Classification of thermal insulation materials
A large number of materials act as heat-insulating materials, they are all divided according to different criteria, including density:

- High, over 250 kg / m3.
- Average, in the range of 100-250 kg / m3.
- Low, less than 100 kg / m3.
All modern materials for the production of thermal insulation works have high quality characteristics, most of them are environmentally friendly. There is a wide range of such products on the market, but before buying them, you need to carefully familiarize yourself with them and their characteristics, areas of application, installation features.
All materials can be divided into three more groups:
- organic;
- inorganic;
- mixed.
By their structure, heat-insulating materials are divided into:
- fibrous;
- cellular;
- grainy.
Also, all materials can be with or without a binder. By fire resistance, they are divided into:
- Combustible.
- Fireproof.
- Hardly combustible.
Each material for thermal insulation works has a certain vapor permeability, humidity, water absorption, biostability, temperature resistance. Therefore, when choosing a particular material, you need to compare them and select the most acceptable one that meets all the requirements.
Airgel - silicon oxide insulation


It has good thermal conductivity, it can be transparent, and its porosity sometimes reaches 99%. This type of insulation is used in the construction of railway passenger transport and space suits, but its popularity in the global construction market is equally high.


The silicate aerosol condenses and transforms into a gel, and after hardening, it is marketed as slabs, granules or rolls. The airgel is very porous, and its density reaches 143 kg / m3.


In addition, it is extremely resistant to compression. Its thermal conductivity ranges from 0.012 to 0.030 W / (mK).
ShareLikeClass TweetPinSubscribeWhatsappTelegram
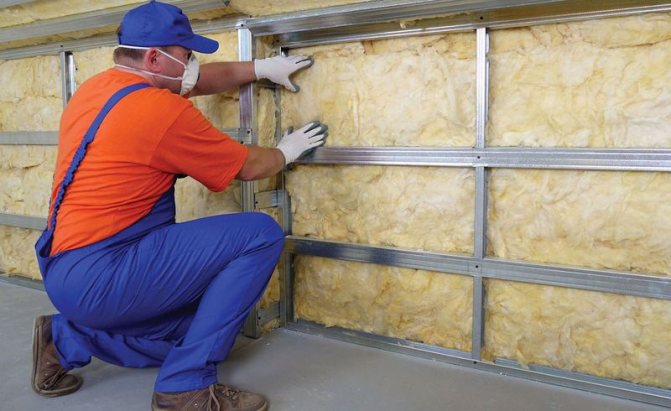
Mineral wool
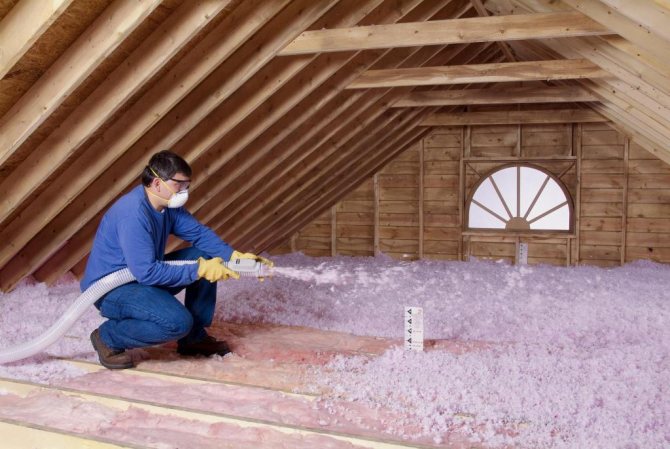


Mineral wool is highly porous and has a high thermal insulation capacity. It is considered one of the most common materials for working in a domestic environment.
Thermal insulation works with it have the following advantages:
- ease of use;
- cheapness;
- does not burn;
- well ventilated;
- noise-insulating and frost-resistant;
- long service life.
But in addition to the obvious advantages, mineral wool also has disadvantages:
- after contact with water, it loses its heat-insulating properties;
- it is not a vapor barrier and waterproofing, therefore, additional materials will be required for insulation;
- not durable.
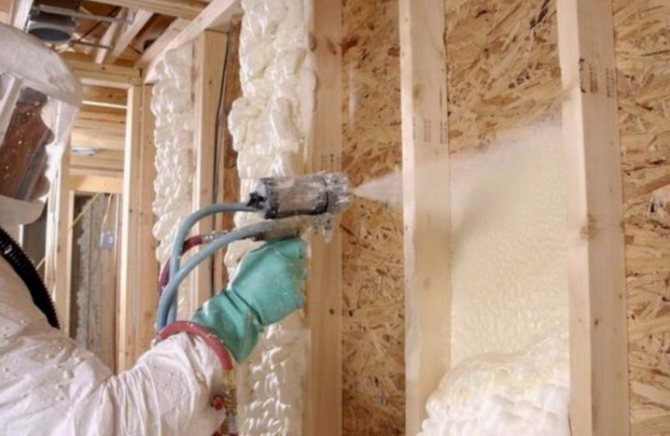
Home insulation technologies
A comparative analysis was made of the thermal insulation system of a two-story house, installed according to the old and modern thermal protection standards. The house has an attic, the total area of the building is 205 sq.m. According to the calculations, the initial heating system capacity was 30 kW. After work on the insulation of the house, no more than 15 kW is required for optimal thermal protection.

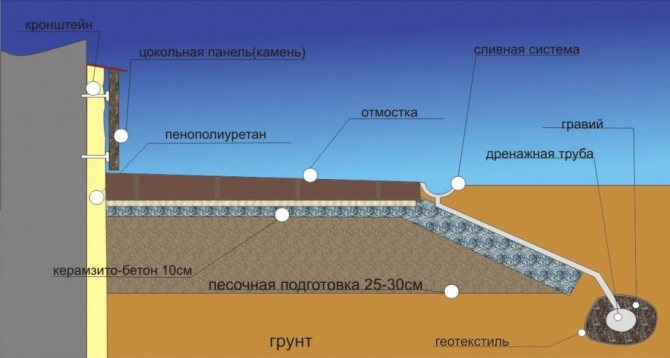
Consider the possible options for the location of the insulation, noting the advantages and disadvantages of each type. 1. Insulation is installed on the inside of the wall
Thermal insulation works are carried out indoors, which allows the house to be insulated at any time of the year, regardless of the weather.In addition, the exterior finish remains intact, any type of material can be used and the latest technology provided for the interior can be applied.
The main disadvantages of this technology include the loss of usable area, and the higher the thermal conductivity of the selected material, the more tangible the loss.
Insulation of internal walls can lead to an increase in the level of moisture in the walls: water vapor passes through the insulation, but does not have the ability to escape outside, accumulating directly in the wall or between the insulation and the wall surface.
If the method of internal insulation was chosen as the thermal insulation system, it is necessary to protect the wall from moisture penetration and its negative impact. For this purpose, an effective ventilation system is created in the room, and a vapor barrier is created on the inside of the thermal insulation system.
2. Insulation is installed inside the wall
Placing the insulation inside the wall is a laborious process and is recommended for installation during the construction of a new building. The fact is that with this type of thermal insulation, the insulation installed on the outside of the wall is covered with a layer of facing brick. To install such insulation on an existing wall, it is necessary to increase the thickness of the entire structure by strengthening the foundation.
3. Insulation is installed from the outside of the wall
The main advantages of outdoor insulation:
• The wall acquires stable protection against temperature changes, and, caused by these fluctuations, freezing and thawing of the wall. • The condensation zone of escaping vapors is carried out outside the bearing wall - the so-called "dew point" is located in the insulation. Thanks to the use of modern thermal insulation materials, nothing prevents moisture from transforming into steam and escaping into the outer space, which significantly reduces the level of moisture in the wall. • Heat is retained in the load-bearing wall and turns it into a kind of heat accumulator - in winter the structure retains heat, and in summer it retains the coolness.
With all its advantages, external thermal insulation needs to be protected from external mechanical and atmospheric influences with a special coating that has high strength and vapor permeability. For this, the external wall is plastered or a "ventilated facade" is installed. To prevent an increase in the level of moisture in the insulation, materials with increased vapor permeability should be used, so the moisture that gets into the layer can evaporate unhindered.
If we compare the above methods of placing insulation, it can be noted with confidence that the installation of external thermal insulation is the most effective and rational.
Insulation of the building facade Facade decoration has two main functions - aesthetic and protective, while it is impossible to talk about each of these factors separately. The attractive appearance of the building, of course, is important, but it is much more important to create comfort and conditions that are optimal for living indoors. Therefore, the goal of competent facade decoration is to insulate the house, protect it from atmospheric phenomena and make it look attractive.
Wooden structures
Wooden structures are considered to be the most difficult ones, since they are very sensitive to the wrong device, as a result of which they can collapse. Depending on the type of building, certain thermal insulation technologies and finishing materials are used.
Among all existing building materials, wood is the most traditional and environmentally friendly and is used for the construction of log and frame houses.Despite all the advantages of wood, it does not have sufficient thermal insulation properties, moreover, it is too sensitive to moisture, susceptible to decay, mold and various diseases. For the insulation of wooden structures, external thermal insulation is recommended, which is a screen with protective and decorative functions, while the ventilation properties provide a gap between the outer skin and the insulation.
Such a system consists of the following components: • Timber support structure • Internal cladding • Vapor barrier • Insulation • Windscreens • Ventilating air gap • External cladding
Thermal insulation materials - use
During the heating season, you can observe the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor spaces. In this case, a heat flow is formed in the wall structure, which moves in the direction "from heat to cold". The wall has a certain thermal conductivity and, absorbing heat from the room, gives it to the street. To prevent heat leakage, walls should be insulated with heat-insulating materials, the use of which is regulated by the regulation on the requirements for thermal protection of structures under number 3 to SNiPU 11-3-79 "Construction heat engineering". Changes to the document were put into effect at the beginning of 2000.
What are the requirements for thermal insulation material?
The main requirement for thermal insulation material is the ability to prevent the leakage of large amounts of heat from the heated room, and the greatest efficiency can be achieved only if the insulation remains dry. As soon as the level of moisture in the thermal insulation material rises, the heat transfer into the space to the street increases. To return the insulation properties to the insulation, it is necessary to find out the reason for the appearance of moisture in it and find possible ways to solve this problem.
Where does moisture come from?
The content of water vapor in the air is about 17.3 g of water per 1 m3 at a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius. In the cold season, the indoor air has a humidity of 55-65%, and this indicator differs significantly from the air humidity outside. As the temperature drops, air loses its ability to retain moisture, and excess steam begins to convert to water. Warm air begins to move from the room to the outside space. Water droplets penetrate the thermal insulation material and moisturize it.
The conversion of heat streams to water vapor can be prevented by creating a vapor barrier. For this purpose, a layer of heat-insulating material is installed from the inside of the room or several layers of oil paint are applied. Then decorative cladding is applied over the thermal insulation, and the moist air is removed from the room using forced insulation.
Another source of moist steam can be warm air emanating from the insulation towards the street. If proper ventilation is not organized on the outer border of the thermal insulation, wet steam can be converted into moisture droplets. Between the outer skin and the heat-insulating material, a special gap and conditions are created that are favorable for the free movement of air flows - "draft", which will bring out the water vapor.
In order to protect the thermal insulation material from weathering and strengthen the vapor barrier effect, the outer side of the wall must be treated with a material that provides protection from wind, insulation from moisture, and at the same time has excellent vapor permeability.
Please note that you cannot install insulation material of the same type from the outside of the wall as was attached from the inside - the vapor barrier material insulates the wall and blocks the air from moving towards the ventilation gap.Thus, the movement of air from heat to cold does not stop, but the whole process takes place inside the thermal insulation system - the heat vapor cools down and releases moisture, which, having no outlet to the outside, remains on the surface of the insulation and is converted into ice. With the arrival of spring, the ice melts and the insulation materials begin to rot.
So, based on the foregoing, it is possible to derive a formula for the effective operation of the thermal insulation system: the structure must remain dry at any time of the year, and this condition will be ensured by a vapor barrier on the inside of the wall and a wind barrier on the outside.
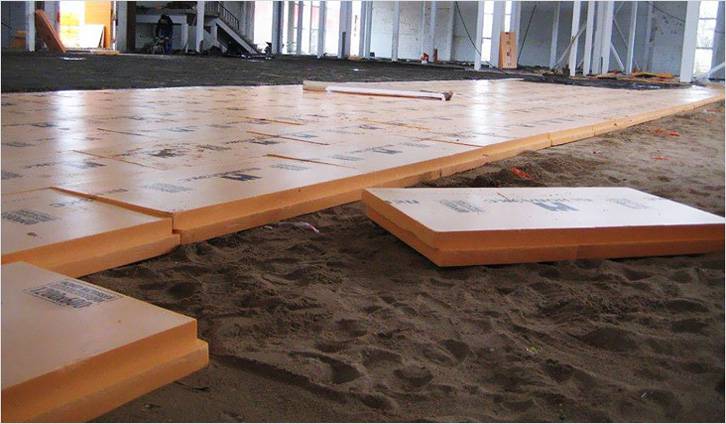
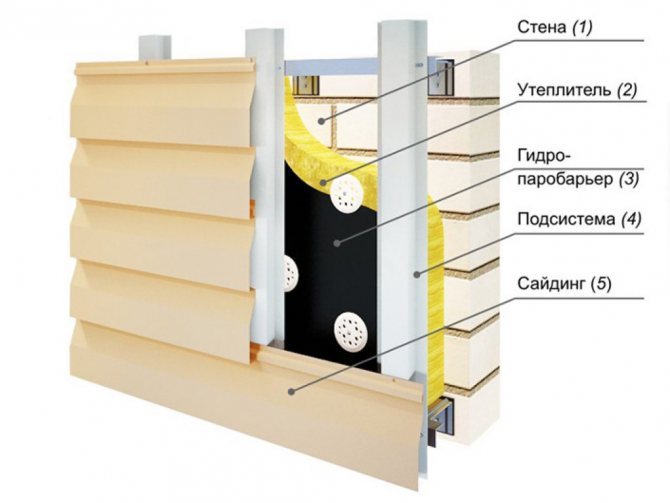
Installation of the lathing
Before proceeding with the installation of the lathing, it is necessary to decide on the material that will be used as a protective screen. Let's consider the principle of installation on one of the examples, when the installation of the lathing for the installation of insulation occurs with the subsequent installation of siding.
To install the structure, you need wooden beams treated with an antiseptic composition, the thickness of which is 50 mm, and the width exceeds the thickness of the insulation sheet. If the insulating material has a thickness of 80 mm, then the beams should have from 100-110 mm, which allows an air gap to be provided. The step of the lathing depends on the width of the insulating material slab. The insulation is laid in the grooves formed between the beams, and then attached to the supporting wall using anchors. The number of anchors per square meter of insulation is calculated based on the density of the material, as a rule, it is 4-8 anchors. Then a layer of windproof material and siding is applied to the insulation.
This system is one of the simplest ways to install the lathing, because it has one significant drawback - wooden beams form "cold bridges" with low thermal resistance. Alternatively, you can apply a lathing installation scheme, in which the insulation sheet is divided into two parts and each layer is laid on its own lathing, and the bars of the upper layer are placed perpendicular to the lower one. This method of installation practically excludes the formation of "cold bridges", although it requires more time and effort to complete.
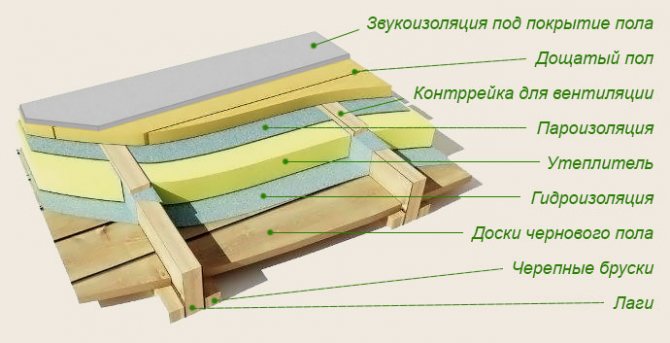
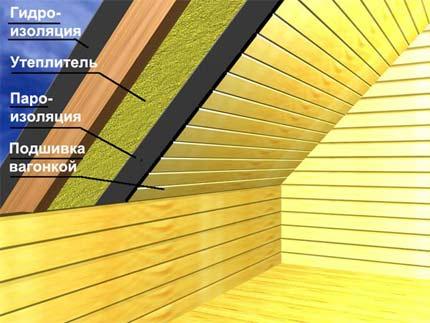
Vapor barrier materials
The vapor barrier is created using vapor barrier materials, which should be selected depending on the type of construction and the method of installation. The installation of the vapor barrier can be carried out both vertically and horizontally from the inner side of the structure that protects the heat-insulating layer. Installation is carried out using galvanized nails with a flat head, or a mechanical stapler. The seams of the vapor barrier screen must be airtight, and the film is integral to prevent the movement of water vapor and moisten the structure.
It is recommended to seal the seams with special connecting tapes based on butyl rubber. In addition, individual strips of the vapor barrier can be overlapped and fixed along the seam with a counter bus. When a vapor barrier is installed on the ceilings of residential premises, attics or in a space with high humidity, a ventilation gap of 2-5 cm must be provided between the inner lining and the vapor barrier to prevent excessive moisture.
Windproof materials
Wind insulation is designed for external protection of the thermal insulation system, to ensure moisture and wind resistance of wall structures, while maintaining the free movement of thermal vapor.
When choosing a windproof material, one should take into account the main requirement - the vapor-permeable resistance should decrease depending on the direction of the heat vapor from the inner space to the street - “from heat to cold”. Thus, it is possible to prevent the formation of condensation in the inner layers of the structure.
Please note that the optimal level of vapor permeability can vary from 150 to 300 g / m2-day at a cost of about 0.5 USD. per square meter. But the use of superdiffusion materials with a vapor permeability of 1000 g / m2-day does not have any special differences, but it will increase the cost of the structure at a price of $ 1. for one square meter.
Wind-insulating materials are installed on the inside of the protective structure, and they are positioned close to the heat-insulating layer. Installation is carried out vertically and horizontally, and the width between the leaves must be at least 150 mm. Manufacturers emphasize the correct positioning of the front and back sides of vapor barriers: if the material is used incorrectly, then the structure instead of the breathable one can turn into an isolated one and disrupt the normal functioning of the entire system.
Vapor barrier materials are reinforced to the structure using galvanized stainless steel nails with a wide head, or special brackets with a pitch of 200 mm. The final stage of installation is fastening with galvanized nails of a beam with a section of 50x50 mm and surface cladding.
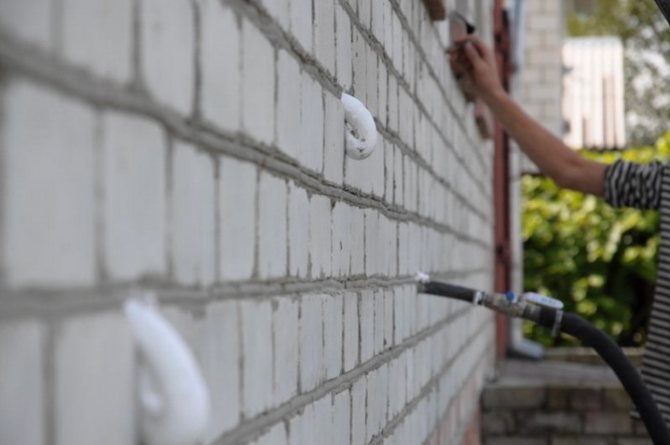
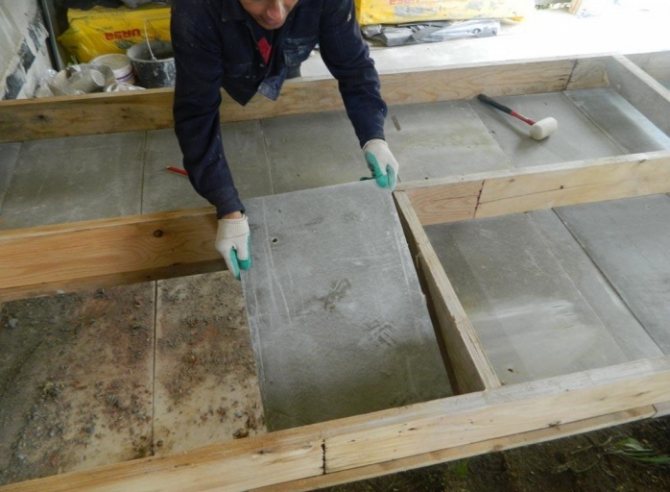
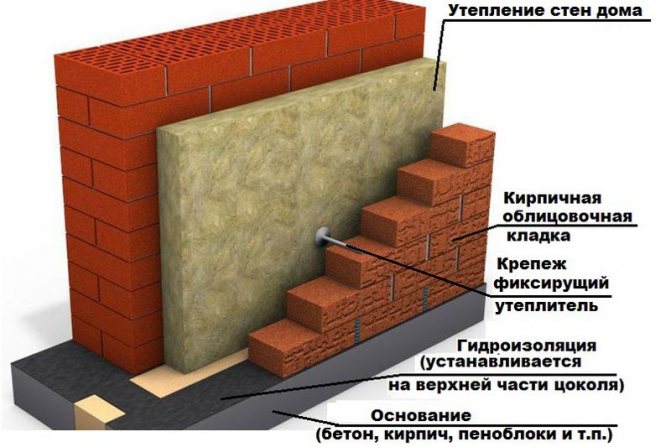
Thermal insulation of a brick (stone) wall
Thermal insulation of a stone wall can be performed in two versions - with further plastering of the surface and the creation of a structure with a ventilated gap. Let's take a closer look at both methods of insulation.
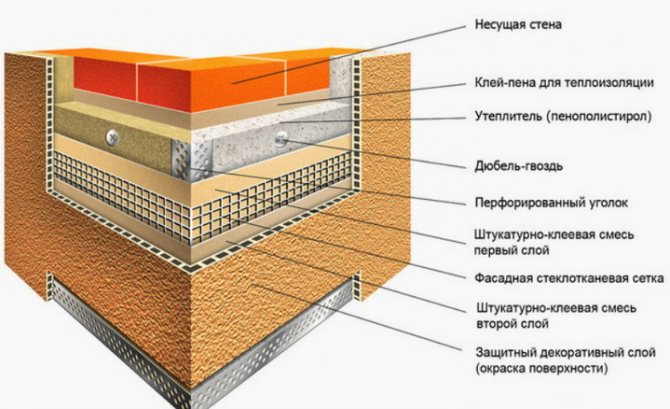
Thermal insulation with surface plastering
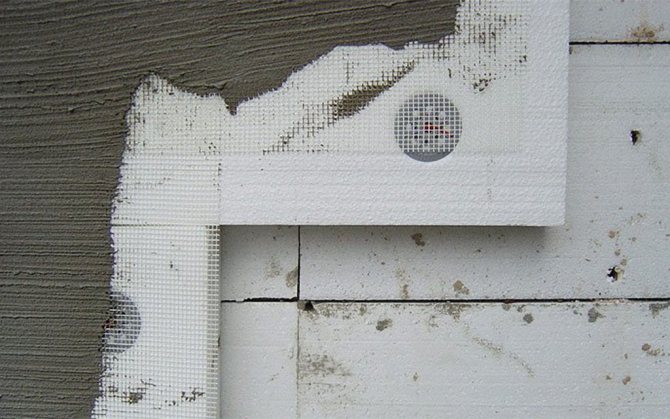
For thermal insulation of stone walls with further plastering, contact facade heat insulators are used, which include the Belarusian "Termoshuba", German Tex-Color, Ceresit, Heck and others. All systems have significant differences between the type of insulation material, the method of its fastening, reinforcing mesh, the composition of the protective layer and glue, as well as their thickness.
The thermal insulation schemes of each system have a common feature - they are attached to the wall using dowels, anchors and frames by glue or mechanical means, and then covered with a vapor-permeable layer of plaster.
Insulation is applied to a dry, clean and durable surface, which can be a concrete, brick, foam-gas concrete wall, both plastered and unplastered. If there are significant irregularities on the wall, they should be leveled with cement mortar. In the case when the surface of the brick wall is flat, you can do without a primer, which cannot be said about other types of walls.
Installation of thermal insulation on a brick (stone) surface is carried out in the following way: first, you should equip a support surface, which can be the protruding edge of the foundation or the edge of a concrete slab. If there is no such support, it is necessary to build a metal or wooden false support - a support rail, and the wooden one must be removed before plastering the surface.
Thermal insulation boards are laid on the wall according to the principle of "bandaging the seams" - very close to each other.
Please note that gluing the slabs on facades of a small area is not necessary, since later they will be mechanically attached. But mechanical fastening is necessary for the structure to be durable.
Plastering should be started two to three days after gluing. First, the door and window slopes are reinforced with aluminum or plastic corner profiles, and only then the main plaster layer is applied. To apply a small layer of plaster, up to 12 mm on a dense mineral insulation, you can use an alkali-resistant fiberglass mesh. If the layer is thick, 2-3 cm and expanded polystyrene will be used, a metal mesh is recommended.
As a rule, a thick layer of plaster is first applied, into the outer third of which the reinforcing mesh is pressed, which allows the structure to respond more gently to temperature changes. The second layer of plaster is made thinner. Each strip of mesh should be overlapped in width and length by approximately 10-20 cm and folded over at the corners of the building.
In the course of work, for gluing plates and basic plaster, you can use solutions of different types, and when plastering, use compounds with microfibers, which gives the structure high strength and prevents cracks.
The final stage of work is the final finishing, which everyone performs at their own discretion.
Please note that with the considered plastering method, the windproof materials are replaced by vapor-permeable plaster, and the supporting structure acts as a vapor barrier. Even if warm water vapor appears in the inner layers of thermal insulation, they will be removed naturally through the layer of plaster and insulation.
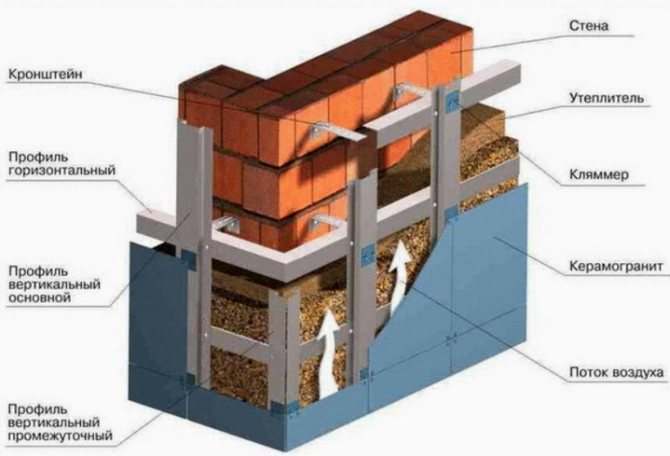
Thermal insulation with a ventilated gap Thermal insulation material is attached to the facade using dowels, then the surface of the structure is covered with a windproof layer and a ventilated gap is introduced, which is covered from the outside with a special screen that performs a protective and decorative function. In low-rise construction, additional sources of convection feed are installed on the surface of the screens, made in the form of slotted air intakes, which are formed at the stage of facade production. The use of a vapor barrier is not required in this case. Both wooden and metal structures can be used as lathing.
The indisputable advantage of this method of thermal insulation is the ability to perform work at any temperature and atmospheric conditions. However, it is quite difficult to carry out the installation of such thermal insulation in cases where the building has a complex architecture, or it is necessary to reproduce the appearance of the facade as accurately as possible.
Glass wool and basalt slabs
Glass wool is sold in rolls. It is widely used for pipe insulation. Stronger than mineral wool. Basalt slab is a subspecies of glass wool. It is made from basalt rocks.


Its advantages:
- increased strength;
- fire resistance;
- does not deform and is durable.
Facades, panels, foundations, roofs of houses - all this is insulated with basalt slabs.
Cork and Styrofoam


Cork is an environmentally friendly material that is popular all over the world.
Cork has many positive aspects:
- does not rot and does not settle due to its low weight;
- strong, but easy to cut;
- durable;
- in the event of a fire, it smolders, without emitting harmful substances.
But the cost of cork is quite high, so few can afford it.
One of the most popular insulating materials is foam. You can buy it at any hardware store. The pluses of foam include:
- high thermal insulation, strength;
- practically does not absorb water;
- ease of use;
- cheapness.
Cons of Styrofoam:
- does not allow air to pass;
- with prolonged exposure to moisture, its structure collapses.
Stages of wall insulation
In order for the result to pay off, you need to take every step seriously. Otherwise, no thermal insulation will work, the appearance will be, to put it mildly, ugly. Depending on the insulation, the technology of thermal insulation work will be slightly different. Preparatory steps:
- Preparing the walls. Thorough stripping of old and peeling coatings, cleaning of cables, drains, plates and other things.
- Sealing cracks, potholes, upholstery of bumps.
Installation heat-insulating work during plastering work consists of the following processes:
- Fastening of auxiliary profiles.
- Insulation gluing and additional fixation on anchors or dowels.
- Slopes and ebb tides are fastened.
- Reinforcing coating application.
- Sanding and painting.
At the same time, it is important to space the work until each layer is completely dry.
Frame systems are attached as follows:


- Subsystem axes marking.
- Division of the facade into small sections.
- Determination of reference points, installation of screws in them and tension of the cord along them.
- Installation of support elements and frame chords.
- Fastening insulation.
- The waterproofing membrane is fixed on top.
- Thermal insulation plaster for outdoor use is used as a finishing layer.
When performing internal work, all of the above materials are used. The sequence of all actions is practically the same. Thermal insulating plaster for interior work is used only as a finishing layer.
Why is it better to insulate the walls from the outside, not from the inside?
When the insulation layer is located inside the room, the outer wall is negatively affected by the environment - temperature drops, frost, ultraviolet radiation, precipitation. All this gradually destroys the material. Another serious point that must be taken into account when insulating the interior is that the dew point gets into the thickness of the wall. Consequently, in cold weather, condensation will constantly collect in it.
Wet walls are an excellent breeding ground for mold and mildew, which will be almost impossible to get rid of. Not to mention the fact that with the internal installation of insulation, you will have to sacrifice living space.
All these negative points are irrelevant if you insulate the walls of the house from the outside. You will save useful areas of the premises, and the walls will receive additional protection from moisture, sun and extreme temperatures. At the same time, the quality of thermal insulation will be no worse.
Recommendation! When solving the issue of house insulation, it is necessary first of all to consider the external installation of the material. And only in the absence of such an opportunity, work is carried out indoors. In this case, it is important to perform a high-quality vapor barrier.
General norms of SNiP
Thermal insulation works can be carried out at an air temperature of +60 ° C to -30 ° C. If water compounds are used during operation, then the minimum temperature value is +5 ° С.
At the base under the roof and insulation, according to the project, you need to perform:
- Sealing joints between precast panels.
- Installation of temperature and shrinkage joints.
- Installation of embedded elements.
- Plastering sections of vertical surfaces of stone structures.
Thermal insulation work must be carried out without any defects; for this, all compounds and materials must be applied evenly. After drying, each layer must be sanded.
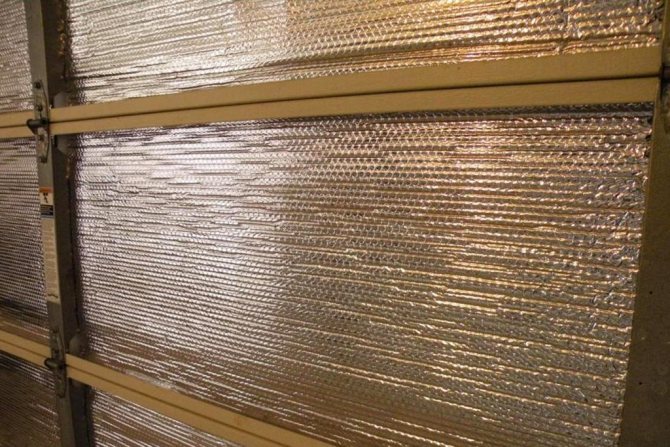
Thermal insulation with foil
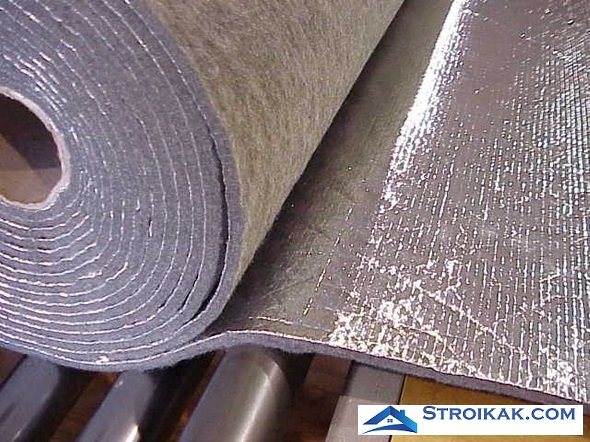


Thermal radiation is reflected off the shiny, glossy surface, which traps heat in the home. To reflect heat radiation, metal foil is used, which is produced and stored in thin rolls. Their structure is layered. Polyester or bubble wrap spacers are placed between two layers of reinforced aluminum foil. Such a film is attached, like a vapor barrier, with staples to a wooden base or double-sided gluing to steel structures.


Low weight, low cost and excellent thermal insulation (thermal conductivity coefficient can reach 0.019 W / (mK)) are the hallmarks of this type of thermal insulation. The shiny surface of the coating is able to reflect up to 92% of radiant heat.