist of two steel profiled sheets and a thermal insulation material between them. The panels are fixed to the wall with special fasteners supplied with the panels. Seams between panels are filled with silicone sealant or other insulating compounds and covered with profiled steel strips, with the same coating as on the main panel.
Option 3 - well masonry. It is advisable to use this option when there is a relatively light and low-thermal conductivity material available for filling the inner space of the walls. Slag, expanded clay, crushed stone or sand of light rocks, antiseptic sawdust, shavings, etc. can be used as such materials.Mineral materials that are not biodegradable can be used in the form of dry backfill, organic materials - necessarily in the form of lightweight concrete based on inorganic binders: cement, lime, gypsum or clay. The disadvantage of well masonry is the weakening of the bearing capacity of the wall, therefore, in places reinforced concrete floors reinforcement of the walls with a reinforced concrete belt with mandatory reinforcement is required.
Website "How to build a house" wishes you the best of luck.
Heaters
In the last century, in order to save money, the well laying of the house was carried out with filling with earth or clay with sawdust. This option did not justify itself due to the shrinkage of the earth layer, labor intensity and increased load on the foundation.
In Moscow and its region, as well as in Tatarstan, well masonry is prohibited for use in houses built at the expense of budgetary funds. And the point is not in the negative aspect of this method, but in the impossibility of controlling the quality of the installation of the insulation. Inspection of the commissioned objects on a thermal imager showed significant violations and heat loss.
In private buildings, the method is successfully applied, where the customer can directly participate in the construction process, or receive a step-by-step photo report of the work being carried out.
The cavities in the well masonry are filled with:
- jellied compounds (polystyrene concrete, penoizol, sawdust concrete);
- backfill insulation (expanded clay, mineral wool crumbs, foam glass gravel, ball foam);
- blocks of mineral wool (for vertical insulation) or foam of various thicknesses.
Since each layer of well masonry has different temperature conditions, installation and ventilation gaps play an important role. For example, mineral wool and foam insulation must be fixed with anchor reinforced spacers.
Experts advise to wrap mineral wool with polyethylene before installation and fix it with a ventilation gap. Before that, treat the inner part of the wall in the well itself with a primer.
In the upper and lower rows, for the movement of air flows, in order to avoid condensation on the walls, narrow vertical hoods are placed between the bricks.
Brick insulation options
Insulation of a house under a brick is attached in two versions, this is on the outside and on the inside. Although it is worth noting that internal insulation is less effective than external insulation and is used less often. But there are options when only it is suitable. If your exterior finish is made with facing material, clinker tiles can also be attributed here, then internal insulation is mainly chosen.
Attention: With any insulation, a high-quality waterproofing of the brick must be done. Otherwise, all the work will be done in vain and you will not achieve the desired result.
Let's take a look at when each type is applied:
External insulation
This option solves the main problem, this is the complete saving of heat. In this case, you avoid the appearance of dampness in the room and the formation of fungus. When choosing this option, all work consists of the following stages:
- Application of adhesive material;
- Thermal insulation application;
- Application of a reinforcing layer;
- Application of facing material.
Now let's see what we achieve by applying it:
Positive aspects Negative aspects
|
|
Internal insulation
Insulation for walls under a brick in this version is laid most often. This is especially true for multi-storey buildings. In this case, the work will be much cheaper. But there are also downsides.
Arrangement technique


According to SNiP methods, when erecting three-layer walls with insulation made of mineral wool or foam, the inner wall is first removed, thermal insulation is attached to it, and then the outer part of the well is removed with the necessary ventilation gap, observing the location of the jumpers. At the same time, cotton wool is covered with a diffuse membrane for waterproofing.


On collapsible and highly heaving soils, the bearing and facing part of the well masonry of the structure is reinforced with monolithic belts of each floor level. This option excludes the possibility of cracking.
With the filling option:
- On the waterproofing layer of the foundation, 2-4 layers of dense brickwork are laid, at the corners starting from the butt sides. Each row is reinforced with a reinforced mesh.
- The base of the bearing and facing wall is formed with the required clearance for the selected heat-insulating material.
- Jumpers are laid out along the length of the wall after 60-120 cm. The gap from the lintel to the wall is from 2.5 cm, this excludes the formation of cold bridges in winter. Subsequently, since the lintels are located vertically to the entire height of the wall, the floor beams will be laid in place of their formation.
- Backfilling of walls with expanded clay or other thermal insulation is carried out no higher than 5-7 rows with tamping and filling with mortar.
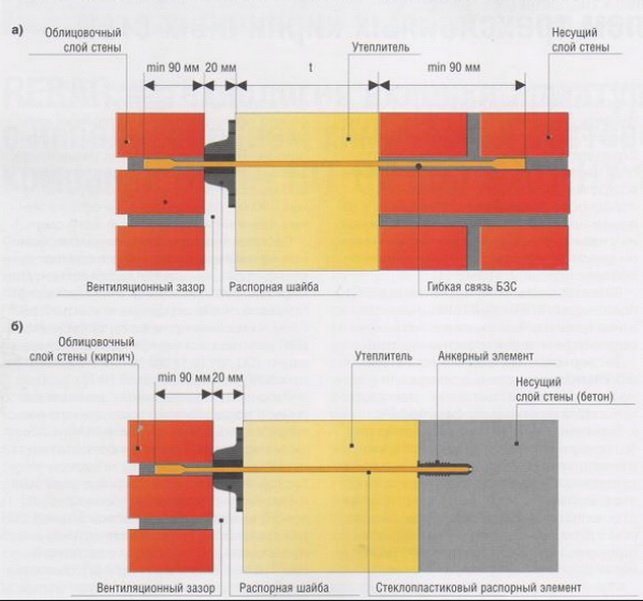
- A reinforced mesh is installed on the poured solution to give rigidity to the structure, or in the process of laying between the layers in a checkerboard pattern, connect 2 walls with reinforcing bundles with bent edges and an anti-corrosion coating. Flexible ties are an alternative to reinforcement. They are made of fiberglass or basalt plastic, they are not subject to corrosion, with a spray of coarse sand for greater fixation and a built-in retainer for attaching the insulation to the wall.
- All corners of the building are fixed with reinforced mesh with anti-corrosion coating. Also, at the intersection of walls, external corners and in the belt in front of the roof, flexible ties are additionally installed. Under the window and door openings, for any type of brickwork, 2-3 rows of a solid layer of brick are formed.
- The final 5-7 rows of the well masonry of the structure are laid out similarly to the initial rows with dense brickwork.
To reduce the load, in order to avoid wall delamination, the transverse seams are shifted by one quarter of the brick size, and the longitudinal seams are applied to 0.5 bricks. This ensures the solidity of the wall and the strength of the buildings.
The economical well masonry has many opponents. The main argument that they put forward is the impossibility of partial repair of the insulation of a house when it shrinks or deforms, but modern technologies make it possible to repair houses built more than 50 years ago. Thermal imagers see places where heat is lost, and foam insulation units fill the voids with high-quality insulation through small holes.
How is brickwork with insulation
Due to its incombustibility, it will not only not support combustion, but also create a fire retardant layer inside the masonry. Numerous family of mineral fiber-based insulation materials have excellent heat-saving characteristics.
They are made by whipping molten minerals in a centrifuge: glass, basalt, slag, etc. A low level of heat transfer in this case is achieved due to the high porosity of the material - air spaces do not allow cold to penetrate through the mineral wool. Mineral insulation is absolutely non-flammable, but it is very afraid of dampness.
Wall insulation
When wet, it almost completely loses its heat-saving properties, therefore, when laying it, it is necessary to take care of an effective waterproofing device. Expanded polystyrene is another thermal insulation material often used in three-layer masonry.
Brick is the most common material for the construction of load-bearing walls.It is successfully used both in high-rise industrial construction and in private low-rise buildings. The only drawback of bricks is low thermal insulation qualities.
It is produced by saturating liquid polystyrene with air, which, after solidification, takes the form of porous round granules. For filling wells in the wall, it can be used in sheet form or as bulk material. It is much less afraid of dampness than mineral wool, but unlike it is flammable, so walls insulated with expanded polystyrene should be protected from open fire. Even if the fire does not damage the brickwork, it will cause the styrofoam inside to burn out and melt.
To replace the insulation, you will have to carry out time-consuming and expensive work to dismantle the facing part of the wall.
Blog feed Lightweight brickwork with insulation. Lightweight brickwork with insulation. Lightweight insulated brickwork Insulated brick walls are increasingly used in private buildings. Well masonry is more complex than usual, but nevertheless, it can be easily mastered by anyone who has at least a little experience in working with bricks. This is an ordinary masonry, lined with insulation inside, using mortar beacons.
In private construction, sometimes three-layer masonry is made with backfilling of internal wells with various mineral fillers: slag, expanded clay, etc. This technique is somewhat cheaper and simpler than laying minelabs or sheets of expanded polystyrene, but its effectiveness is much lower.
What design of a three-layer wall to choose
For regions with cold winters, in the case of using vapor-transparent heaters, mineral wool or aerated concrete 100 kg / m3, the presence of a ventilation gap in the wall is mandatory to ensure its normal condition.
In this case, the ventilation gap remains open under the roof, and in the lower part of the wall for air supply, vertical seams between the bricks are left unfilled, slotted bricks are used, so that the area of the holes is at least 75 cm square. by 20 square meters. masonry.
Mineral wool with a density of up to 80 kg / m2 must be covered by a windproof superdiffusion membrane that prevents air from blowing through its layer. Membrane and wool layers are fixed with 10 disc dowels. per sq. m. into the load-bearing wall.
PPS, aerated concrete, are erected with the use of glue, in accordance with the recommendations above. Additional fixation is usually 3 - 5 plastic dowels per square meter.

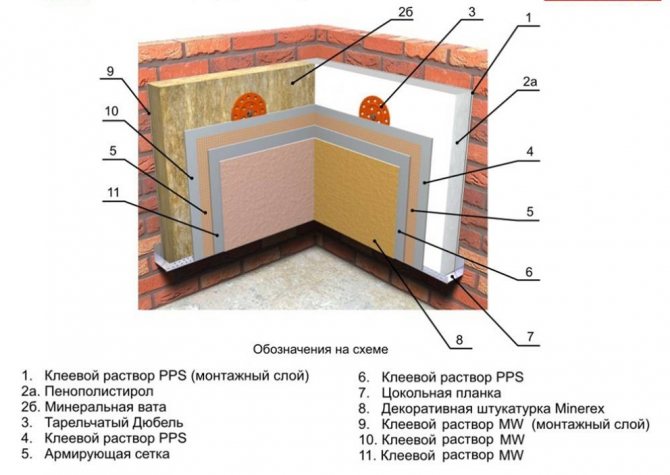
In a three-layer wall, it is recommended to use a masonry mesh, which connects all layers (and brick cladding). In this case, the step of installing the mesh vertically is 500 - 600 mm, according to the dimensions of the insulation plate (as small as possible). If fiberglass ties are used, then their number should not be less than 4 pcs. per square meter, and the horizontal installation step is not more than 500 mm., near the openings, at the corners of the shaft of the installation of ties is reduced, to 8 pcs. per sq. m.
The brick cladding is reinforced with a masonry mesh with a vertical step of no more than 1.2 meters, with the mesh being inserted into the load-bearing wall.
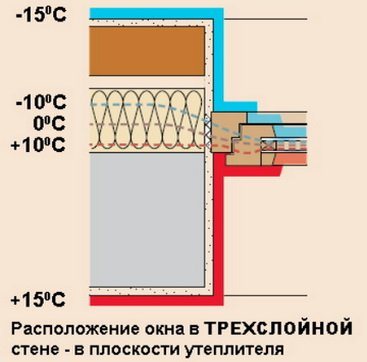
Doors and windows are placed along the depth of the wall opposite the border of the insulation-bearing wall. In this case, better heat savings in the openings are achieved, and the risk of fogging of the glasses is also reduced.

Strengths and weaknesses of heat blocks
One of the main advantages of using heat blocks is its low cost compared to similar building materials. The use of heat-efficient blocks in the construction of a house or building will bring you significant economic benefits. If you evaluate this building material on a five-point system, there will be a solid 5 here.
The heat block (as a building material) has the following strengths:
- The light weight of the materials will allow for transportation without much difficulty, and also not to use lifting mechanisms in construction;
- The fact that the blocks are attached using glue will save on the purchase of sand and cement;
- The masonry speed will also increase thanks to an assortment of geometries and block sizes;
- No need for insulation and cladding of the building;
There are also some disadvantages that are inherent in heat blocks, namely:
- a wall made of a heat-efficient block is not intended for cladding with bricks and some other building materials;
- the incorrectly selected width of the internal insulation may be insufficient for certain geographic areas.
Requirements and types of insulation
The construction of a brick wall with insulation is an important and rather difficult task. Regardless of the type of insulation, each of them must have the appropriate requirements.
First, resistance to deformation. This is a fairly weighty factor, since under the action of natural factors, the insulation can change its structure, which will not in a productive way affect the integrity of the structure and its properties.
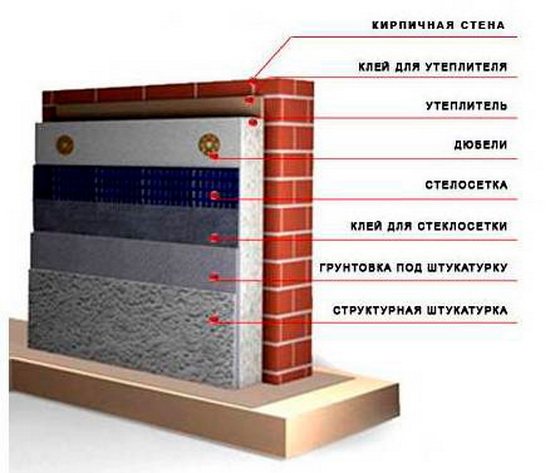

The next criterion for a good insulation is excellent moisture resistance. Although the insulation is carried out inside the structure, this does not mean that moisture cannot enter it. Often this fact leads to very negative consequences, thus destroying the material. The thermal insulation properties of the entire structure are lost.
As for the installation of a particular material, this factor also plays a significant role. For example, fixing foam to a brick wall is not much different from the same technology and to foam. But the former has improved properties that make it much more effective.
Reinforcement types
Reinforcement on brickwork can have a different arrangement:
- longitudinal;
- transverse;
- vertical.
A mesh for reinforcement is bought in a store or made on its own at a construction site before laying.
Longitudinal reinforcement of brickwork
Longitudinal reinforcement is used to strengthen the building under lateral loads and bending. In this case, the mesh is mounted quite rarely, mainly steel rods, corners, strips, wire are laid. The armature is placed in a longitudinal position when laying enclosing structures and partitions. The elements of the reinforcing layer can be located on the inside or outside of the wall.
Features of construction from heat-efficient blocks
The technology of laying three-layer blocks has much in common with the process of erecting walls from gas silicate blocks. The fundamental difference is the prohibition on cutting blocks to preserve their integrity and the unity of the initial textured pattern.


The laying is carried out using construction glue, maintaining the thickness of the joints in the range from 2 to 4 mm. Tight installation reduces heat loss through mortar joints, improving the thermal insulation properties of the wall. The adhesive is applied with a notched trowel to the inner and outer layers of the block. The solution is not applied to the insulation. The construction of the walls is carried out with the bandaging of the seams in ½ block.
Vertical joints when laying blocks of heat walls are sealed in a special way. In the insulation zone, they are sealed with construction foam. The outer and inner seams in the expanded clay area are sealed with mortar using a construction gun.
Wall insulation with foam
Insulation of brickwork with foam will significantly save on building material when erecting walls. Thus, it is quite enough to build a wall with an average thickness and then insulate it with 50 mm foam with a density of 25 kg / m3. Fastening the foam to a brick wall does not require any special skills.
Foam bonding
The process of gluing itself does not differ in particular laboriousness and takes a couple of days on the strength.Fastening the insulation to a brick wall begins with spreading a sheet of foam plastic with a tiled spatula with a special glue. It must be mixed in a bucket in advance. Next, we apply the material to the wall and press it well. You need to lightly tap on it, you can use your palm.


Fixing with dowels
After that, the foam is attached to the brick wall using dowels (four in the corners and one in the center, if the sheet is 1x1 meter). Then you have to tinker with the slopes, with which there is always more work.
Putty
When the fixing of the foam to the brick wall is complete, you can proceed with the putty. For this, one of the materials of the Ceresit line is quite suitable, for example, CM11. First, you need to glue a painting metal corner on all corners.


Then you can start the putty process itself. It is no different from the usual putty process, only the layer needs to be applied so that the reinforcing mesh can be drowned.
One layer of putty will not be enough. The next day you need to walk with her again. It is important not to overdo it with glue, as in the sun the foam begins to move quite strongly due to thermal expansion. This can lead to cracks on the facade of the house - the facade will need to be repaired.
Well, that's all! The process of fixing the foam to the brick wall and its subsequent priming is complete.
See more on this topic on our website:
- Brickwork - cost per square meter and cubic meter of brickwork One of the main cost items in building a house and arranging the facade is brickwork. The cost of brickwork from different types of bricks varies significantly, equal to ...
- How many bricks in 1m³ of masonry in a three-layer wall with insulation Three-layer method of wall laying is used when it is required to significantly insulate a house, a building. This type of laying is most relevant in areas where dampness and cold, strong ...
- The number of bricks in 1m3 of masonry - we consider the estimate for the construction of a brick private house Brick construction has remained popular for several centuries, despite the fact that every year manufacturers of building materials invent new, more convenient, cheap and practical materials. Benefits ...
- Lintels for aerated concrete blocks for a private house - types and characteristics The most common variant of lintels is those made of reinforced aerated concrete. This is the most common way. Ready-made lintels for aerated concrete blocks are an independent load-bearing part, ...
- The cost of laying bricks per cube - with and without materials for building a house When the stage of laying the foundation of a future house is over, it's time to move on to building walls. Wall masonry is one of the most important stages of construction - it is she ...